2. Java Basics. Data Types презентация
Содержание
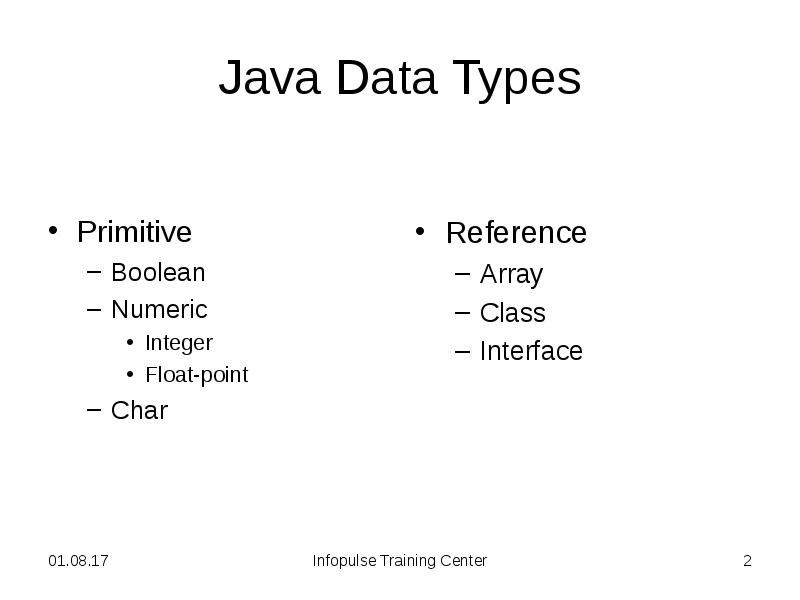
- 2. Java Data Types Primitive Boolean Numeric Integer Float-point Char
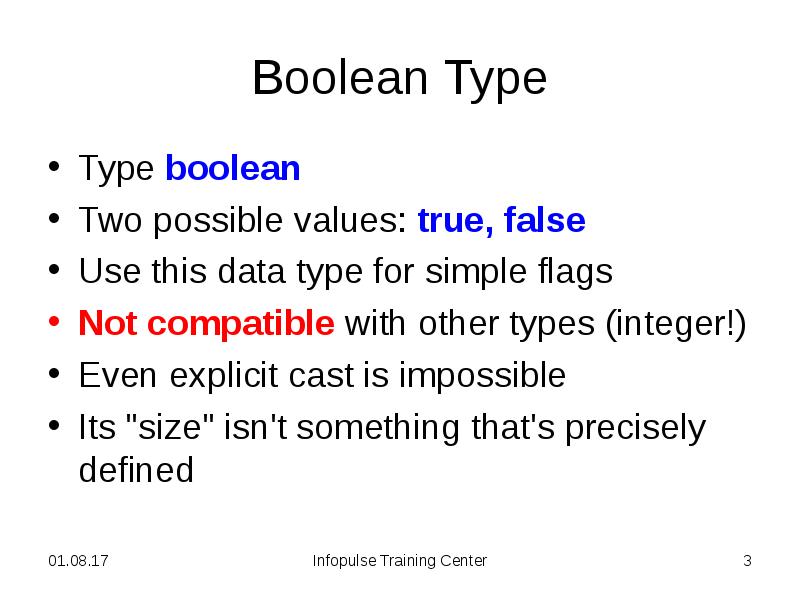
- 3. Boolean Type Type boolean Two possible values: true, false Use this
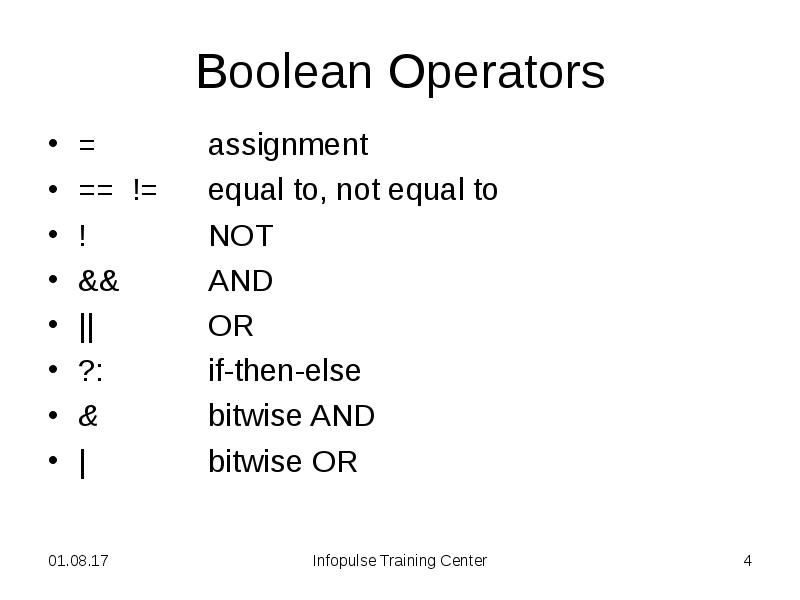
- 4. Boolean Operators = assignment == != equal to,
- 5. If-Then-Else Boolean Operator expression1 ? expression2 : expression3 Examples:
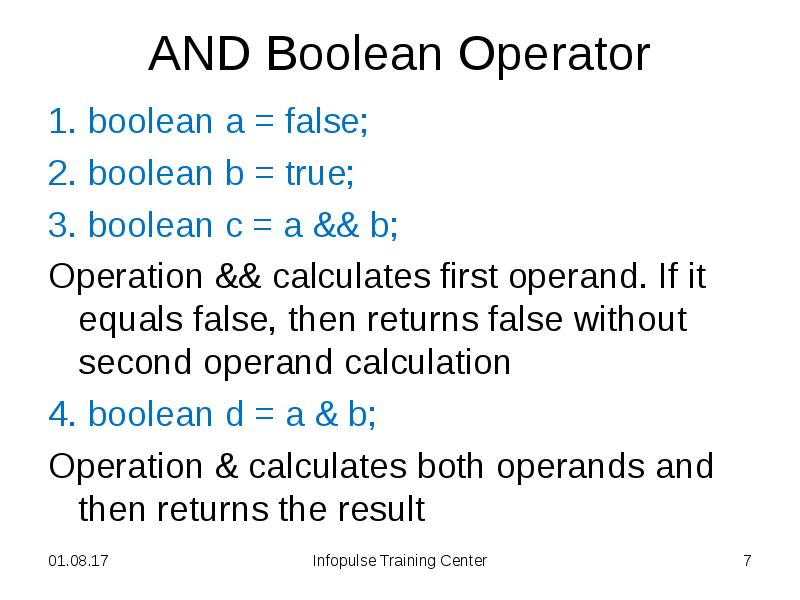
- 6. AND Boolean Operator 1. boolean a = false; 2. boolean b
- 7. AND Boolean Operator 1. boolean a = false; 2. boolean b
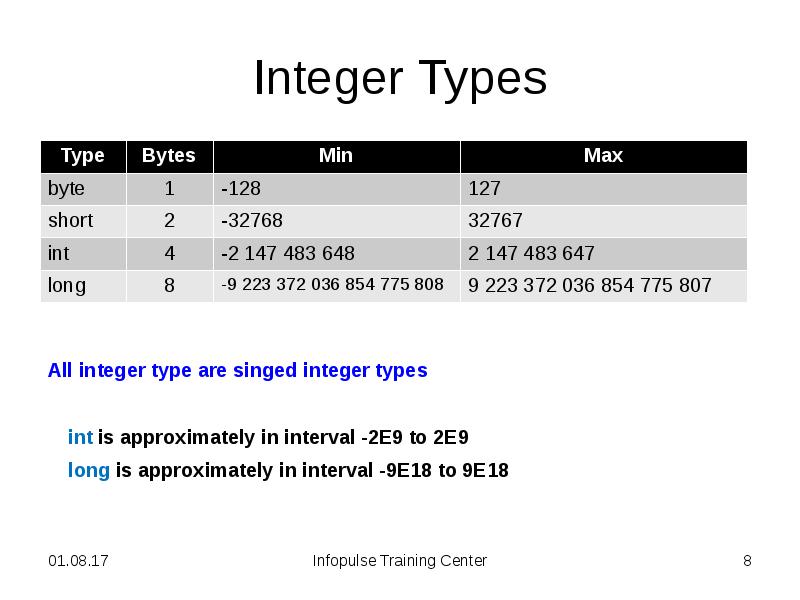
- 8. Integer Types
- 9. Integer Literals Decimal constant should start with nonzero digit Leading zero
- 10. Integer Arithmetic Operations + add - subtract * multiply / divide % get reminder
- 11. Integer Addition byte a = 120; byte b = 10; byte
- 12. Integer Arithmetic Operations If one operand has long type then other
- 13. Integer Assignment The integer assignment performs implicit type conversion if neither
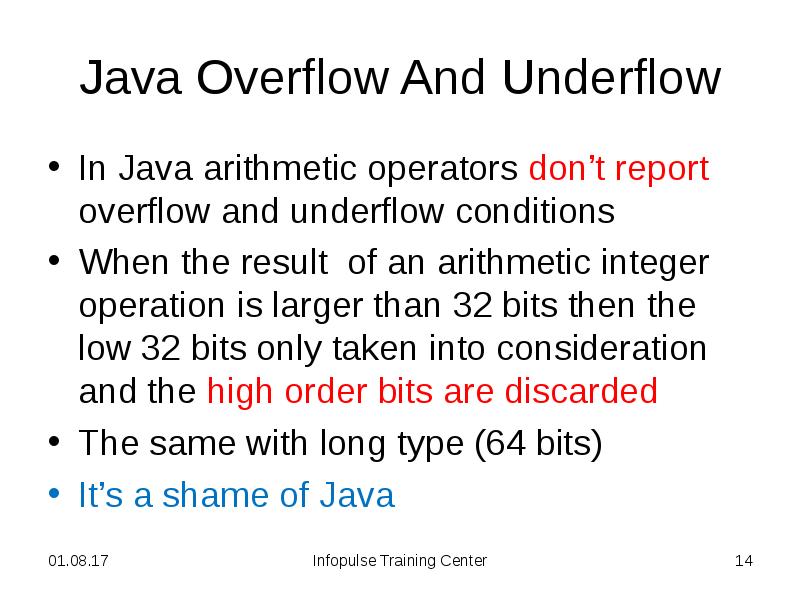
- 14. Java Overflow And Underflow In Java arithmetic operators don’t report overflow
- 15. The Overflow Problem In Java arithmetic overflow will never throw an
- 16. Integer Division x = a / b r = a %
- 17. Integer Division Division by 0 leads to runtime ArithmeticException: int a
- 18. The Integer Unary Operators + Unary plus operator - Unary minus operator ++ Increment
- 19. What will be a value? int x = 8; int a
- 20. What will be done? int c = 10; int d =
- 21. What will be done? int c = 10; int d =
- 22. Bitwise Operators ~ inverts a bit & bitwise AND | bitwise OR
- 23. Bitwise Operators int a = 45; int b = 34; int
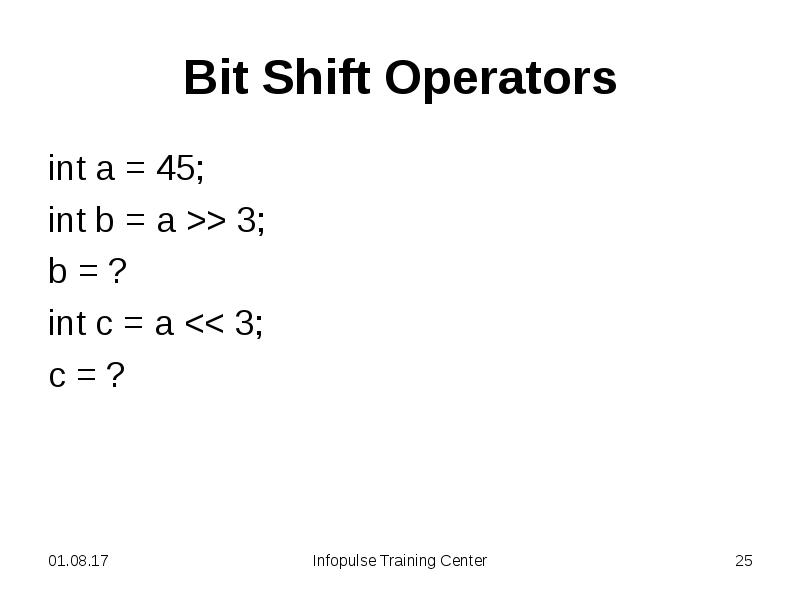
- 24. Bit Shift Operators << signed left shift operator >> signed right shift
- 25. Bit Shift Operators int a = 45; int b = a
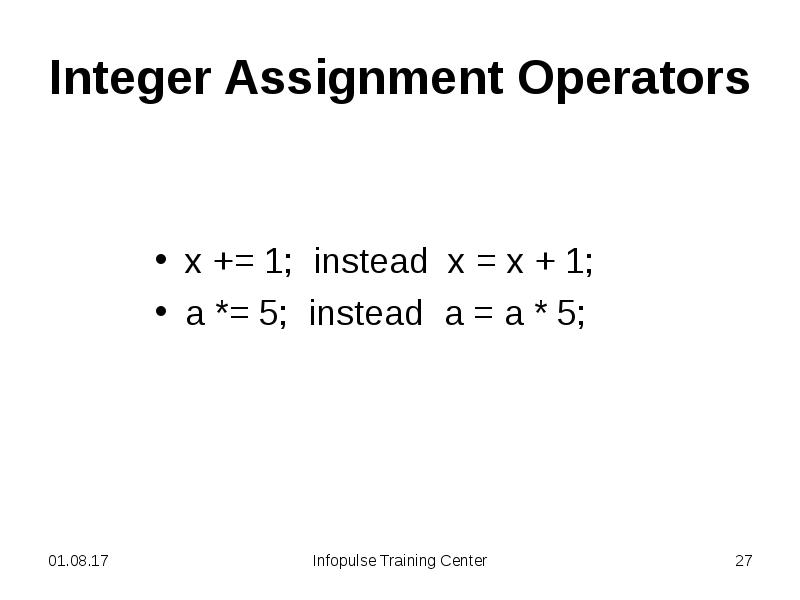
- 26. Integer Assignment Operators = +=, -=, *=, /= <<=, >>=, >>>=
- 27. Integer Assignment Operators x += 1; instead x = x +
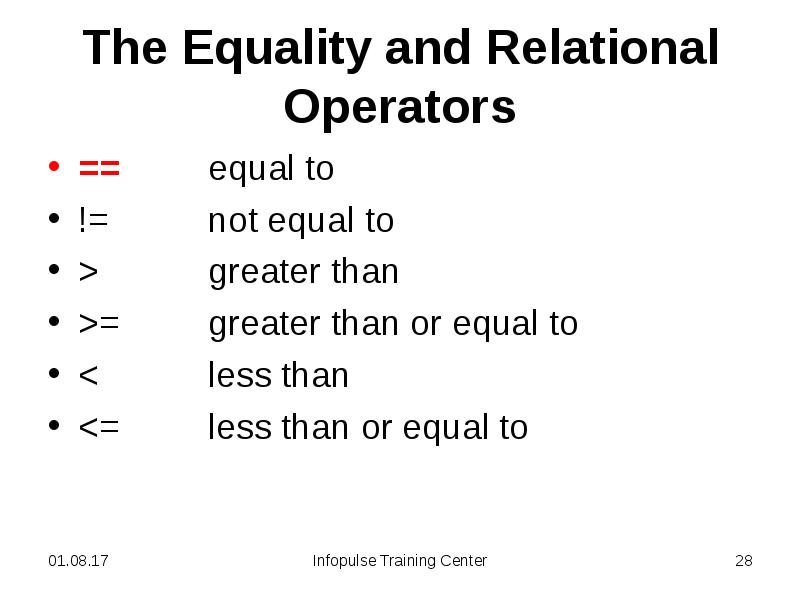
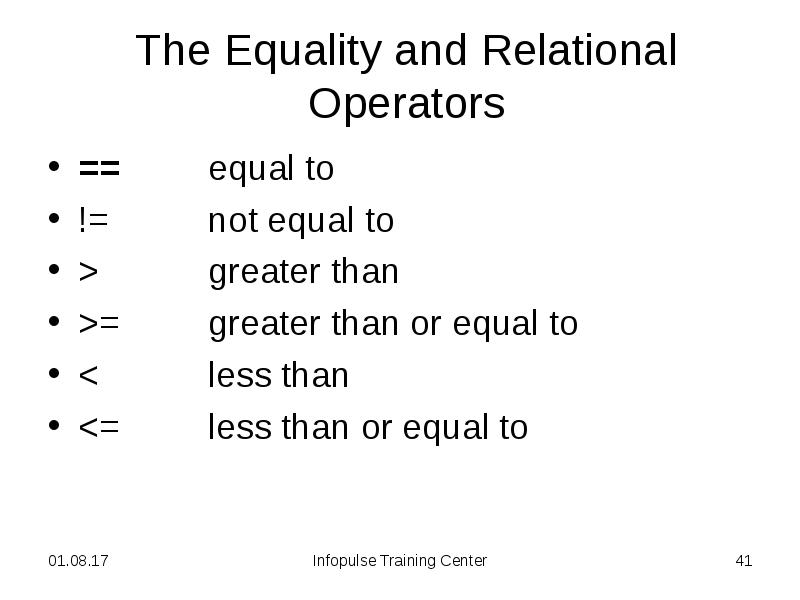
- 28. The Equality and Relational Operators == equal to != not
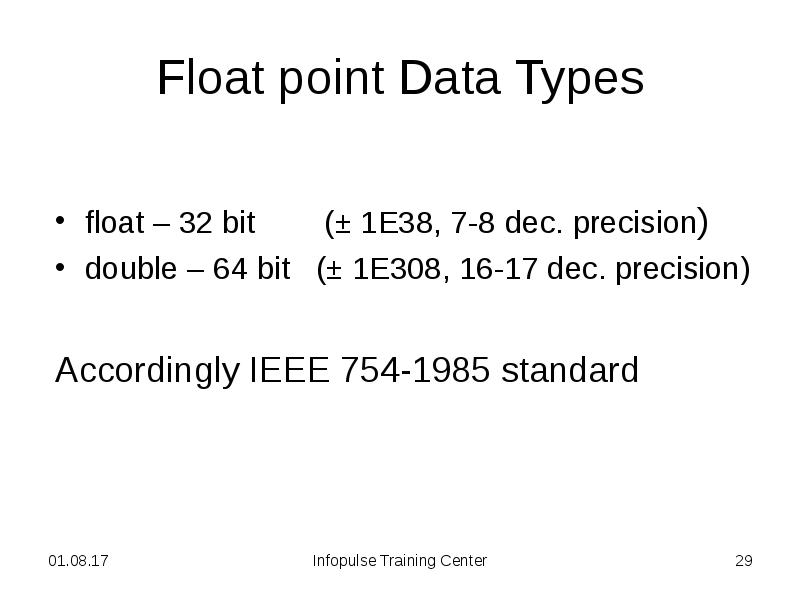
- 29. Float point Data Types float – 32 bit (± 1E38,
- 30. Float point Arithmetic Operations + add - subtract * multiply / divide
- 31. Float point Arithmetic Operations If one operand has double type then
- 32. What will be c and d value? double a = 2.2;
- 33. Special Float Point Values -Infinity +Infinity NaN In previous code c
- 34. Precision Problem I double a = 2.0; double b = a
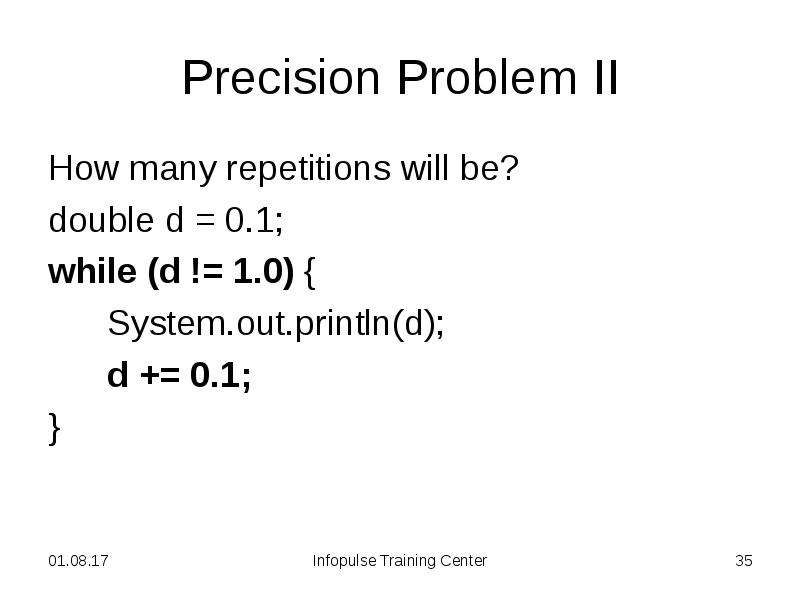
- 35. Precision Problem II How many repetitions will be? double d =
- 36. Debugging in Eclipse Start debugging: press Debug icon and use F6
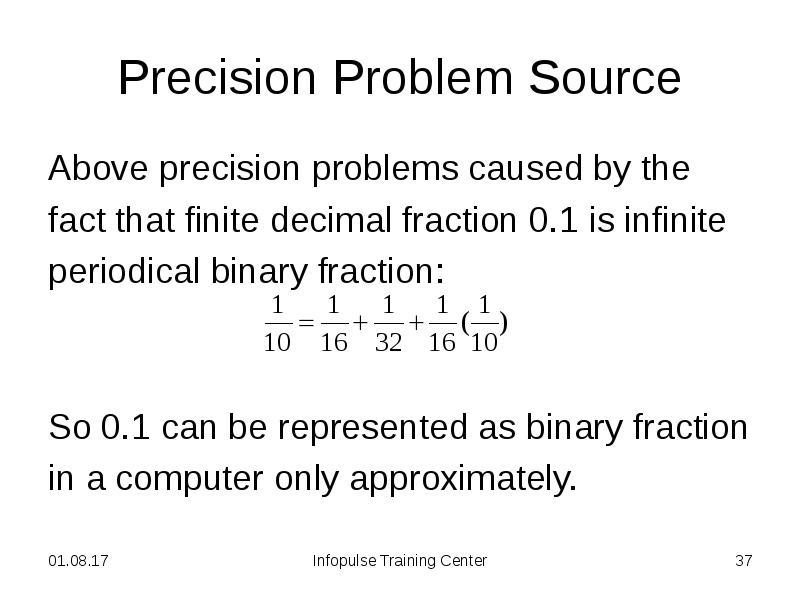
- 37. Precision Problem Source Above precision problems caused by the fact
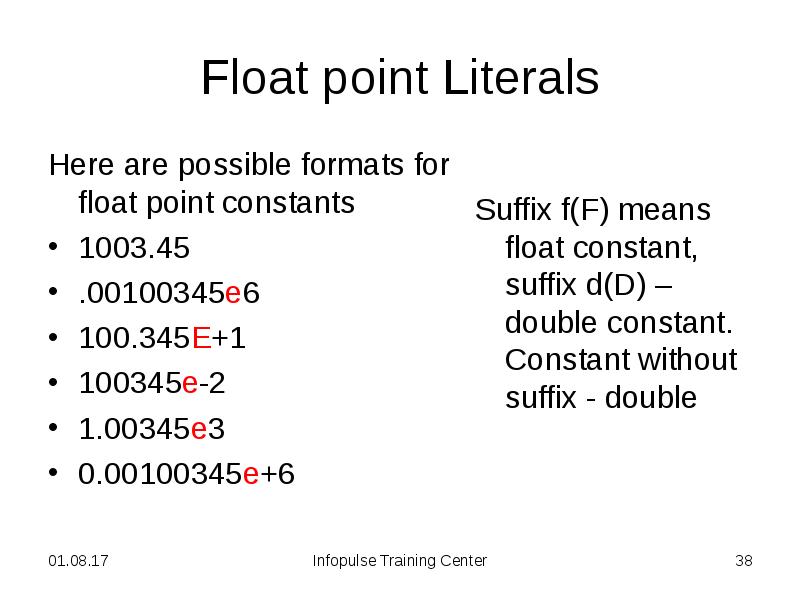
- 38. Float point Literals Here are possible formats for float point constants
- 39. The Float point Unary Operators + Unary plus operator - Unary minus operator
- 40. Float point Assignment Operators = +=, -=, *=, /=
- 41. The Equality and Relational Operators == equal to != not
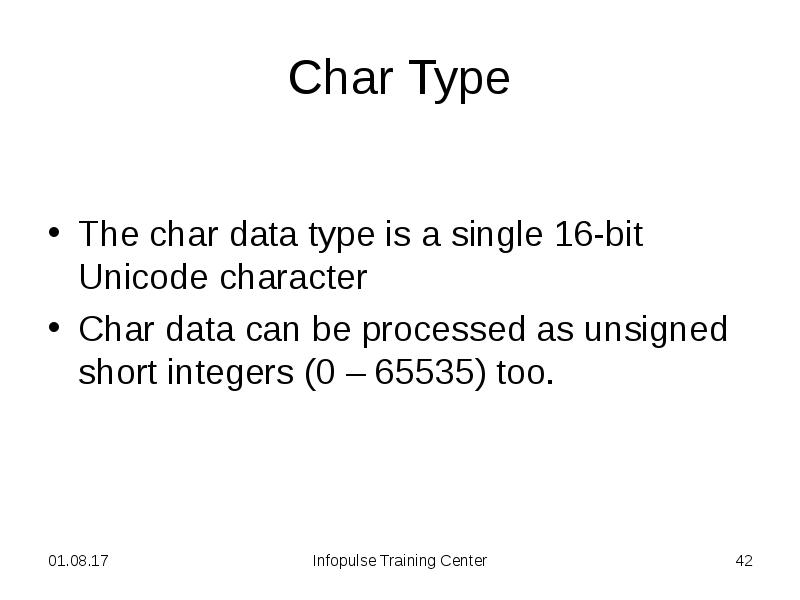
- 42. Char Type The char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode
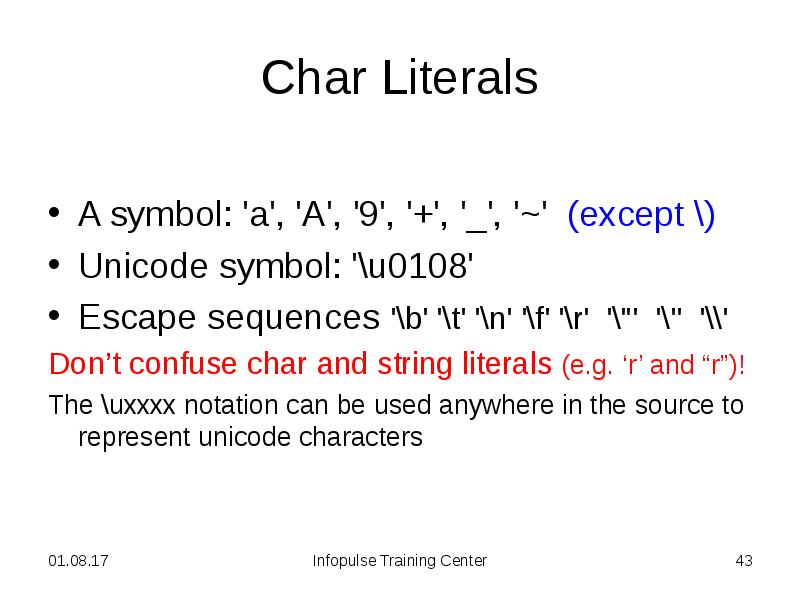
- 43. Char Literals A symbol: 'a', 'A', '9', '+', '_', '~' (except
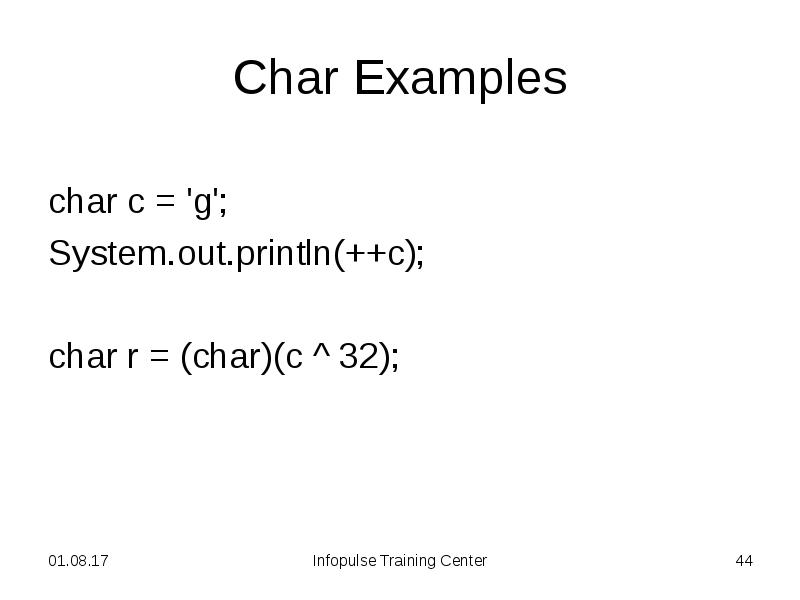
- 44. Char Examples char c = 'g'; System.out.println(++c); char r = (char)(c
- 45. Expressions. Operator precedence . [] () +
- 46. Casting (1 of 2) Any integer type can be casted to
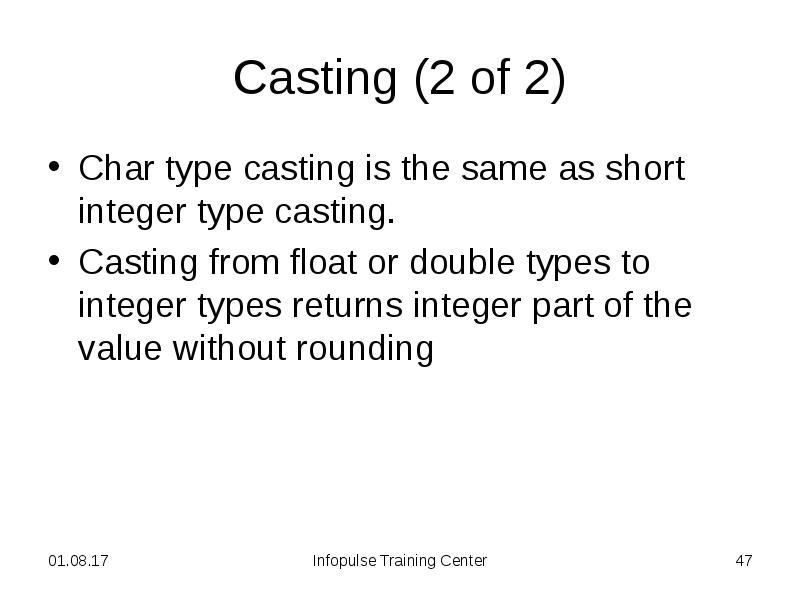
- 47. Casting (2 of 2) Char type casting is the same as
- 48. Casting operators (1 of 2) Implicit casting: byte
- 49. Casting operators (2 of 2) int b = 168;
- 50. Manuals Learning the Java Language. Language Basics Thinking in Java. Operators.
- 51. Скачать презентацию



























![Expressions. Operator precedence
. [] ()
Expressions. Operator precedence
. [] ()](/documents_3/9fb4843061f99d54d70b974ba49cc102/img44.jpg)




Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























