3. Java Persistence API. 4. Entity Relationships презентация
Содержание
- 2. Basics A foreign key can be one or more columns that
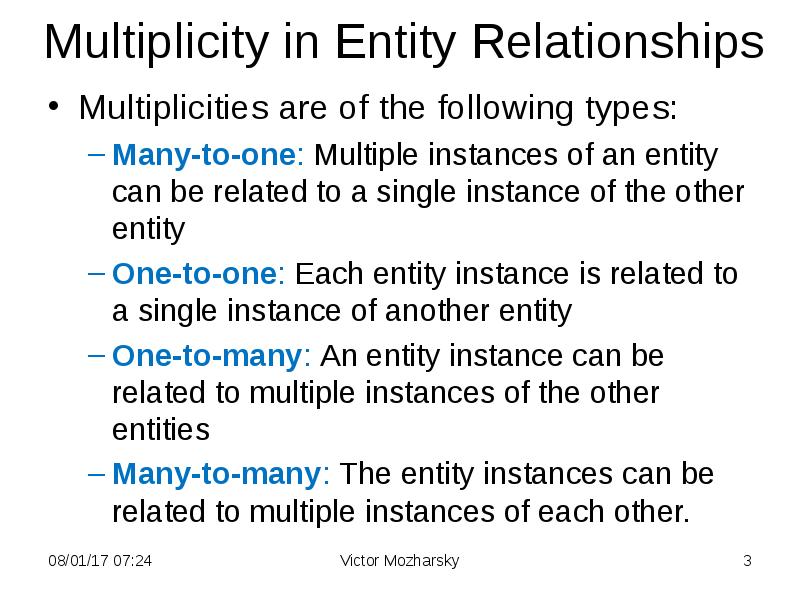
- 3. Multiplicity in Entity Relationships Multiplicities are of the following types: Many-to-one:
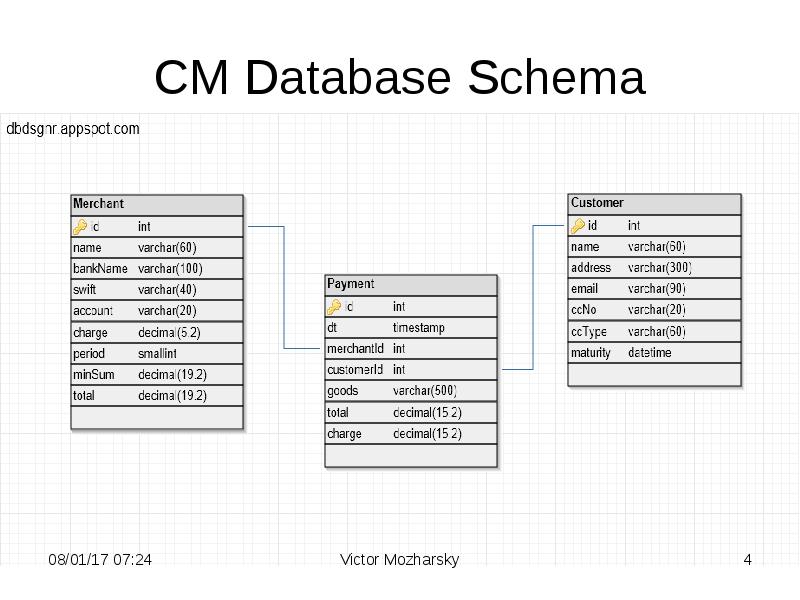
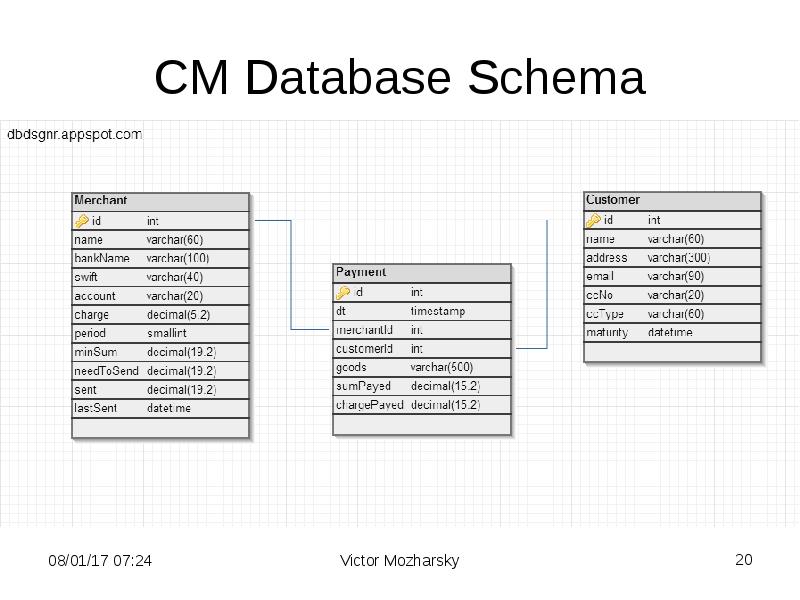
- 4. CM Database Schema
- 5. Many-to-One Mappings A many-to-one mapping is defined by annotating the attribute
- 6. Exercise: Read a Payment Create a project for read payment data
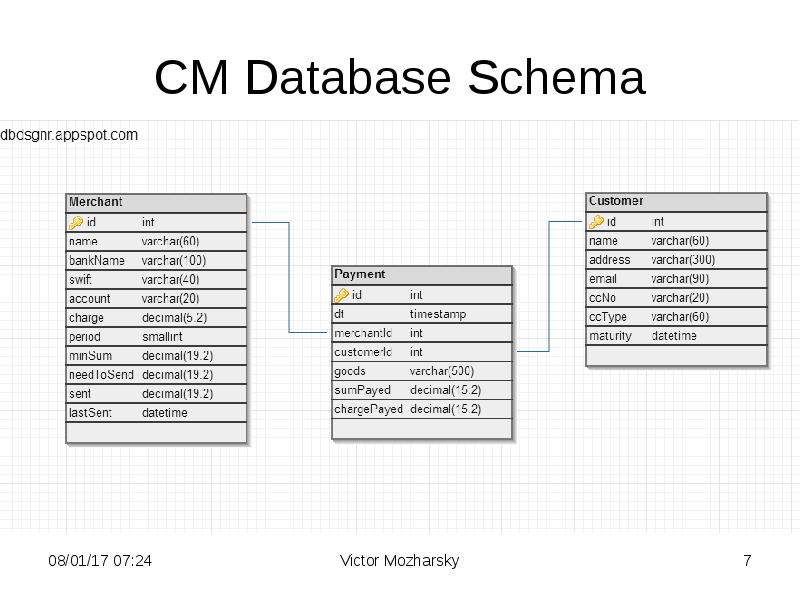
- 7. CM Database Schema
- 8. Payment Entity (1 of 2) @Entity public class Payment { @Id
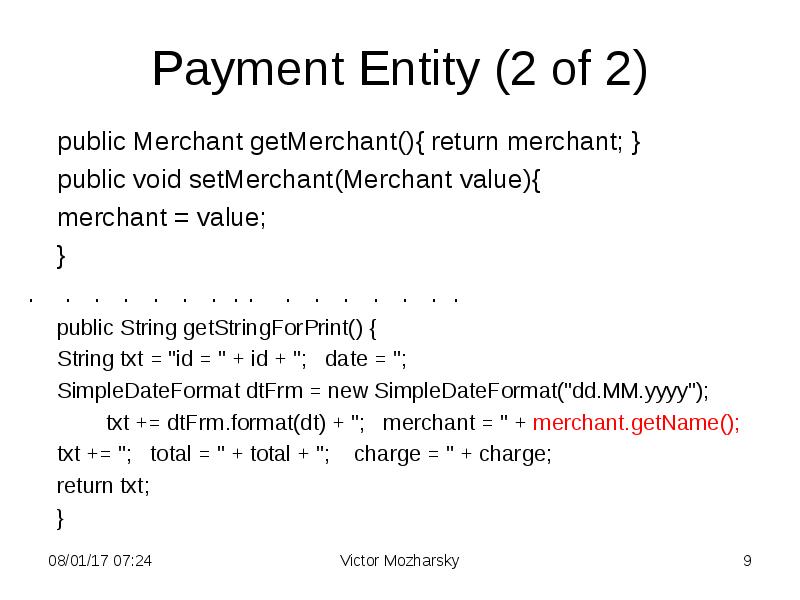
- 9. Payment Entity (2 of 2) public Merchant getMerchant(){ return merchant; }
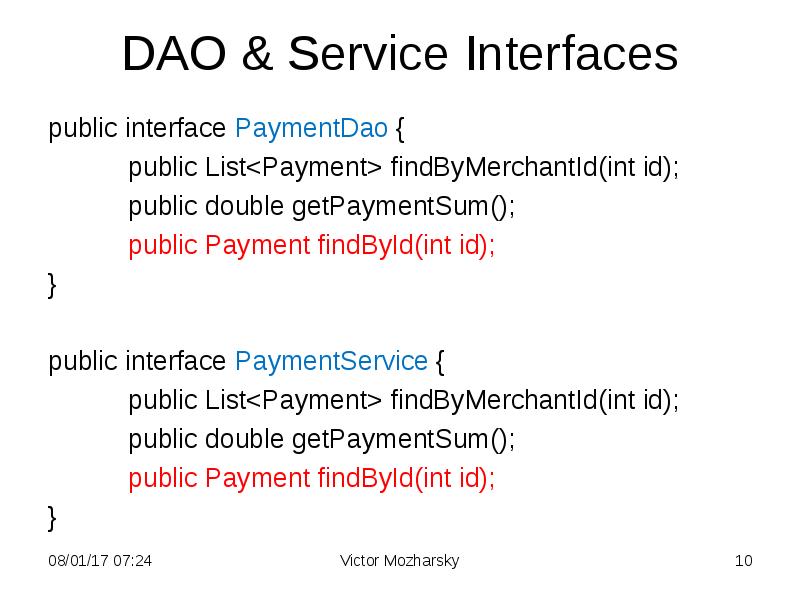
- 10. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List<Payment> findByMerchantId(int
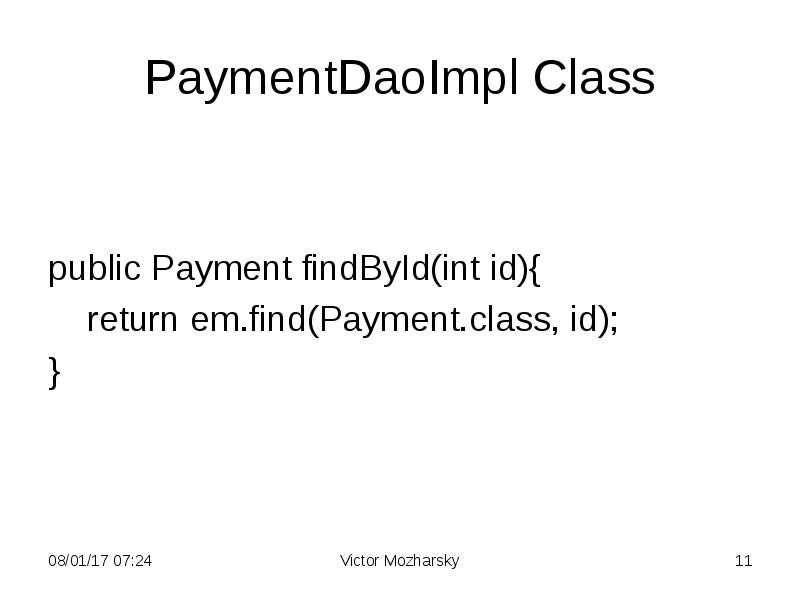
- 11. PaymentDaoImpl Class public Payment findById(int id){ return em.find(Payment.class, id); }
- 12. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 13. Exercise: Read a Payment See P351ReadPayment project for the full text
- 14. Exercise: Group Payments Modify P237Grouping project using entities from the previous
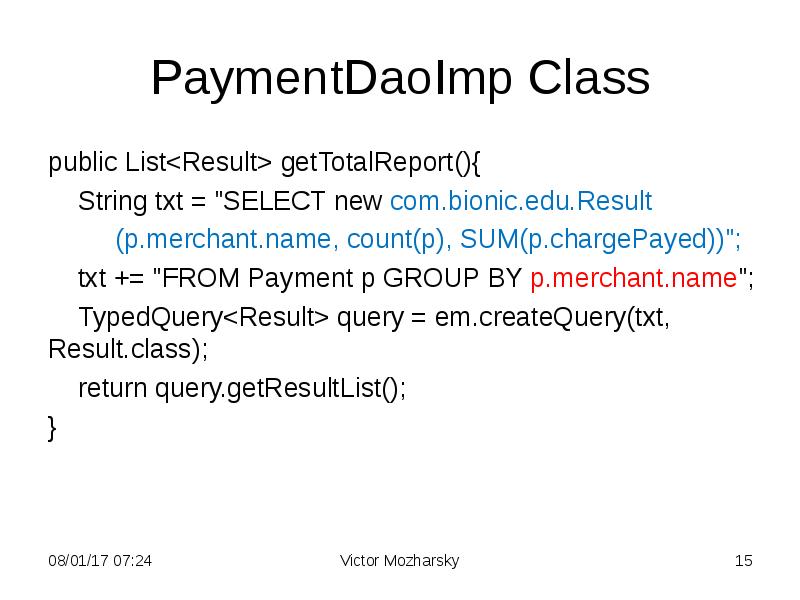
- 15. PaymentDaoImp Class public List<Result> getTotalReport(){ String txt = "SELECT new
- 16. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 17. Exercise: Group Payments See P352GroupPayment project for the full text
- 18. One-to-Many Mappings An entity instance can be related to multiple instances
- 19. Exercise: Read a Merchant’s Payments Create a project for read payment
- 20. CM Database Schema
- 21. Merchant Entity @Entity public class Merchant { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) private int
- 22. Main Class (1 of 2) @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args)
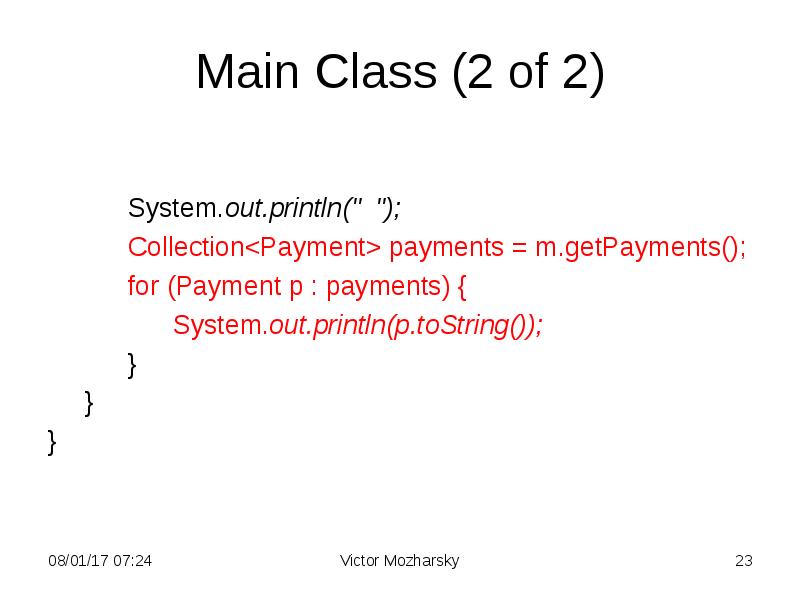
- 23. Main Class (2 of 2) System.out.println(" "); Collection<Payment> payments = m.getPayments();
- 24. Exercise: Read a Merchant’s Payments See P353MerchantPayments project for the full
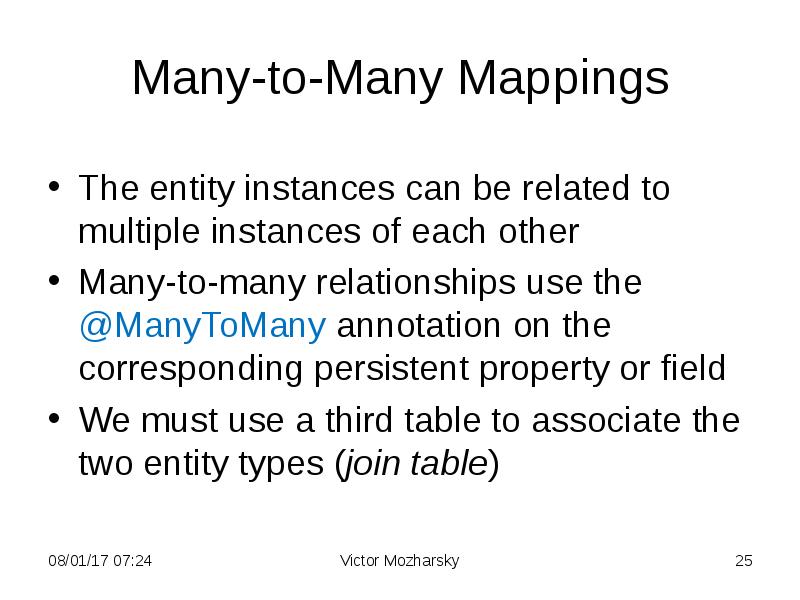
- 25. Many-to-Many Mappings The entity instances can be related to multiple instances
- 26. @JoinTable Annotation @JoinTable(name=“table name”, joinColumns=@JoinColumn(name=“c1Id”), inverseJoinColumns= @JoinColumn(name=“c2Id”))
- 27. Exercise: Read Customer’s Merchants Create a project to read data about
- 28. Customer Entity (1 of 2) @Entity public class Customer { @Id
- 29. Customer Entity (2 of 2) @ManyToMany @JoinTable(name="Payment", joinColumns=@JoinColumn(name="customerId"), inverseJoinColumns=@JoinColumn(name="merchantId")) private
- 30. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 31. Exercise: Read Customer’s Merchants See P354CustAndMerch project for the full text
- 32. Lazy Relationships The fetch mode can be specified on any of
- 33. One-to-One Mappings Each entity instance is related to a single instance
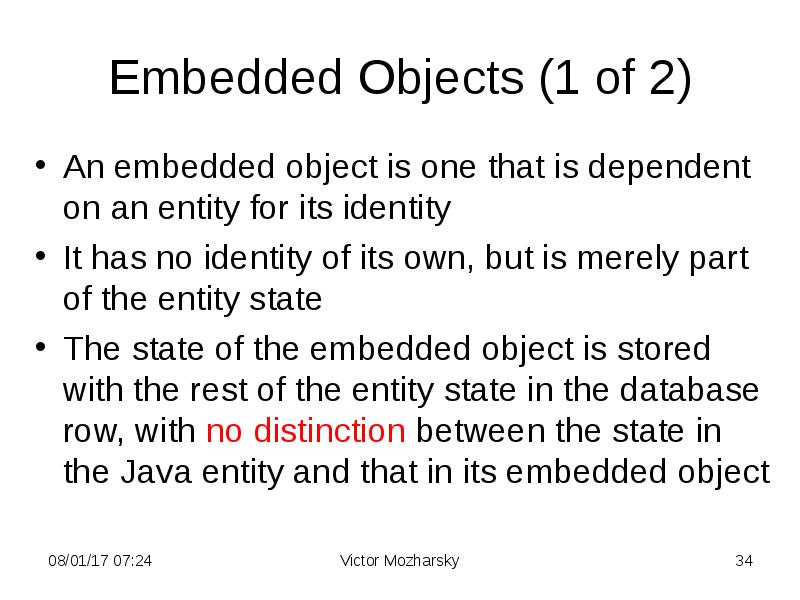
- 34. Embedded Objects (1 of 2) An embedded object is one that
- 35. Embedded Objects (2 of 2) We can share the same embedded
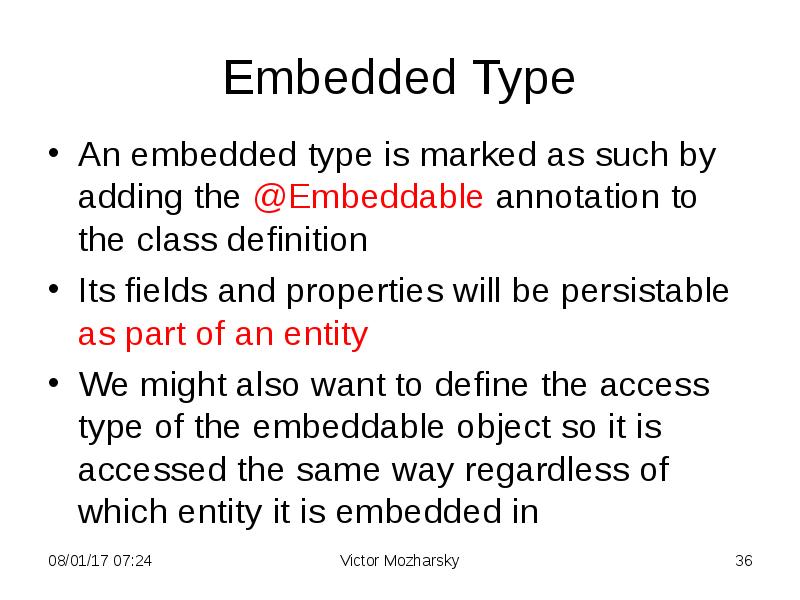
- 36. Embedded Type An embedded type is marked as such by adding
- 37. Address Embedded Type @Embeddable @Access(AccessType.FIELD) public class Address {
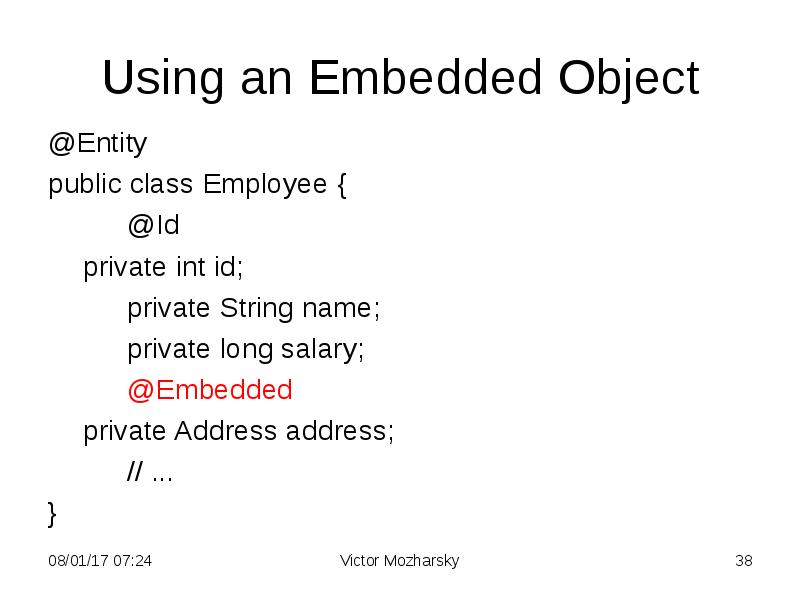
- 38. Using an Embedded Object @Entity public class Employee {
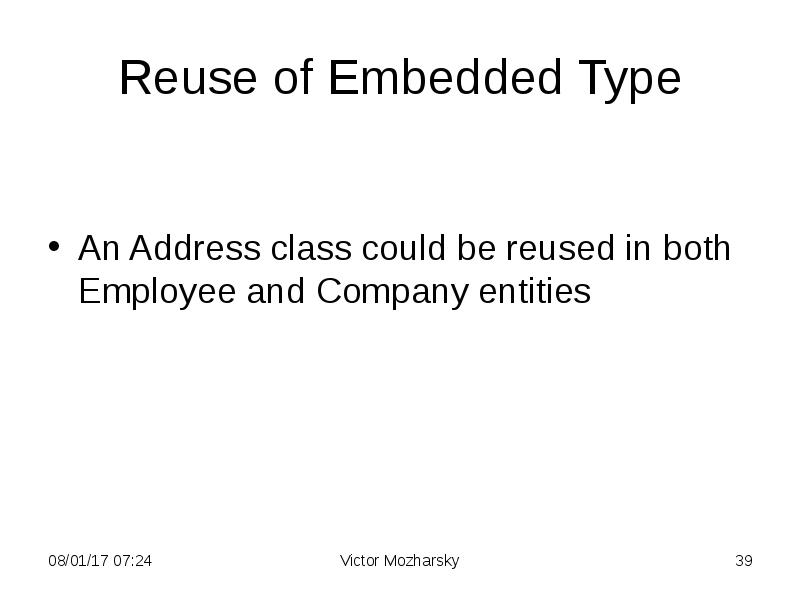
- 39. Reuse of Embedded Type An Address class could be reused in
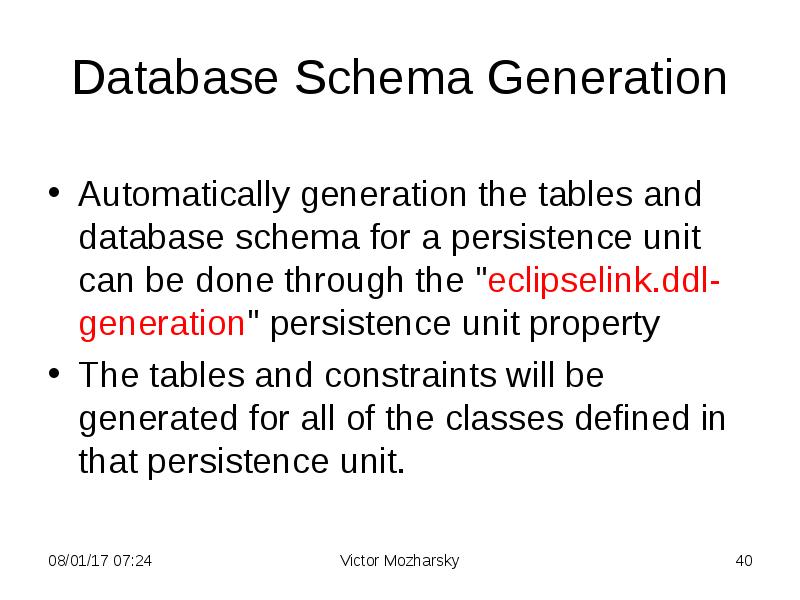
- 40. Database Schema Generation Automatically generation the tables and database schema for
- 41. eclipselink.ddl-generation Values create-tables – if the table already exists then it
- 42. Schema Generation Practice One of the complaints around schema generation is
- 43. Schema Generation Practice If every database-tuning option were exposed through JPA
- 44. Скачать презентацию





![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/9cfb44c2736edaa1a1d9d26925789578/img11.jpg)


![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/9cfb44c2736edaa1a1d9d26925789578/img15.jpg)




![Main Class (1 of 2)
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) Main Class (1 of 2)
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args)](/documents_3/9cfb44c2736edaa1a1d9d26925789578/img21.jpg)





![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/9cfb44c2736edaa1a1d9d26925789578/img29.jpg)






Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему 3. Java Persistence API. 4. Entity Relationships можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























