3. Java Persistence API. 4. Java Persistence Query Language презентация
Содержание
- 2. Queries (1 of 2) In JPA: SQL -> JP QL (Java
- 3. Queries (2 of 2) A query can be issued at runtime
- 4. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao { public Merchant findById(int
- 5. MerchantDaoImpl Class @Repository public class MerchantDaoImpl implements MerchantDao{ @PersistenceContext
- 6. MerchantServiceImpl Class @Named public class MerchantServiceImpl implements MerchantService{ @Inject
- 7. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 8. Java Persistence Query Language Java Persistence Query Language (JP QL)
- 9. Filtering Results JP QL supports the WHERE clause to set conditions
- 10. Exercise: Find Payments Find all payments to the given merchant
- 11. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List<Payment> findByMerchantId(int
- 12. PaymentDaoImpl Class @Repository public class PaymentDaoImpl implements PaymentDao{ @PersistenceContext
- 13. PaymentServiceImpl Class @Named public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService{ @Inject
- 14. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 15. Exercise: Find Payments See P342PaymentsWhere project for the full text
- 16. Joins Between Entities Just as with SQL and tables, if
- 17. Join Example Get names of customers who payed more then 500.0
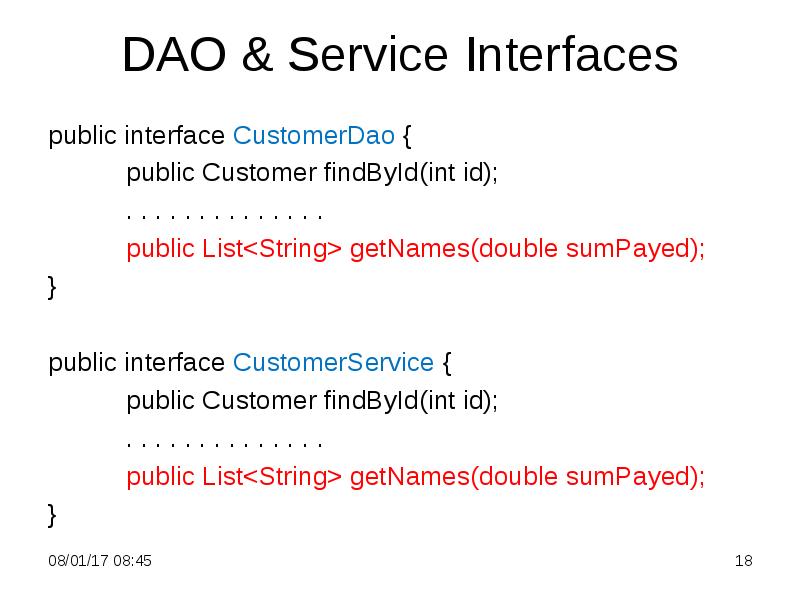
- 18. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface CustomerDao { public Customer findById(int
- 19. CustomerDaoImpl Class public List<String> getNames(double sumPayed){ String txt = "SELECT
- 20. CustomerServiceImpl Class public List<String> getNames(double sumPayed){ return customerDao.getNames(sumPayed); }
- 21. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 22. Join Example See P343PaymentJoin project for the full text
- 23. Aggregate Queries There are five supported aggregate functions (AVG, COUNT, MIN,
- 24. Aggregate Example Find the sum of all payments
- 25. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List<Payment> findByMerchantId(int
- 26. PaymentDaoImpl Class public double getPaymentSum(){ TypedQuery<Double> query = em.createQuery ("SELECT
- 27. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 28. Aggregate Example See P344Aggregation project for the full text
- 29. Query Positional Parameters Parameters are indicated in the query string by
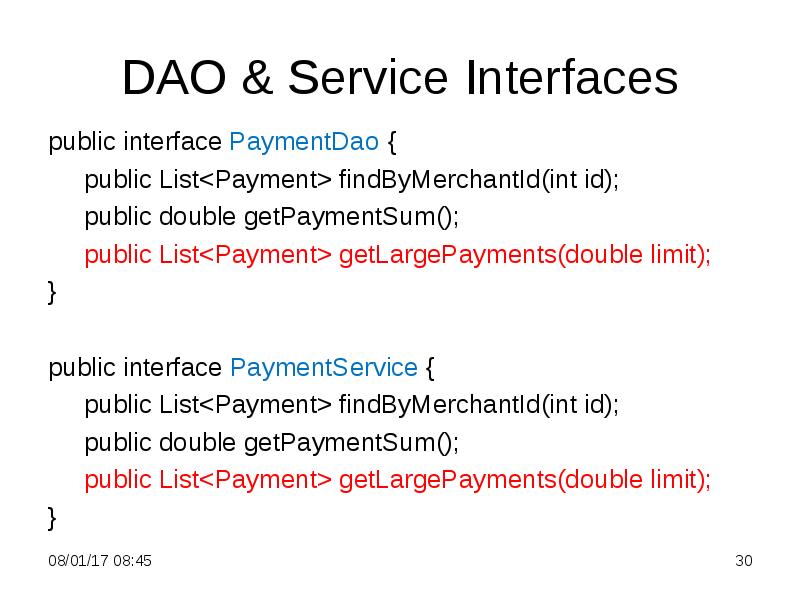
- 30. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List<Payment>
- 31. PaymentDaoImpl Class public List<Payment> getLargePayments(double limit){ TypedQuery<Payment> query = em.createQuery
- 32. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 33. Query Named Parameters Named parameters may also be used and are
- 34. PaymentDaoImpl Class public List<Payment> getLargePayments(double limit){ TypedQuery<Payment> query = em.createQuery
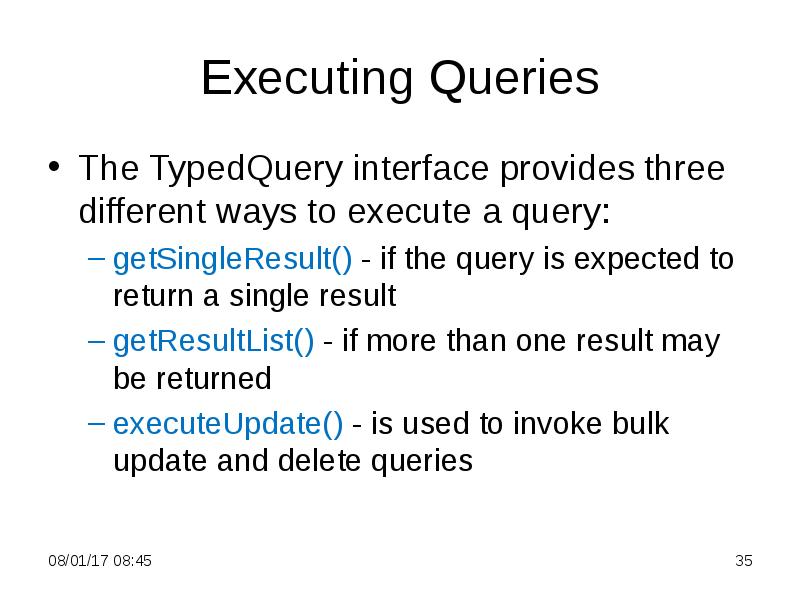
- 35. Executing Queries The TypedQuery interface provides three different ways to execute
- 36. getResultList() Method Returns a collection containing the query results If the
- 37. Exercise: Sort Merchants Create a project to sort merchants by the
- 38. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao { public Merchant findById(int
- 39. MerchantDaoImpl Class public List<Merchant> getSortedByNeedToPay(){ String txt = "SELECT m
- 40. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 41. Exercise: Sort Merchants See P346Sort project for the full text
- 42. getSingleResult() Method Instead of iterating to the first result in a
- 43. Working with Query Results The result type of a query is
- 44. Constructor expressions (1/2) Provide developers with a way to map array
- 45. Constructor expressions (2/2) The argument to the NEW operator is the
- 46. Example: Grouping Payments Get general sum of charge for every merchant
- 47. Class Result public class Result { private String name; private double
- 48. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao { public Merchant findById(int
- 49. MerchantDaoImpl Class public List<Result> getTotalReport(){ String txt = "SELECT new
- 50. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext
- 51. Example: Grouping Payments See P347Grouping project for the full text
- 52. Скачать презентацию






![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img6.jpg)






![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img13.jpg)





![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img20.jpg)





![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img26.jpg)



![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img31.jpg)






![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img39.jpg)









![Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {](/documents_3/8a6bf9ebf6f58e1a65b2f27b802093b8/img49.jpg)

Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему 3. Java Persistence API. 4. Java Persistence Query Language можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























