C# Collections. Generic Collections презентация
Содержание
- 2. Agenda
- 3. Array Array is a data structure that contains several variables of
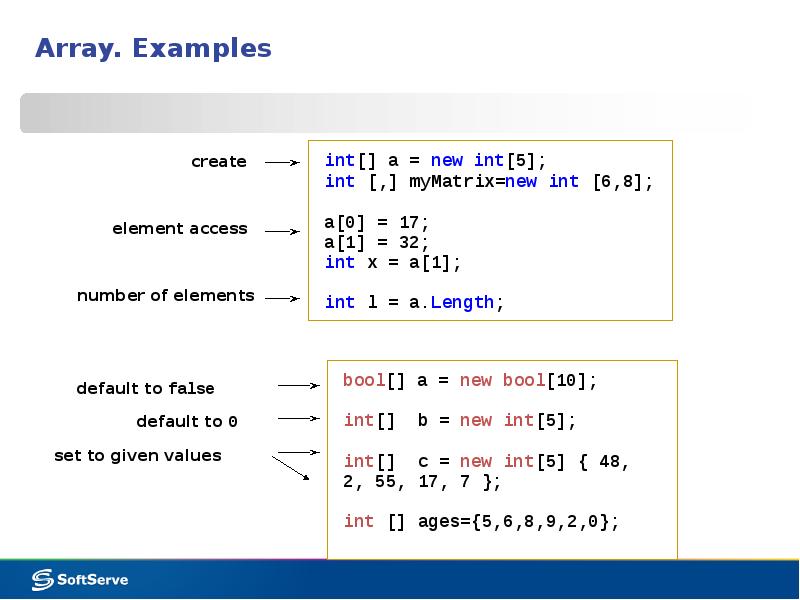
- 4. Array. Examples
- 5. Array. Examples Multidimensional arrays: string [ , ] names = new
- 6. Array. Benefits. Limitations Benefits of Arrays: Easy to use: arrays are
- 7. System.Collections. ArrayList System.Collections namespace ArrayList, HashTable, SortedList, Queue, Stack: A collection
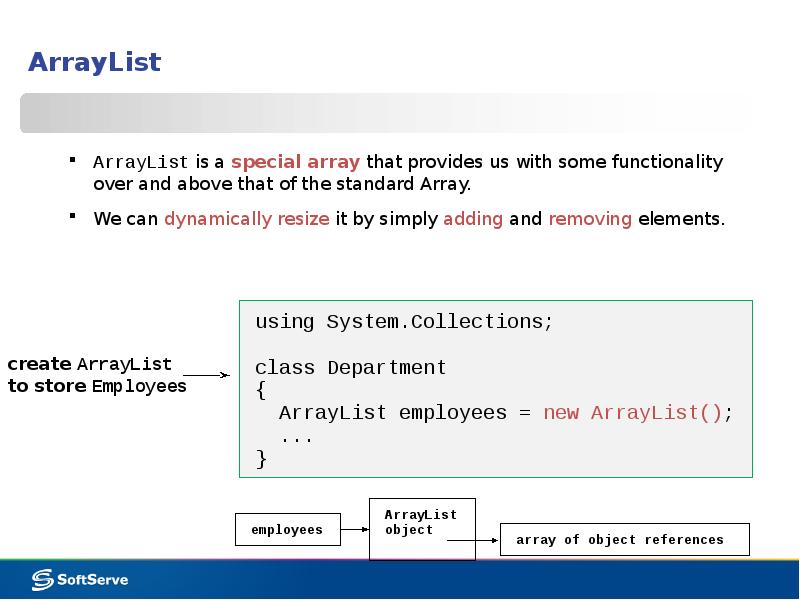
- 8. ArrayList ArrayList is a special array that provides us with some
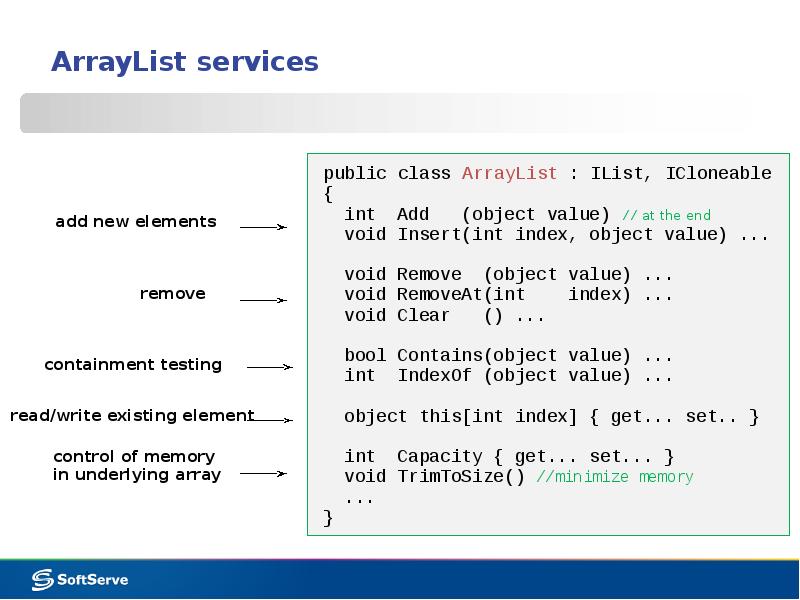
- 9. ArrayList services
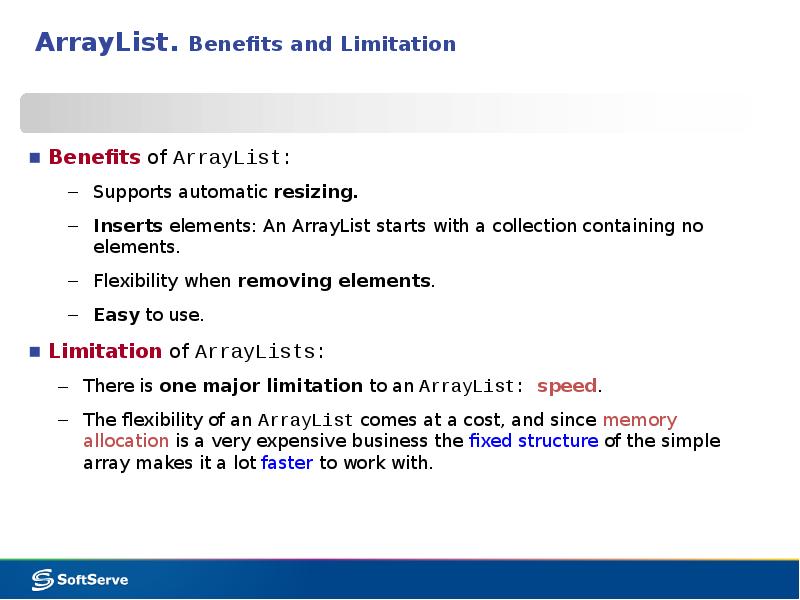
- 10. ArrayList. Benefits and Limitation Benefits of ArrayList: Supports automatic resizing.
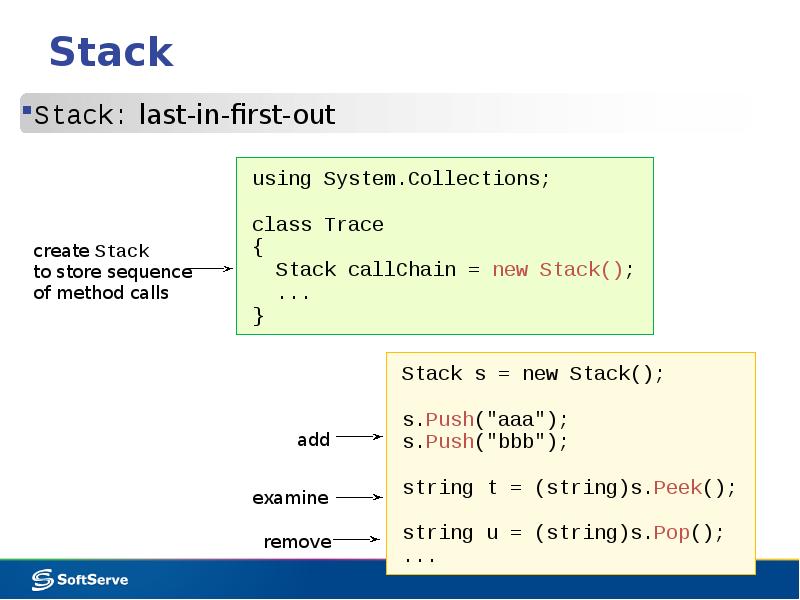
- 11. Stack Stack: last-in-first-out
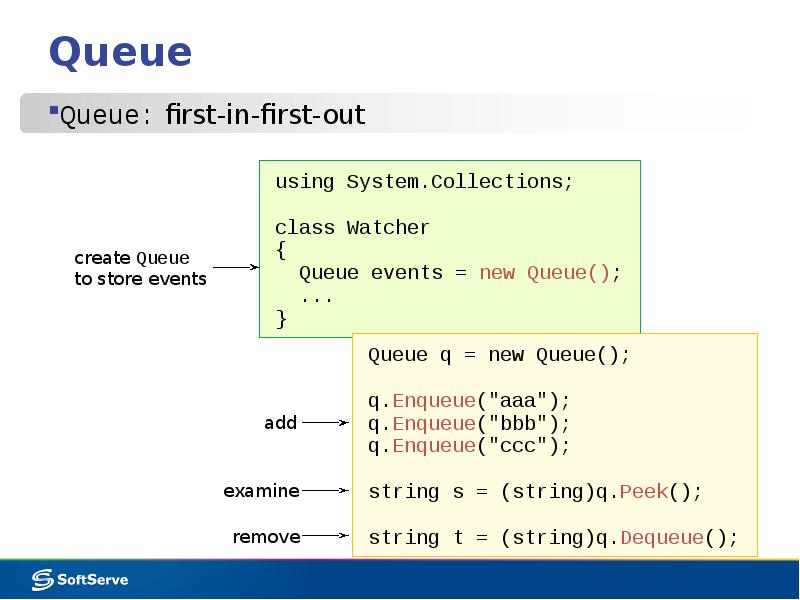
- 12. Queue Queue: first-in-first-out
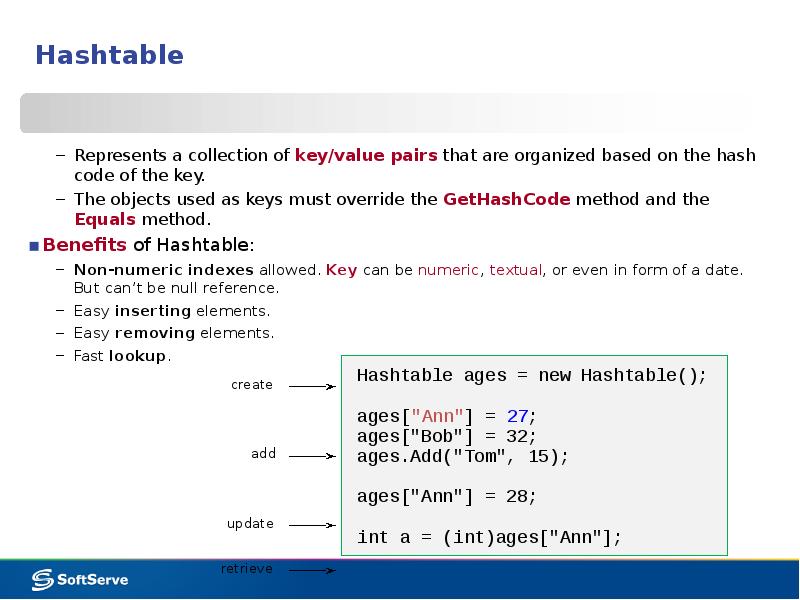
- 13. Hashtable Represents a collection of key/value pairs that are organized based
- 14. Hashtable Limitations of Hashtable: Performance and speed: Hashtable objects are slower
- 15. SortedList Represents a collection of key/value pairs that are sorted by
- 16. SortedList [SerializableAttribute] [ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public class SortedList : IDictionary,
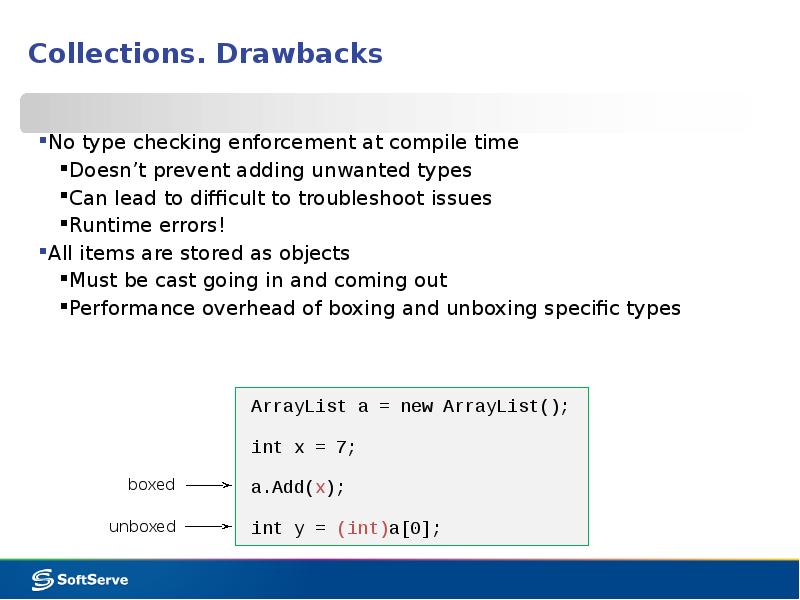
- 17. Collections. Drawbacks No type checking enforcement at compile time Doesn’t prevent
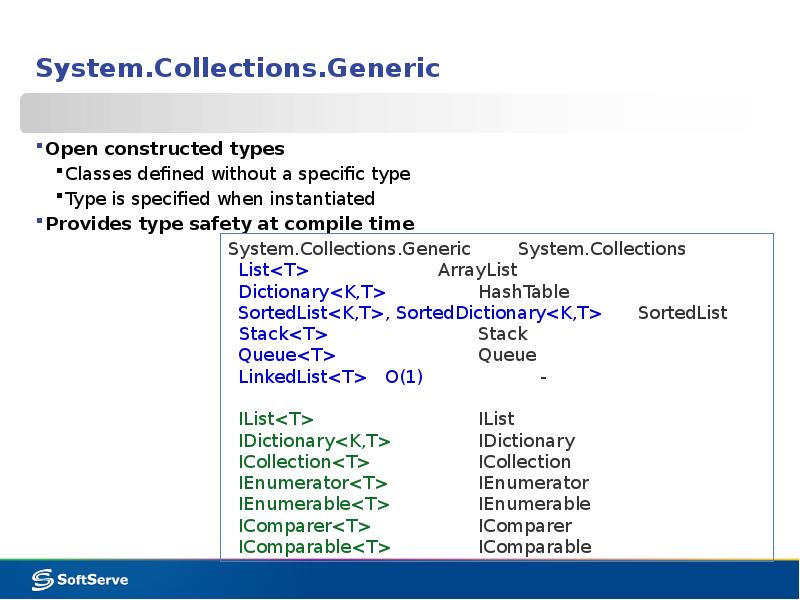
- 18. System.Collections.Generic Open constructed types Classes defined without a specific type
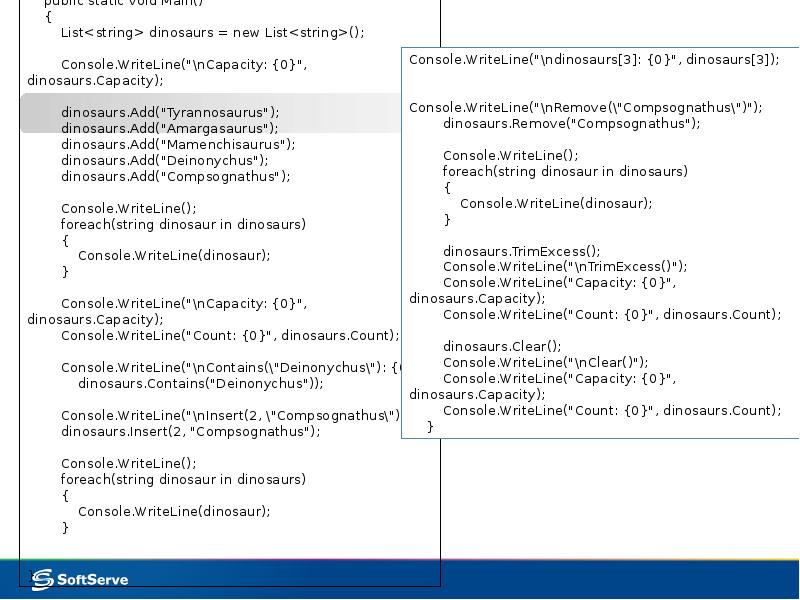
- 19. List<T> List generic class: [SerializableAttribute] public class List<T> : IList<T>,
- 20. List<T> Methods such as BinarySearch and Sort use an ordering comparer
- 22. Questions?
- 23. Скачать презентацию



![Array. Examples
Multidimensional arrays:
string [ , ] names = new Array. Examples
Multidimensional arrays:
string [ , ] names = new](/documents_3/c9b8a2bfc8645dc7ba2daa0638d309ea/img4.jpg)




![SortedList
[SerializableAttribute]
[ComVisibleAttribute(true)]
public class SortedList : IDictionary,
SortedList
[SerializableAttribute]
[ComVisibleAttribute(true)]
public class SortedList : IDictionary,](/documents_3/c9b8a2bfc8645dc7ba2daa0638d309ea/img15.jpg)
![List<T>
List generic class:
[SerializableAttribute]
public class List<T> : IList<T>, List<T>
List generic class:
[SerializableAttribute]
public class List<T> : IList<T>,](/documents_3/c9b8a2bfc8645dc7ba2daa0638d309ea/img18.jpg)


Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему C# Collections. Generic Collections можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























