C# Exception handling. Handling Errors during the Program Execution презентация
Содержание
- 2. Agenda What are Exceptions? Handling Exceptions The System.Exception Class Types of
- 3. What are Exceptions? The exceptions in .NET Framework are classic implementation
- 4. Handling Exceptions In C# the exceptions can be handled by the
- 5. Handling Exceptions – Example
- 6. The System.Exception Class Exception is a base class for all exceptions
- 7. Exception Properties – Example
- 8. Exception Properties The Message property gives brief description of the problem
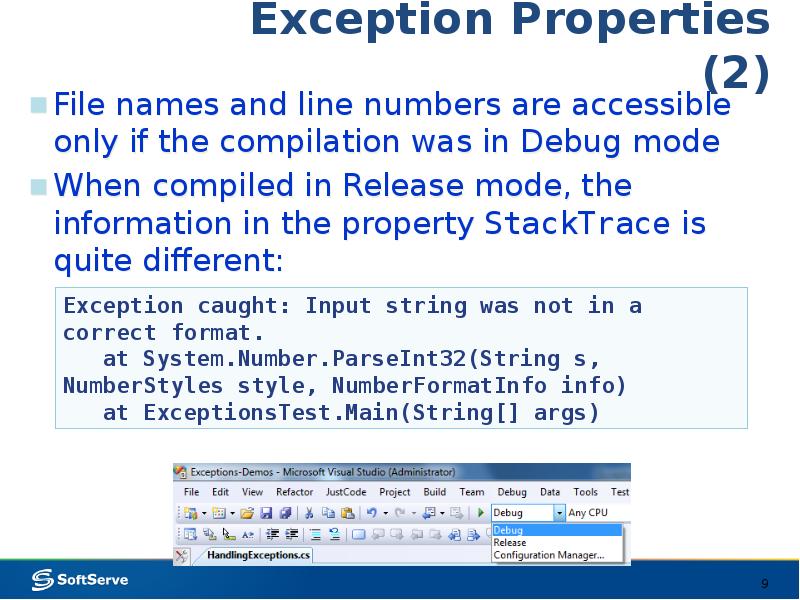
- 9. Exception Properties (2) File names and line numbers are accessible only
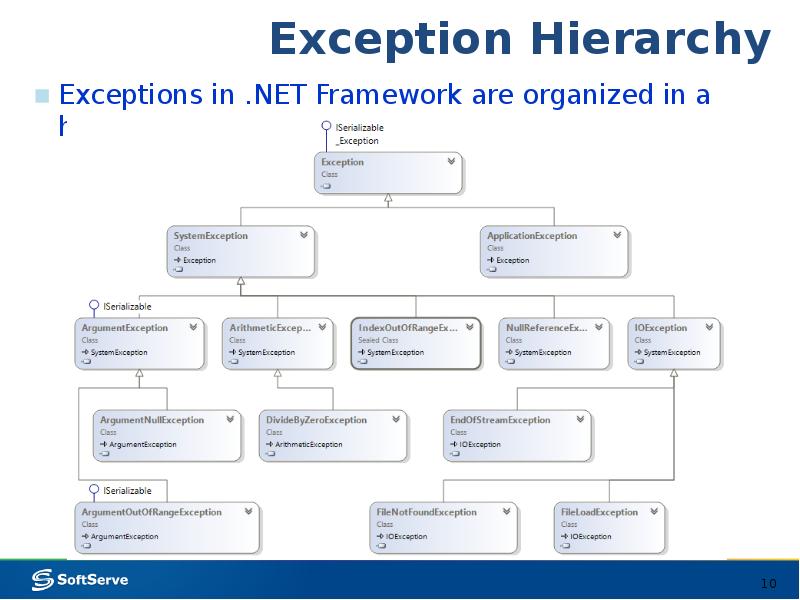
- 10. Exception Hierarchy Exceptions in .NET Framework are organized in a hierarchy
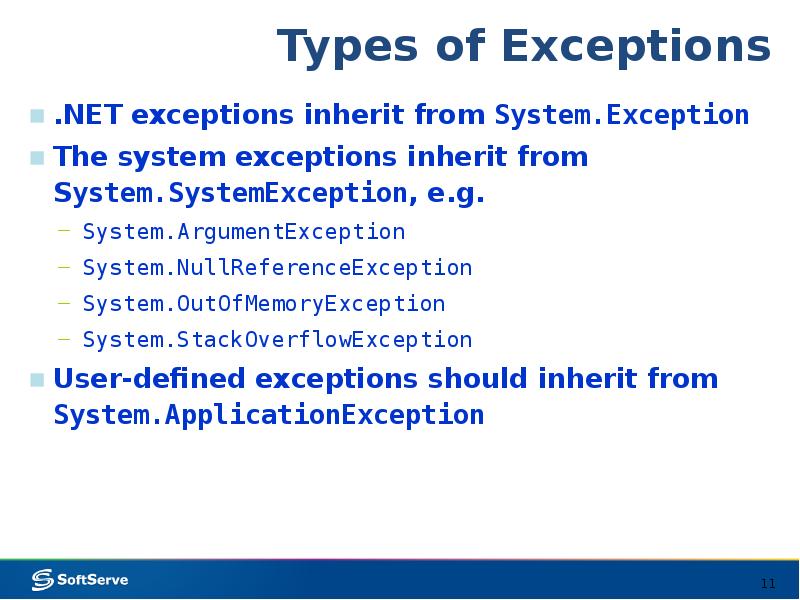
- 11. Types of Exceptions .NET exceptions inherit from System.Exception The system exceptions
- 12. Handling Exceptions When catching an exception of a particular class, all
- 13. Find the Mistake!
- 14. Handling All Exceptions All exceptions thrown by .NET managed code inherit
- 15. Throwing Exceptions Exceptions are thrown (raised) by throw keyword in C#
- 16. How Exceptions Work?
- 17. Using throw Keyword Throwing an exception with an error message: Exceptions
- 18. Re-Throwing Exceptions Caught exceptions can be re-thrown again:
- 19. Throwing Exceptions – Example
- 20. Choosing the Exception Type When an invalid parameter is passed to
- 21. The try-finally Statement The statement: Ensures execution of given block in
- 22. try-finally – Example
- 23. Exceptions – Best Practices catch blocks should begin with the
- 24. Exceptions – Best Practices (2) When raising an exception always pass
- 25. Exceptions – Best Practices (3) Exceptions can decrease the application performance
- 26. Summary Exceptions provide flexible error handling mechanism in .NET Framework Allow
- 27. Exceptions Handling
- 28. Скачать презентацию






















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему C# Exception handling. Handling Errors during the Program Execution можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























