Computer Security: Principles and Practice. Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems. Chapter 9 презентация
Содержание
- 2. Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems Effective means of protecting LANs Internet
- 3. Firewall Access Policy A critical component in the planning and implementation
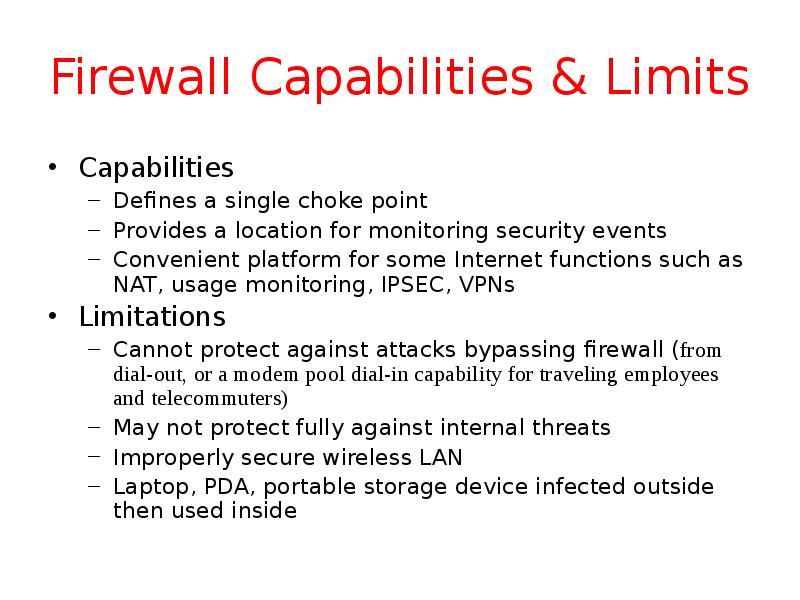
- 4. Firewall Capabilities & Limits Capabilities Defines a single choke point Provides
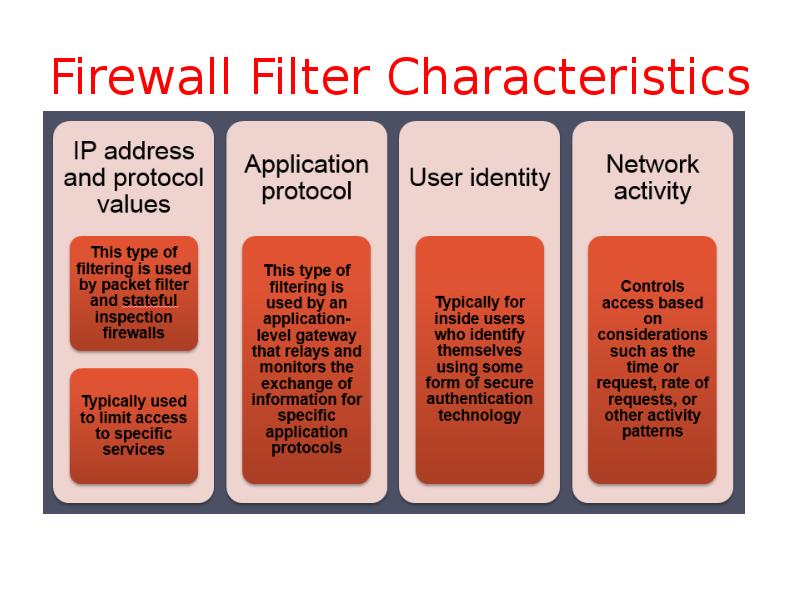
- 5. Firewall Filter Characteristics
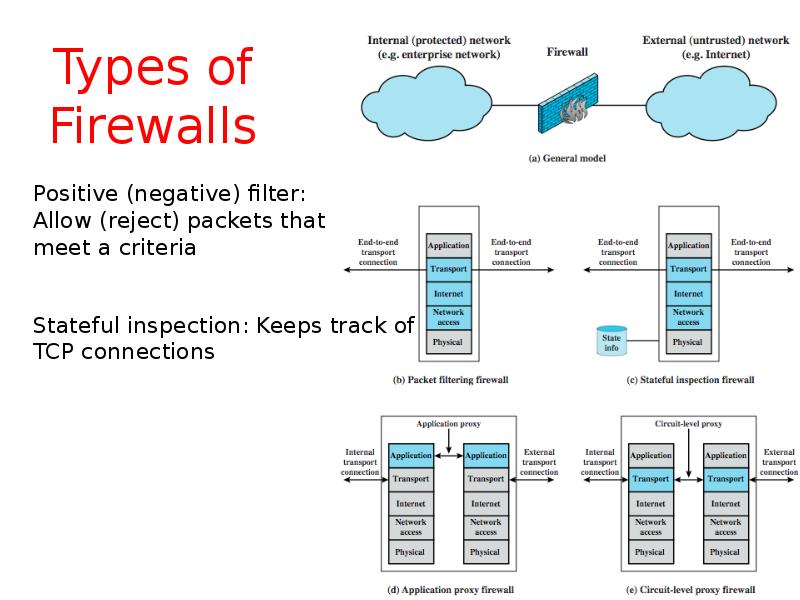
- 6. Types of Firewalls
- 7. Packet Filtering Firewall Applies rules to packets in/out of firewall based
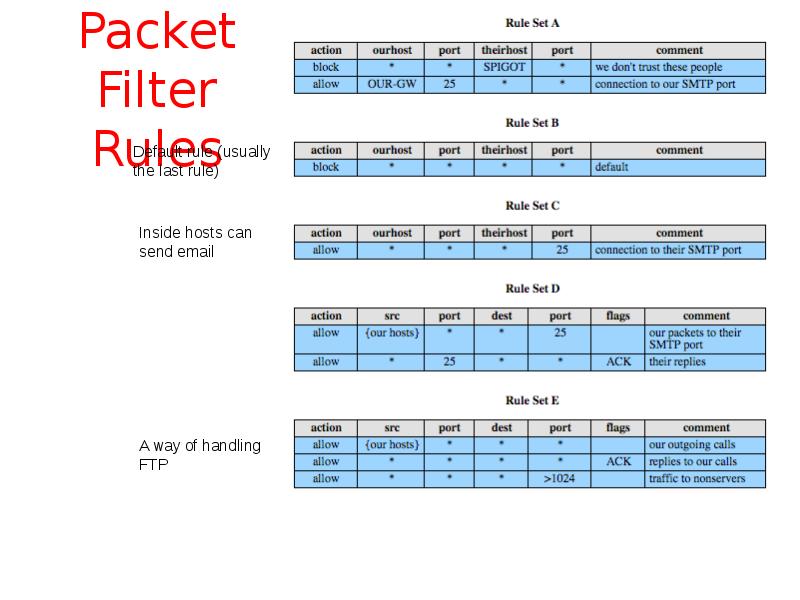
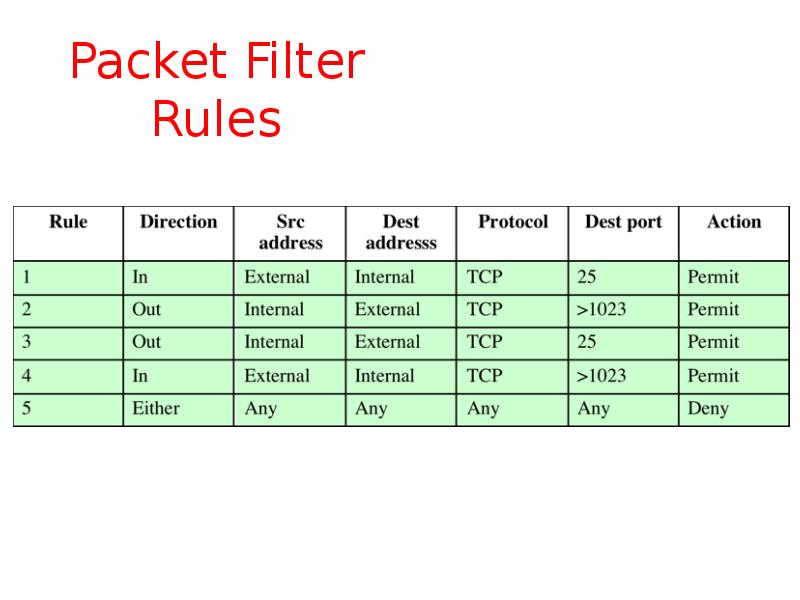
- 8. Packet Filter Rules
- 9. Packet Filter Rules
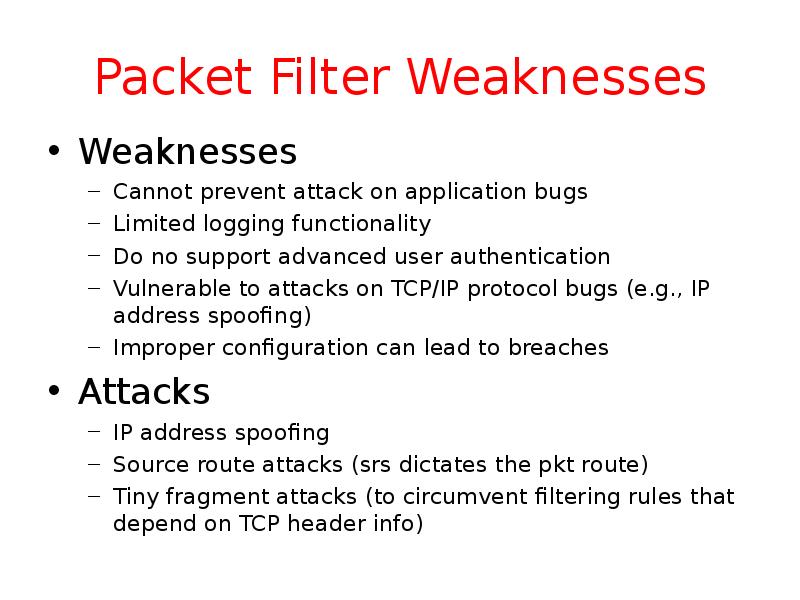
- 10. Packet Filter Weaknesses Weaknesses Cannot prevent attack on application bugs Limited
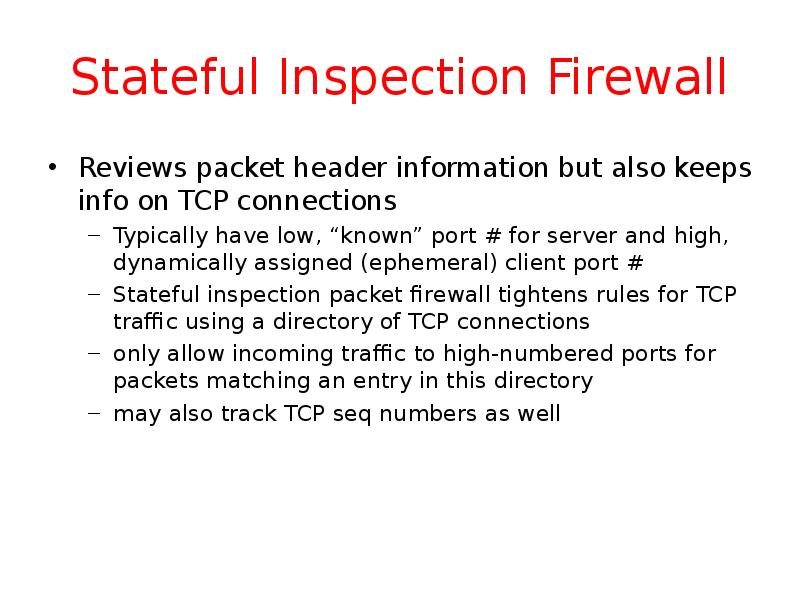
- 11. Stateful Inspection Firewall Reviews packet header information but also keeps info
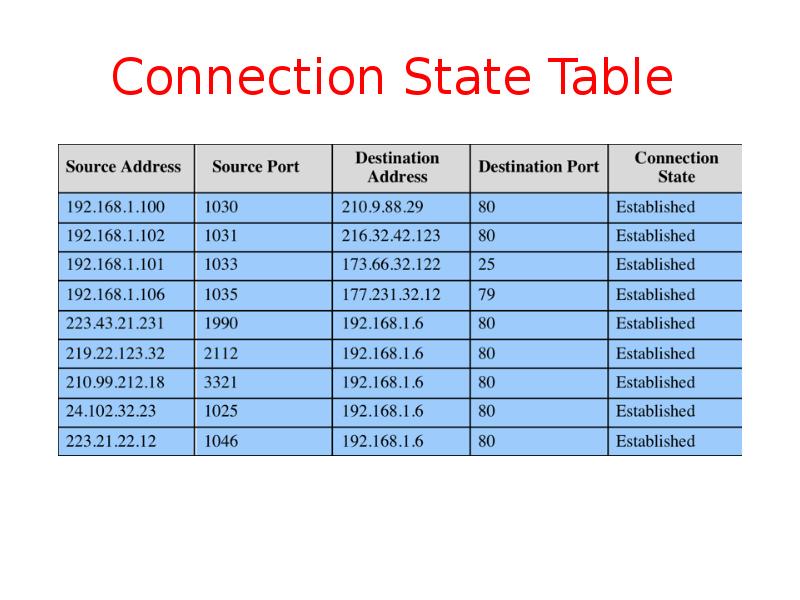
- 12. Connection State Table
- 13. Application-Level (Proxy) Gateway Acts as a relay of application-level traffic User
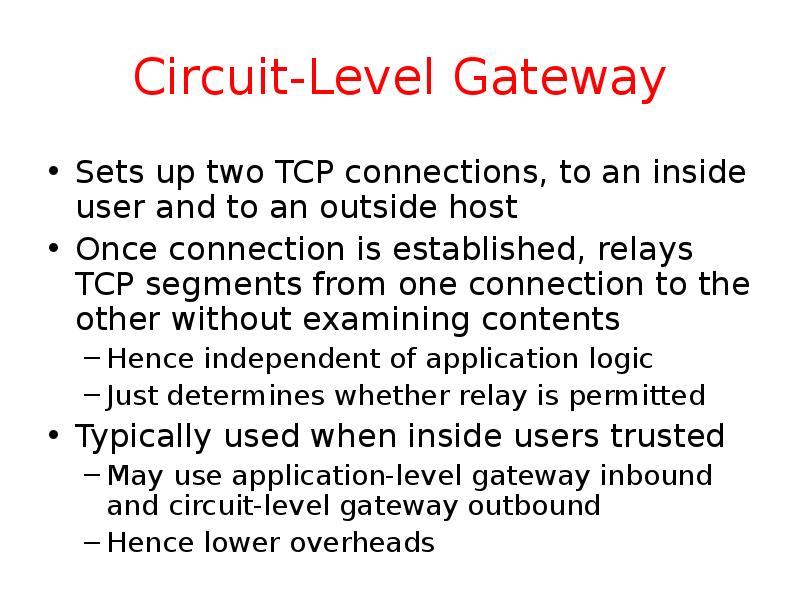
- 14. Circuit-Level Gateway Sets up two TCP connections, to an inside user
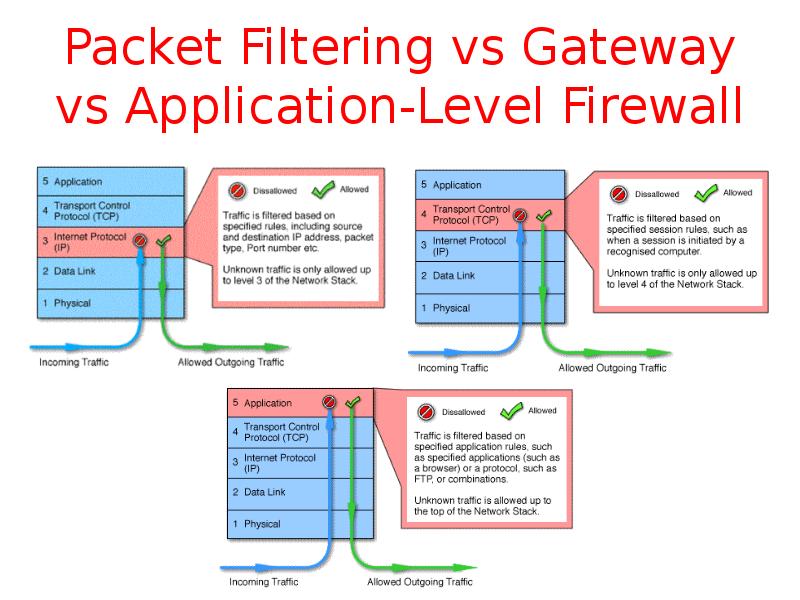
- 15. Packet Filtering vs Gateway vs Application-Level Firewall
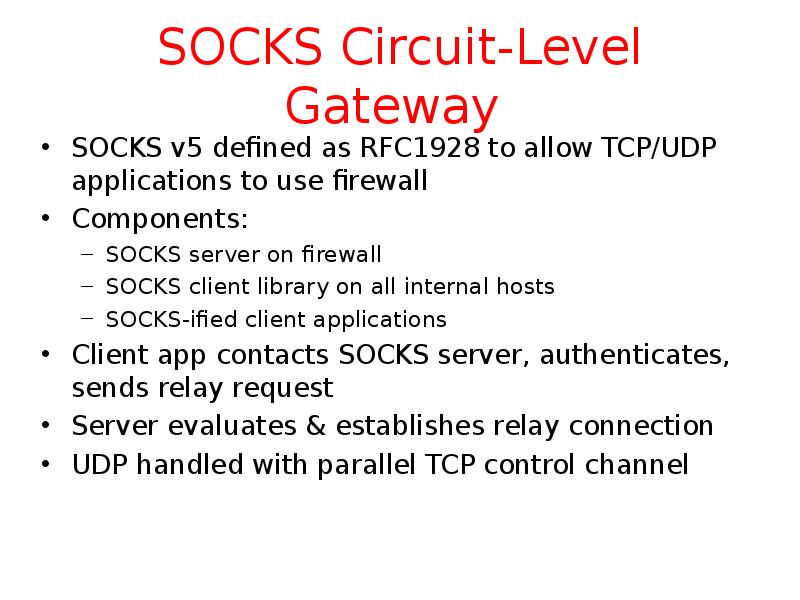
- 16. SOCKS Circuit-Level Gateway SOCKS v5 defined as RFC1928 to allow
- 17. Firewall Basing Several options for locating firewall: Bastion host Individual host-based
- 18. Bastion Hosts Critical strongpoint in network Hosts application/circuit-level gateways Common characteristics:
- 19. Host-Based Firewalls Used to secure individual host Available in/add-on for many
- 20. Personal Firewall Controls traffic flow to/from PC/workstation For both home or
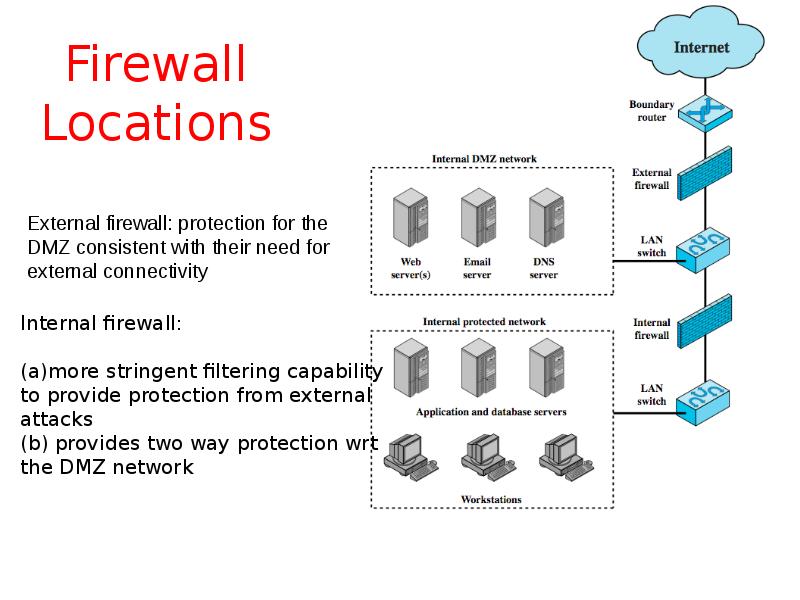
- 21. Firewall Locations
- 22. Virtual Private Networks
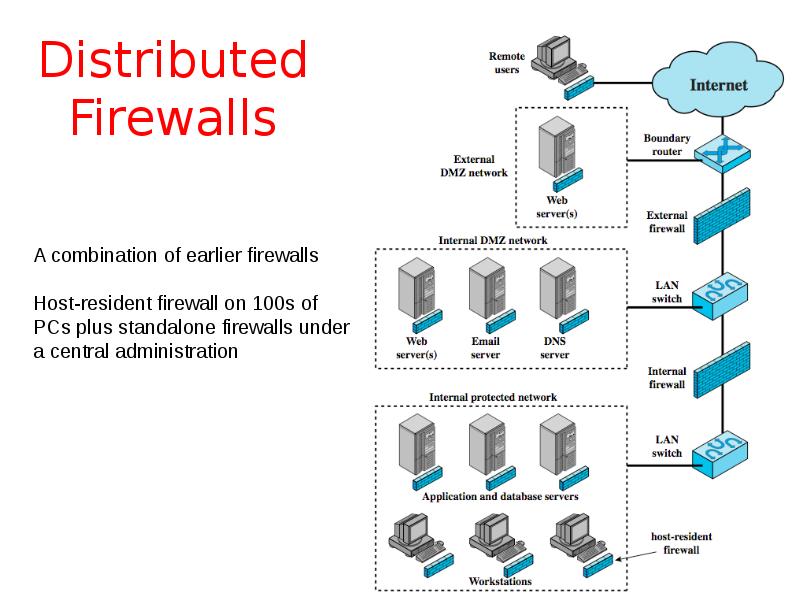
- 23. Distributed Firewalls
- 24. Firewall Topologies Host-resident firewall: personal firewall and firewall on servers (used
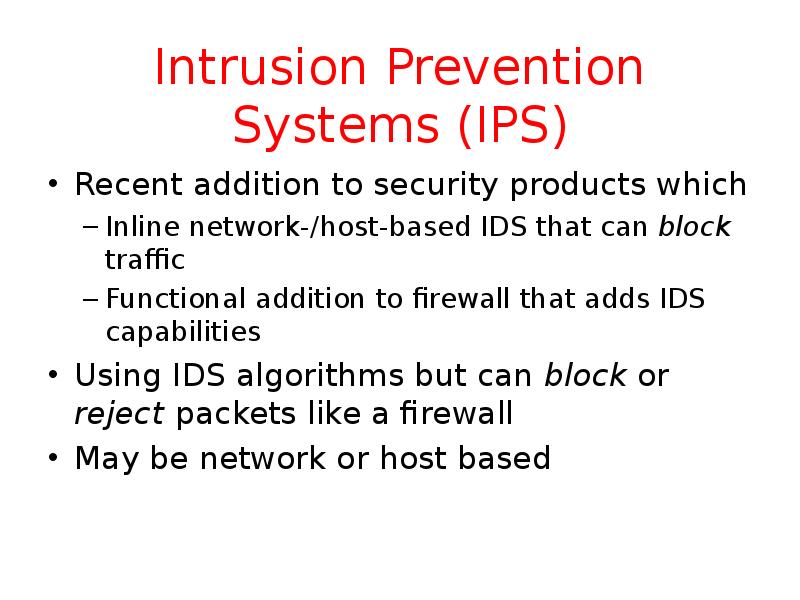
- 25. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) Recent addition to security products which Inline
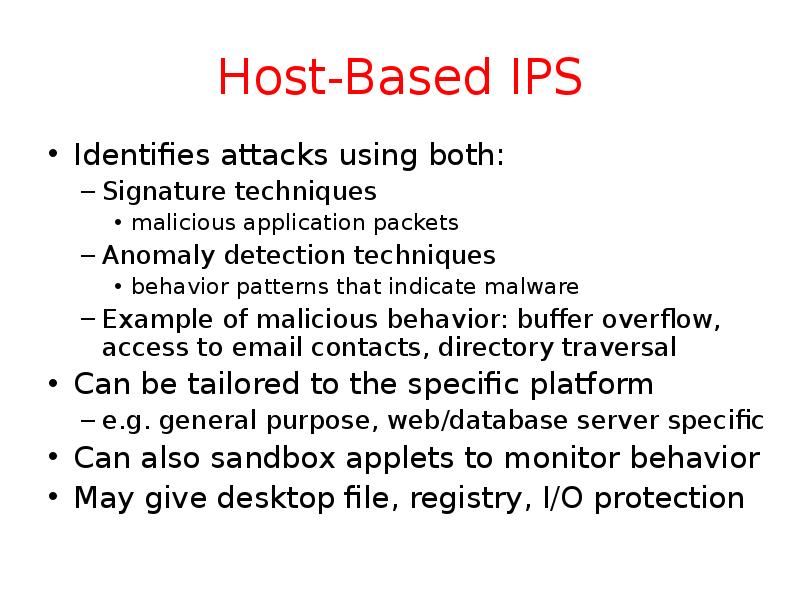
- 26. Host-Based IPS Identifies attacks using both: Signature techniques malicious application packets
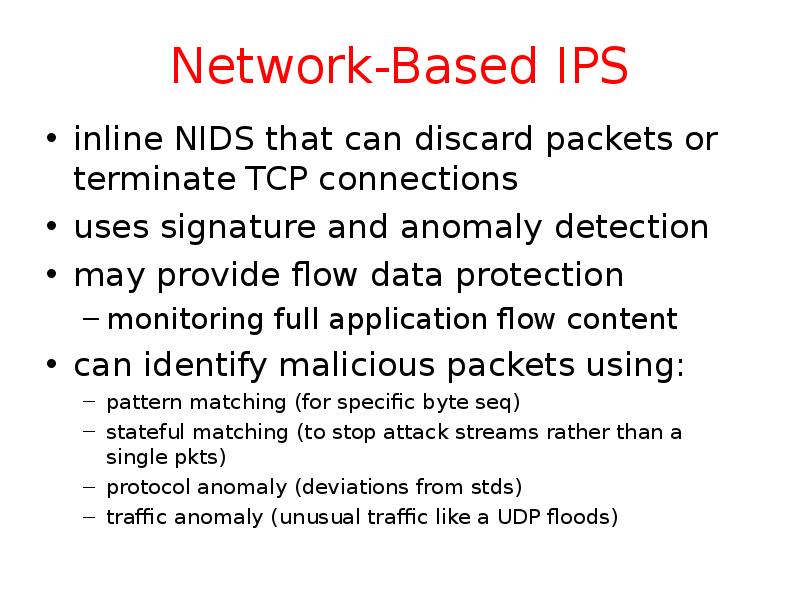
- 27. Network-Based IPS inline NIDS that can discard packets or terminate TCP
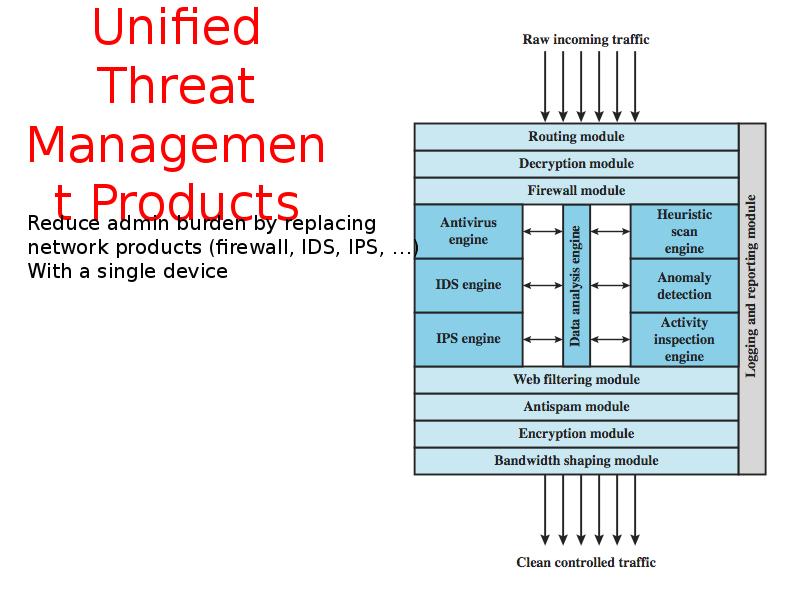
- 28. Unified Threat Management Products
- 29. Summary Introduced need for & purpose of firewalls Types of firewalls
- 30. Скачать презентацию












Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Computer Security: Principles and Practice. Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems. Chapter 9 можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























