Data coding and screening презентация
Содержание
- 2. WHAT IS DATA CODING? “A systematic way in which to condense
- 4. WHEN TO CODE When testing a hypothesis (deductive), categories and codes
- 5. LEVELS OF CODING (FOR QUALITATIVE DATA) Open Break down, compare, and
- 6. WHY DO DATA CODING? It lets you make sense of and
- 7. DATA SCREENING Used to identify miscoded, missing, or messy data Find
- 8. DETERMINING CODES (BOURQUE, 2004) For surveys or questionnaires, codes are finalized
- 9. IMPORTANCE OF CODEBOOK (SHENTON, 2004) Allows study to be repeated and
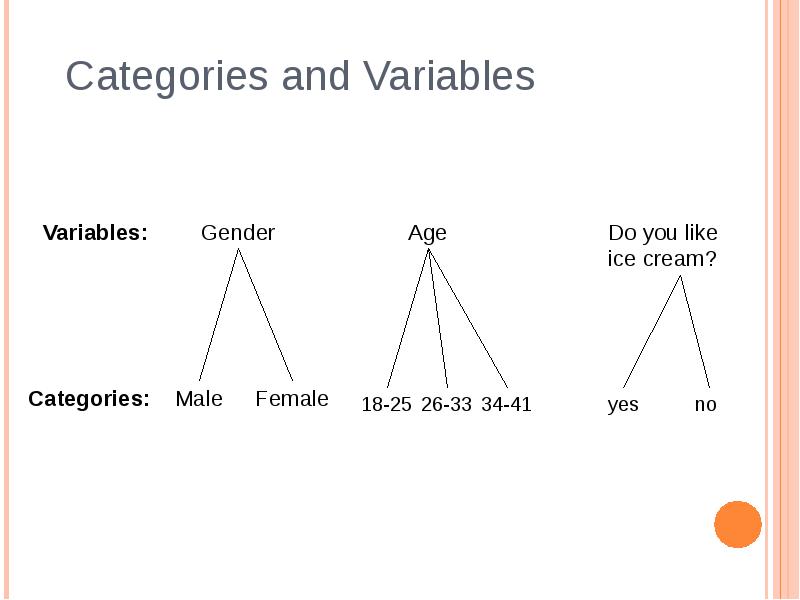
- 10. DETERMINING CODES, CONT. Exhaustive – a unique code number has been
- 11. DETERMINING CODES, CONT. Missing Data - includes conditions such as “refused,”
- 12. CREATING CODE FRAME PRIOR TO DATA COLLECTION (BOURQUE, 2004; EPSTEIN &
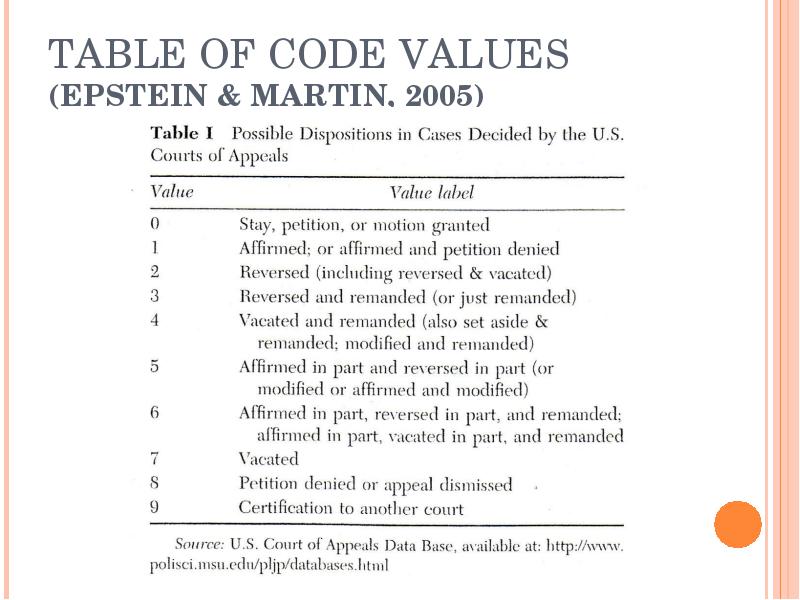
- 13. TABLE OF CODE VALUES (EPSTEIN & MARTIN, 2005)
- 14. TRANSCRIPT (SHENTON, 2004) Appropriate for open-ended answers as in focus groups,
- 15. THREE PARTS TO TRANSCRIPT (SHENTON, 2004) Background information, ex. time, date,
- 16. POSTCODING (SHENTON, 2004) Post-meeting observations Post-transcript review a. Compilation of insightful
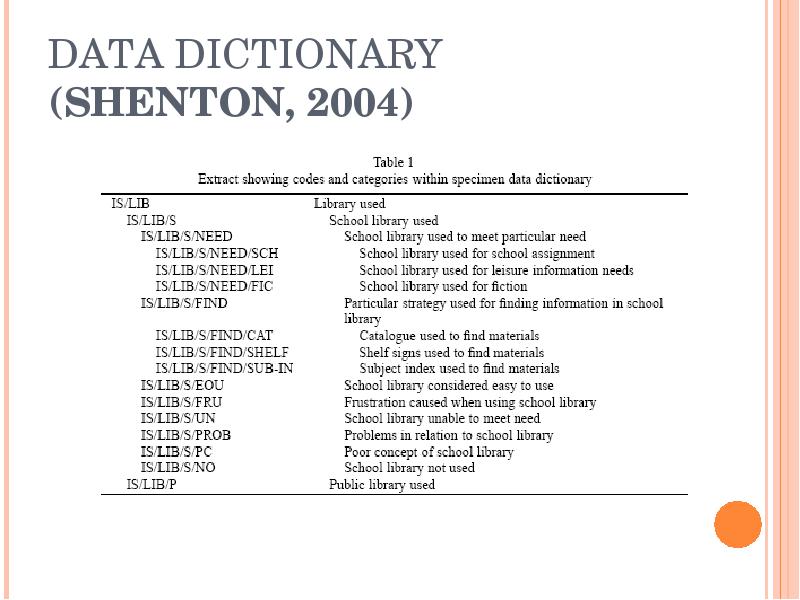
- 17. DATA DICTIONARY (SHENTON, 2004)
- 18. REFERENCES Bourque, Linda B. "Coding." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Social
- 20. Coding Mixed Methods: Advantages and Disadvantages
- 21. Position 1 v. Position 2 “When compared to quantitative research, qualitative
- 22. Move Toward P1 and P2 Cooperation Cooperation – last 25 years
- 23. Advantages of Mixed Methods: Improves validity of findings More in-depth data
- 24. Disadvantages of Mixed Methods Inequality in data sets “Data sets must
- 25. Key Point in Coding Mixed Methods Data “The issue to be
- 26. Examining a Mixed Methods Research Study Makani, S. & Wooshue, K.
- 27. Study Details Population: Purposive population, 10 undergraduates (2 groups) / 5
- 28. Methods Data: Used both qualitative and qualitative data collected through a
- 29. Study Observations Followed 3 groups of business students working on group
- 30. Coding Methods Used pre-selected codes from literature review: Time Efficiency of
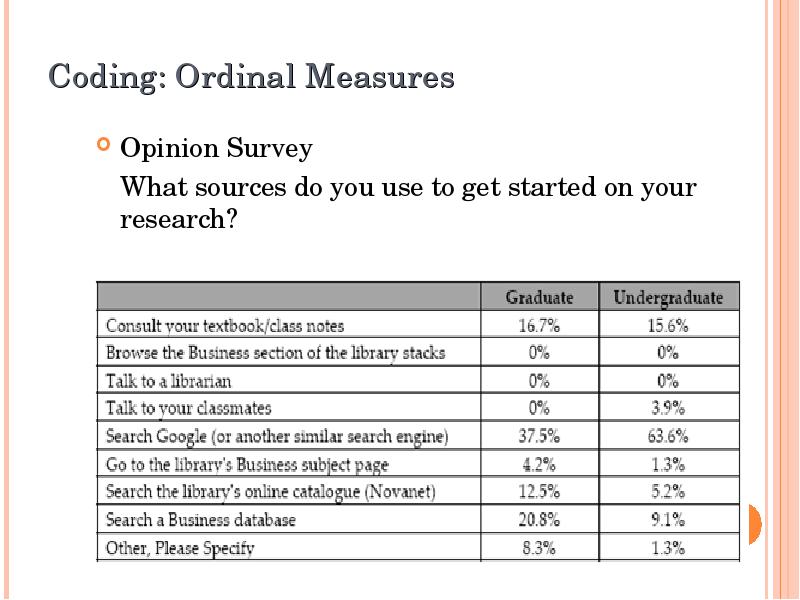
- 31. Coding: Ordinal Measures Opinion Survey What sources do you use to
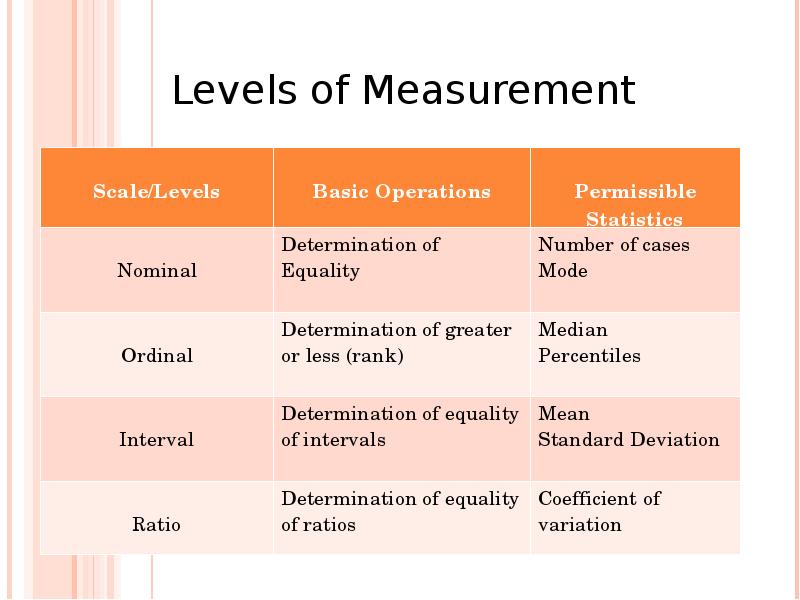
- 32. Examples of Ratio-Interval Coding and Level of Measurement The age of
- 33. Study Conclusions This study reveals that in order to create an
- 34. Study Weaknesses: Use of Mixed Methods Data No discussion of how
- 35. Study Advantages: Use of Mixed Methods Data Numeric data helped create
- 36. OUTLIERS IN DATA ANALYSIS
- 37. WHAT IS AN OUTLIER? Miller (1981): '... An outlier is a
- 38. WHY ARE OUTLIERS IMPORTANT IN DATA ANALYSIS? Outliers can influence the
- 39. ISSUES CONCERNING OUTLIERS Rejection of Outliers “From the earliest efforts to
- 40. What do we do with outliers? There are four basic ways
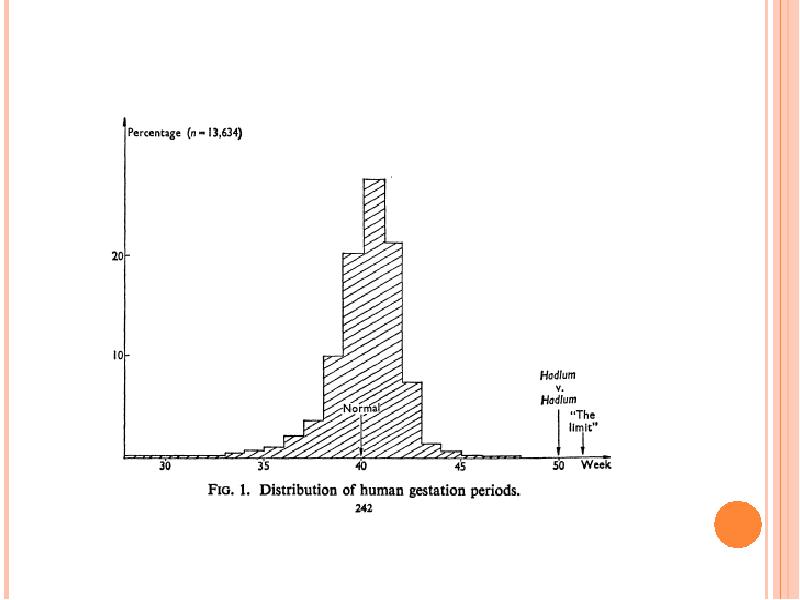
- 41. A CLASSIC EXAMPLE ON THE USE OF OUTLIERS Hadlum vs. Hadlum
- 43. Sources Barnett, Vic. 1978. The study of outliers: purpose and models.
- 44. Скачать презентацию





































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























