Electronic Mail. DNS. P2P file sharing презентация
Содержание
- 2. Overview P2P file sharing (cont.) Socket programming with TCP Socket programming
- 3. P2P file sharing Example Alice runs P2P client application on her
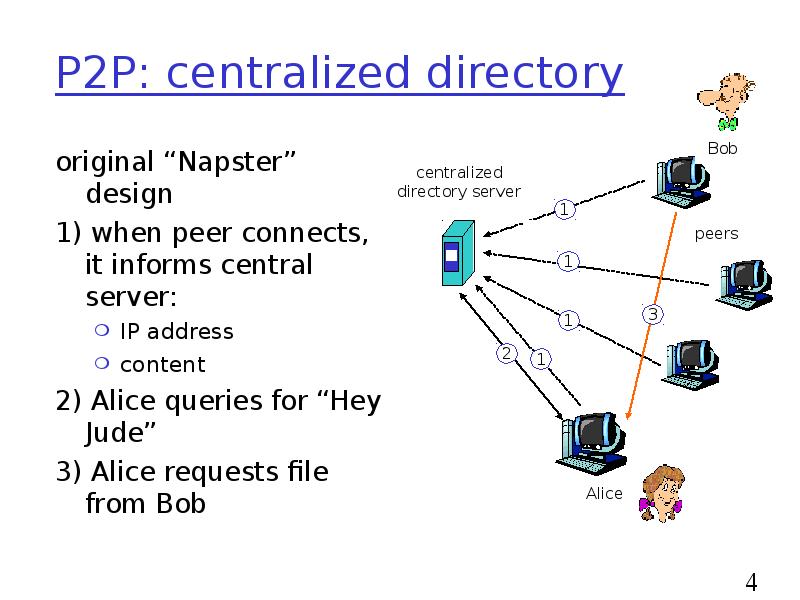
- 4. P2P: centralized directory original “Napster” design 1) when peer connects, it
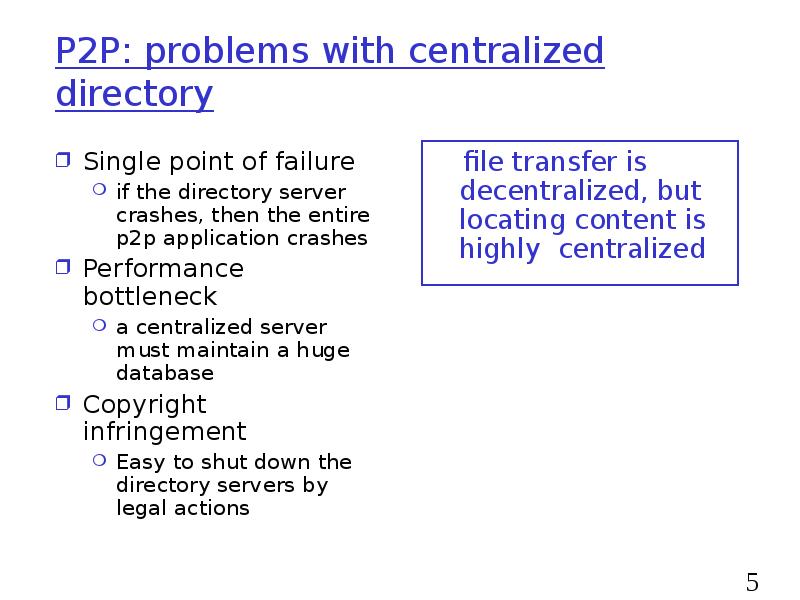
- 5. P2P: problems with centralized directory Single point of failure if the
- 6. Query flooding: Gnutella fully distributed no central server public domain protocol
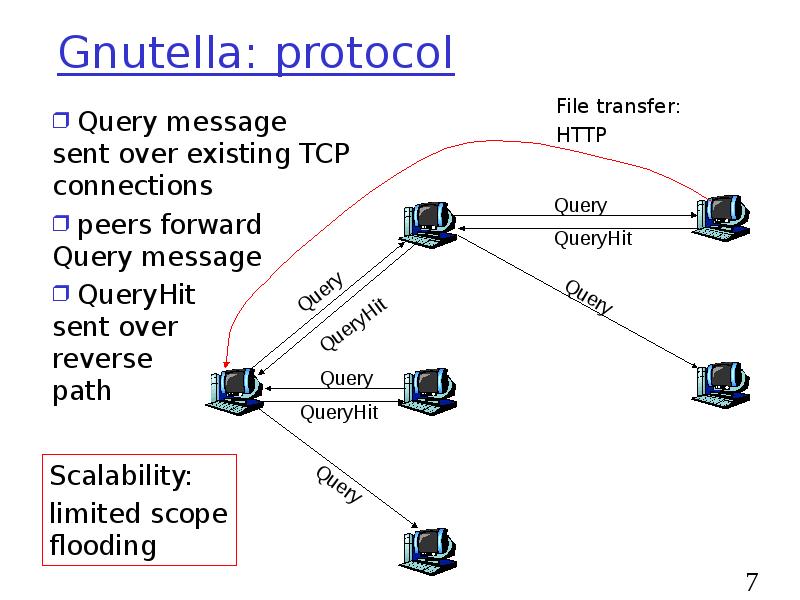
- 7. Gnutella: protocol
- 8. Gnutella: Peer joining Joining peer X must find some other peer
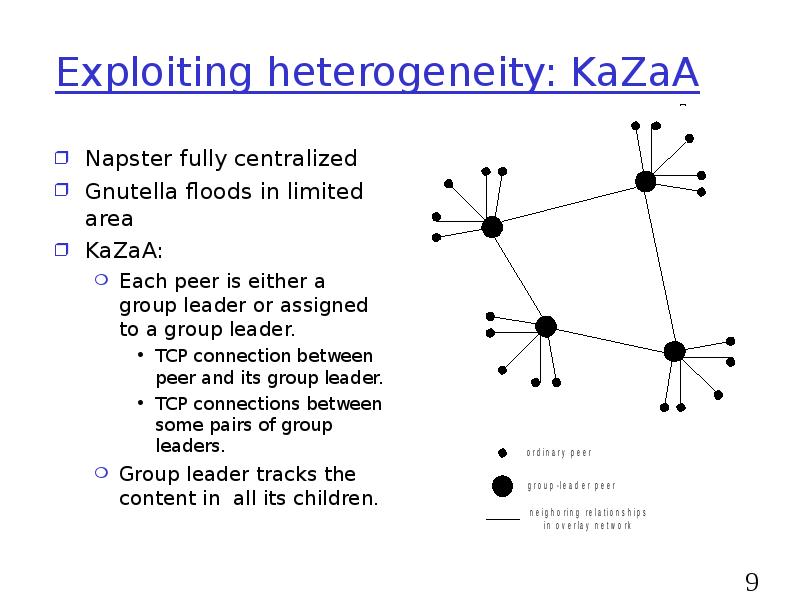
- 9. Exploiting heterogeneity: KaZaA Napster fully centralized Gnutella floods in limited area
- 10. KaZaA: Querying Each file has a hash and a descriptor Client
- 11. DoS resilience in p2p file-sharing systems P2p networks – highly replicated
- 12. DoS resilience in p2p file-sharing systems (cont.) Modeling the propagation of
- 13. Summary P2P file sharing (cont.) Socket programming with TCP Socket programming
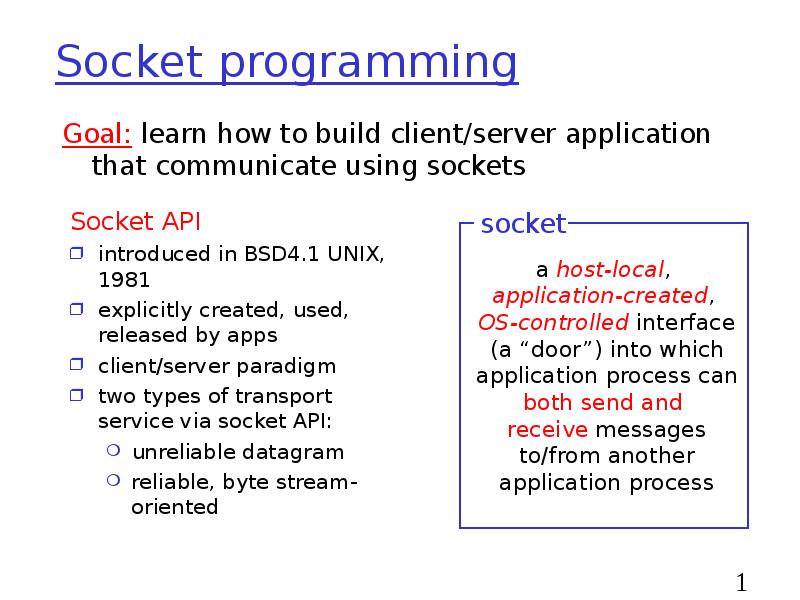
- 14. Socket programming Socket API introduced in BSD4.1 UNIX, 1981 explicitly created,
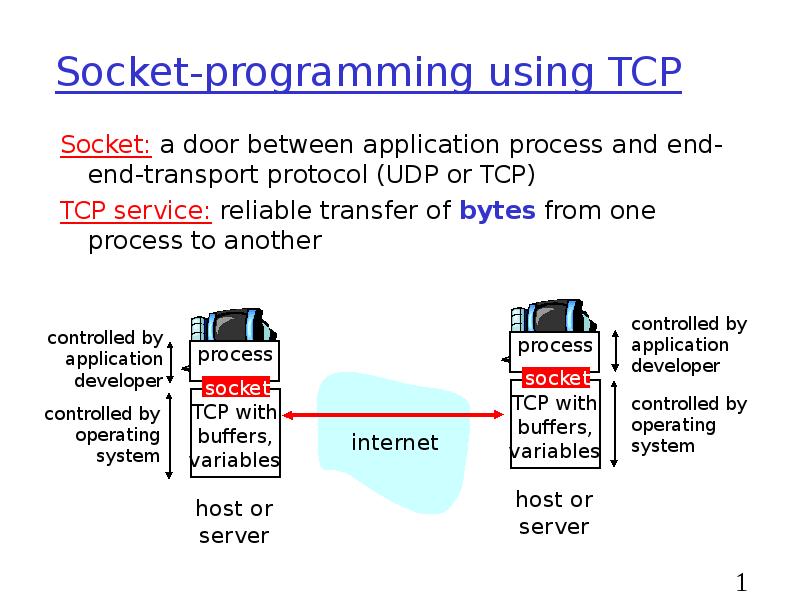
- 15. Socket-programming using TCP Socket: a door between application process and end-end-transport
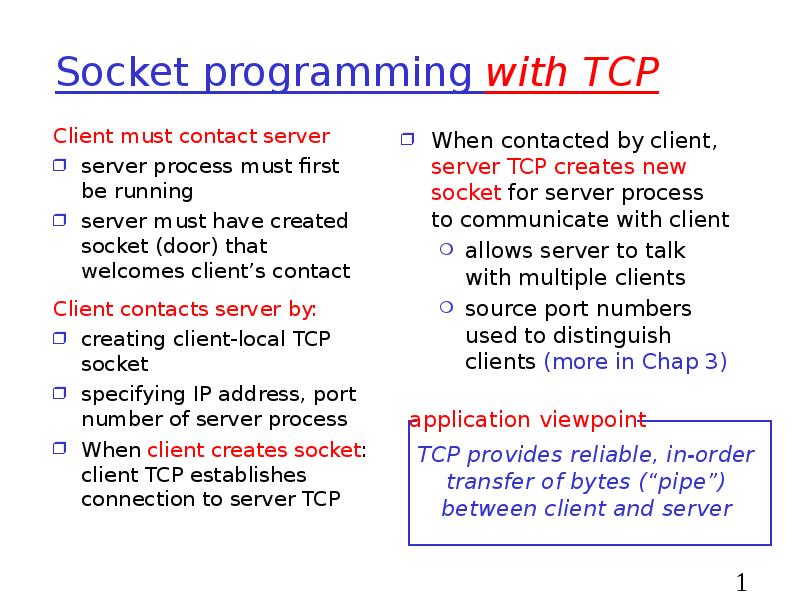
- 16. Socket programming with TCP Client must contact server server process must
- 17. Stream jargon A stream is a sequence of characters that flow
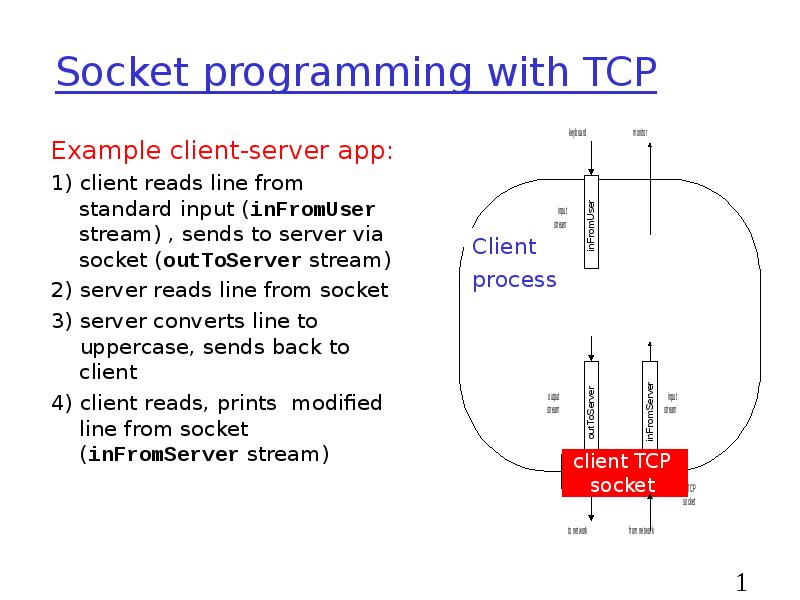
- 18. Socket programming with TCP Example client-server app: 1) client reads line
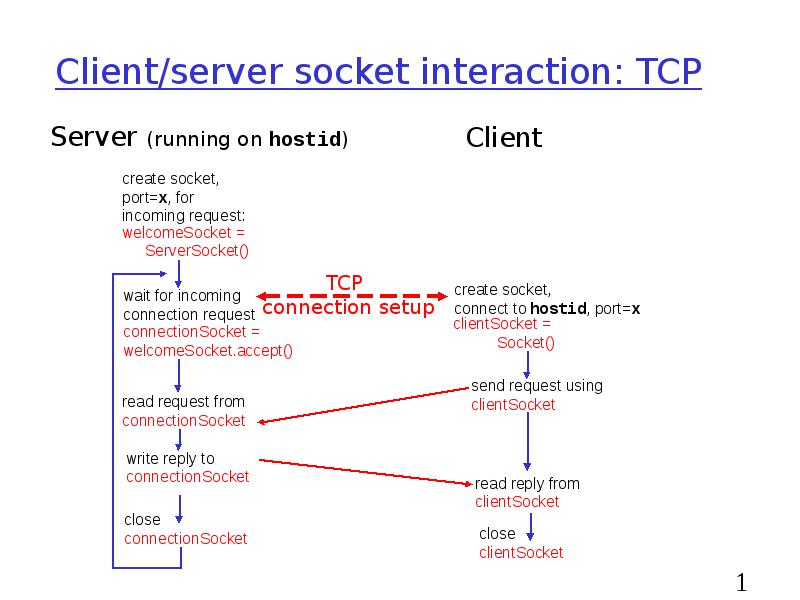
- 19. Client/server socket interaction: TCP
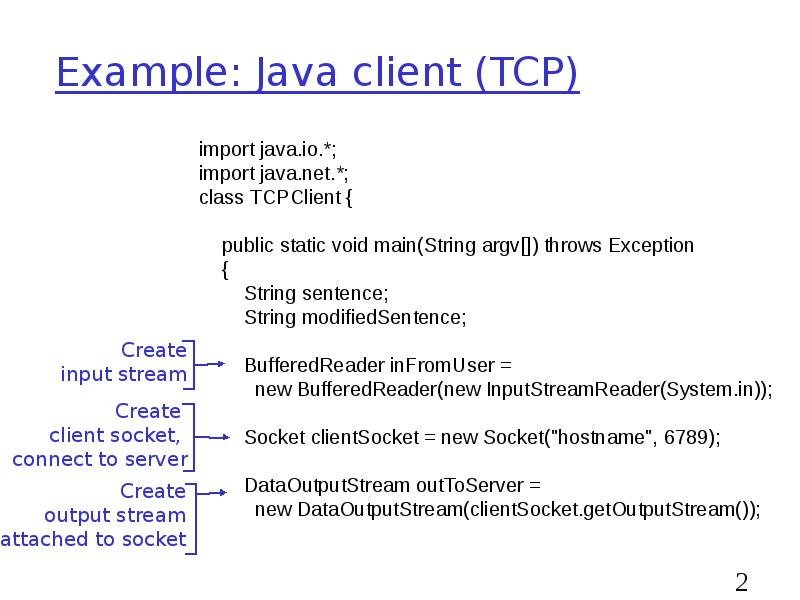
- 20. Example: Java client (TCP)
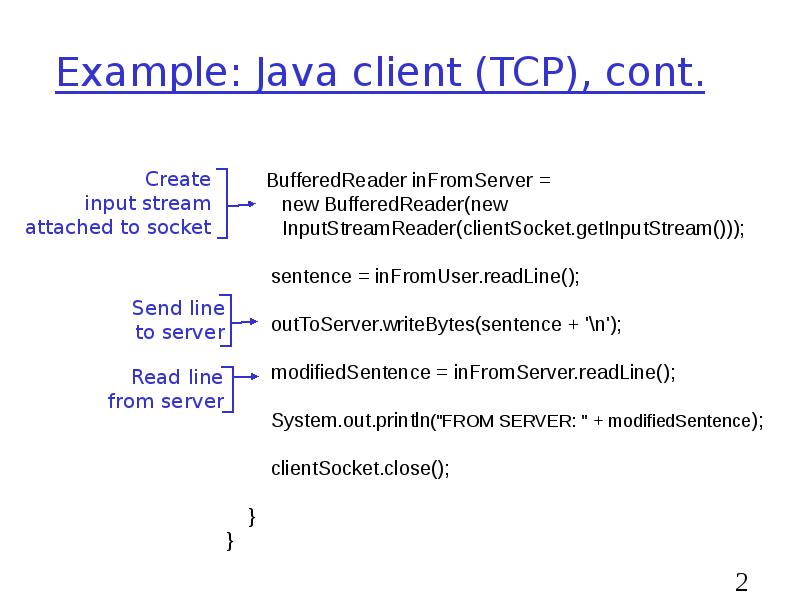
- 21. Example: Java client (TCP), cont.
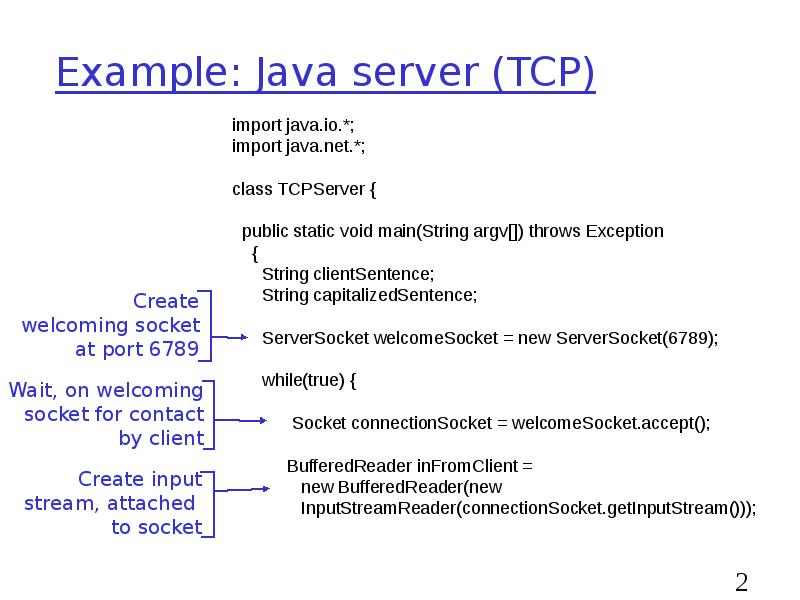
- 22. Example: Java server (TCP)
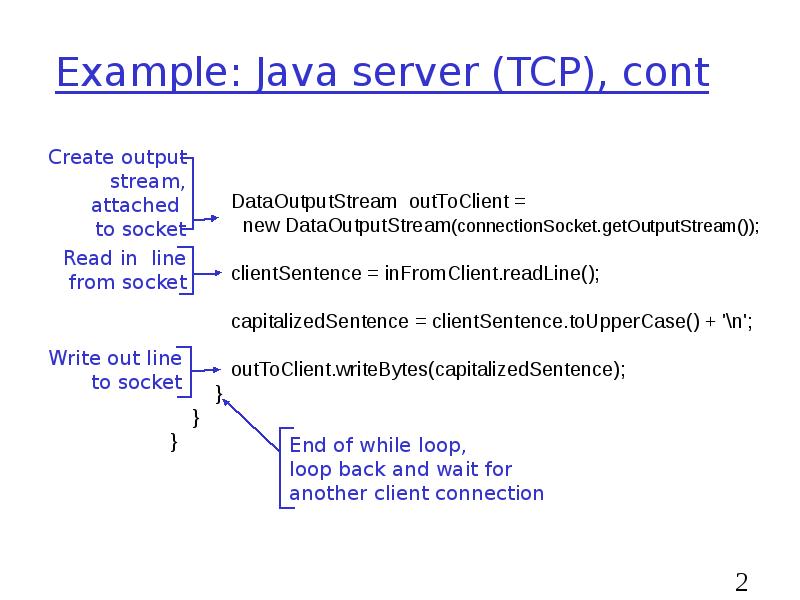
- 23. Example: Java server (TCP), cont
- 24. Outline P2P file sharing (cont.) Socket programming with TCP Socket programming
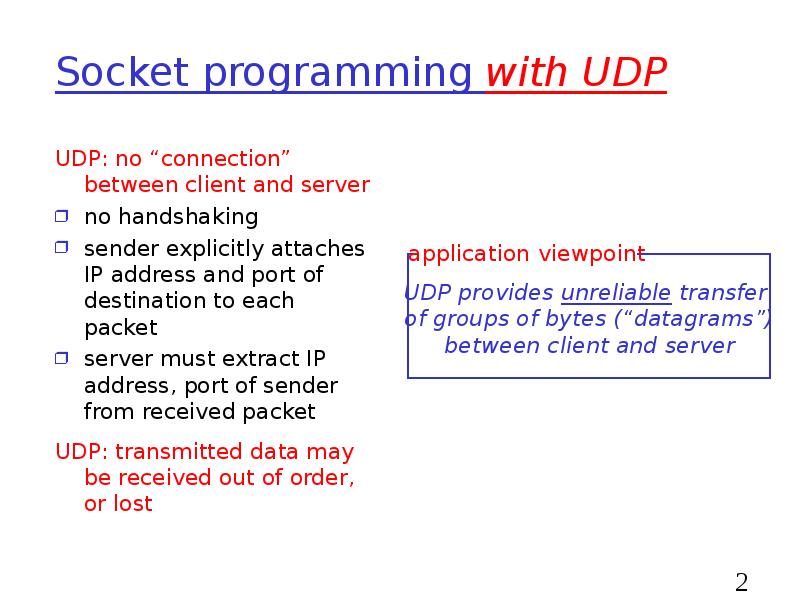
- 25. Socket programming with UDP UDP: no “connection” between client and server
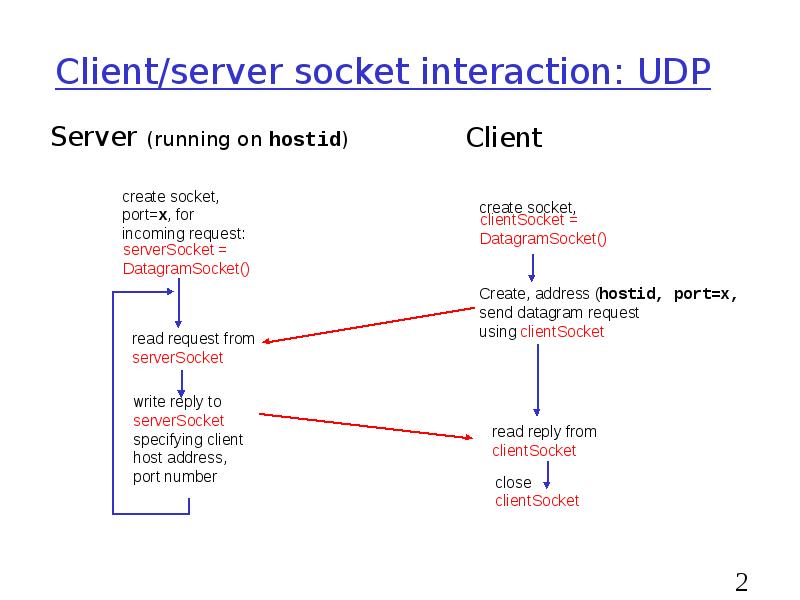
- 26. Client/server socket interaction: UDP
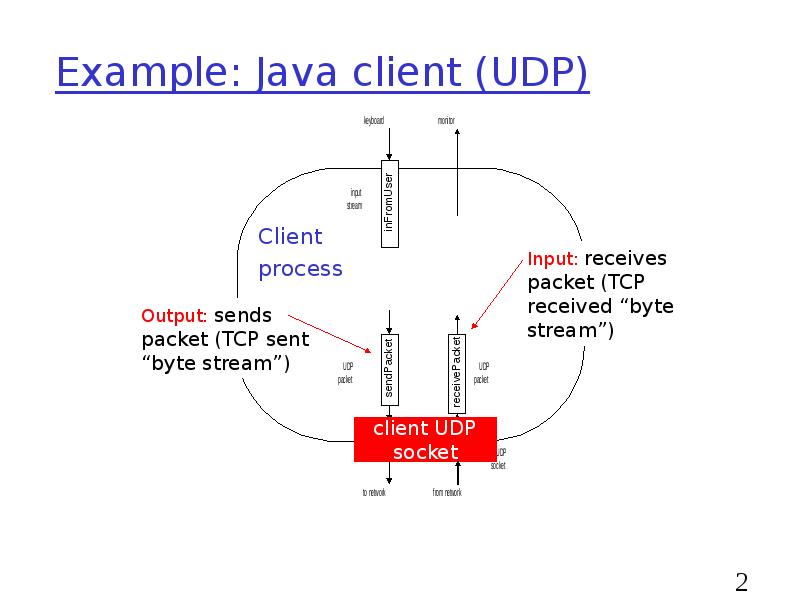
- 27. Example: Java client (UDP)
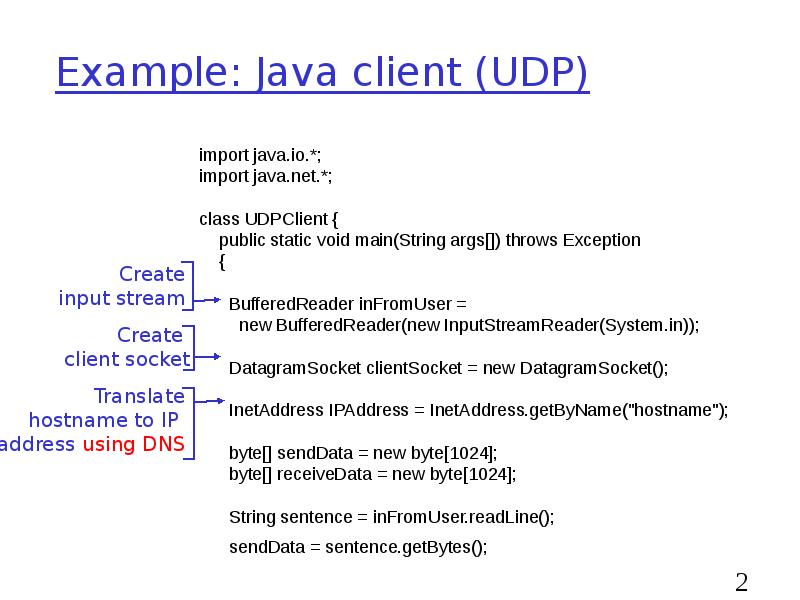
- 28. Example: Java client (UDP)
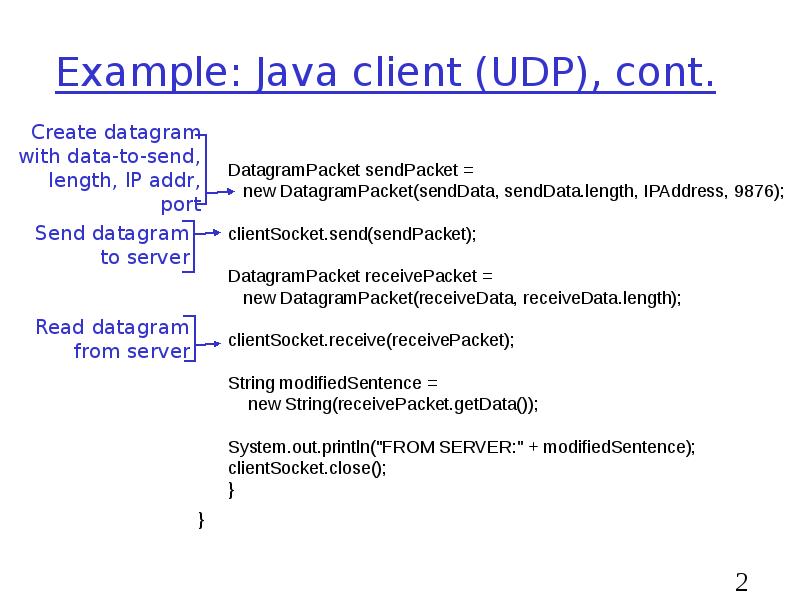
- 29. Example: Java client (UDP), cont.
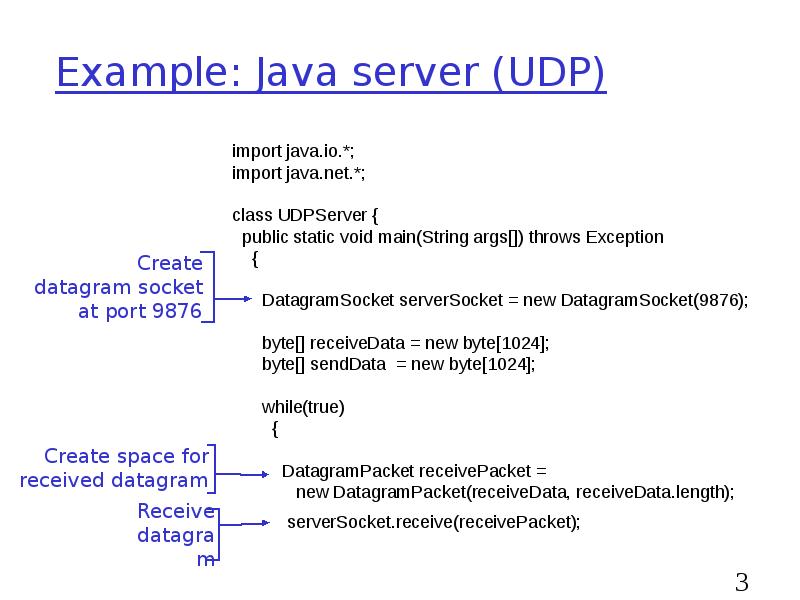
- 30. Example: Java server (UDP)
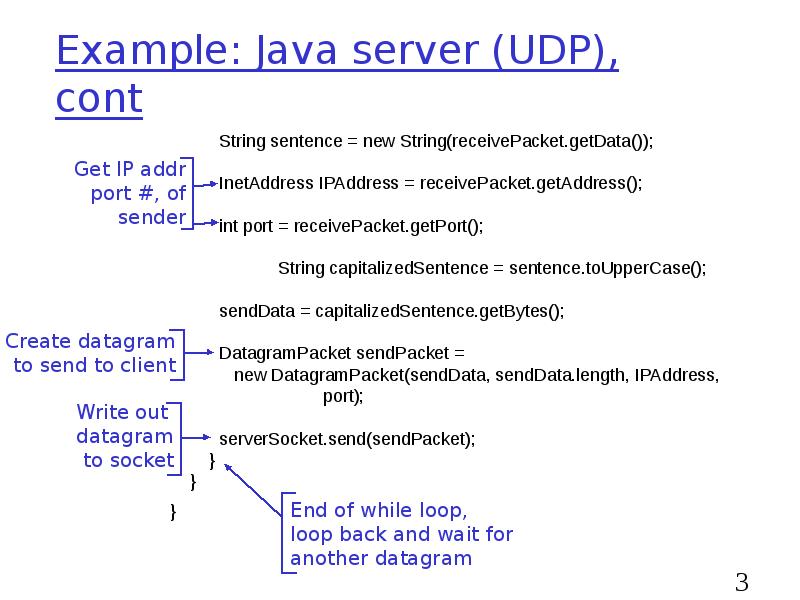
- 31. Example: Java server (UDP), cont
- 32. Summary P2P file sharing (cont.) Socket programming with TCP Socket programming
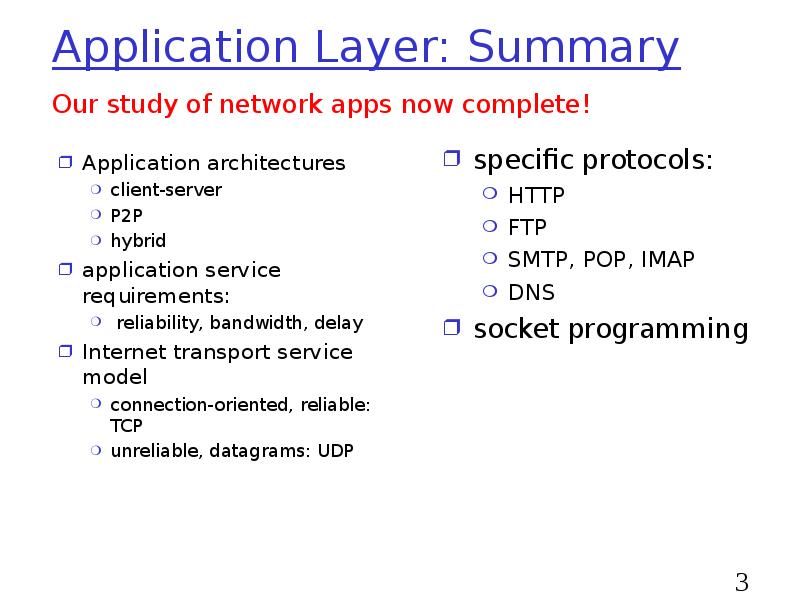
- 33. Application Layer: Summary Application architectures client-server P2P hybrid application service requirements:
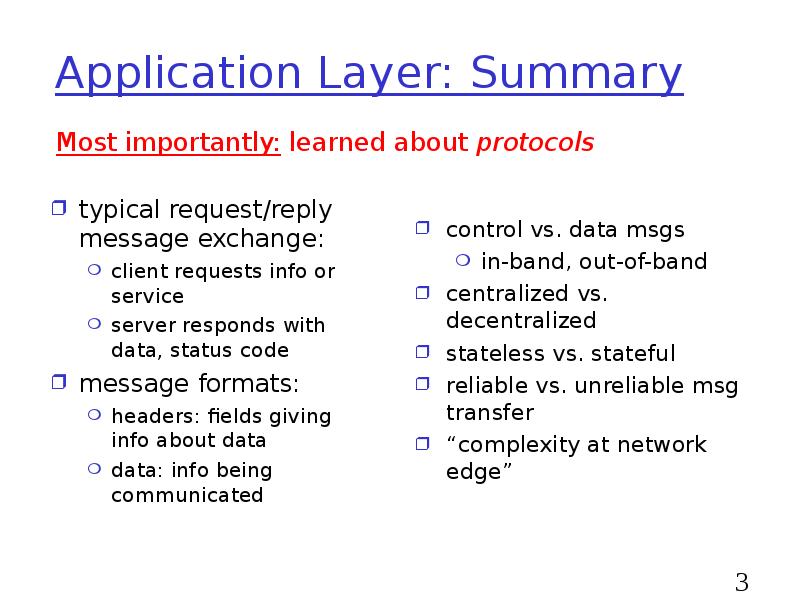
- 34. Application Layer: Summary typical request/reply message exchange: client requests info or
- 35. Quiz (Application Layer) Q1. List four Internet apps and the application
- 36. Quiz Q2. What is the difference between network architecture and application
- 37. Quiz Q3. In what way is instant messaging a hybrid of
- 38. Quiz Q4. For a communication session between a pair of processes,
- 39. Quiz Q5. Do you agree with the statement: “In P2p file
- 40. Quiz Q6. What information is used by a process running on
- 41. Quiz Q9. What is meant by a handshaking protocol?
- 42. Quiz Q10. Why HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP run on
- 43. Quiz Q12. What is the difference between persistent HTTP with pipelining
- 44. Quiz Q15. Why is it said that FTP sends control information
- 45. Quiz Q19. Is it possible for an organization’s Web server and
- 46. Quiz Q22. A UDP-based server needs only one socket, whereas the
- 47. Quiz (Chapter 1) Q3. What is a client program? What
- 48. Quiz Q4. What are the two types of transport services that
- 49. Quiz Q5. What is the difference between flow and congestion control?
- 50. Quiz Q7. What advantage does a circuit-switched network has over a
- 51. Quiz Q8. Why is it said that packet switching employs statistical
- 52. Quiz Q12. List five Internet access technologies. Classify each one
- 53. Quiz Q15. Is cable-modem transmission rate dedicated or shared among users?
- 54. Quiz Q19. Consider sending packet from a sending host to a
- 55. Quiz Q21. What are the five layers in the Internet protocol
- 56. Quiz Q23. Which layers in the Internet protocol stack does a
- 57. Скачать презентацию






























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Electronic Mail. DNS. P2P file sharing можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























