Elementary programming. Motivations презентация
Содержание
- 2. Motivations In the preceding lesson, you learned how to create, compile,
- 3. Introducing Programming with an Example Computing the Area of a Circle
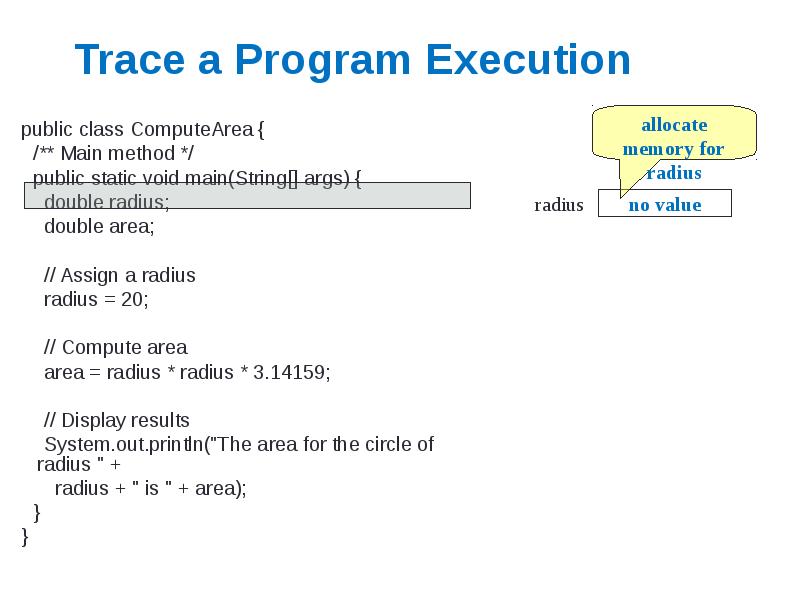
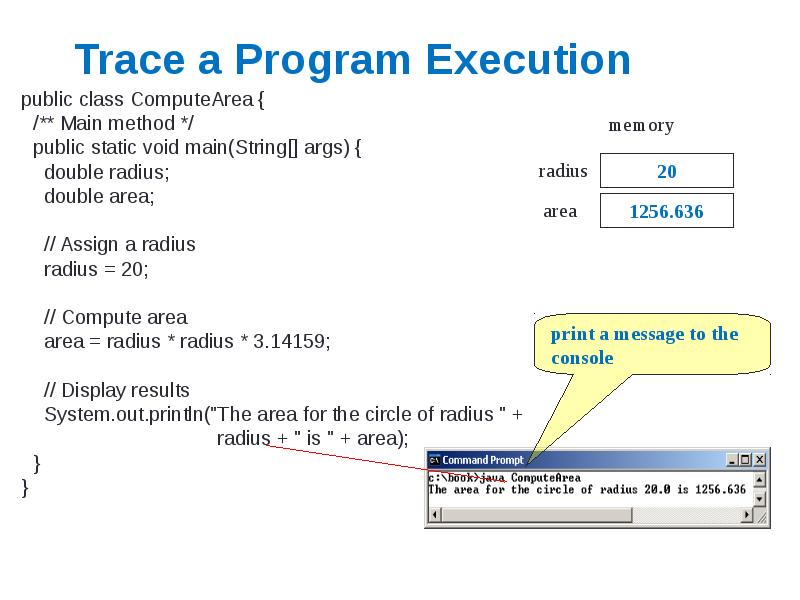
- 4. Trace a Program Execution public class ComputeArea { /** Main method
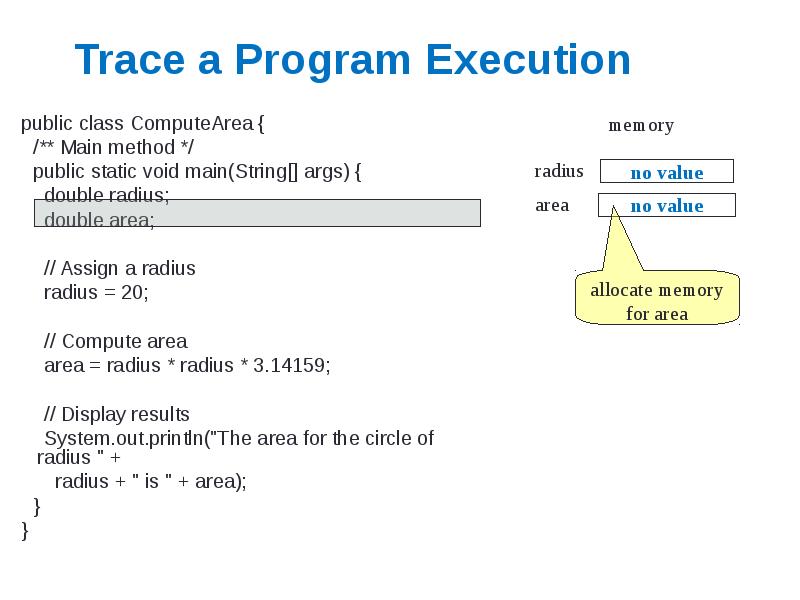
- 5. Trace a Program Execution public class ComputeArea { /** Main method
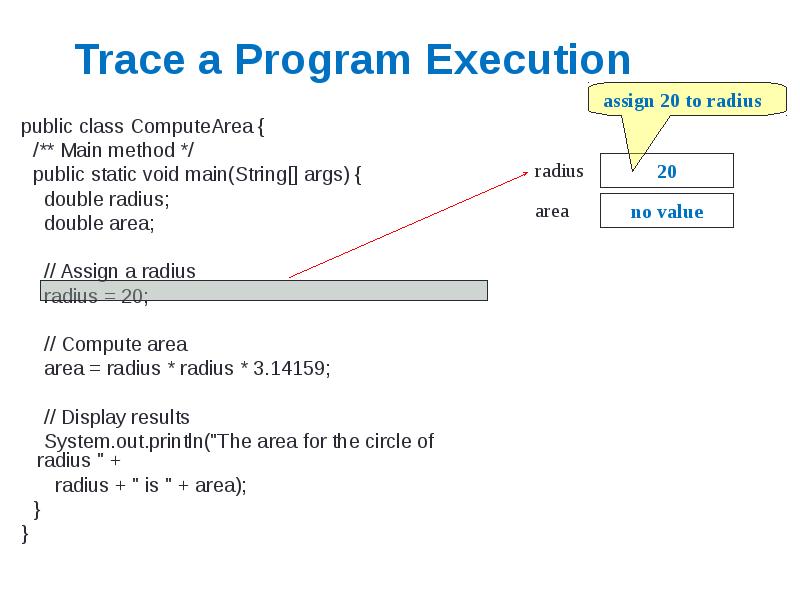
- 6. Trace a Program Execution public class ComputeArea { /** Main method
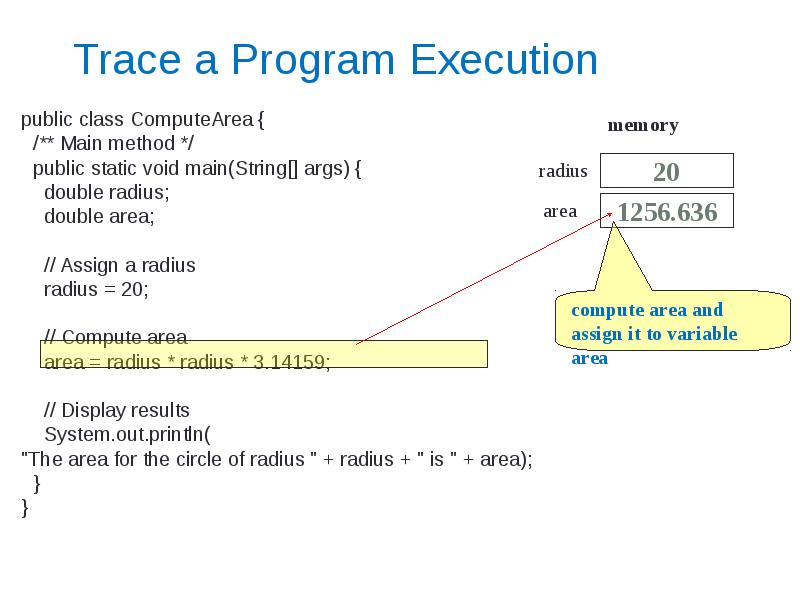
- 7. Trace a Program Execution public class ComputeArea { /** Main method
- 8. Trace a Program Execution public class ComputeArea { /** Main method
- 10. Identifiers An identifier is a sequence of characters that consist of
- 11. Variables // Compute the first area radius = 1.0; area =
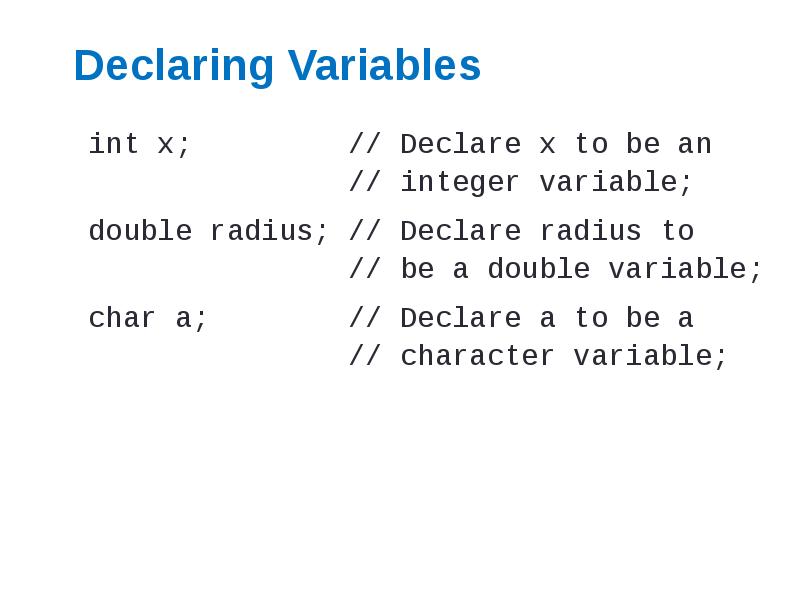
- 12. Declaring Variables int x; // Declare x to be
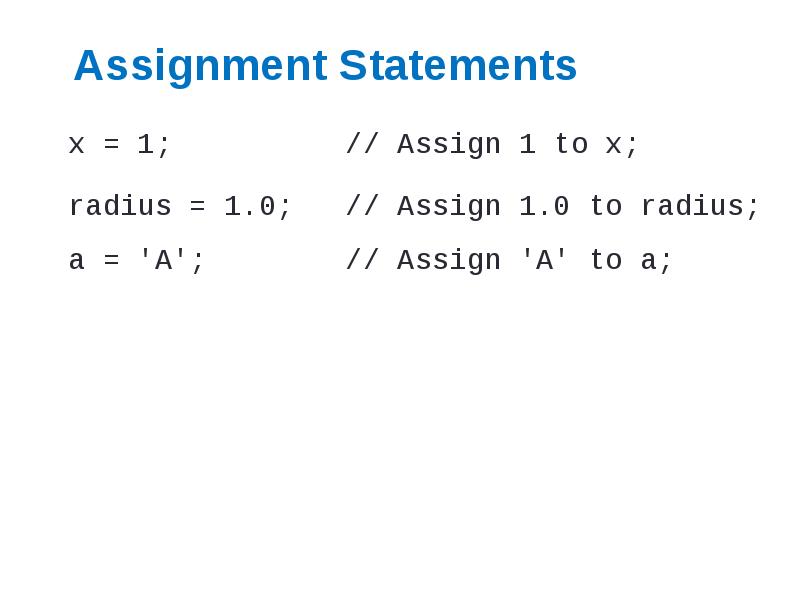
- 13. Assignment Statements x = 1; // Assign 1 to
- 14. Declaring and Initializing in One Step int x = 1; double
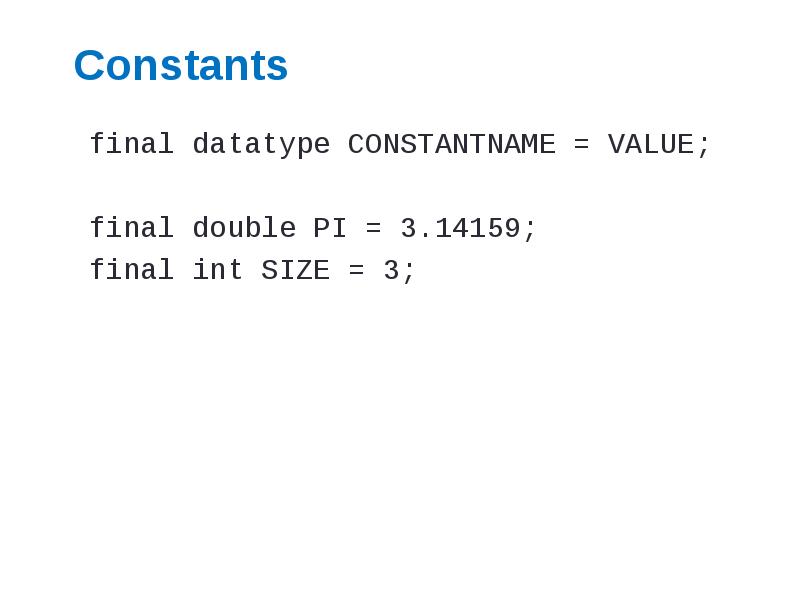
- 15. Constants final datatype CONSTANTNAME = VALUE; final double PI =
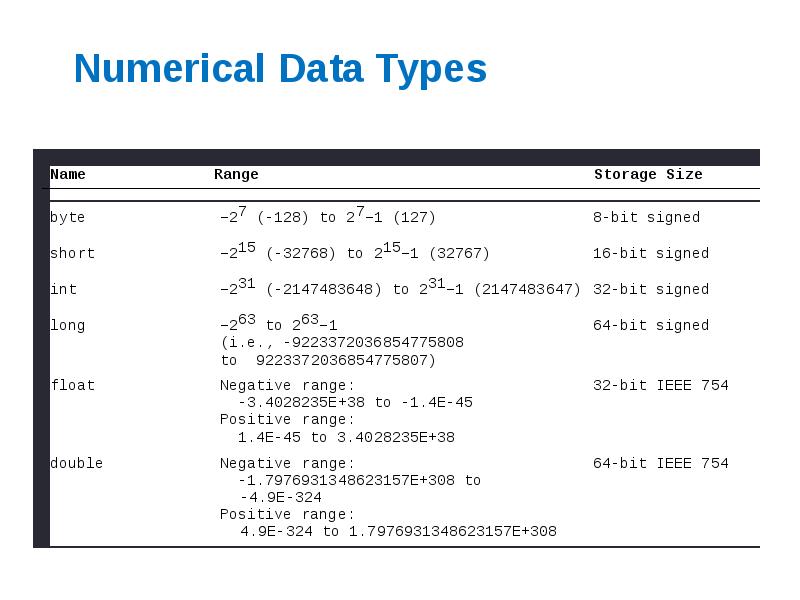
- 16. Numerical Data Types
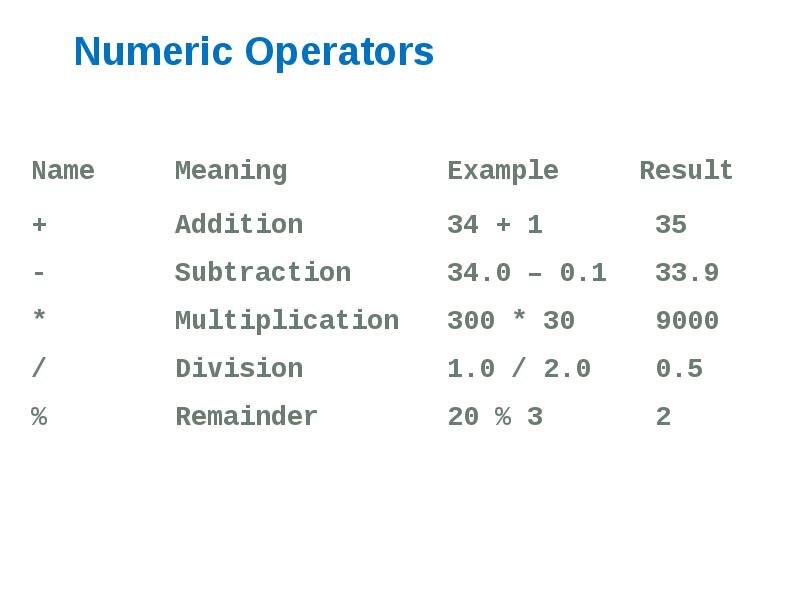
- 17. Numeric Operators
- 18. Integer Division +, -, *, /, and % 5 / 2
- 19. Remainder Operator Remainder is very useful in programming. For example,
- 20. NOTE Calculations involving floating-point numbers are approximated because these numbers are
- 21. Number Literals A literal is a constant value that appears directly
- 22. Integer Literals An integer literal can be assigned to an integer
- 23. Floating-Point Literals Floating-point literals are written with a decimal point. By
- 24. Scientific Notation Floating-point literals can also be specified in scientific notation,
- 25. Arithmetic Expressions
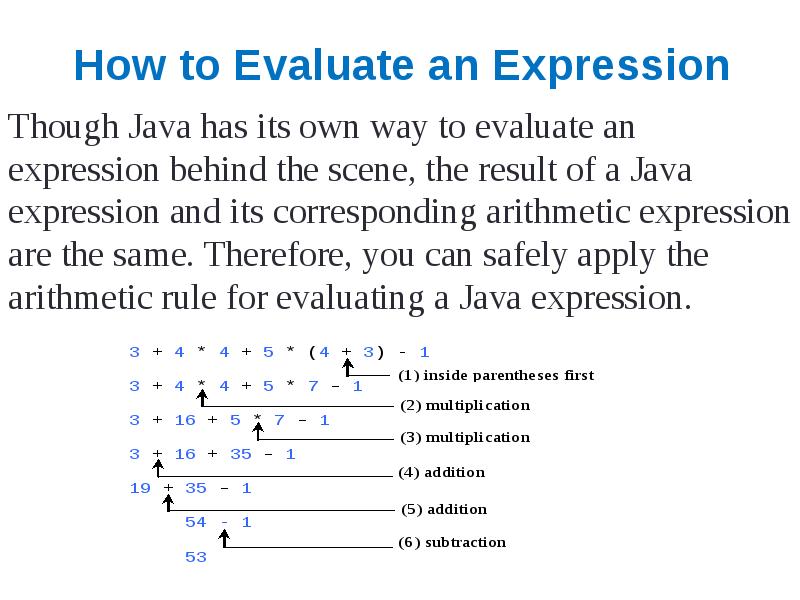
- 26. How to Evaluate an Expression
- 27. Problem: Converting Temperatures Write a program that converts a Fahrenheit degree
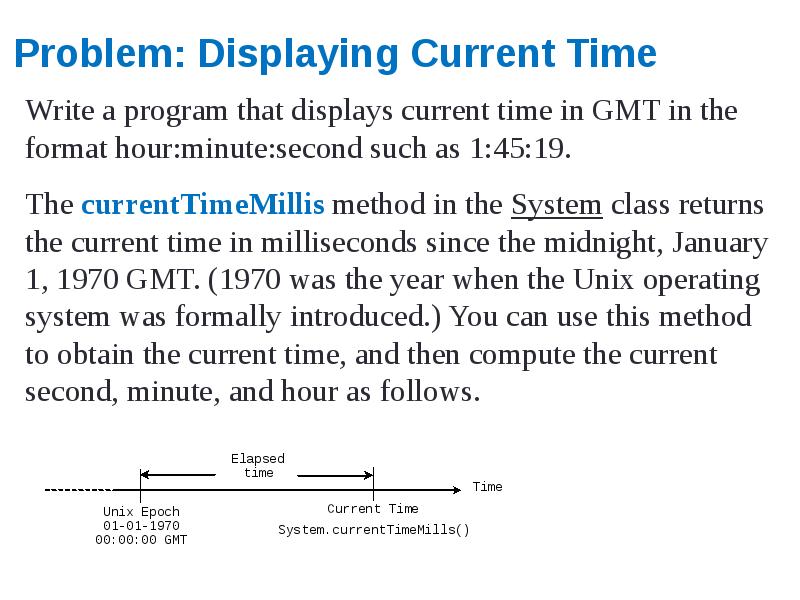
- 28. Problem: Displaying Current Time
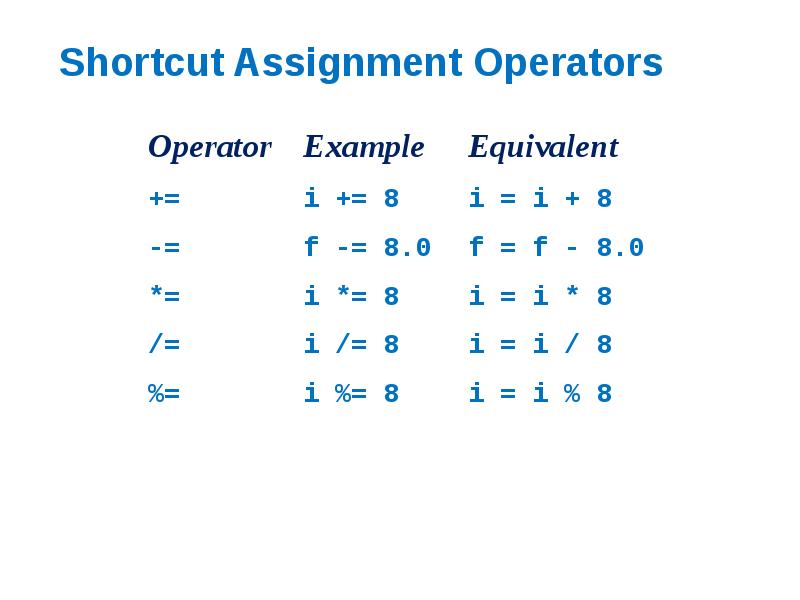
- 29. Shortcut Assignment Operators
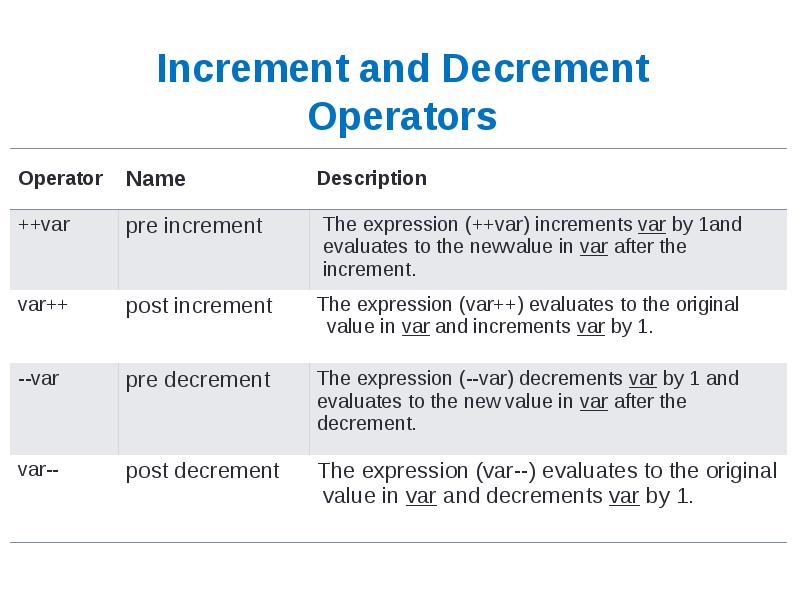
- 30. Increment and Decrement Operators
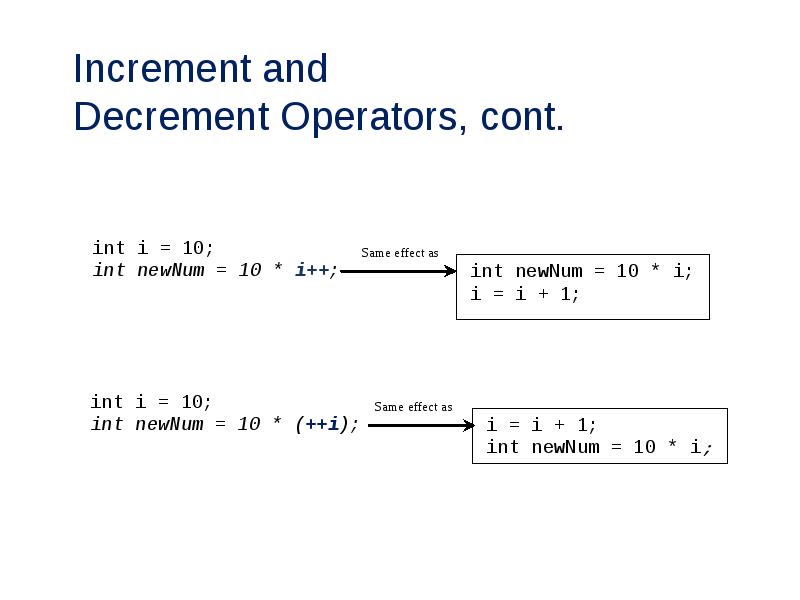
- 31. Increment and Decrement Operators, cont.
- 32. Increment and Decrement Operators, cont.
- 33. Assignment Expressions and Assignment Statements Prior to Java 2, all the
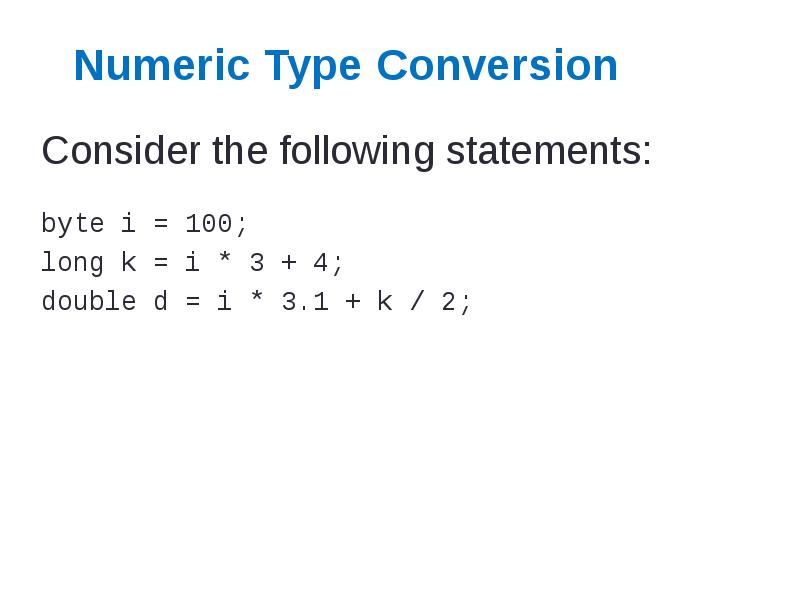
- 34. Numeric Type Conversion Consider the following statements: byte i = 100;
- 35. Conversion Rules When performing a binary operation involving two operands of
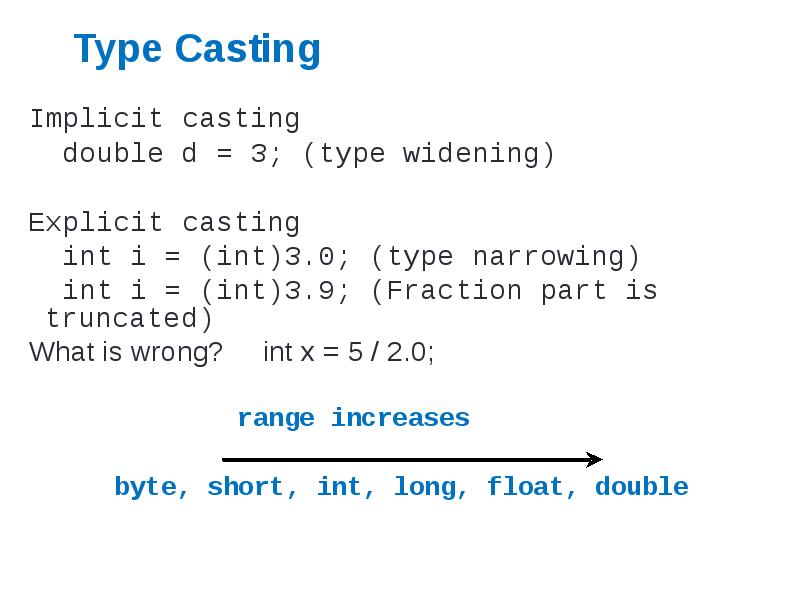
- 36. Type Casting Implicit casting double d = 3; (type widening) Explicit
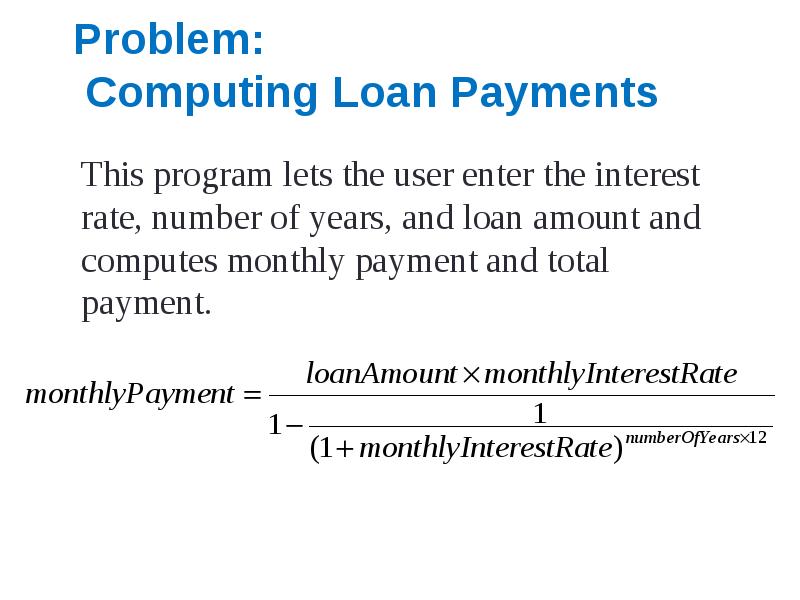
- 37. Problem: Computing Loan Payments
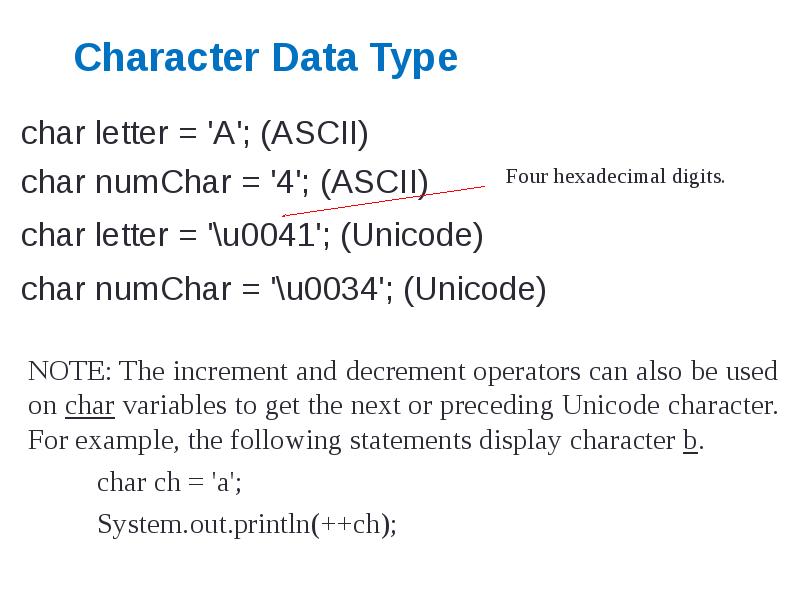
- 38. Character Data Type char letter = 'A'; (ASCII) char
- 39. Unicode Format
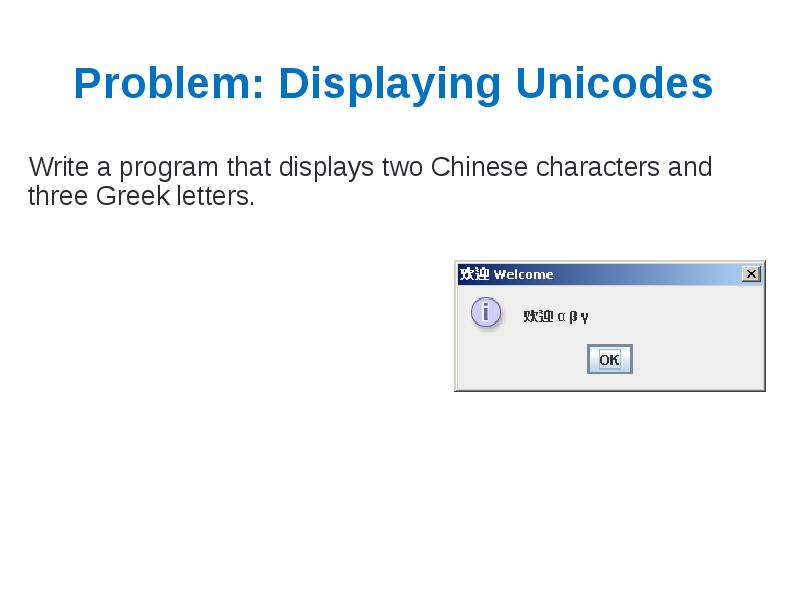
- 40. Problem: Displaying Unicodes Write a program that displays two Chinese characters
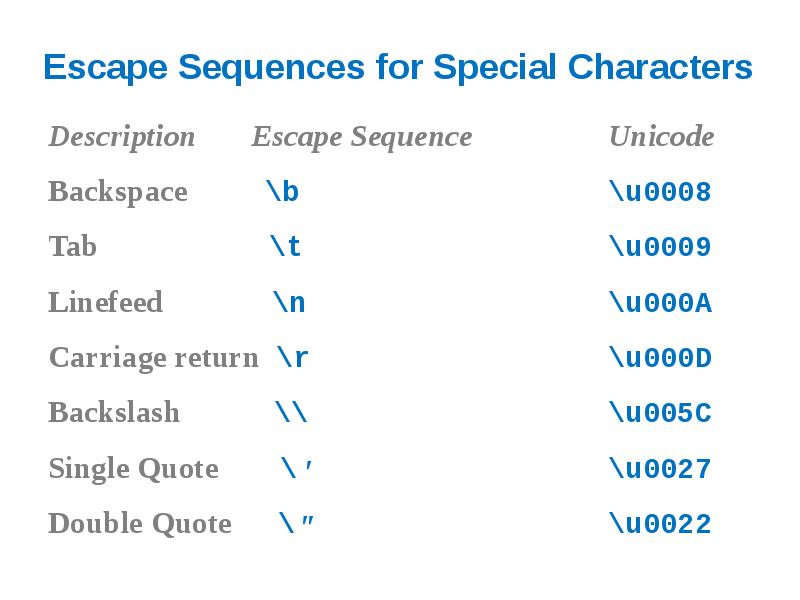
- 41. Escape Sequences for Special Characters
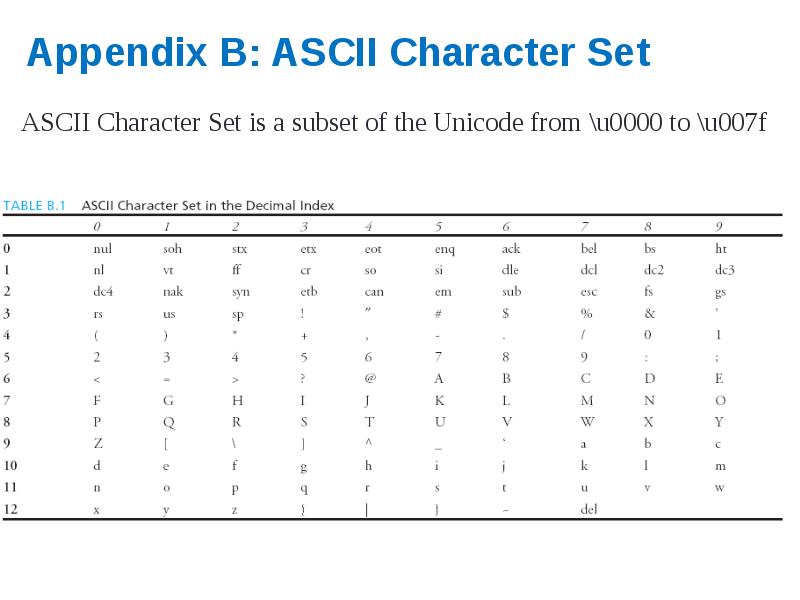
- 42. Appendix B: ASCII Character Set
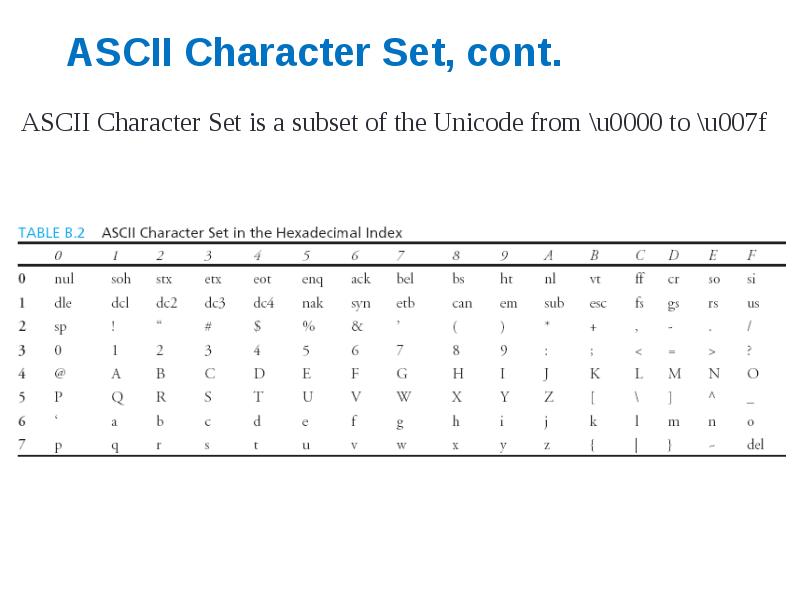
- 43. ASCII Character Set, cont.
- 44. Casting between char and Numeric Types
- 45. The String Type The char type only represents one character.
- 46. String Concatenation // Three strings are concatenated String message =
- 47. Programming Style and Documentation Appropriate Comments Naming Conventions Proper Indentation and
- 48. Appropriate Comments Include a summary at the beginning of the program
- 49. Naming Conventions Choose meaningful and descriptive names. Variables and method names:
- 50. Naming Conventions, cont. Class names: Capitalize the first letter of
- 51. Proper Indentation and Spacing Indentation Indent two spaces. Spacing Use
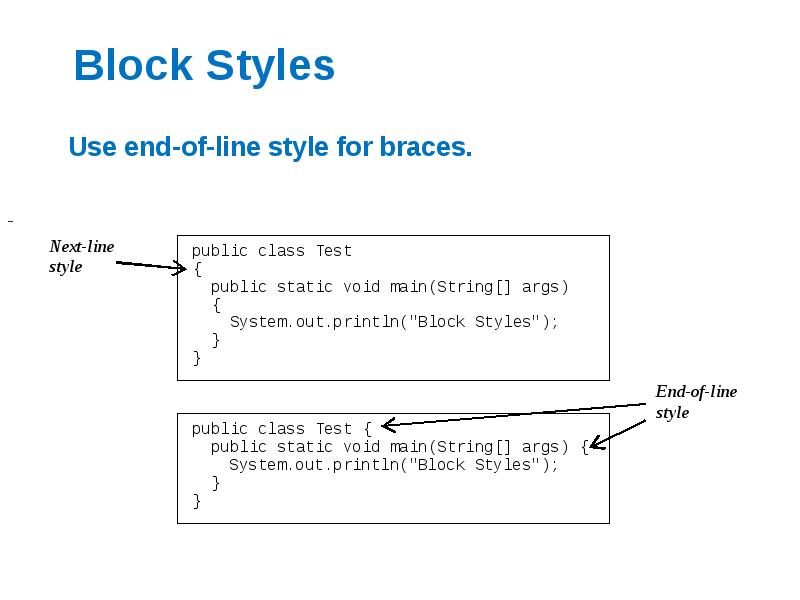
- 52. Block Styles Use end-of-line style for braces.
- 53. Programming Errors Syntax Errors Detected by the compiler Runtime Errors Causes
- 54. Syntax Errors public class ShowSyntaxErrors { public static void main(String[] args)
- 55. Runtime Errors public class ShowRuntimeErrors { public static void main(String[]
- 56. Logic Errors public class ShowLogicErrors { // Determine if a number
- 57. Debugging Logic errors are called bugs. The process of finding and
- 58. Debugger Debugger is a program that facilitates debugging. You can
- 59. JOptionPane Input Two ways of obtaining input. Using the Scanner class
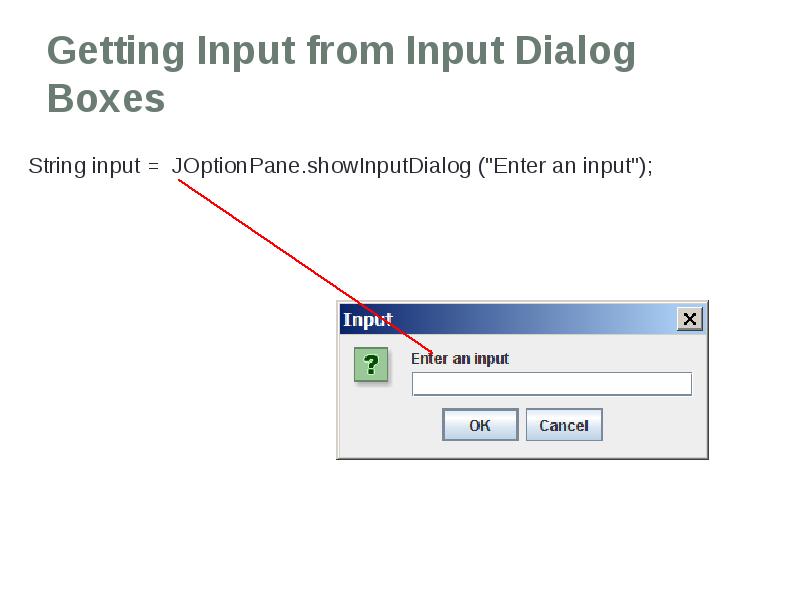
- 60. Getting Input from Input Dialog Boxes String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog
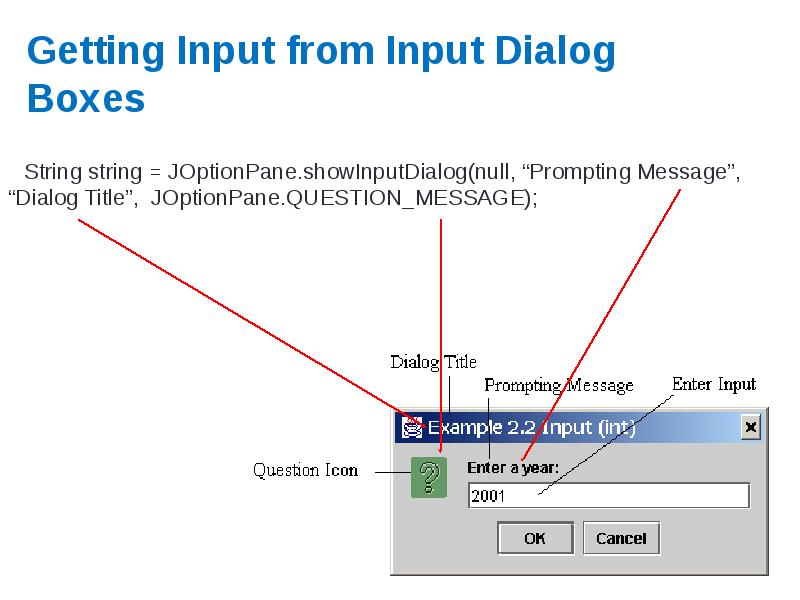
- 61. Getting Input from Input Dialog Boxes String string = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,
- 62. Two Ways to Invoke the Method There are several ways
- 63. Converting Strings to Integers The input returned from the input dialog
- 64. Converting Strings to Doubles To convert a string into a double
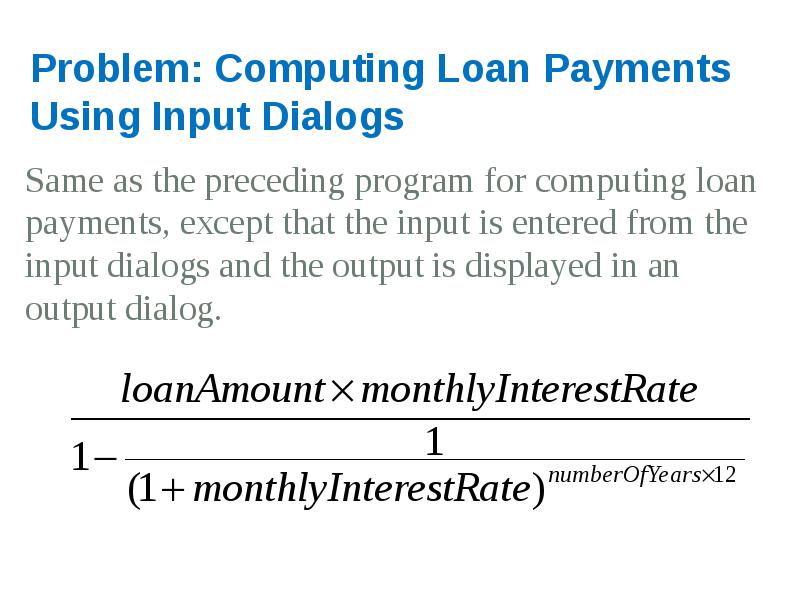
- 65. Problem: Computing Loan Payments Using Input Dialogs
- 66. Скачать презентацию





























![Syntax Errors
public class ShowSyntaxErrors {
public static void main(String[] Syntax Errors
public class ShowSyntaxErrors {
public static void main(String[]](/documents_3/20e1cbac3c6c5d271af9c231666cd472/img53.jpg)








Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Elementary programming. Motivations можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























