Error control. Hamming code презентация
Содержание
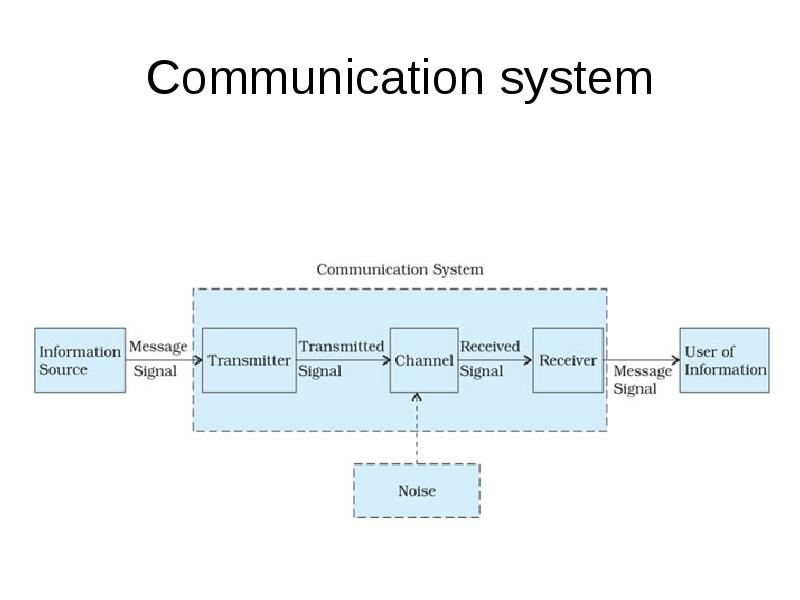
- 2. Communication system
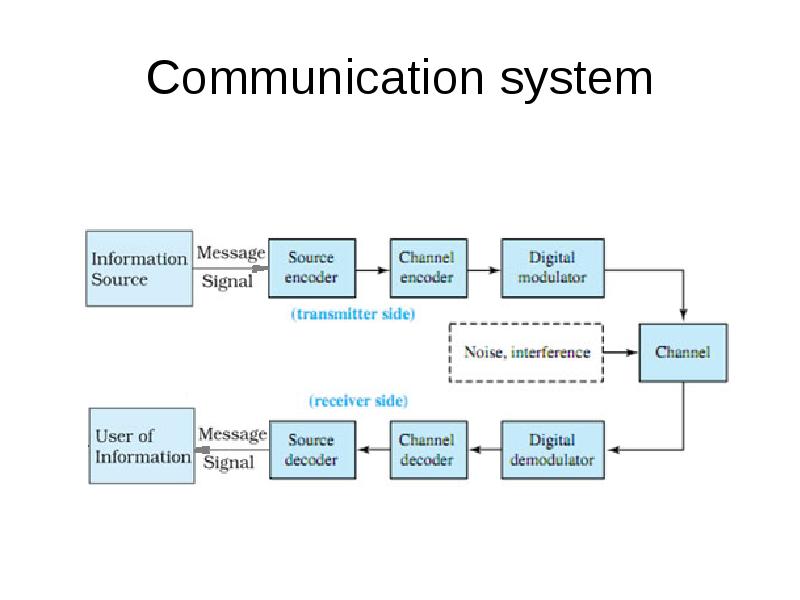
- 3. Communication system
- 4. Error control In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and
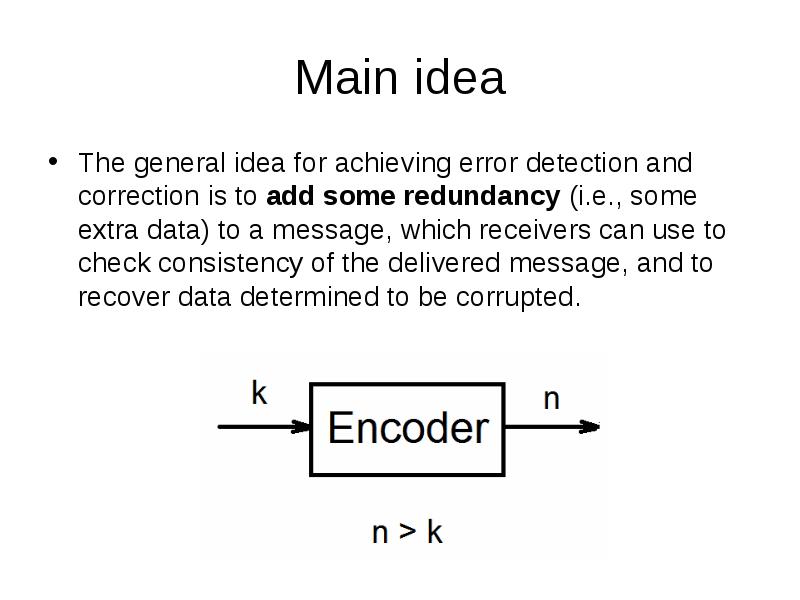
- 5. Main idea The general idea for achieving error detection and correction
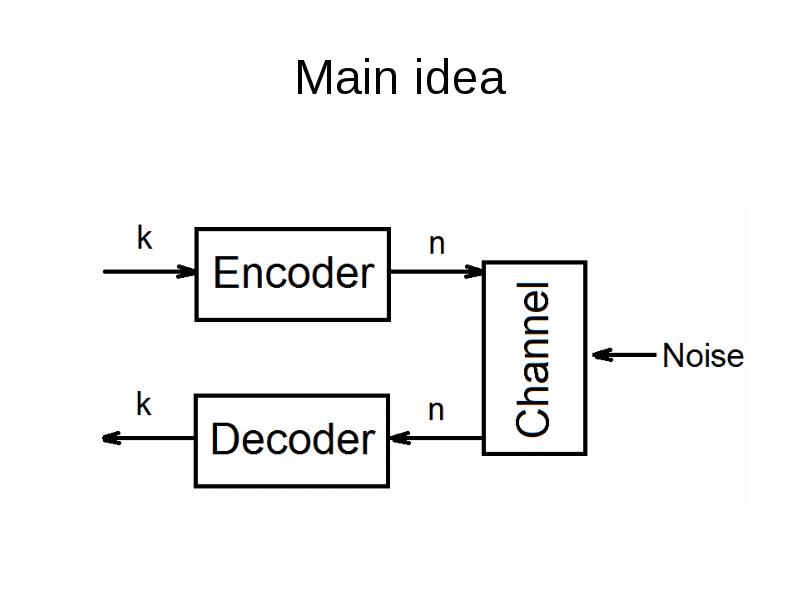
- 6. Main idea
- 7. Error control Different techniques of coding: Block code Convolutional code
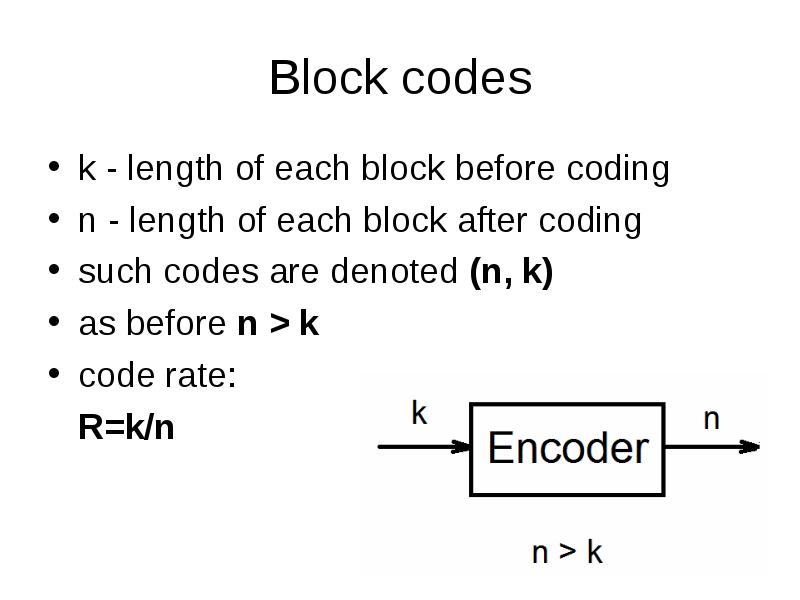
- 8. Block codes k - length of each block before coding n
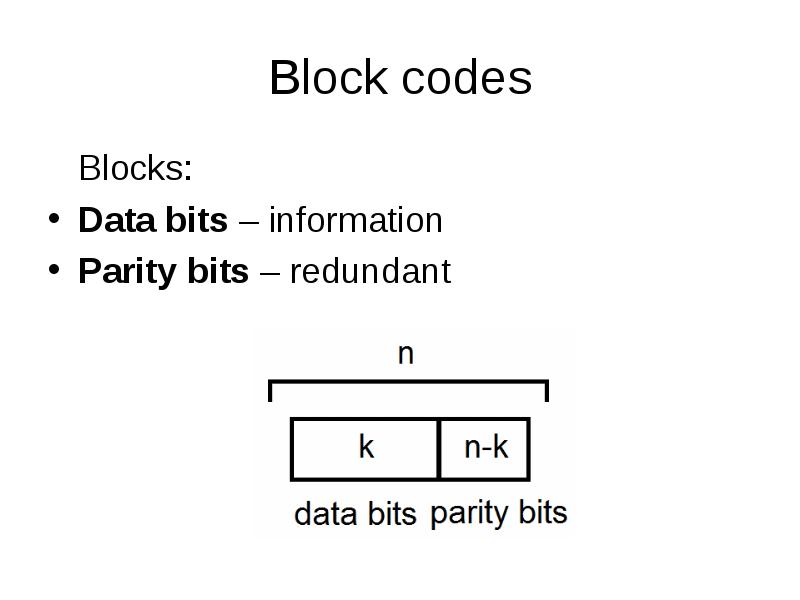
- 9. Block codes Blocks: Data bits – information Parity bits – redundant
- 10. Example Parity bit: 0 – if number of “1” in code
- 11. Different combinations Types of code combinations after a channel: permissible (allowable)
- 12. Detection or correction? Hamming distance between two strings of equal length is the
- 13. Hamming distance: examples "karolin" and "kathrin" is 3. "karolin" and "kerstin"
- 14. Example 1: Hamming distance=1 When d=1 all code combinations are allowable
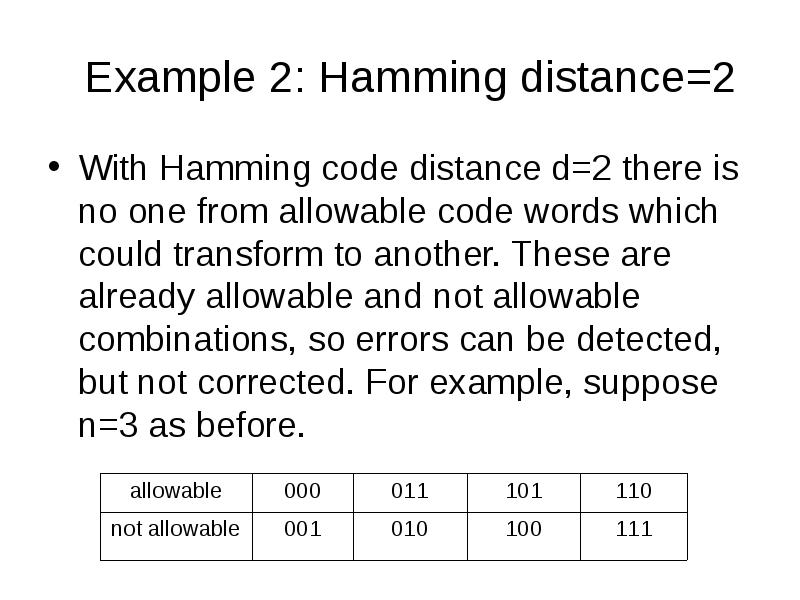
- 15. Example 2: Hamming distance=2 With Hamming code distance d=2 there is
- 16. Example 3: Hamming distance=3 In this example Hamming distance is enough
- 17. Basic formulas Detect errors of multiplicity r: dmin >= r+1
- 18. Hamming code Hamming codes are a family of linear error-correcting codes that generalize
- 19. Main ideas Hamming was interested in two problems at once: increasing
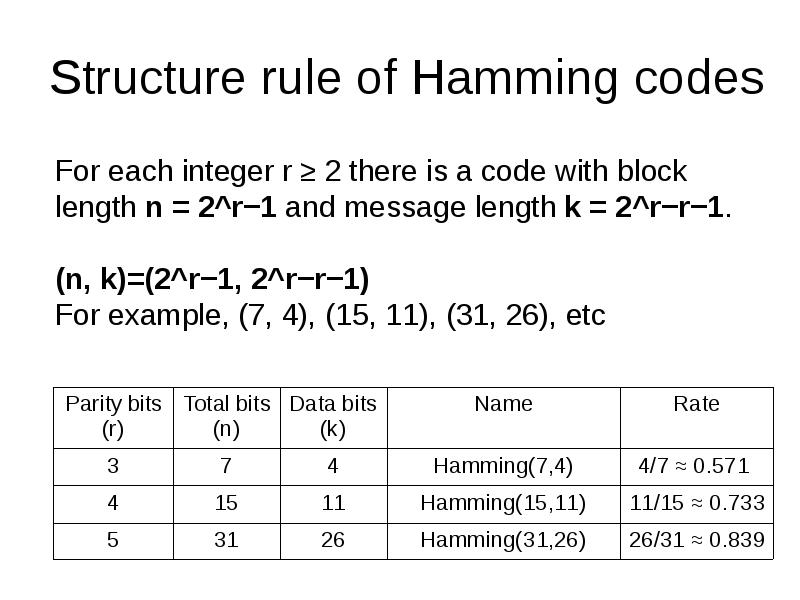
- 20. Structure rule of Hamming codes
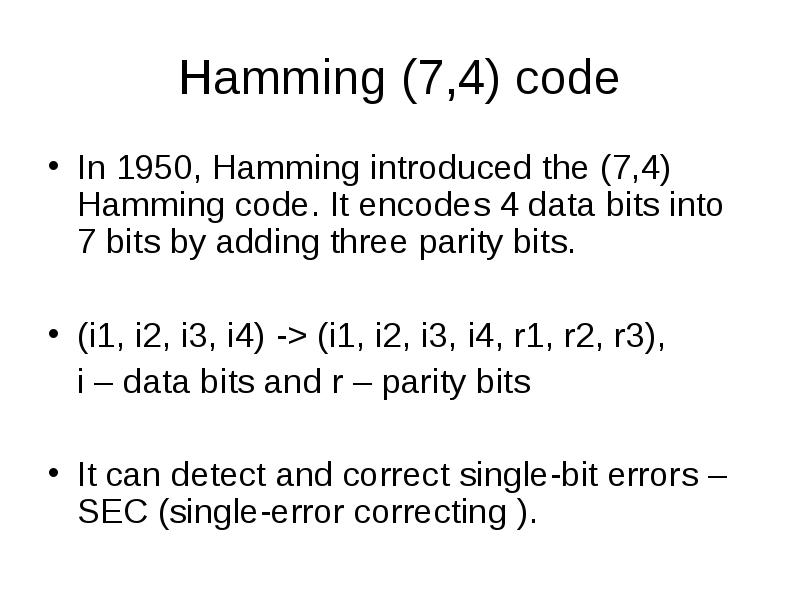
- 21. Hamming (7,4) code In 1950, Hamming introduced the (7,4) Hamming code.
- 22. Encoding Hamming(7,4) The key thing about Hamming Codes is that any
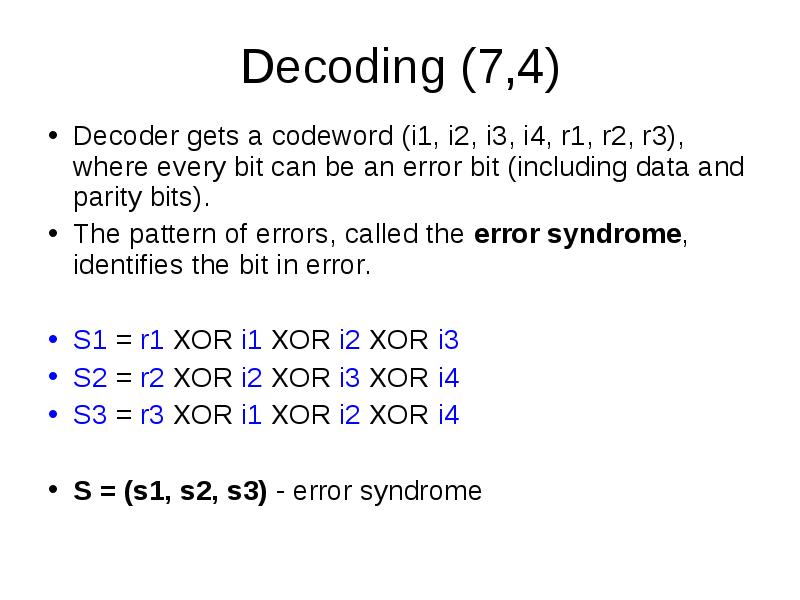
- 23. Decoding (7,4) Decoder gets a codeword (i1, i2, i3, i4, r1,
- 24. Decoding (7,4)
- 25. Example 1: an error in data bit Combination before encoding: 1001
- 26. Example 2: an error in parity bit Combination before encoding: 1001
- 27. General algorithm To compare different approaches consider Hamming(7,4) as example. However
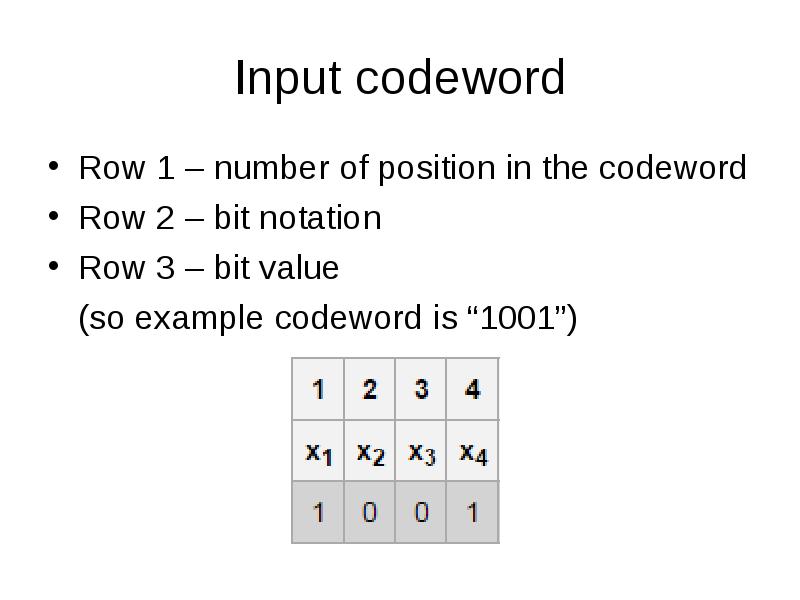
- 28. Input codeword Row 1 – number of position in the codeword
- 29. Number of parity bits In general, the number of parity bits
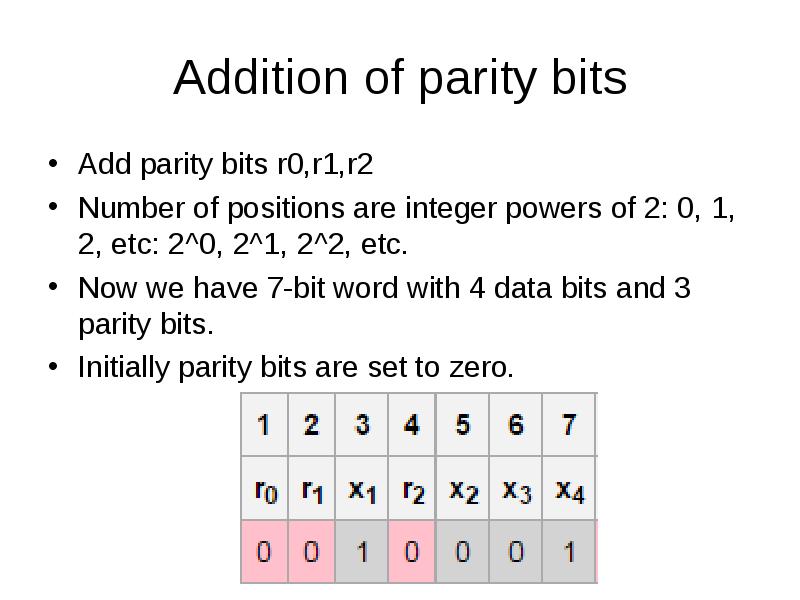
- 30. Addition of parity bits Add parity bits r0,r1,r2 Number of positions
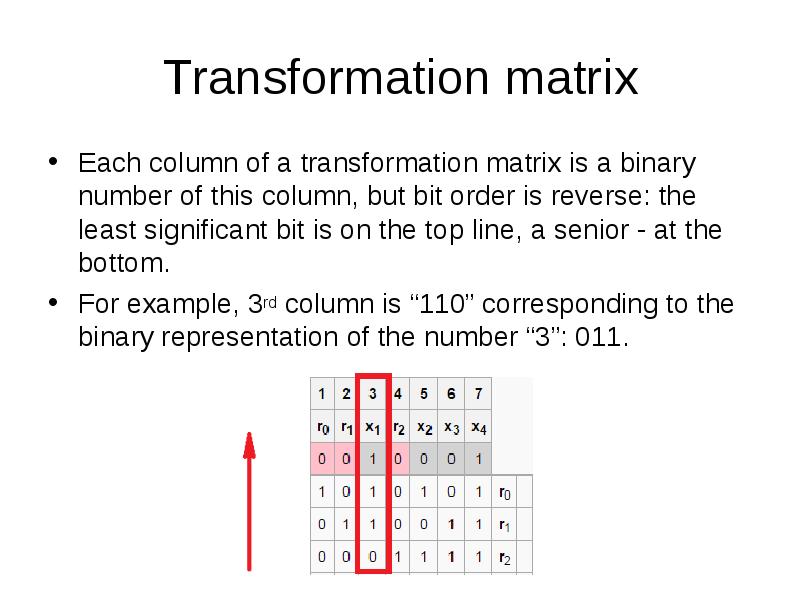
- 31. Transformation matrix Add to table 3 rows (number of parity bits)
- 32. Transformation matrix Each column of a transformation matrix is a binary
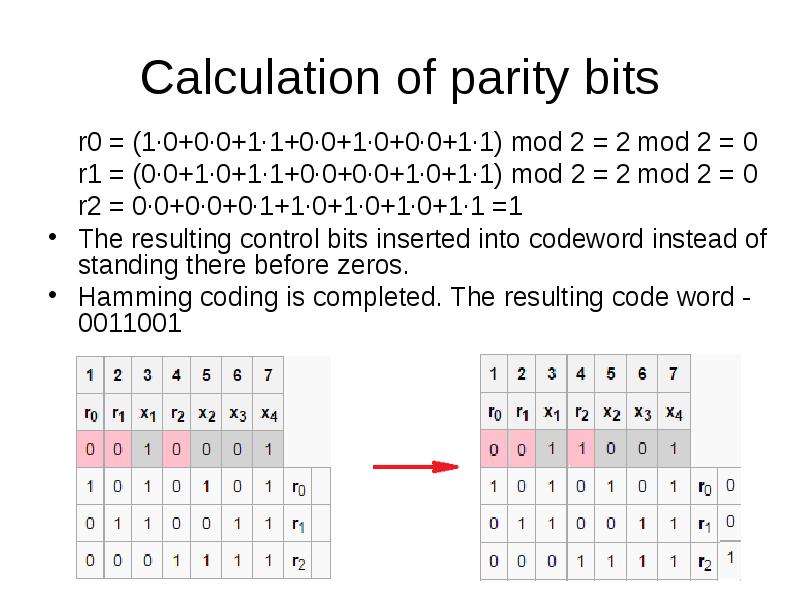
- 33. Calculation of parity bits r0 = (1·0+0·0+1·1+0·0+1·0+0·0+1·1) mod 2 = 2 mod
- 34. Decoding Algorithm of decoding is absolutely identical to encoding algorithm. Goal
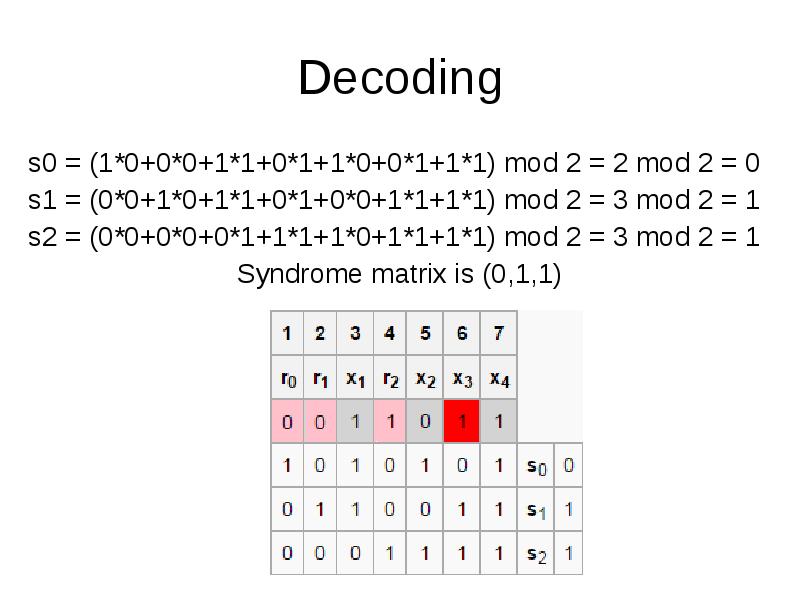
- 35. Decoding s0 = (1*0+0*0+1*1+0*1+1*0+0*1+1*1) mod 2 = 2 mod 2 =
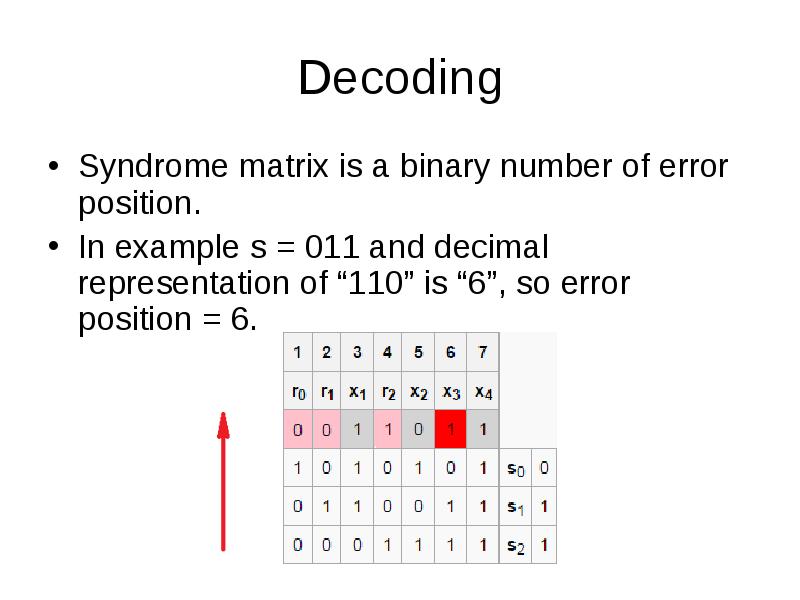
- 36. Decoding Syndrome matrix is a binary number of error position. In
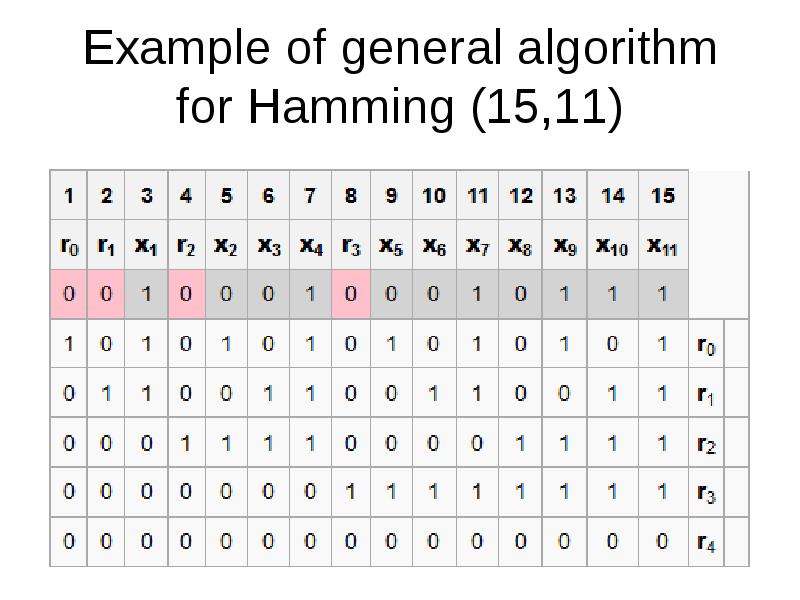
- 37. Example of general algorithm for Hamming (15,11)
- 38. References Arndt C. Information Measures: Information and its Description in Science and Engineering.
- 39. Скачать презентацию



















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























