Generic Collections Java Core презентация
Содержание
- 2. Agenda Wrapper Pattern Generic in Java Arrays in Java Collections in
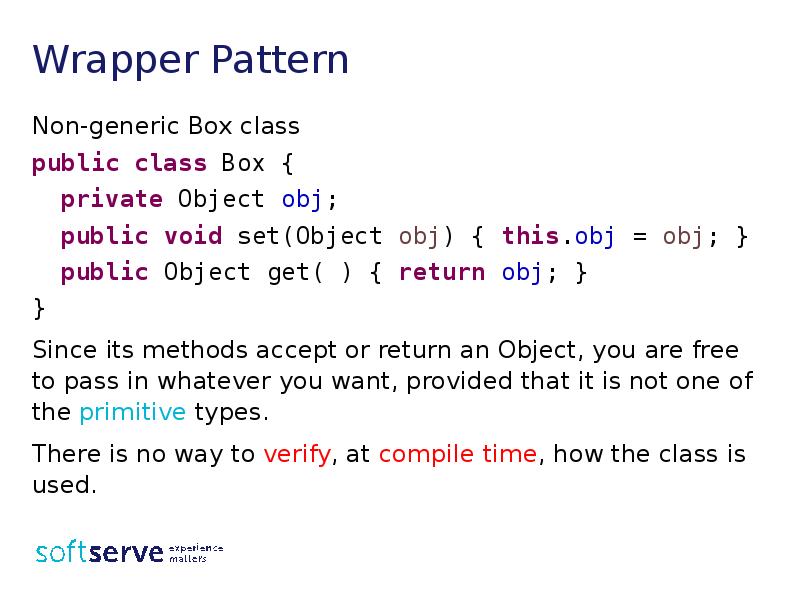
- 3. Wrapper Pattern Non-generic Box class public class Box { private Object
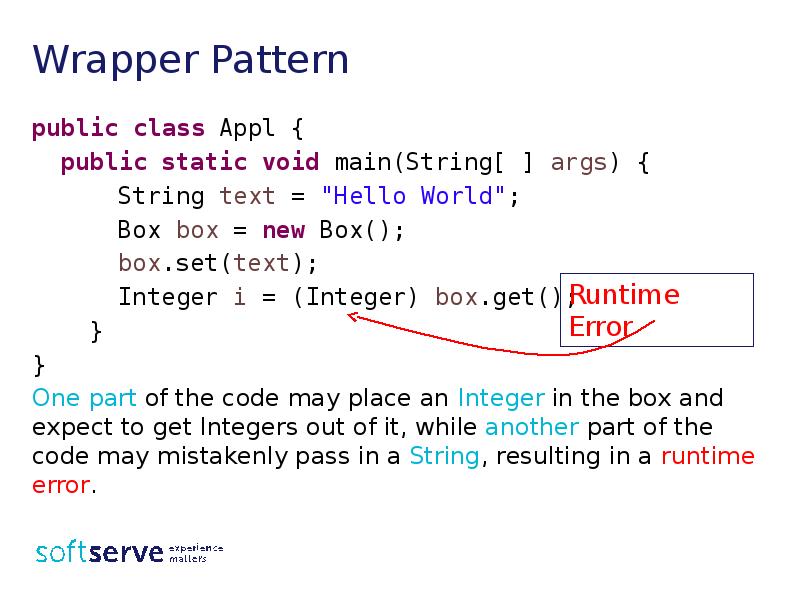
- 4. Wrapper Pattern public class Appl { public static void main(String[ ]
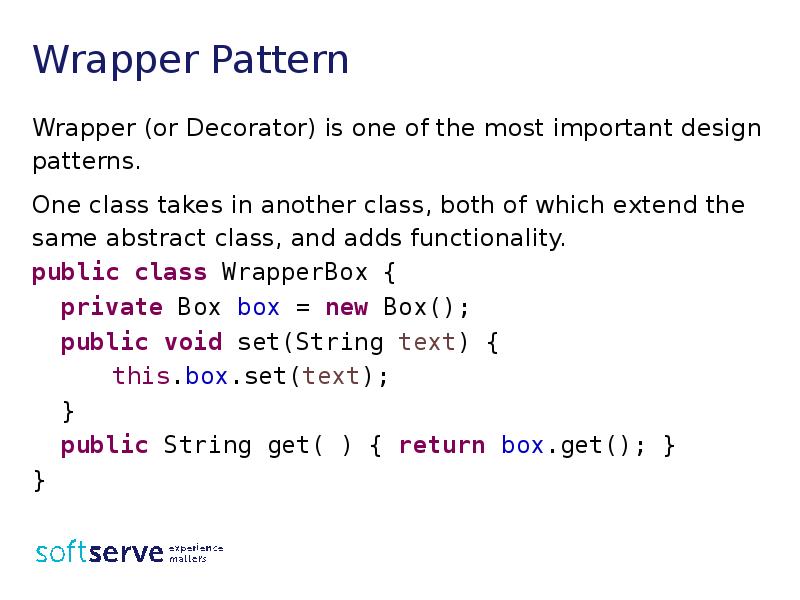
- 5. Wrapper Pattern Wrapper (or Decorator) is one of the most important
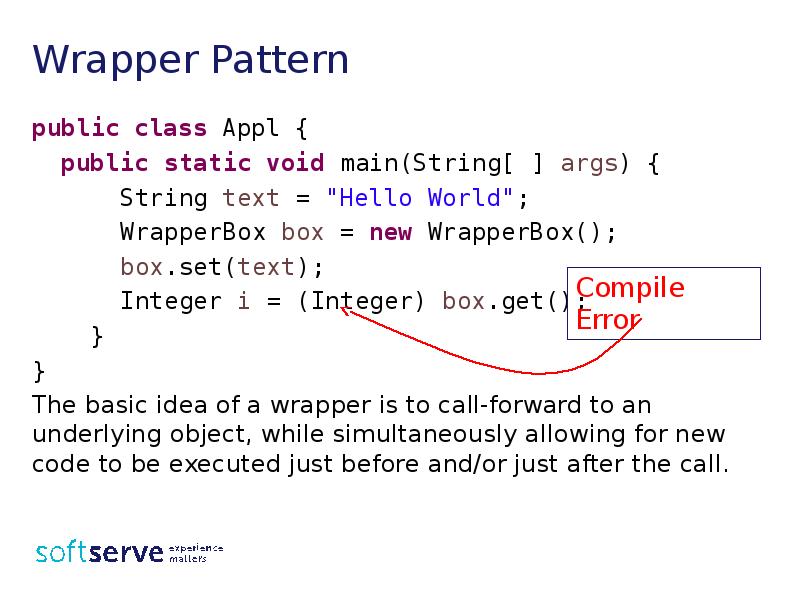
- 6. Wrapper Pattern public class Appl { public static void main(String[ ]
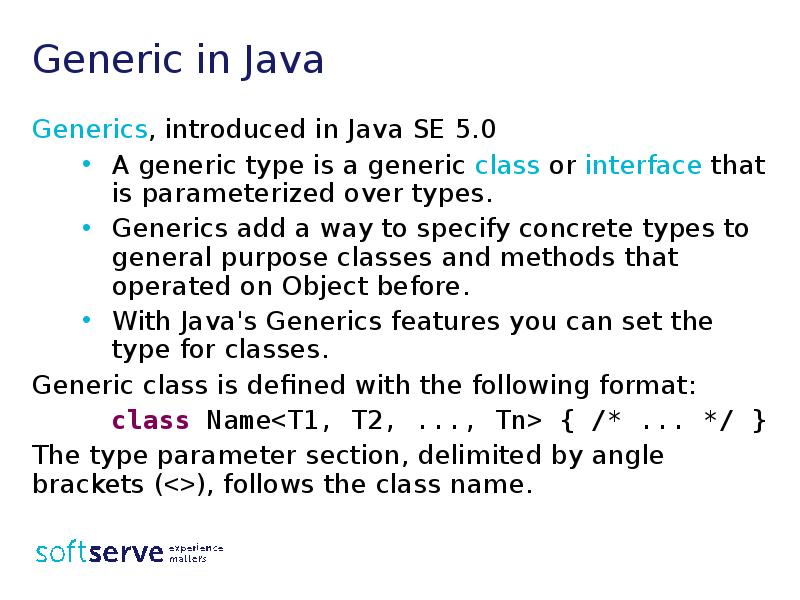
- 7. Generic in Java Generics, introduced in Java SE 5.0 A generic
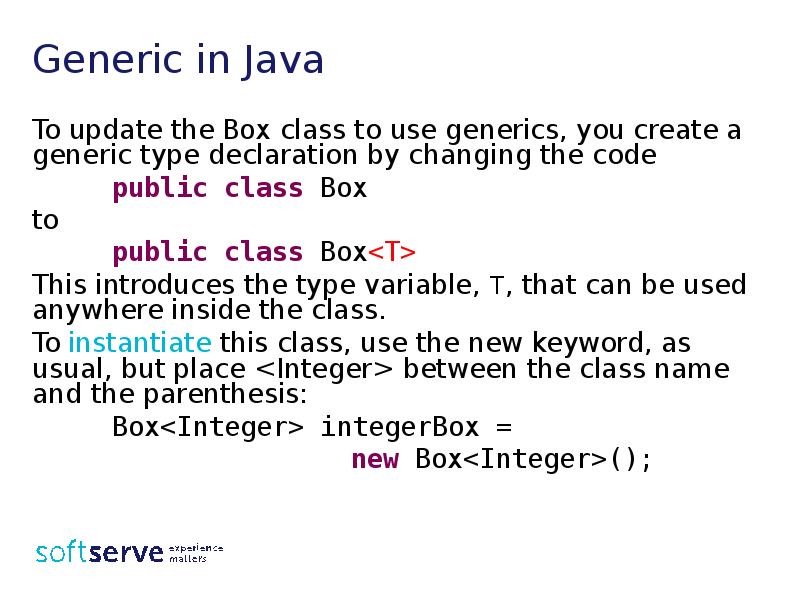
- 8. Generic in Java To update the Box class to use generics,
- 9. Generic in Java public class Box<T> { // T stands
- 10. Generic in Java public class Appl { public static void main(String[
- 11. Generic in Java Java method can be parametrized, too: <T>
- 12. Generic in Java Disadvantages Generic-fields can not be static. Static methods
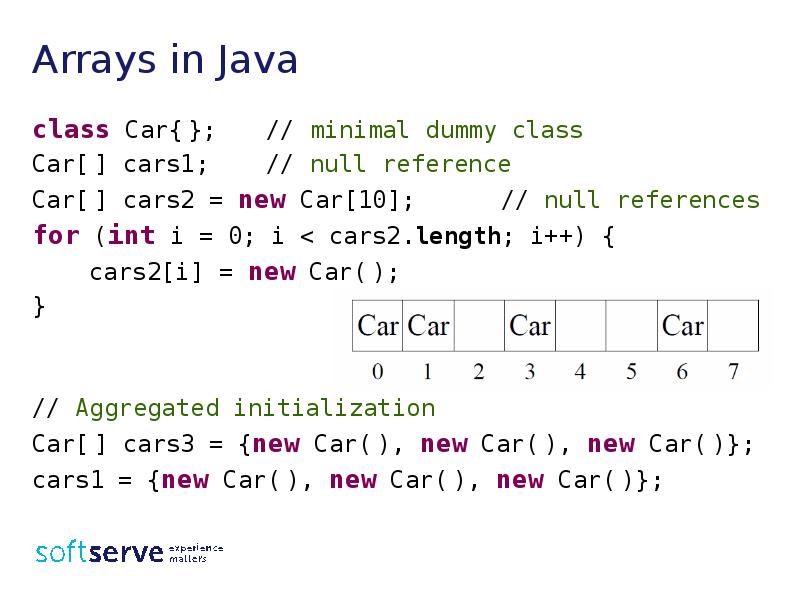
- 13. Arrays in Java class Car{ }; // minimal dummy class Car[
- 14. Arrays in Java Most efficient way to hold references to objects.
- 15. Collections in Java Collection is a container of Objects, it groups
- 16. Benefits of collections reduces programming effort increases program speed and quality
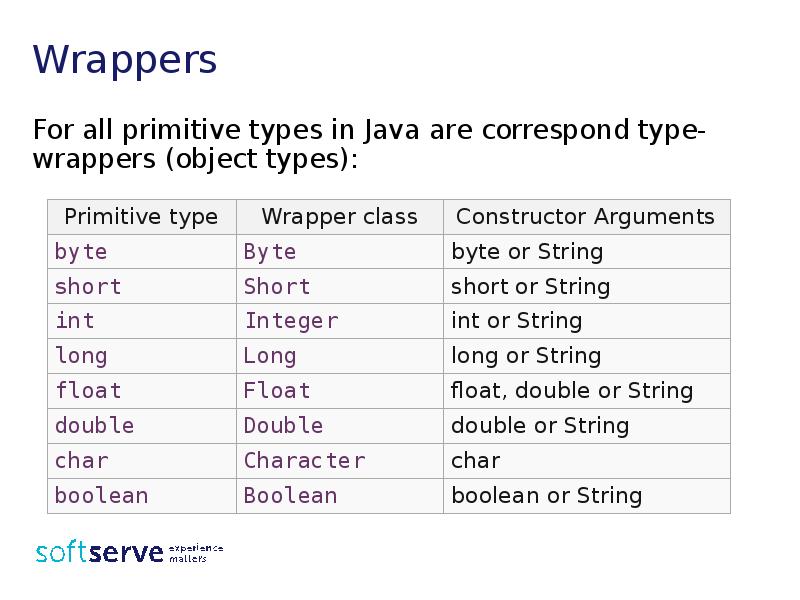
- 17. Wrappers For all primitive types in Java are correspond type-wrappers (object
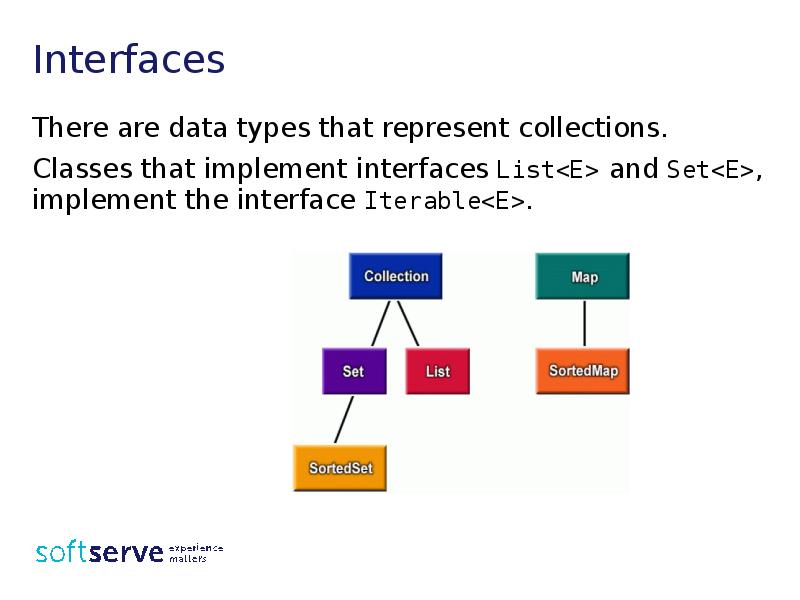
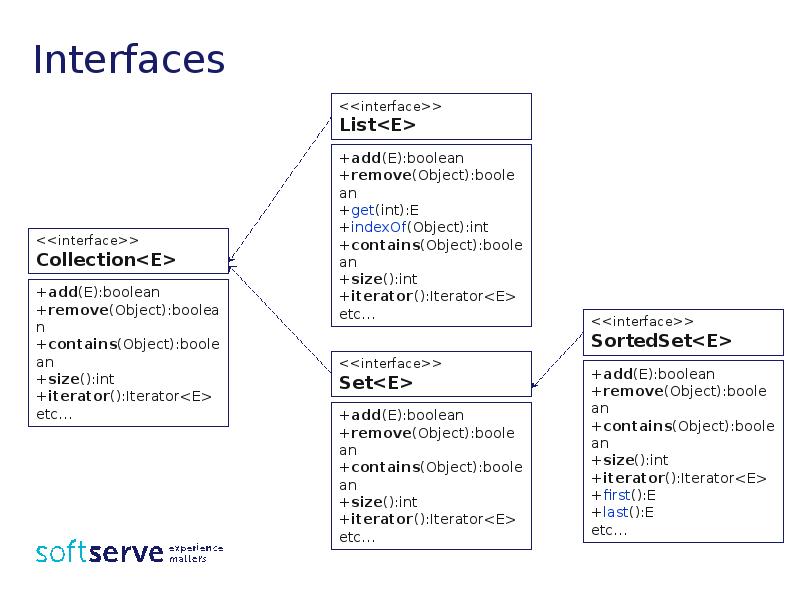
- 18. Interfaces There are data types that represent collections. Classes that implement
- 19. Collections in Java The interface Collection<E> defined methods: boolean add(E
- 20. Collections in Java boolean isEmpty() – returns true, if the collection
- 21. Interfaces
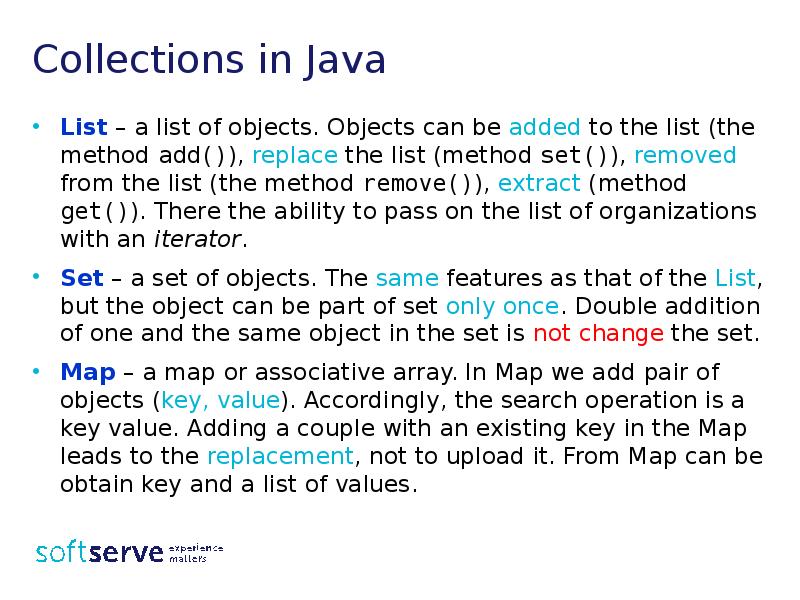
- 22. Collections in Java List – a list of objects. Objects can
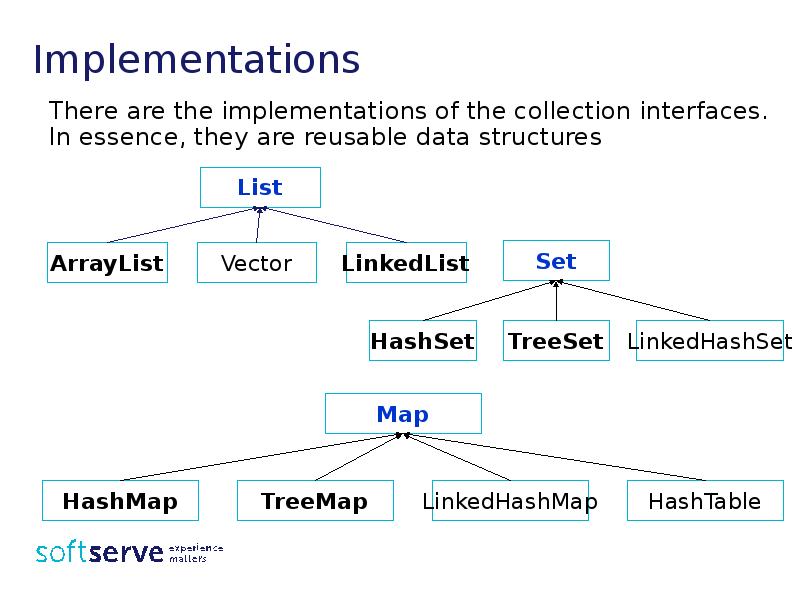
- 23. Implementations There are the implementations of the collection interfaces. In essence,
- 24. List Since List is an interface you need to instantiate a
- 25. ArrayList Adding elements List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("First element"); list.add("Second
- 26. Iterator Iterator – a helper object. Used to iterate over collection
- 27. ArrayList Removing Elements remove(Object element) remove(int index) Cleaning a list list.clear();
- 28. LinkedList LinkedList has the same functionality as the ArrayList. Different way
- 29. Example public static void main (String[ ] args) { ArrayList
- 30. Set A Set is a collection that does not contain any
- 31. Example import java.util.*; public class FindDups { public static void
- 32. Wrapper public class MyList { private ArrayList v = new
- 33. Sorting public static void main(String[] args) { int[] x =
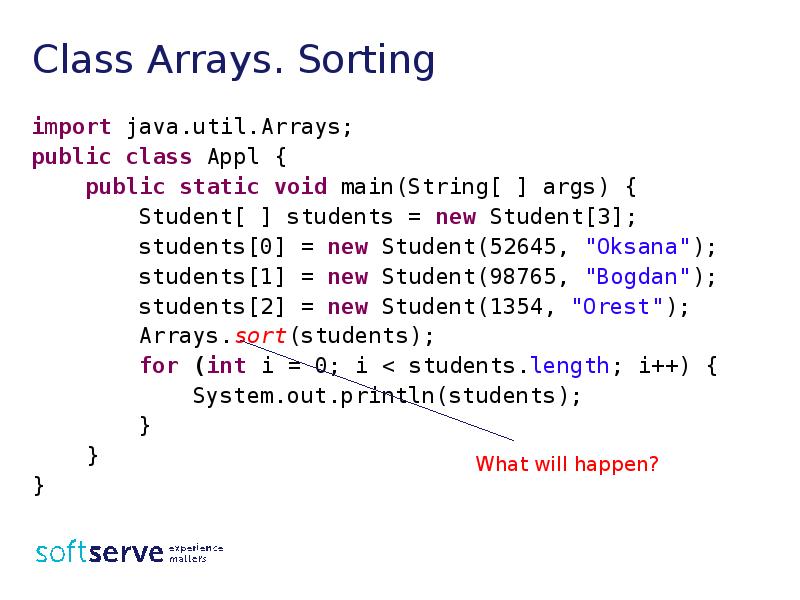
- 34. Class Arrays. Sorting import java.util.Arrays; public class Appl { public
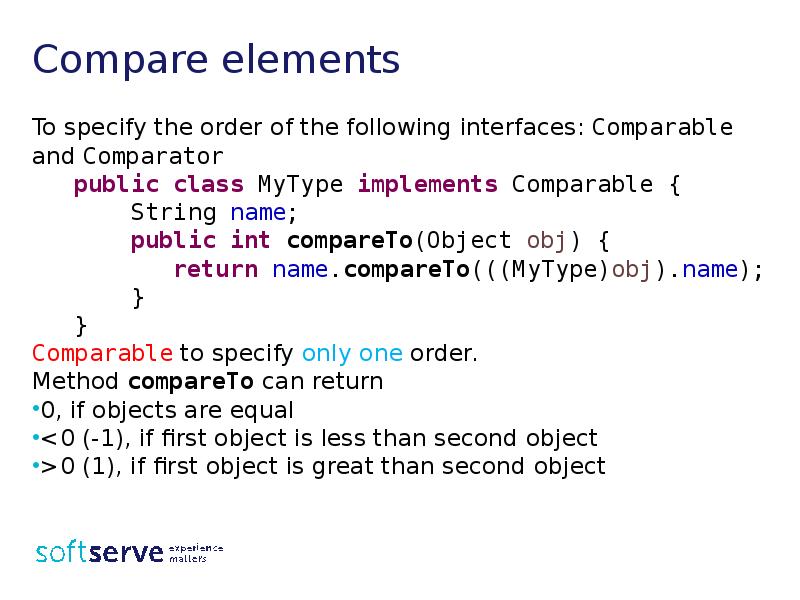
- 35. Compare elements To specify the order of the following interfaces: Comparable
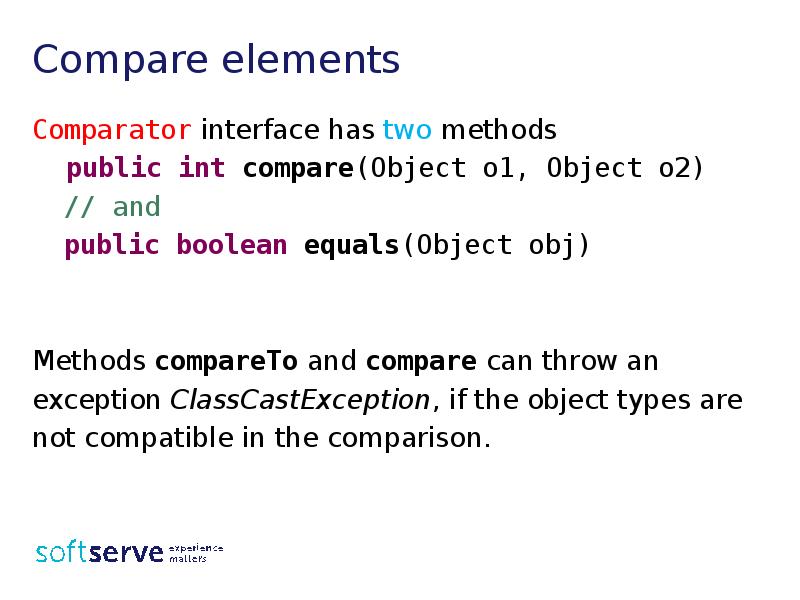
- 36. Compare elements Comparator interface has two methods public int compare(Object
- 37. Example 1
- 38. Example 1
- 39. Example 1
- 40. Example 2 public class Employee { int tabNumber;
- 41. Example 2 static class NameComparator implements Comparator { public int compare(Object
- 42. Example 2 public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Employee> set =
- 43. Map The most commonly used Map implementations are HashMap and TreeMap.
- 44. Map
- 45. Practical task 1 Declare collection myCollection of 10 integers and fill
- 46. Practical task 2 In the main() method declare map employeeMap of
- 47. Homework Write parameterized methods union(Set set1, Set set2) and intersect(Set set1,
- 48. Homework Write class Student that provides information about the name of
- 49. The end
- 50. Скачать презентацию
















![Example
public static void main (String[ ] args) {
Example
public static void main (String[ ] args) {](/documents_3/3d98cd1ca0d96d68c8816401a27038d9/img28.jpg)



![Sorting
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] Sorting
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]](/documents_3/3d98cd1ca0d96d68c8816401a27038d9/img32.jpg)





![Example 2
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Employee> set = Example 2
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Employee> set =](/documents_3/3d98cd1ca0d96d68c8816401a27038d9/img41.jpg)







Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























