Information Security review презентация
Содержание
- 2. What is Security? (cont’d.) The protection of information and its critical
- 3. Introduction Information security: a “well-informed sense of assurance that the information
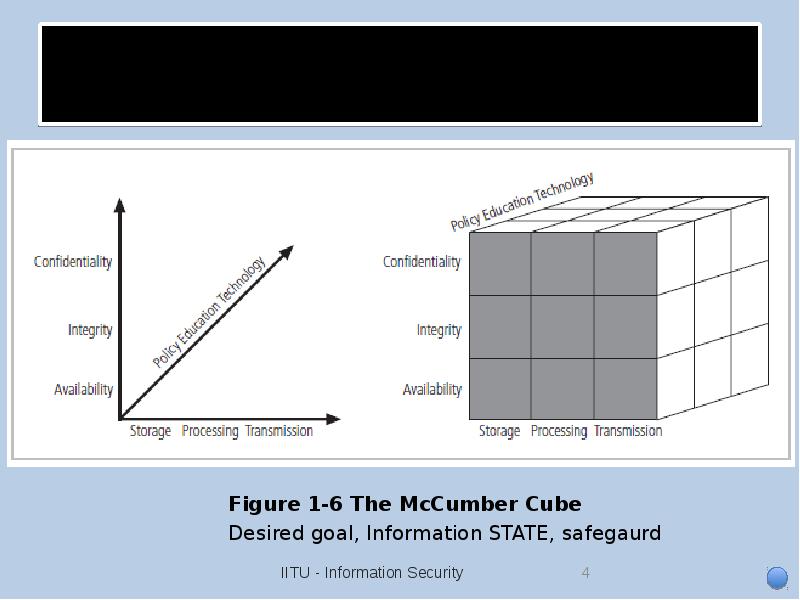
- 4. CNSS Security Model
- 5. Components of an Information System Information system (IS) is entire set
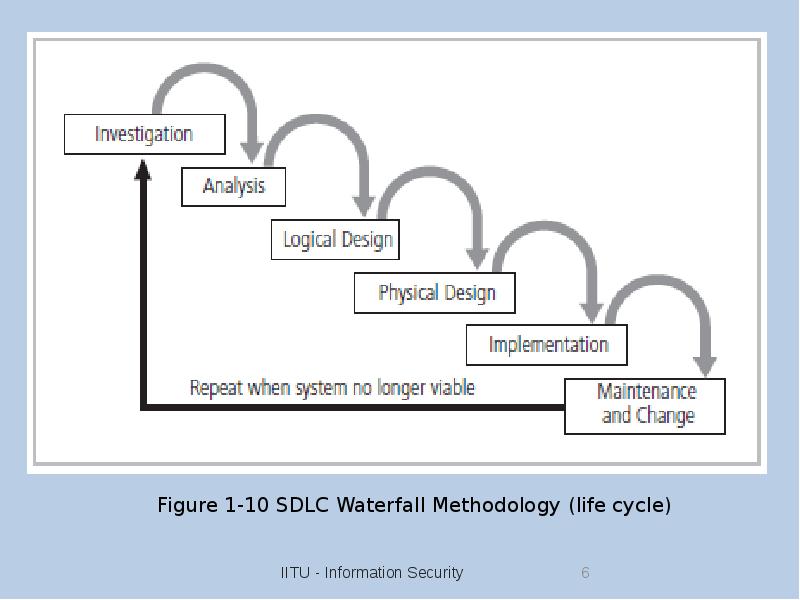
- 7. Analysis Documents from investigation phase are studied Analysis of existing security
- 8. Implementation Security solutions are acquired, tested, implemented, and tested again Personnel
- 9. Summary Information security is a “well-informed sense of assurance that the
- 10. Everything needs a break.
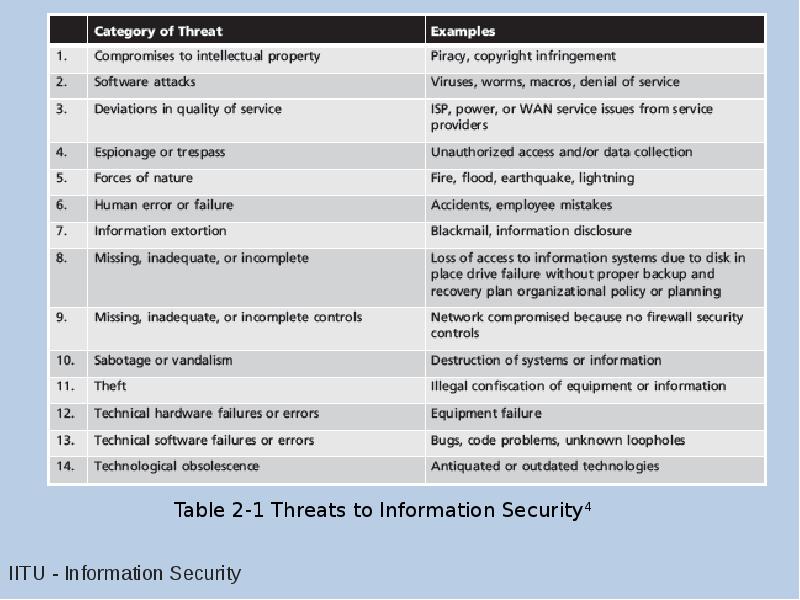
- 11. Threats Threat: an object, person, or other entity that represents a
- 13. Deliberate Software Attacks Malicious software (malware) designed to damage, destroy, or
- 14. More about previous slide Deliberate Software Attacks Deliberate software attacks occur
- 15. Espionage or Trespass (cont’d.) Expert hacker Develops software scripts and program
- 16. Attacks Attacks Acts or actions that exploits vulnerability (i.e., an identified
- 17. Attacks (cont’d.) Types of attacks (cont’d.) Back door: gaining access to
- 18. Attacks (cont’d.) Types of attacks (cont’d.) Denial-of-service (DoS): attacker sends large
- 19. Attacks (cont’d.) Types of attacks (cont’d.) Spoofing: technique used to gain
- 20. Attacks (cont’d.) Types of attacks (cont’d.) Sniffers: program or device that
- 21. Attacks (cont’d.) Types of attacks (cont’d.) Social engineering: using social skills
- 22. Take a deep breath
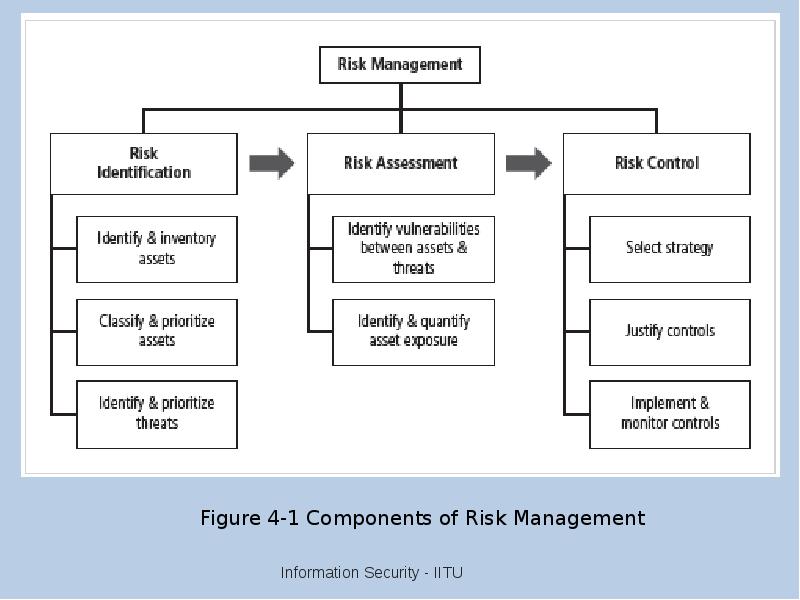
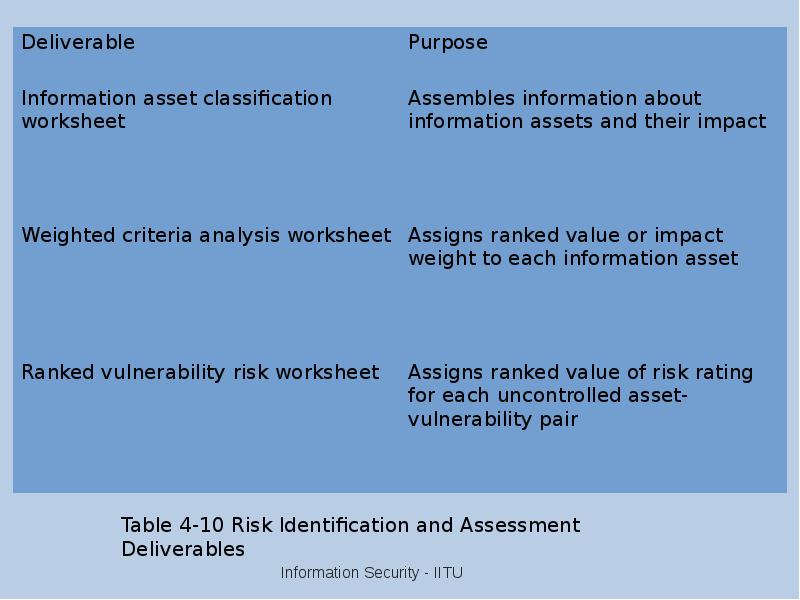
- 24. Risk Identification Risk management involves identifying, classifying, and prioritizing an organization’s
- 25. Risk Assessment Risk assessment evaluates the relative risk for each vulnerability
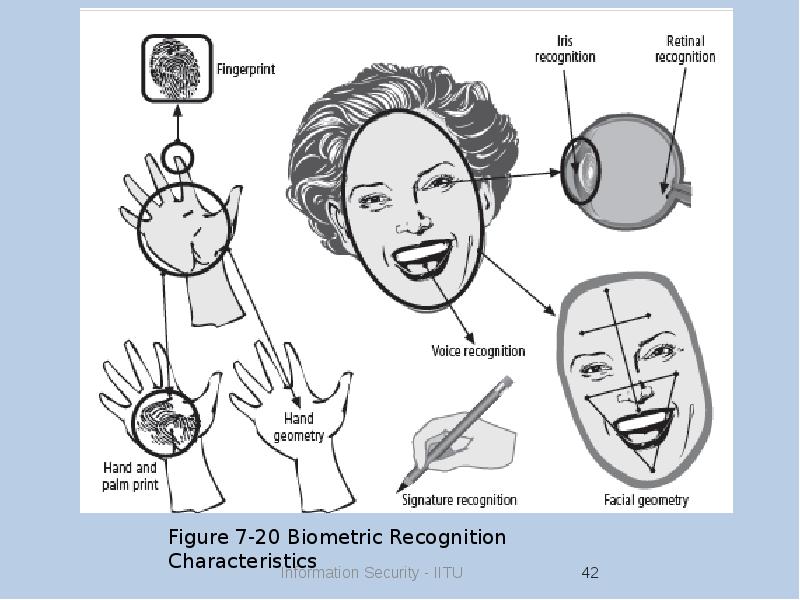
- 27. Access Control Access control: method by which systems determine whether and
- 28. Identification Identification: mechanism whereby an unverified entity that seeks access to
- 29. Authentication Authentication: the process of validating a supplicant’s purported identity Authentication
- 30. Authorization Authorization: the matching of an authenticated entity to a list
- 31. Take a rest
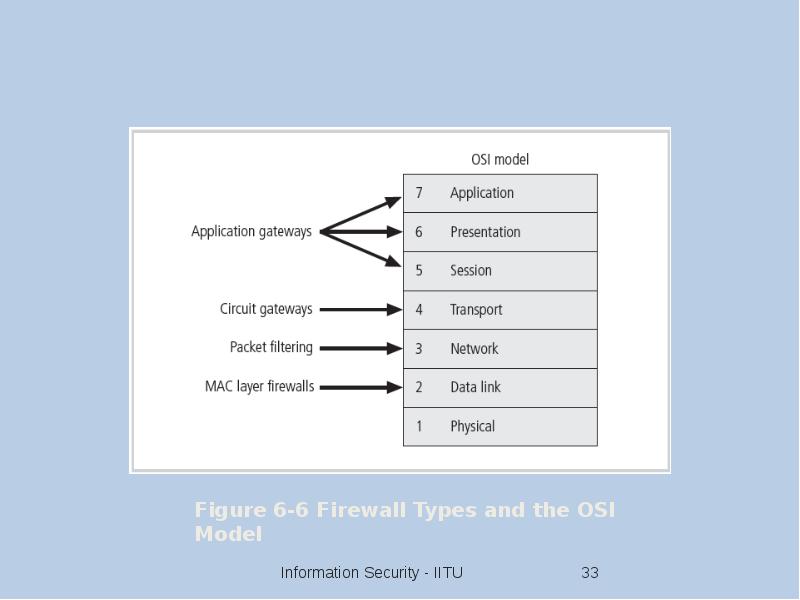
- 32. Firewalls Processing Modes Five processing modes by which firewalls can be
- 34. Firewall Architectures (cont’d.) Dual-homed host firewalls Bastion host contains two network
- 35. Firewalls Processing Modes (cont’d.) Application gateways Frequently installed on a
- 36. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Private and secure network connection between systems;
- 37. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (cont’d.) Intrusion detection: consists of procedures
- 38. Honeypots, Honeynets, and Padded Cell Systems Honeypots: decoy systems designed to
- 39. Firewall Analysis Tools Several tools automate remote discovery of firewall rules
- 40. Scanning and Analysis Tools Typically used to collect information that attacker
- 41. Scanning and Analysis Tools (cont’d.) Fingerprinting: systematic survey of all of
- 43. Have some rest
- 44. Cryptology: science of encryption; combines cryptography and cryptanalysis Cryptography: process of
- 45. Substitution Cipher Substitute one value for another Monoalphabetic substitution: uses only
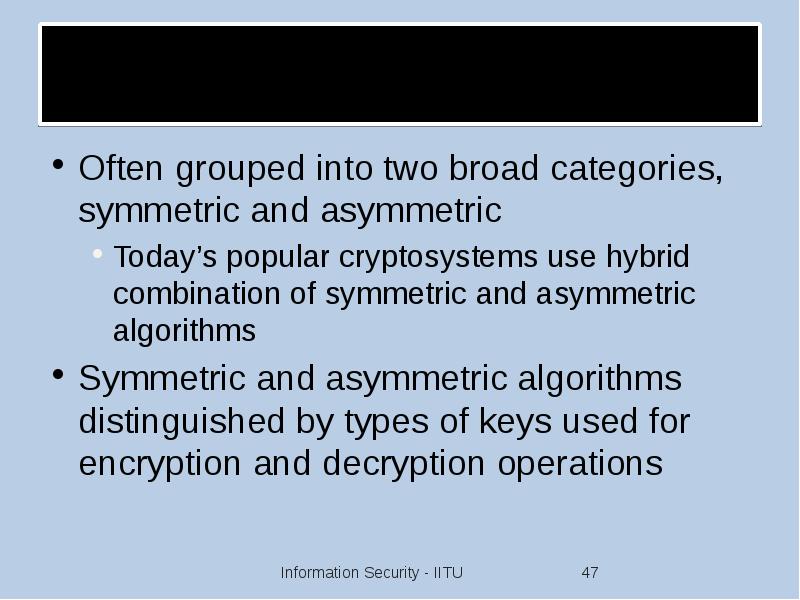
- 47. Cryptographic Algorithms Often grouped into two broad categories, symmetric and asymmetric
- 48. Symmetric Encryption (cont’d.) Data Encryption Standard (DES): one of most popular
- 49. Asymmetric Encryption Also known as public-key encryption Uses two different but
- 50. Asymmetric Encryption Also known as public-key encryption Uses two different but
- 51. Symmetric Encryption (cont’d.) Data Encryption Standard (DES): one of most popular
- 52. Symmetric Encryption Uses same “secret key” to encipher and decipher message
- 53. Securing Internet Communication with S-HTTP and SSL Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
- 54. Securing e-mail with S/MIME, PEM, and PGP Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail
- 55. Securing Web transactions with SET, SSL, and S-HTTP Secure Electronic Transactions
- 56. Securing Wireless Networks with WEP and WPA Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP):
- 57. Steganography Process of hiding information Has been in use for a
- 58. Do you want a cup of coffee?!
- 59. Introduction Physical security addresses design, implementation, and maintenance of countermeasures that
- 60. Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) In case of
- 61. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Areas within heating, ventilation, and air
- 62. Physical Security Controls (cont’d.) Electronic Monitoring Records events where other types
- 63. Summary Threats to information security that are unique to physical security
- 64. Introduction SecSDLC implementation phase is accomplished through changing configuration and operation
- 65. Developing the Project Plan Creation of project plan can be done
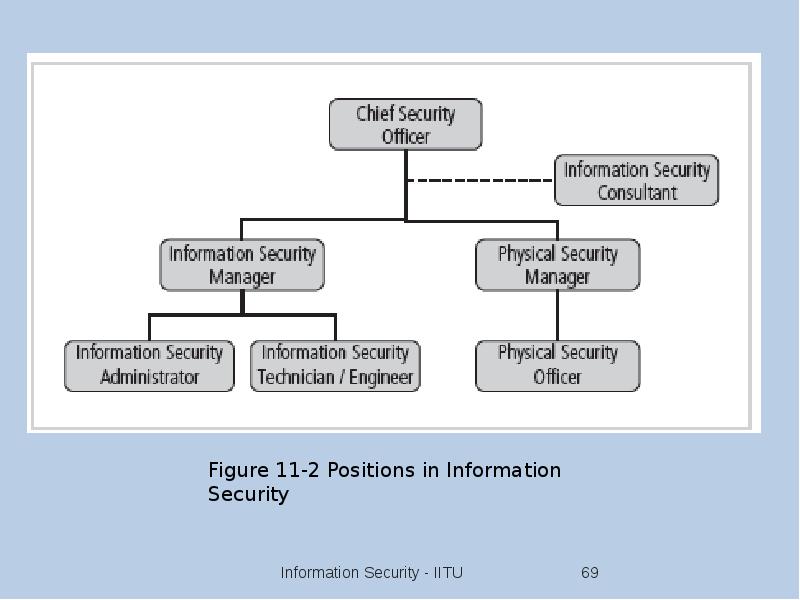
- 67. Positioning and Staffing the Security Function The security function can be
- 68. Positioning and Staffing the Security Function The security function can be
- 70. Staffing the Information Security Function (cont’d.) Chief Information Security Officer (CISO
- 71. Staffing the Information Security Function (cont’d.) Security manager Accountable for day-to-day
- 72. Staffing the Information Security Function (cont’d.) Security technician Technically qualified individuals
- 73. It might be a bad day, not a bad life
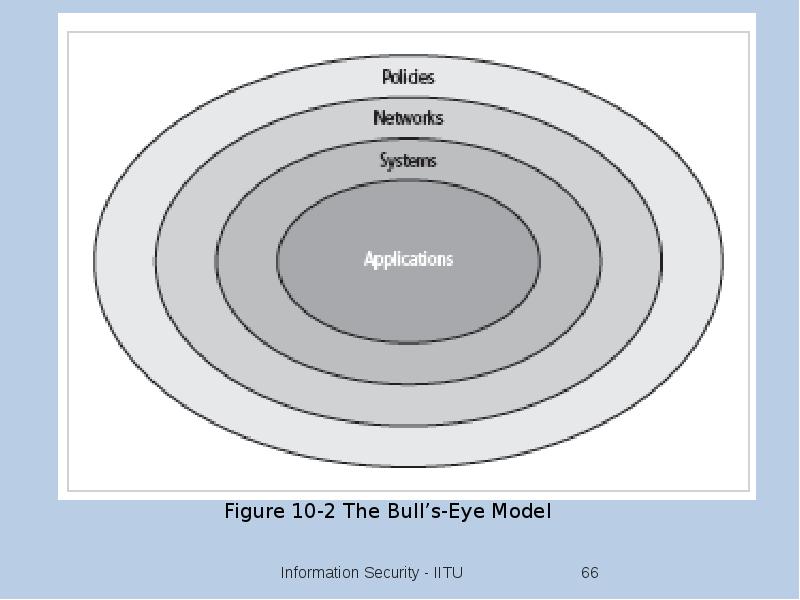
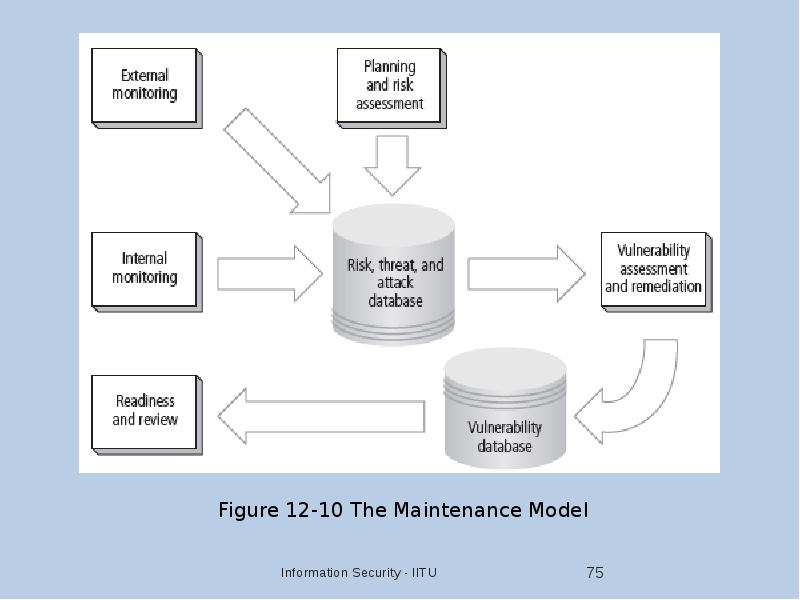
- 74. The Security Maintenance Model Designed to focus organizational effort on maintaining
- 76. Monitoring the External Environment Objective to provide early awareness of new
- 77. Monitoring the Internal Environment Maintain informed awareness of state of organization’s
- 78. Planning and Risk Assessment Primary objective is to keep lookout over
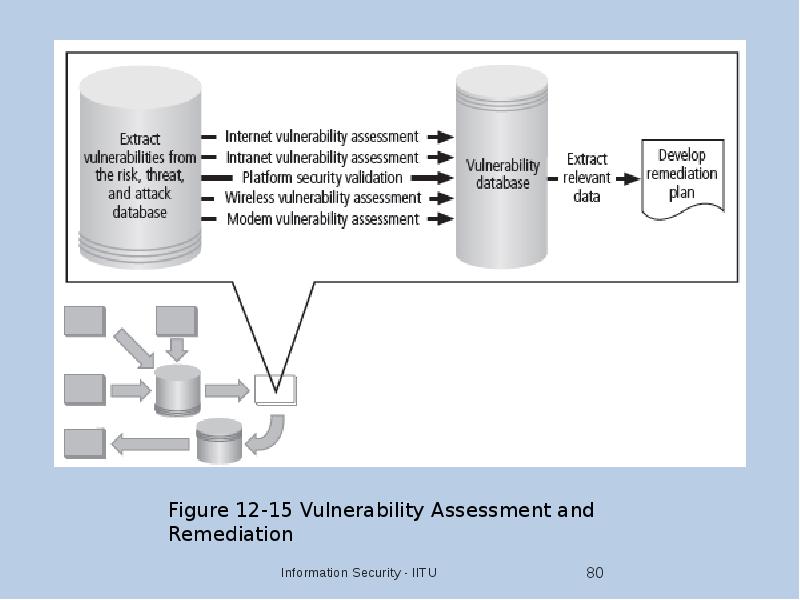
- 79. Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation Primary goal: identification of specific, documented vulnerabilities
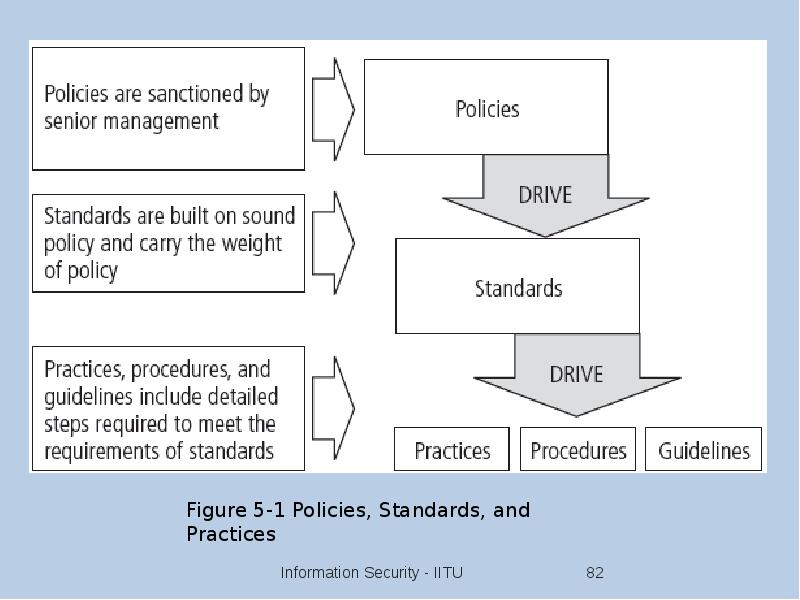
- 81. Definitions Policy: course of action used by organization to convey instructions
- 83. The ISO 27000 Series One of the most widely referenced and
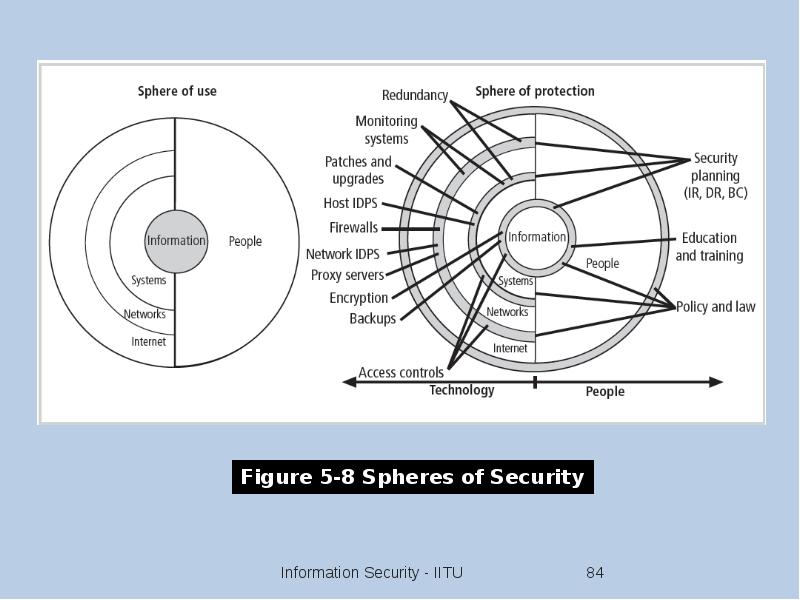
- 85. Design of Security Architecture (cont’d.) Firewall: device that selectively discriminates against
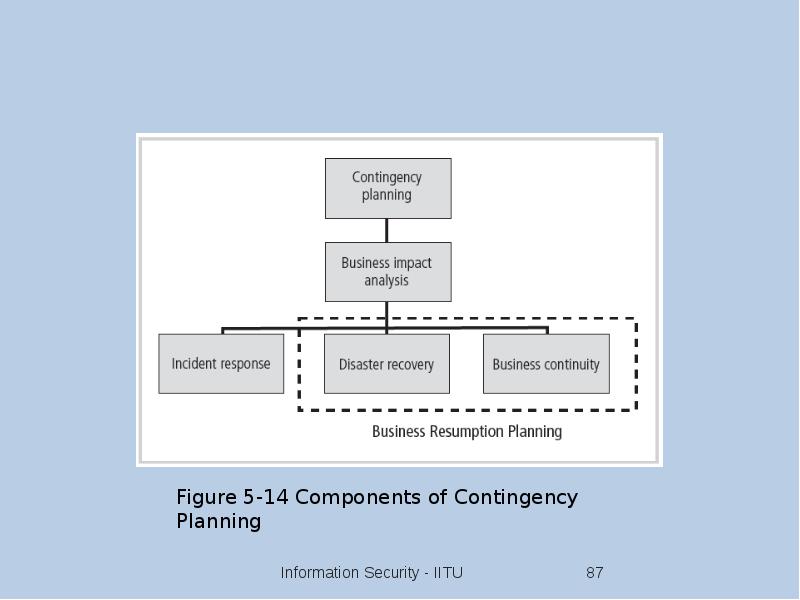
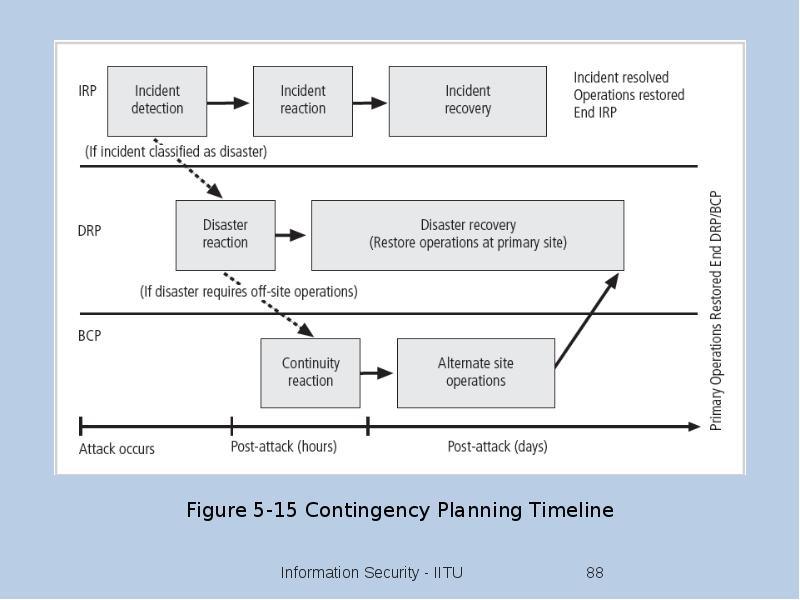
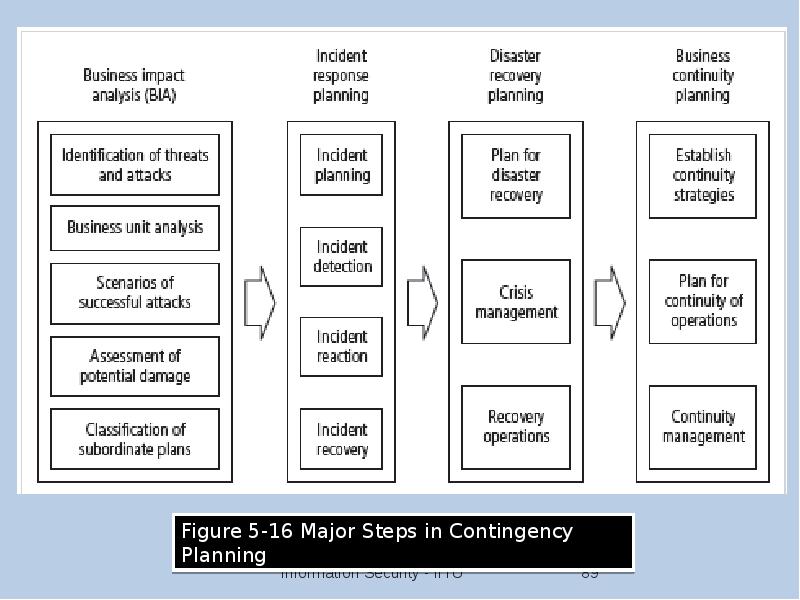
- 86. Continuity Strategies Incident response plans (IRPs); disaster recovery plans (DRPs); business
- 90. You have done enough today
- 91. Скачать презентацию








































































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























