Introduction to Maya презентация
Содержание
- 2. Biography Naiqi Weng --
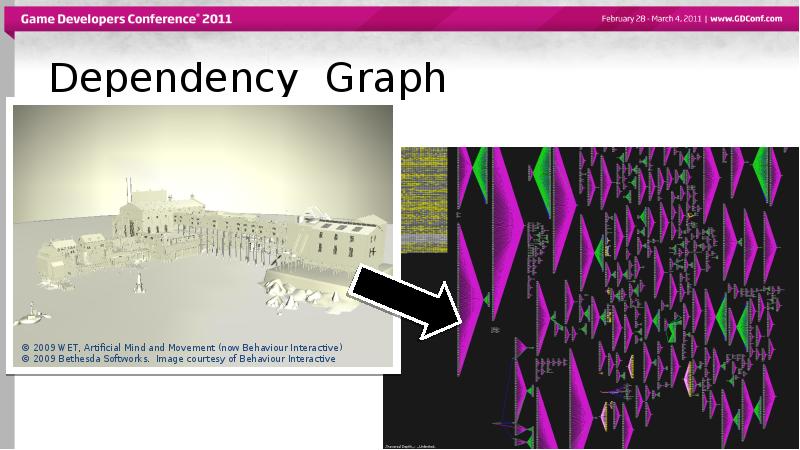
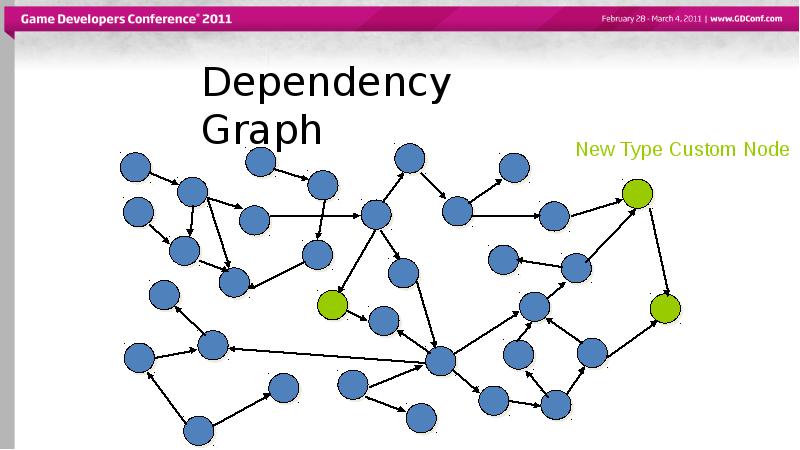
- 3. Dependency Graph
- 4. Agenda What is Dependency Graph (DG)? Concepts/Elements of DG Nodes
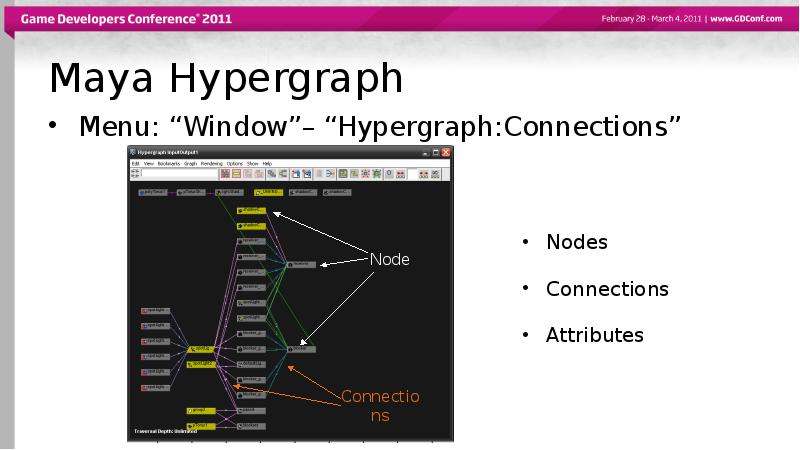
- 5. Maya Hypergraph Menu: “Window”– “Hypergraph:Connections”
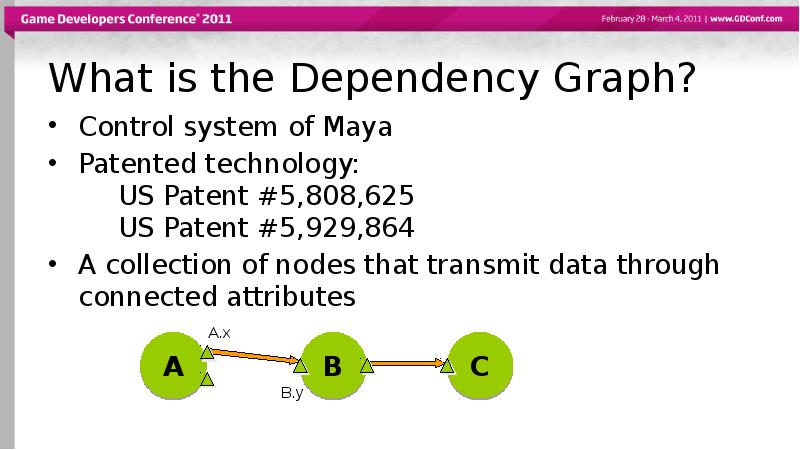
- 6. What is the Dependency Graph? Control system of Maya Patented technology:
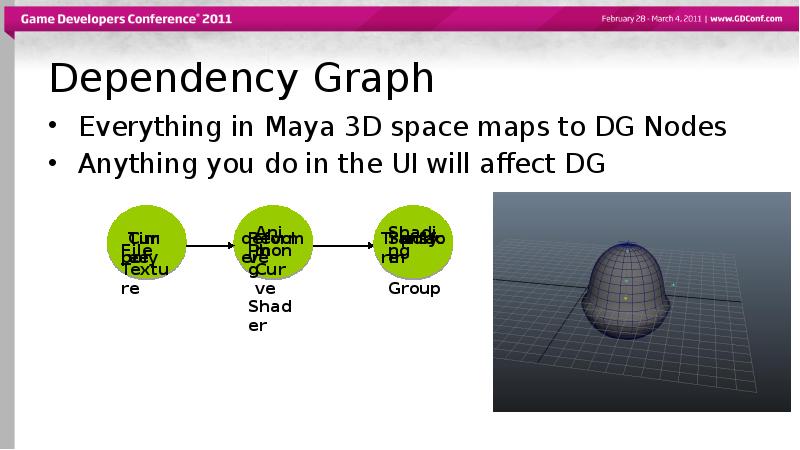
- 7. Dependency Graph Everything in Maya 3D space maps to DG Nodes
- 8. Dependency Graph
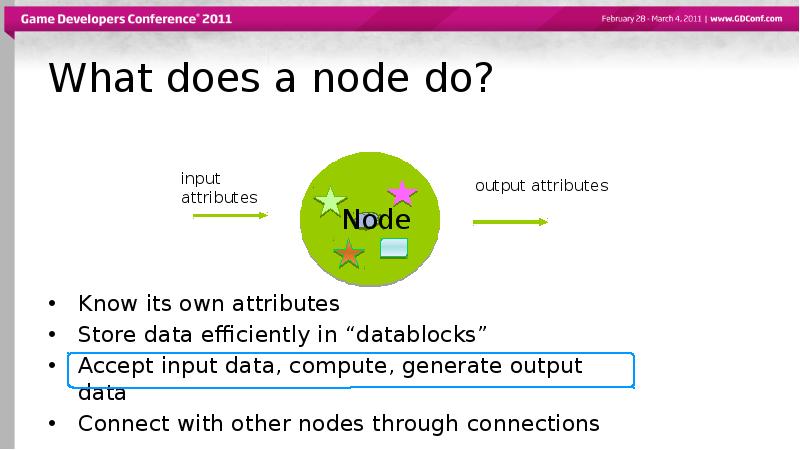
- 10. What does a node do? Know its own attributes Store data
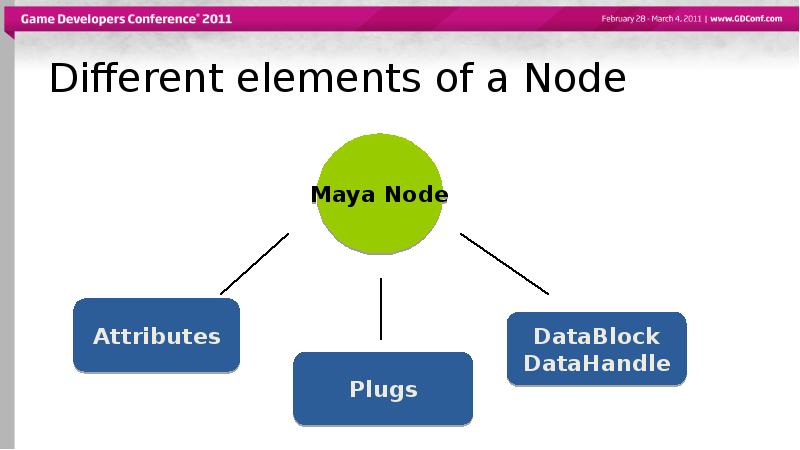
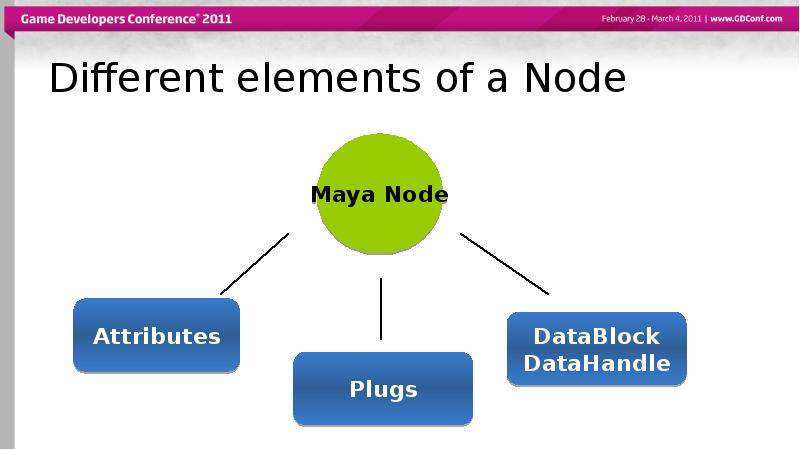
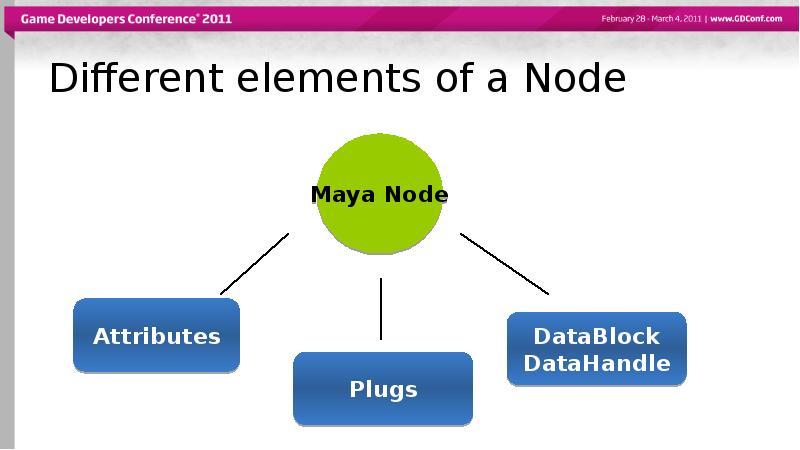
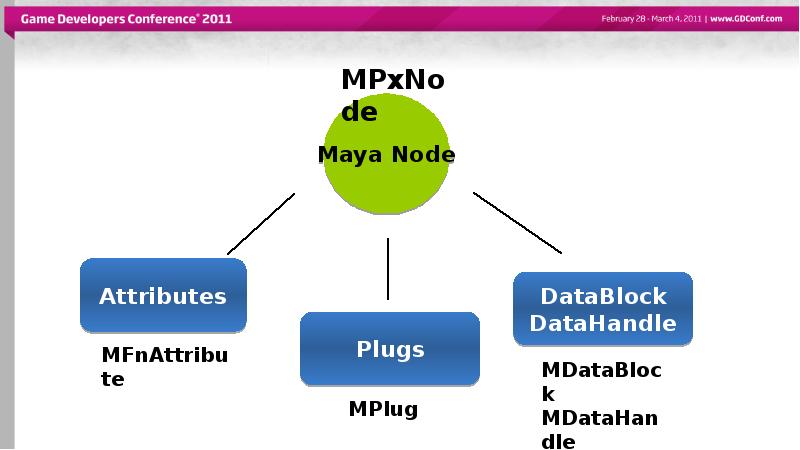
- 11. Different elements of a Node
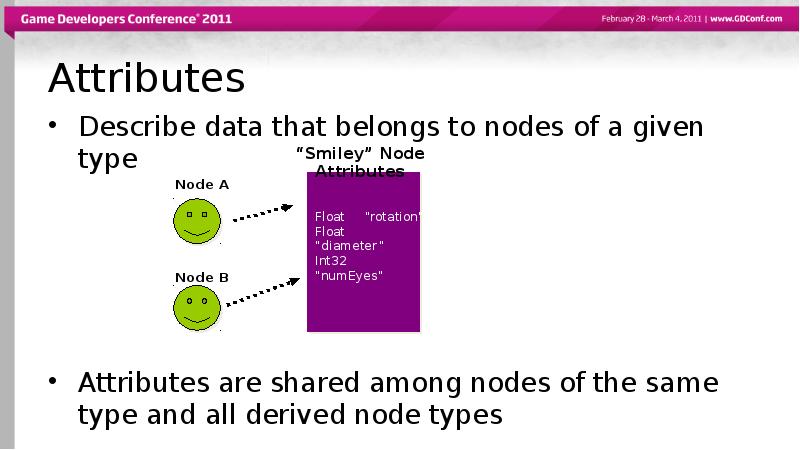
- 12. Attributes Describe data that belongs to nodes of a given type
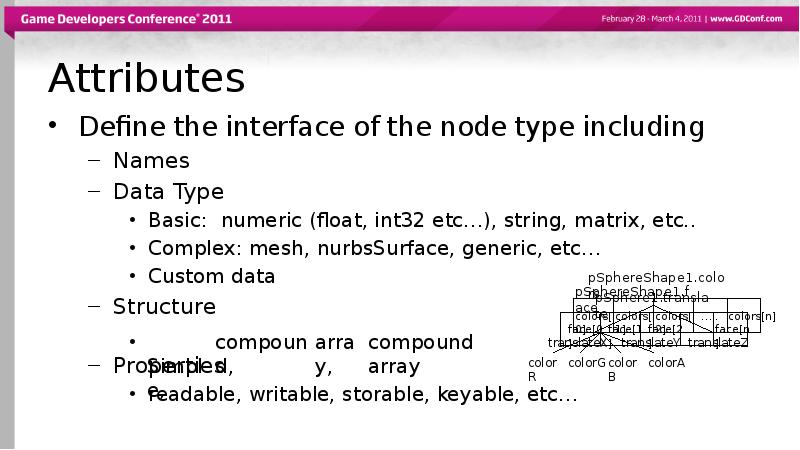
- 13. Attributes Define the interface of the node type including Names Data
- 14. API Classes for Attributes Base Class: MFnAttribute Takes care of
- 15. Different elements of a Node
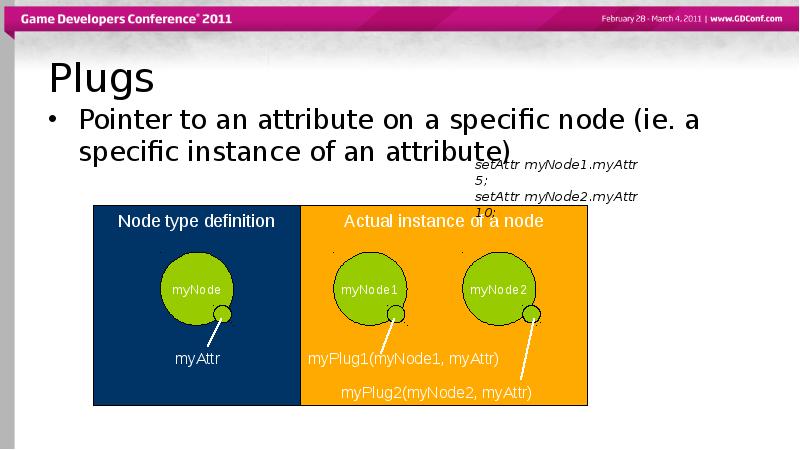
- 16. Plugs Pointer to an attribute on a specific node (ie. a
- 17. Plugs Plugs can be used to: query / set a value
- 18. Different elements of a Node
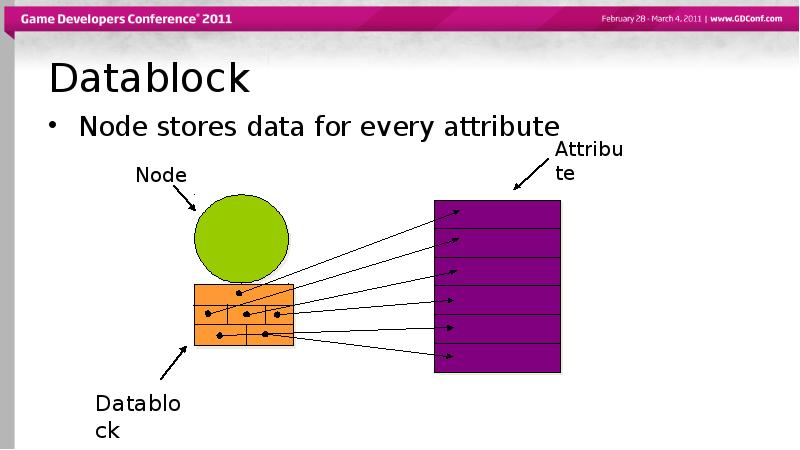
- 19. Datablock Node stores data for every attribute
- 20. Datablocks Datablock is the actual storage for the input and output
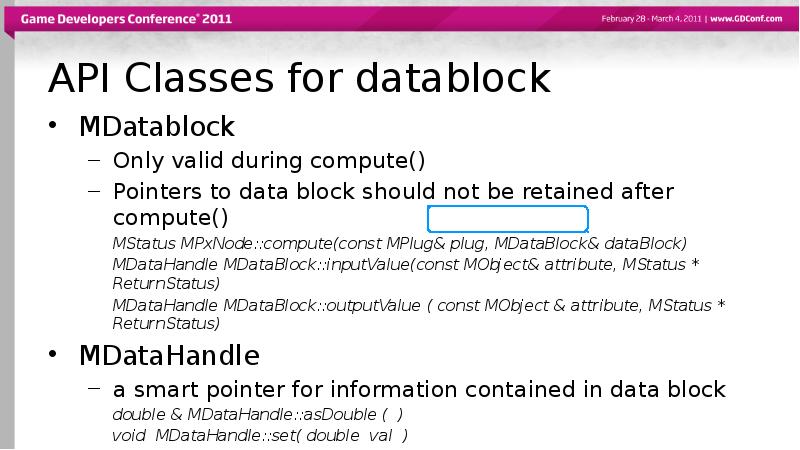
- 21. API Classes for datablock MDatablock Only valid during compute() Pointers to
- 23. Custom Node Plug-in Implementation
- 24. Custom DG Node in Maya Entirely new operations MPxNode: base class
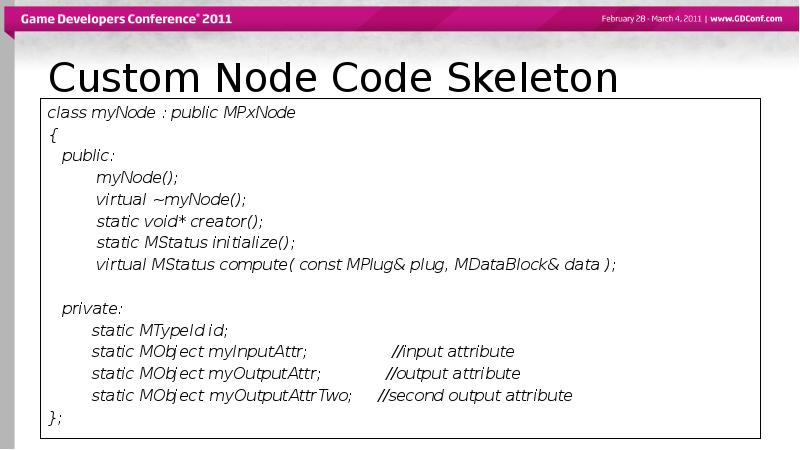
- 25. Custom Node Code Skeleton class myNode : public MPxNode {
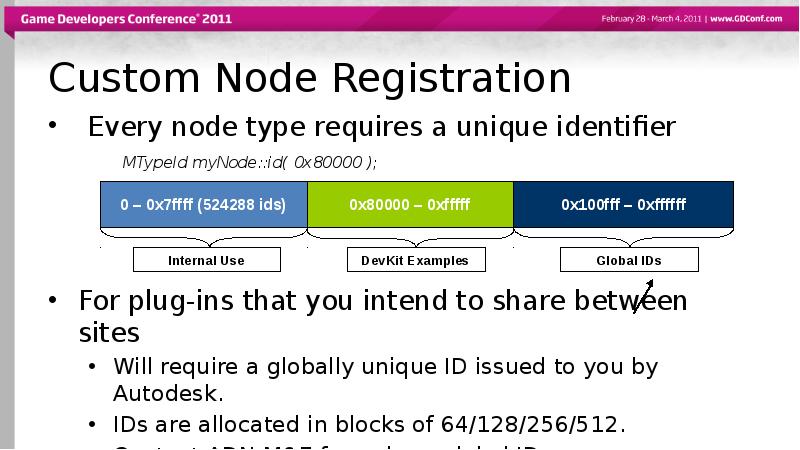
- 26. Custom Node Registration Every node type requires a unique identifier
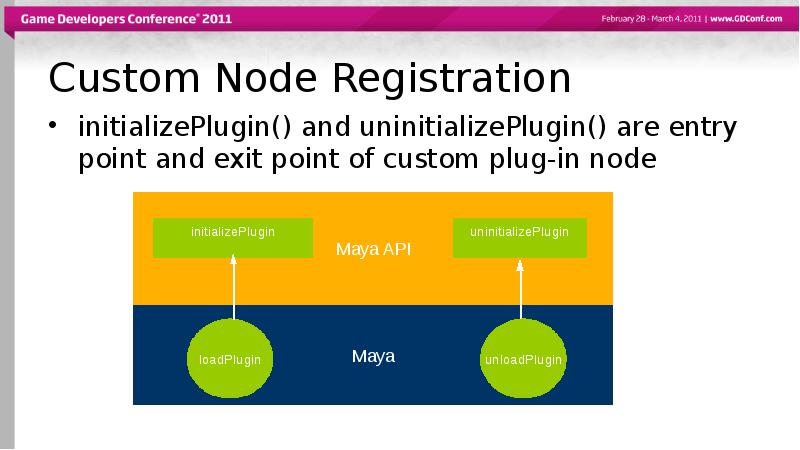
- 27. Custom Node Registration initializePlugin() and uninitializePlugin() are entry point and exit
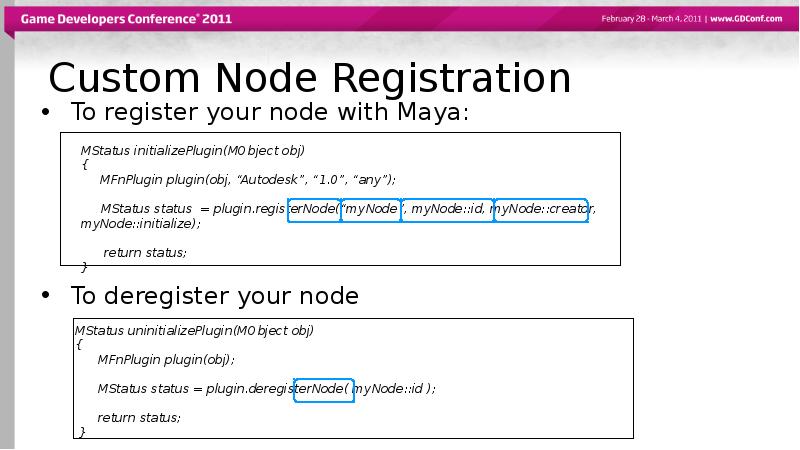
- 28. Custom Node Registration To register your node with Maya: To deregister
- 29. Custom Node Code Skeleton MPxNode::creator() The creator method is called to
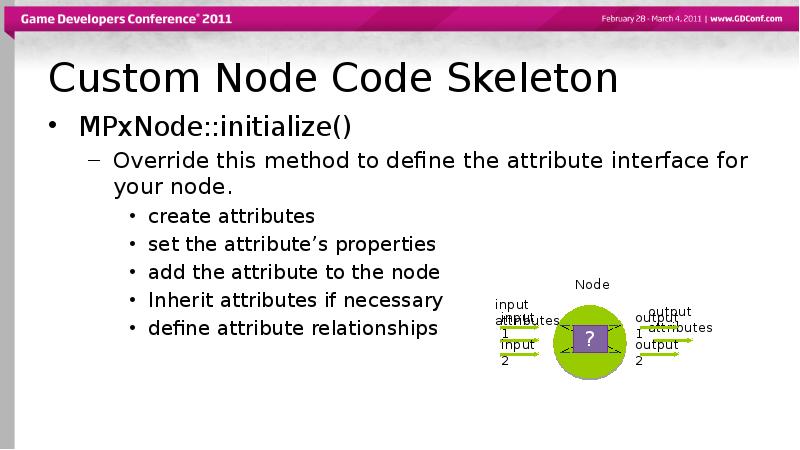
- 30. Custom Node Code Skeleton MPxNode::initialize() Override this method to define the
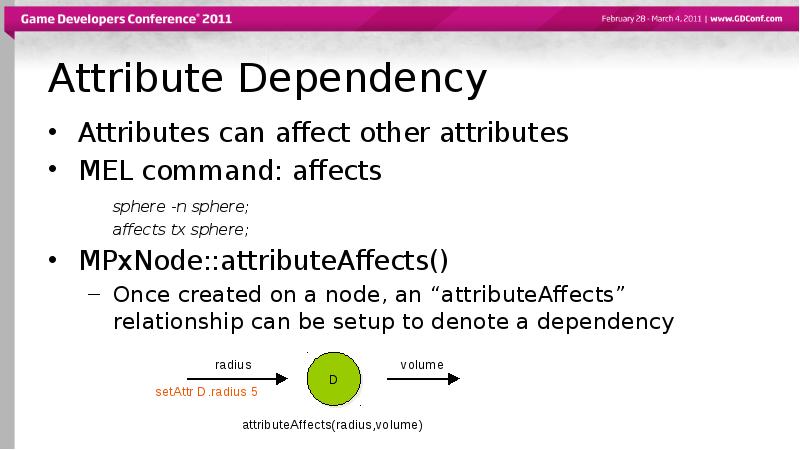
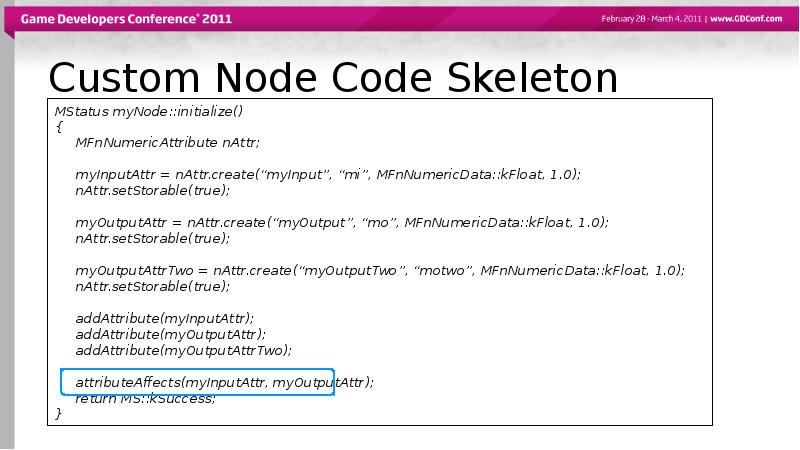
- 31. Attribute Dependency Attributes can affect other attributes MEL command: affects sphere
- 32. Custom Node Code Skeleton
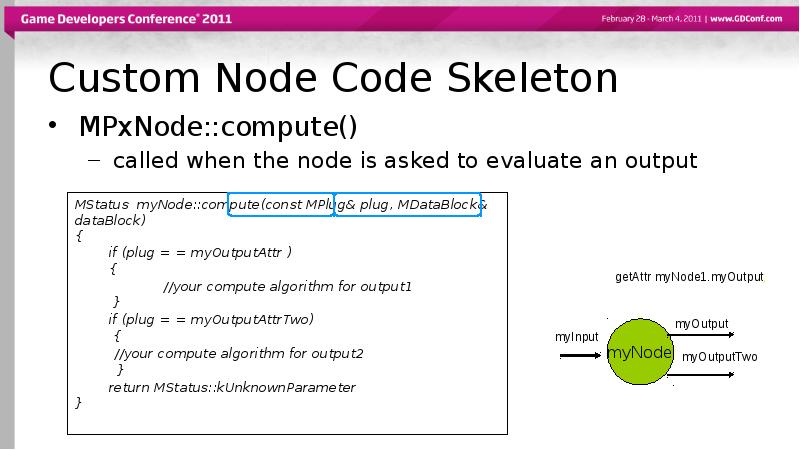
- 33. Custom Node Code Skeleton MPxNode::compute() called when the node is asked
- 34. Examples Devkit Plug-in Examples: C:\Program Files\Autodesk\Maya2011\devkit\plug-ins The Maya API Documentation contains
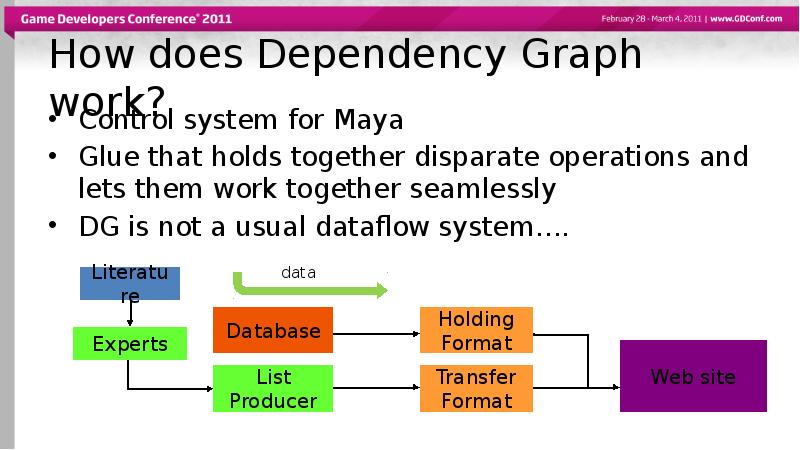
- 35. How does Dependency Graph work? Control system for Maya Glue that
- 36. How does Dependency Graph Work? Two step Push-Pull mechanism: Dirty Propagation
- 37. Dirty Propagation Maya DG caches values Uses dirty system to denote
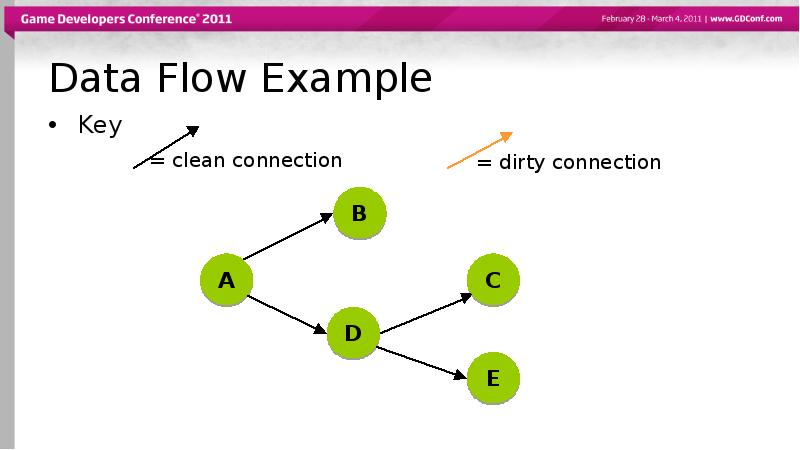
- 38. Data Flow Example Key
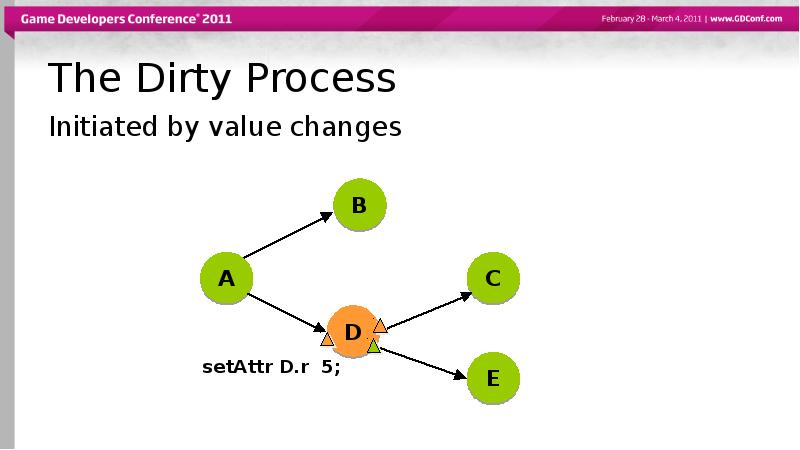
- 39. The Dirty Process Initiated by value changes
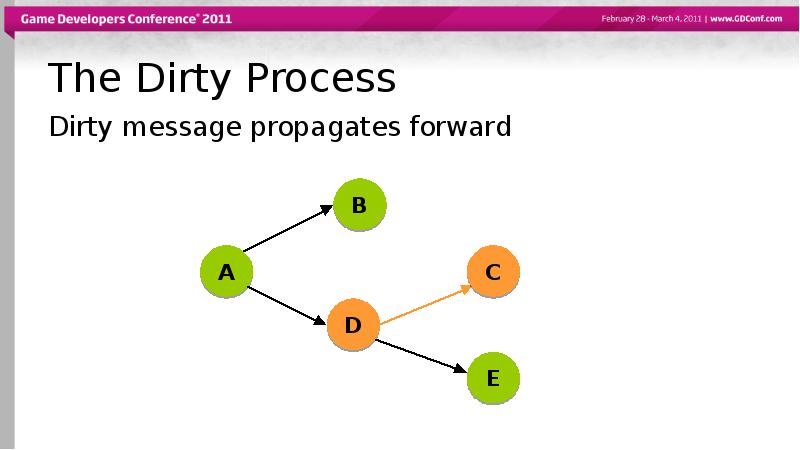
- 40. The Dirty Process Dirty message propagates forward
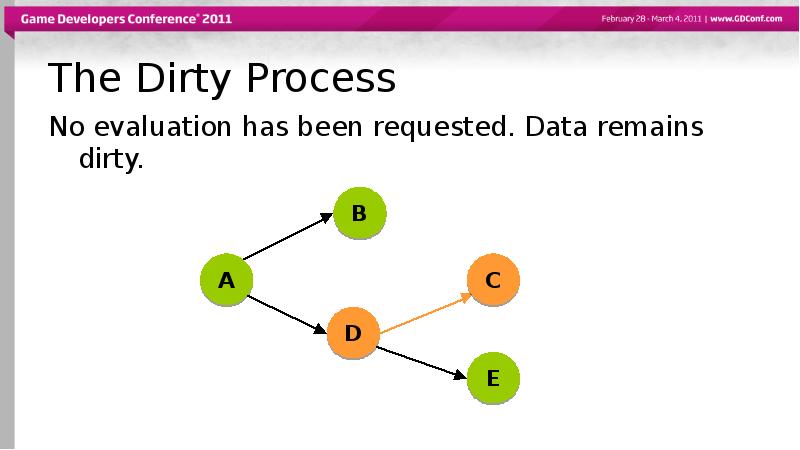
- 41. The Dirty Process No evaluation has been requested. Data remains dirty.
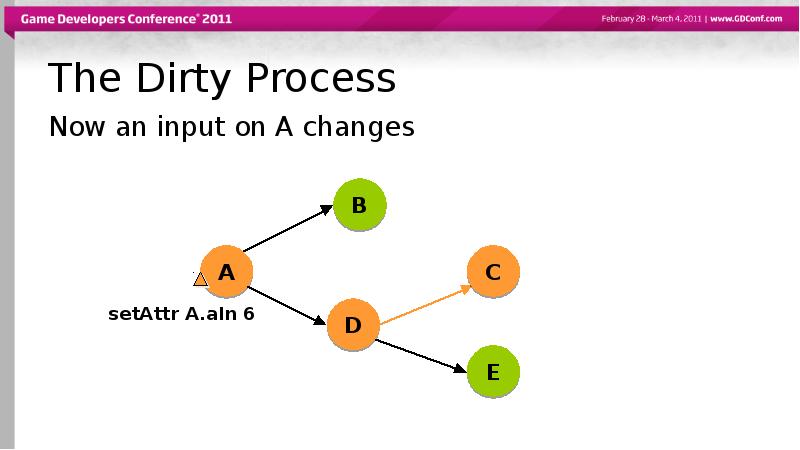
- 42. The Dirty Process Now an input on A changes
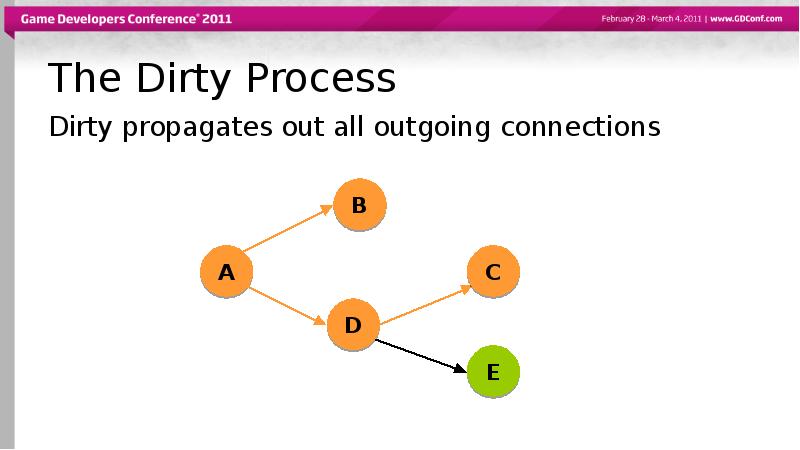
- 43. The Dirty Process Dirty propagates out all outgoing connections
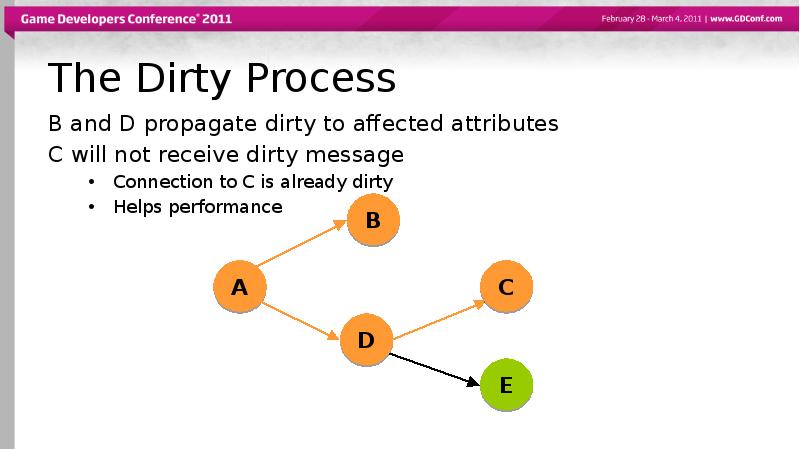
- 44. The Dirty Process B and D propagate dirty to affected attributes
- 45. The Evaluation Process Lazy Evaluation: On demand Evaluation is trigged when
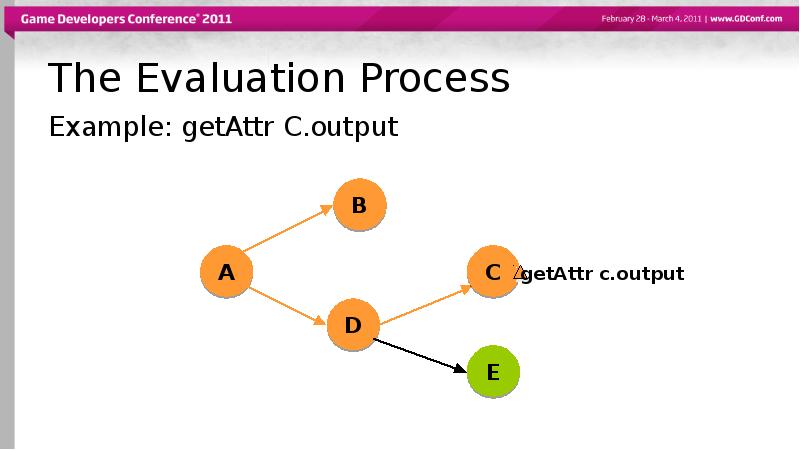
- 46. The Evaluation Process Example: getAttr C.output
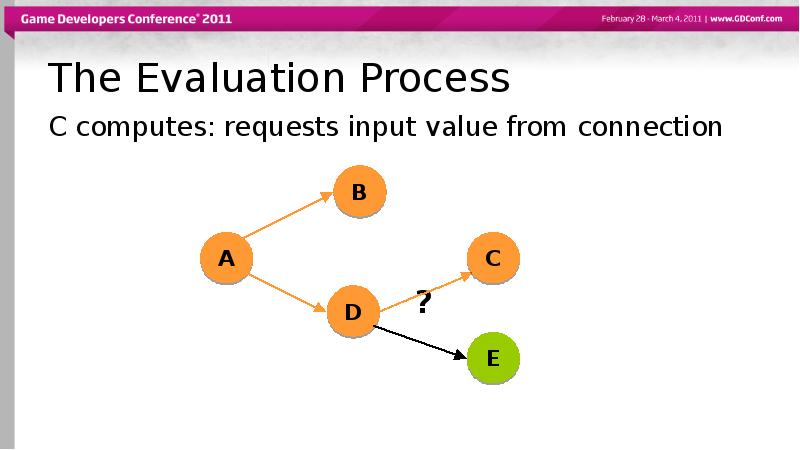
- 47. The Evaluation Process C computes: requests input value from connection
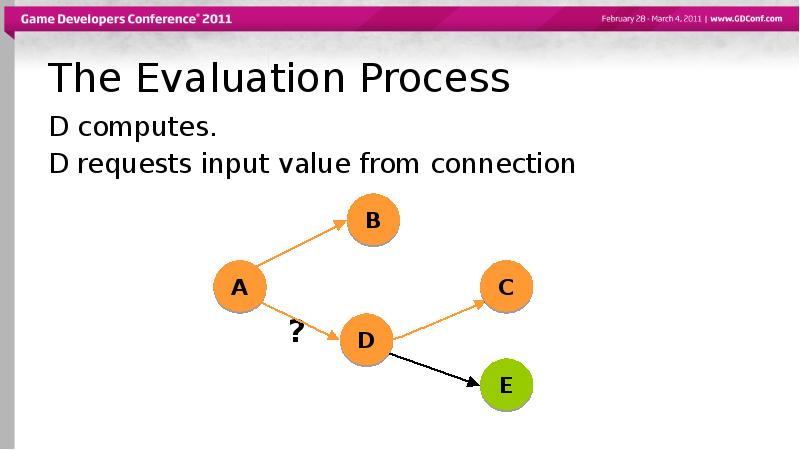
- 48. The Evaluation Process D computes. D requests input value from connection
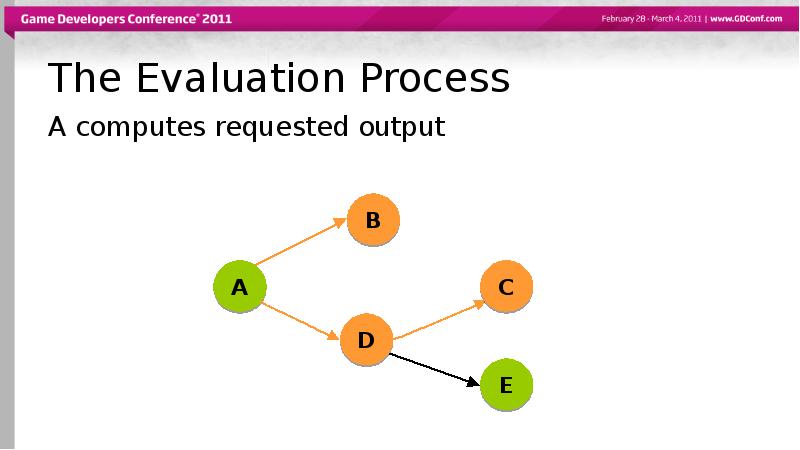
- 49. The Evaluation Process A computes requested output
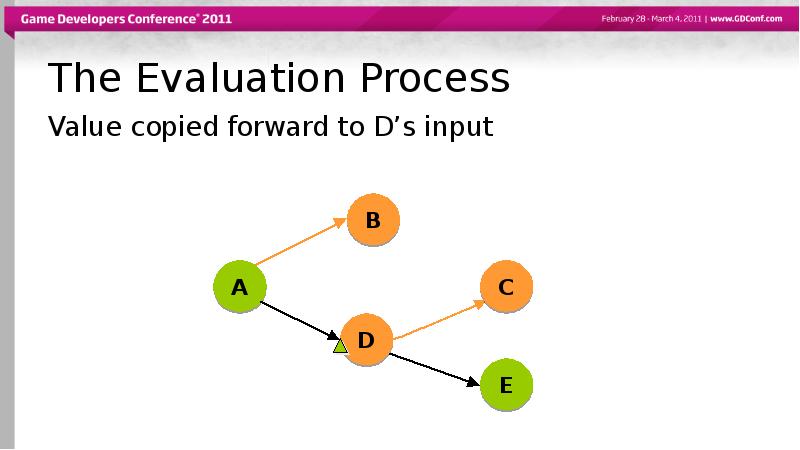
- 50. The Evaluation Process Value copied forward to D’s input
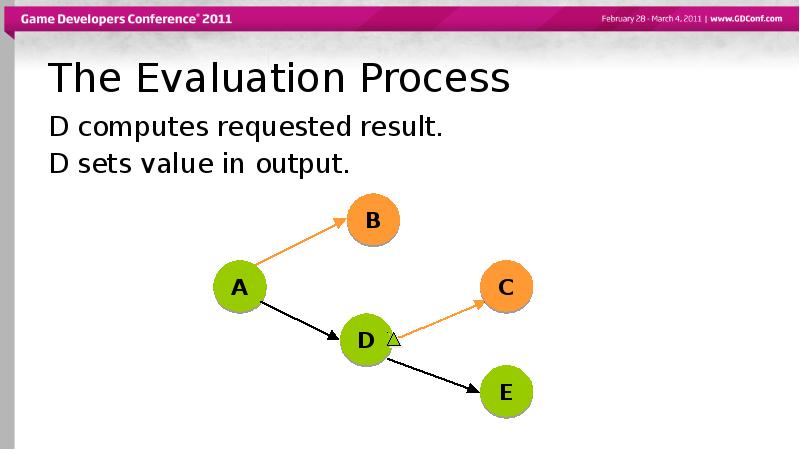
- 51. The Evaluation Process D computes requested result. D sets value in
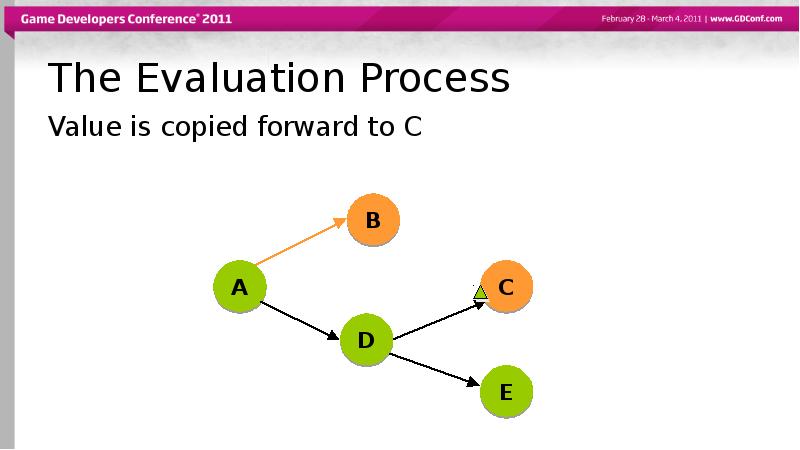
- 52. The Evaluation Process Value is copied forward to C
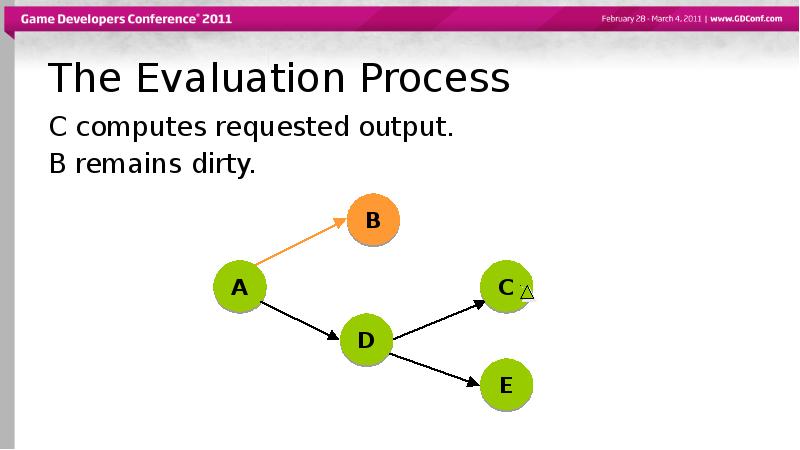
- 53. The Evaluation Process C computes requested output. B remains dirty.
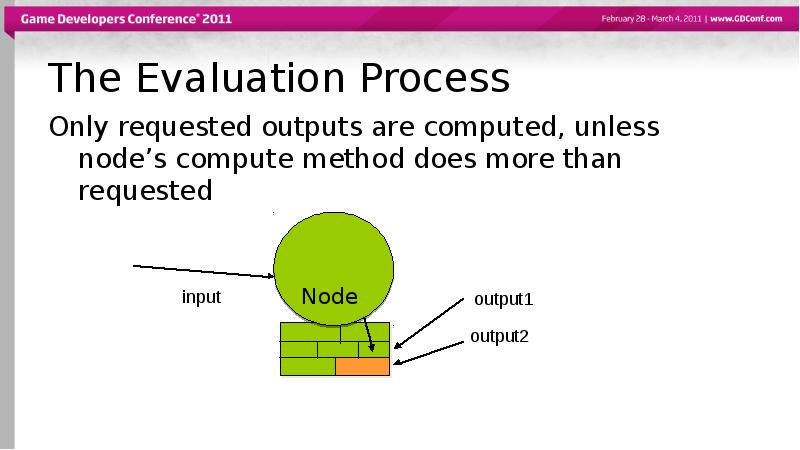
- 54. The Evaluation Process Only requested outputs are computed, unless node’s compute
- 55. Correct Coding with DG
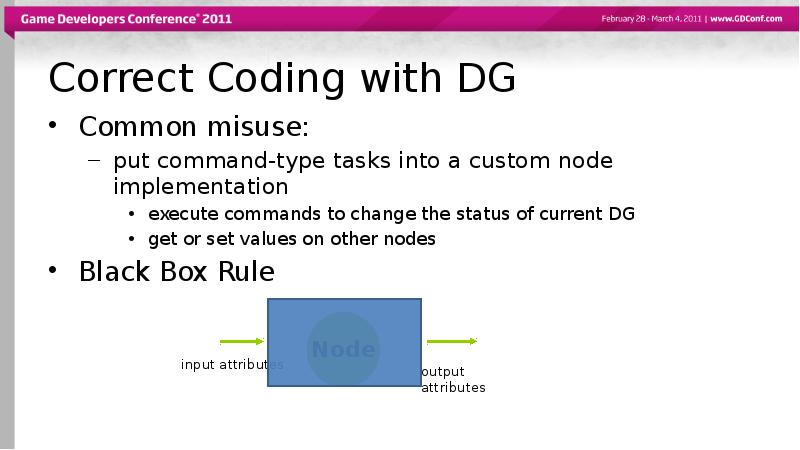
- 56. Correct Coding with DG Common misuse: put command-type tasks into
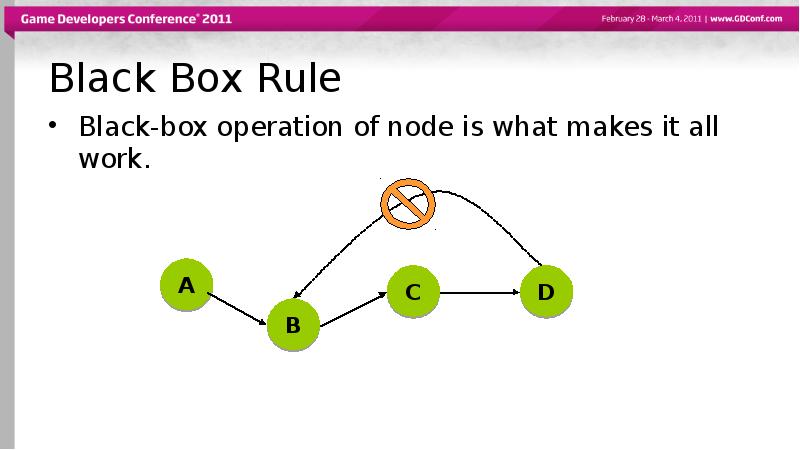
- 57. Black Box Rule Black-box operation of node is what makes it
- 58. A Closer Look at MPxNode::compute() You can not control when compute()
- 59. A Closer Look at MPxNode::compute() Inside compute(): avoid sending dirty messages
- 60. Learning Resources Maya Developer Center: http://www.autodesk.com/developmaya Questions and Problems: ADN http://www.autodesk.com/adn
- 61. Q & A
- 62. Thank you!
- 63. Скачать презентацию
















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























