Introduction to computer systems. Architecture of a computer systems презентация
Содержание
- 2. Plan of Lecture: The development of computer architecture. Von Neumann architecture.
- 3. Technology The technology is moving very quickly 19th century: attempts to
- 4. Charles Babbage In the early 1800’s Charles Babbage designed two machines:
- 5. Fast forward a hundred years In the 1940’s the Electronic Numerical
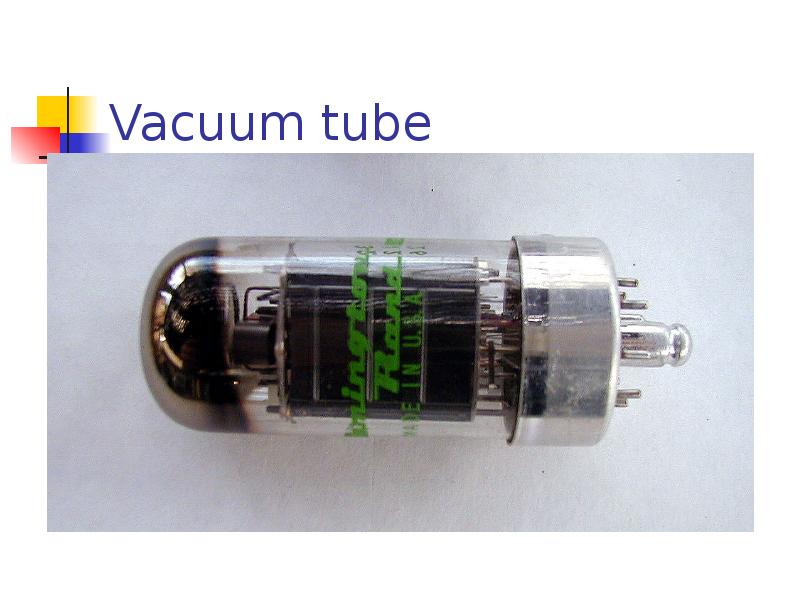
- 6. ENIAC The ENIAC consisted of 17,480 vacuum tubes operating at 100,000
- 7. Vacuum tube
- 8. Von Neumann Architecture John von Neumann was a consultant to the
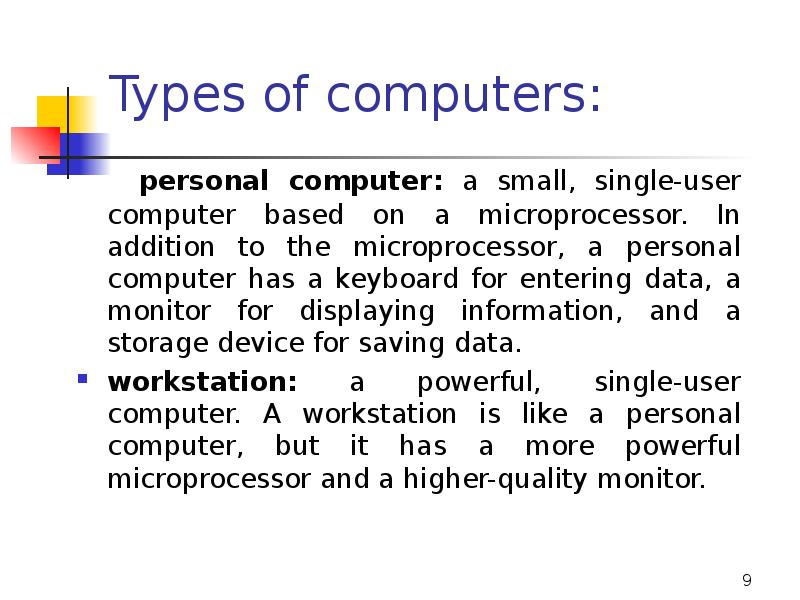
- 9. Types of computers: personal computer: a small, single-user computer based
- 10. Types of computers: minicomputer: a multi-user computer capable of supporting from
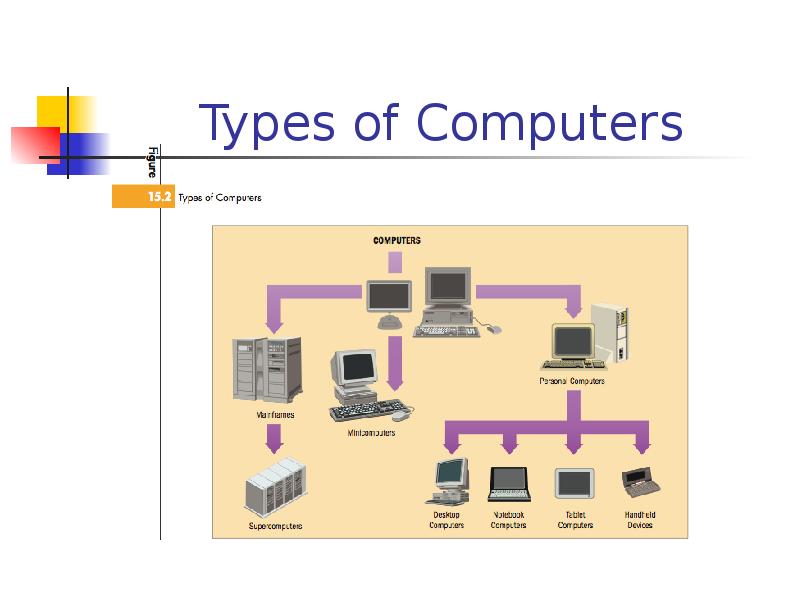
- 11. Types of Computers
- 12. Servers Computers connected in a network environment. Manage network resources Holds
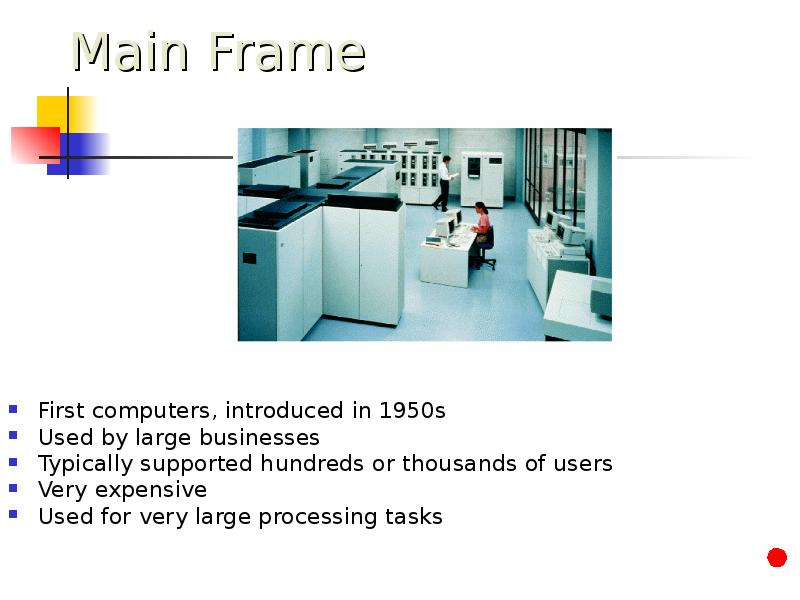
- 13. First computers, introduced in 1950s First computers, introduced in 1950s
- 14. Supercomputers High capacity (высокая емкость) Used by very large organizations Tracking
- 15. Typically supported hundreds of users Typically supported hundreds of users No
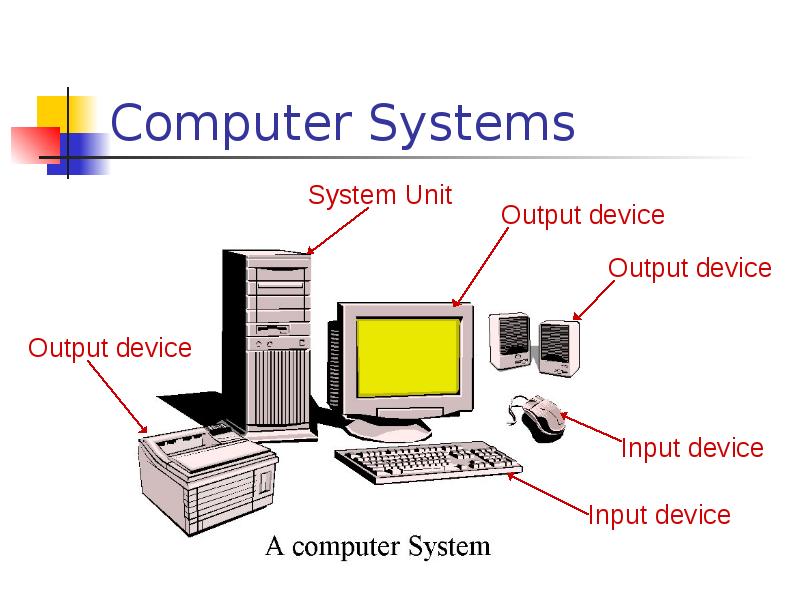
- 16. Computer Systems
- 17. Motherboard A motherboard is the central printed circuit board
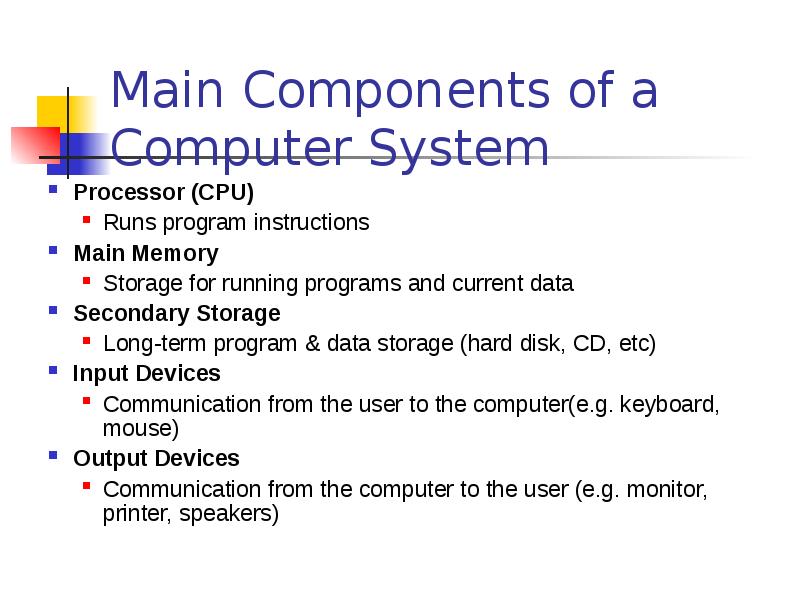
- 18. Main Components of a Computer System Processor (CPU) Runs program instructions
- 19. The Processor
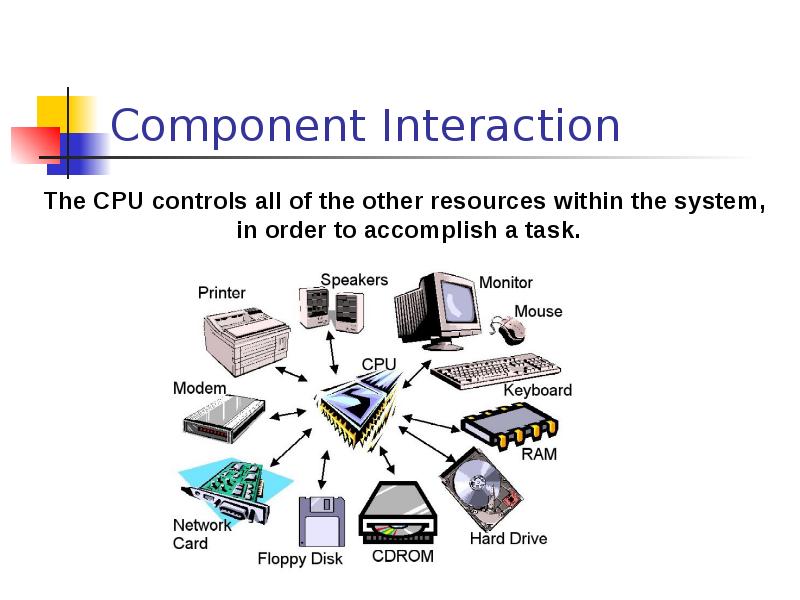
- 20. Component Interaction
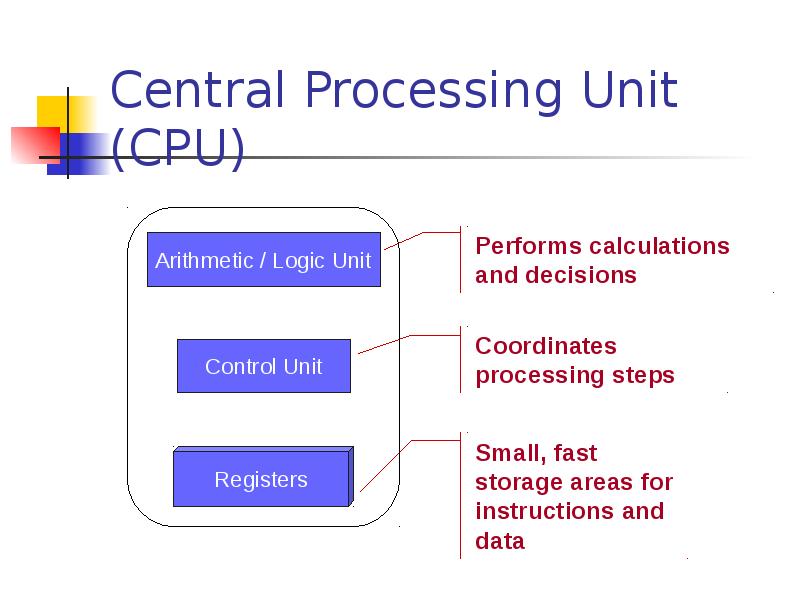
- 21. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- 22. Registers
- 23. CHARACTERISTICS of Processor
- 24. Memory Computer Memory - millions/billions of on/off charges Divided into: Bits 0
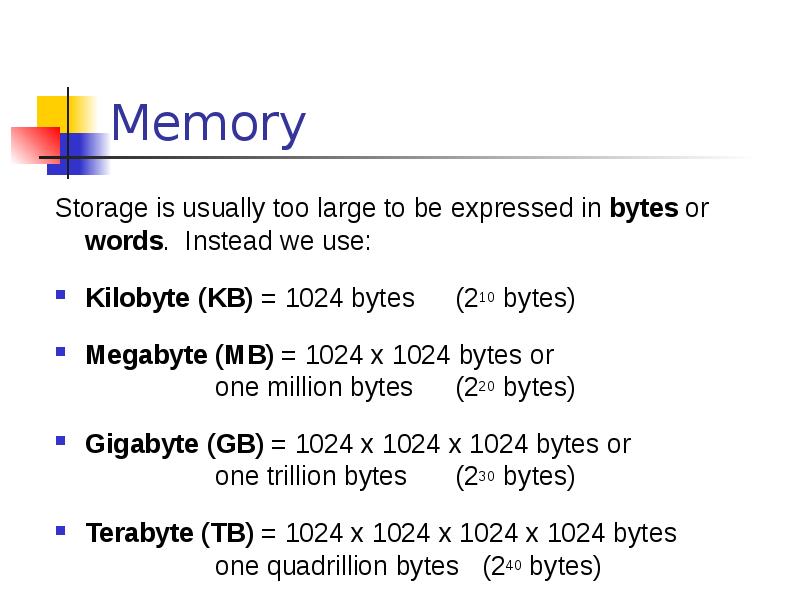
- 25. Memory Storage is usually too large to be expressed in bytes
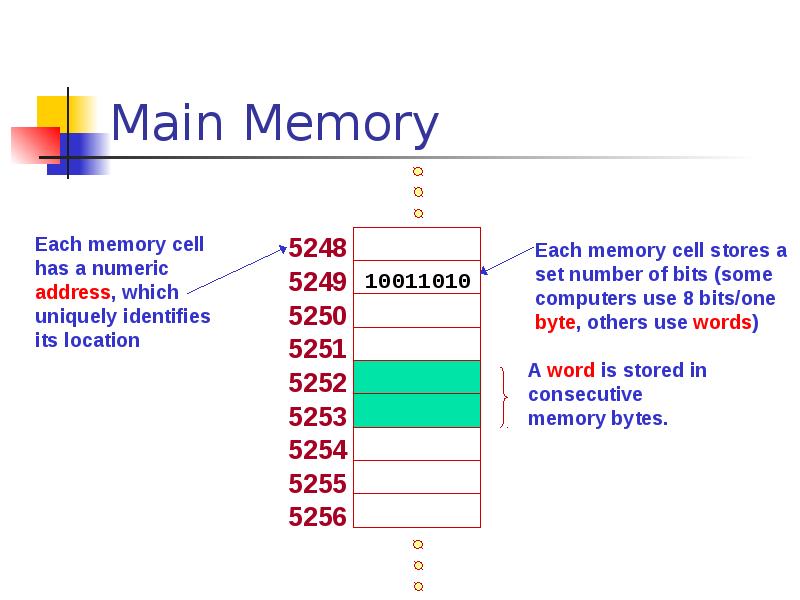
- 26. Main Memory
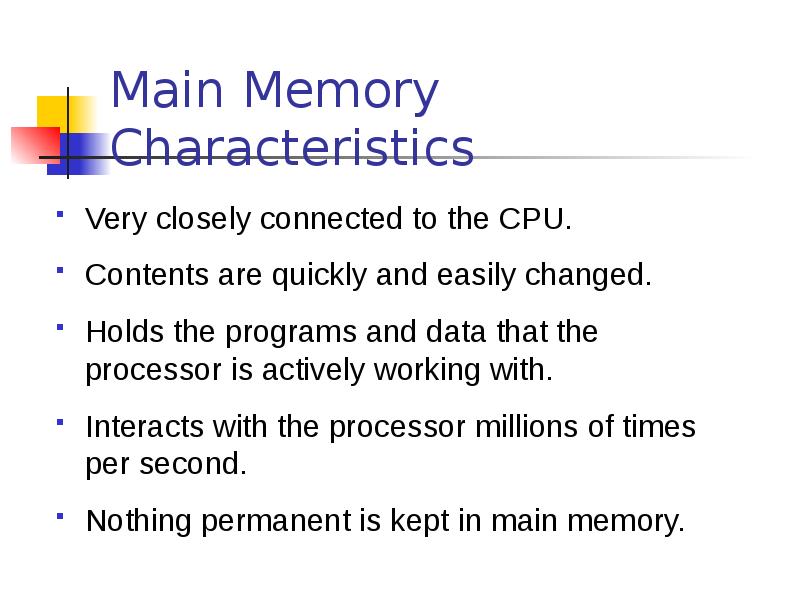
- 27. Main Memory Characteristics Very closely connected to the CPU. Contents are
- 28. Program Instructions
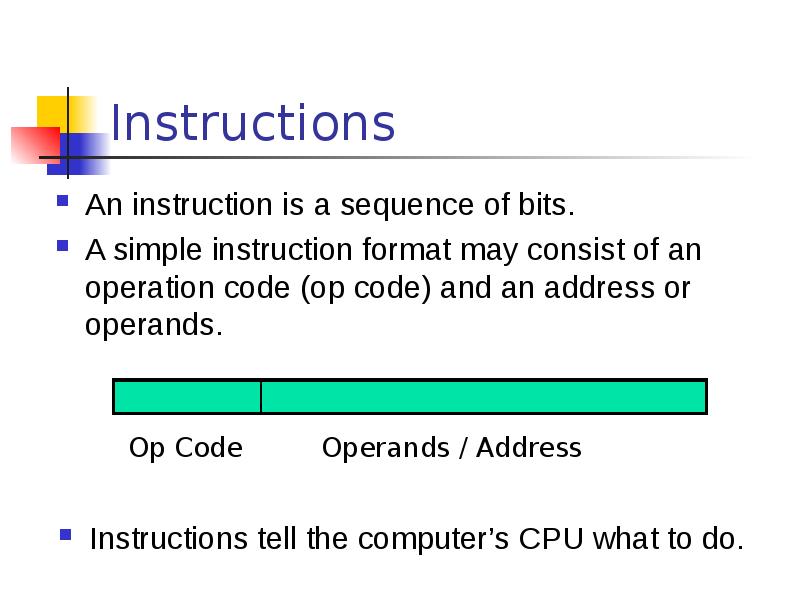
- 29. Instructions An instruction is a sequence of bits. A simple
- 30. Instructions The operation code specifies the operation the computer is to
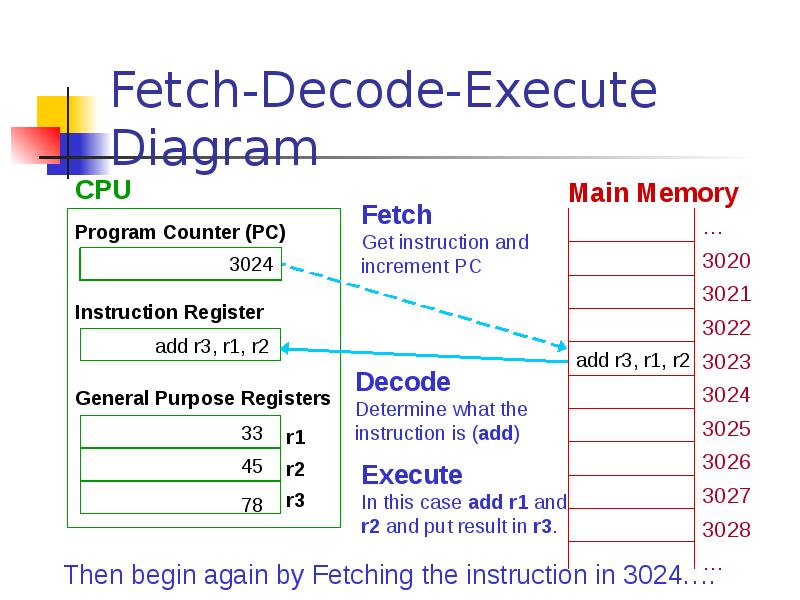
- 31. Fetch-Decode-Execute Diagram
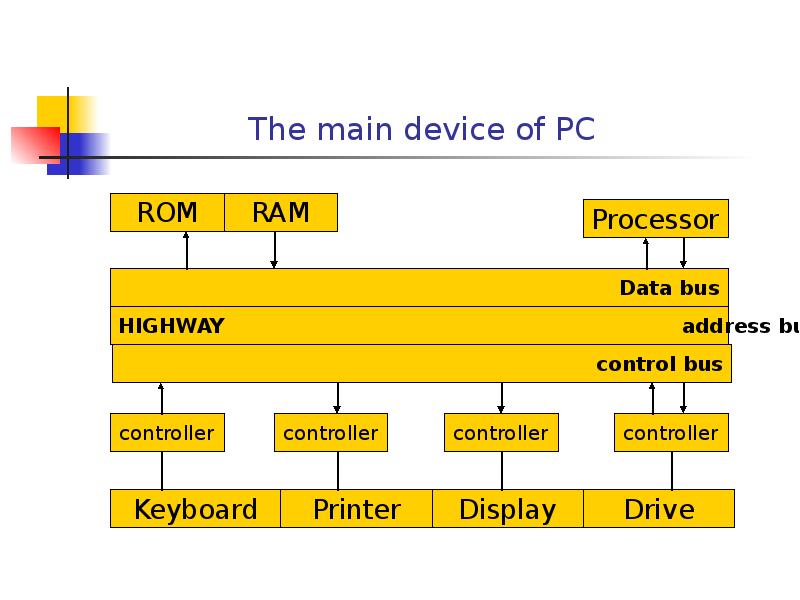
- 32. The main device of PC
- 33. System bus The processor sets the address bus memory address, which
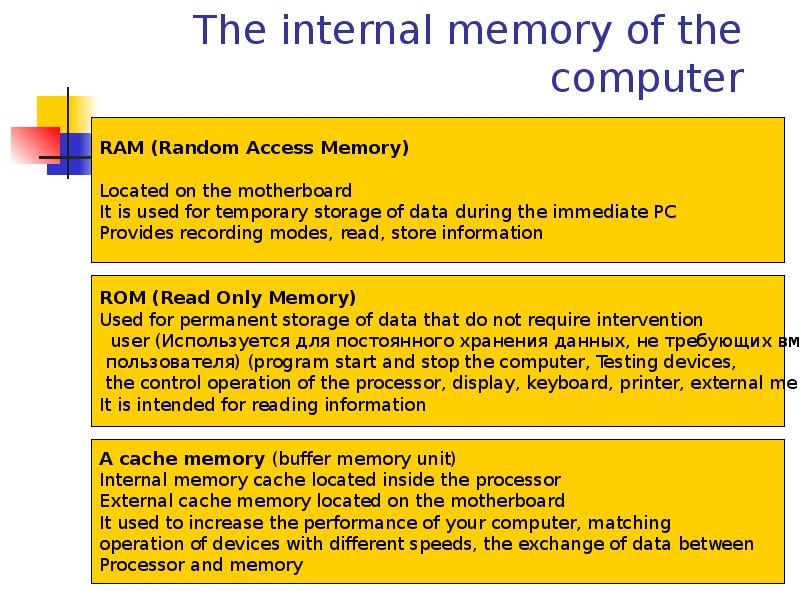
- 34. The internal memory of the computer
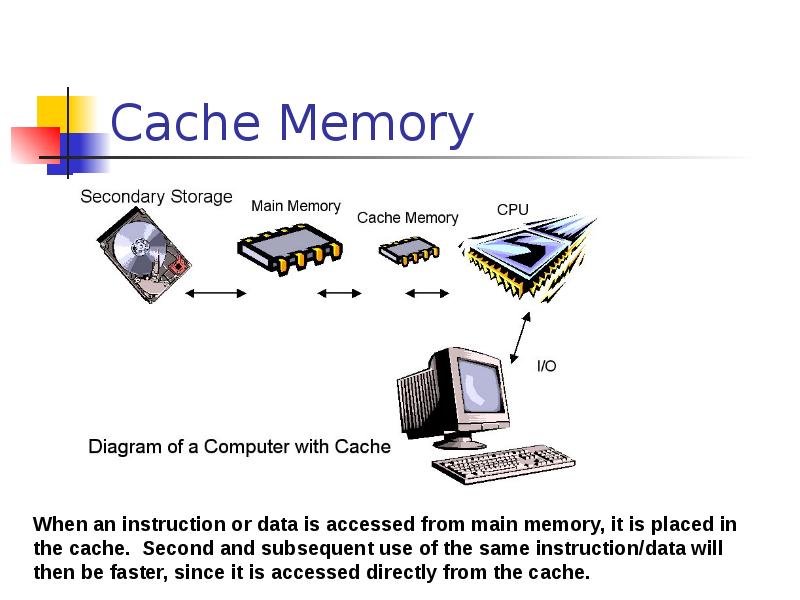
- 35. Cache Memory
- 36. Controllers Decodes the signal received from processor (Декодирует сигнал, поступающий от
- 37. TEST Open Internet site Socrative.com Press button Student login Write Room
- 38. Скачать презентацию

















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Introduction to computer systems. Architecture of a computer systems можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























