Intrusion Detection. Chapter 8. Computer Security: Principles and Practice презентация
Содержание
- 2. Classes of intruders: criminals Individuals or members of an organized crime
- 3. Classes of intruders: activists Are either individuals, usually working as insiders,
- 4. Intruders: state-sponsored Groups of hackers sponsored by governments to conduct espionage
- 5. Intruders: others Hackers with motivations other than those previously listed Include
- 6. Skill level: apprentice Hackers with minimal technical skill who primarily use
- 7. Skill level: journeyman Hackers with sufficient technical skills to modify and
- 8. Skill level: master Hackers with high-level technical skills capable of discovering
- 9. Intruders: another classification Masquerader: unauthorized individuals who penetrates a system Misfeasor:
- 10. User and software trespass User trespass: unauthorized logon, privilege abuse Software
- 11. Example of intrusion Remote root compromise Web server defacement Guessing/cracking passwords
- 12. Intruder behavior Target acquisition and information gathering Initial access Privilege escalation
- 13. Hacker behavior example Select target using IP lookup tools Map
- 14. Criminal intruder behavior Act quickly and precisely to make their activities
- 15. Insider intruder behavior Create network accounts for themselves and their friends
- 16. Insider attacks Among most difficult to detect and prevent Employees have
- 17. Security intrusion & detection (RFC 2828) Security intrusion: a security event,
- 18. Intrusion techniques Objective to gain access or increase privileges Initial attacks
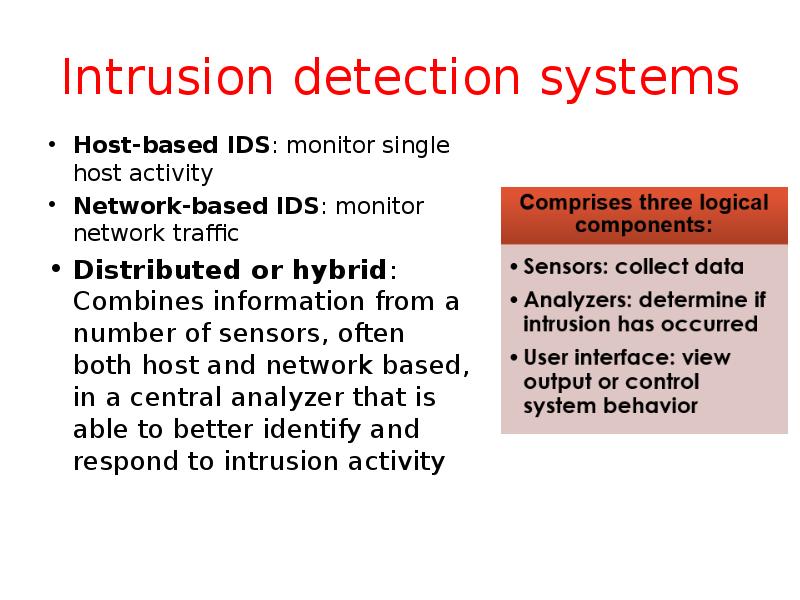
- 19. Intrusion detection systems Host-based IDS: monitor single host activity Network-based IDS:
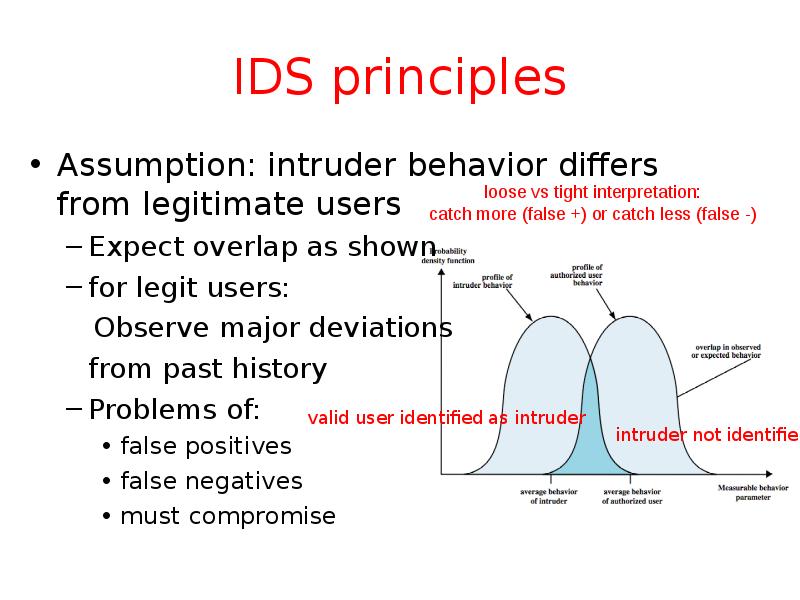
- 20. IDS principles Assumption: intruder behavior differs from legitimate users Expect overlap
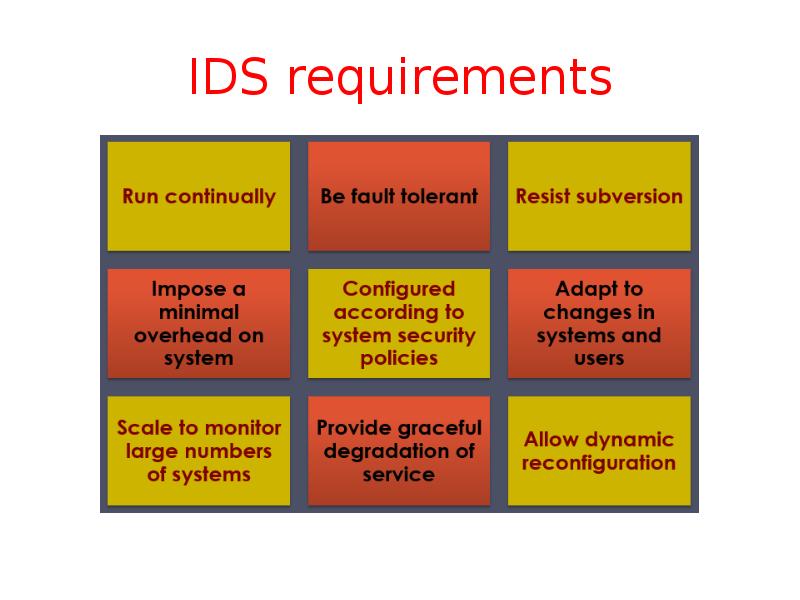
- 21. IDS requirements
- 22. IDS requirements Run continually with minimal human supervision Be fault tolerant:
- 23. Detection techniques Anomaly (behavior) detection Signature/heuristic detection
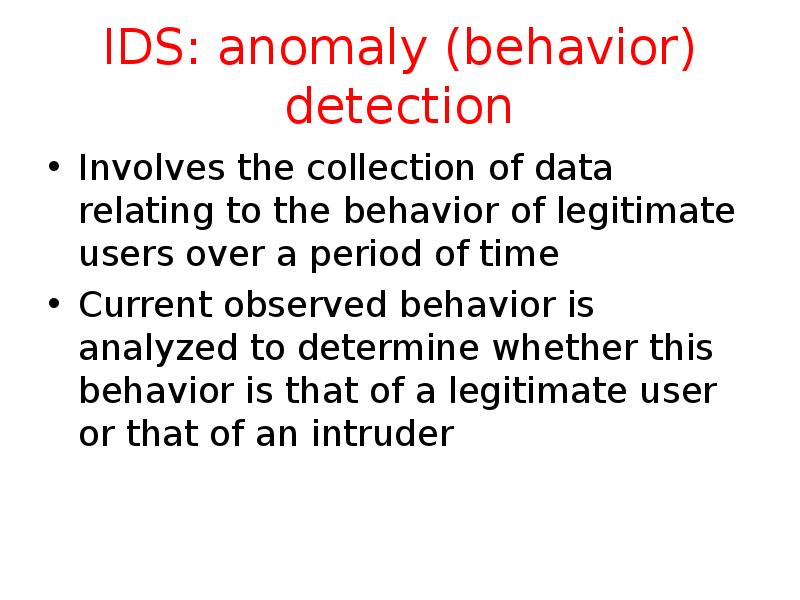
- 24. IDS: anomaly (behavior) detection Involves the collection of data relating to
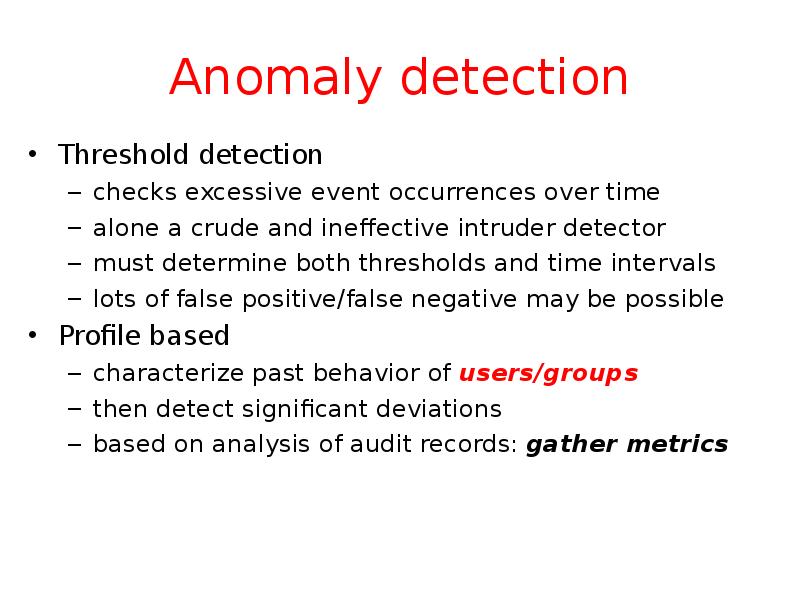
- 25. Anomaly detection Threshold detection checks excessive event occurrences over time alone
- 26. Example of metrics Counters: e.g., number of logins during an hour,
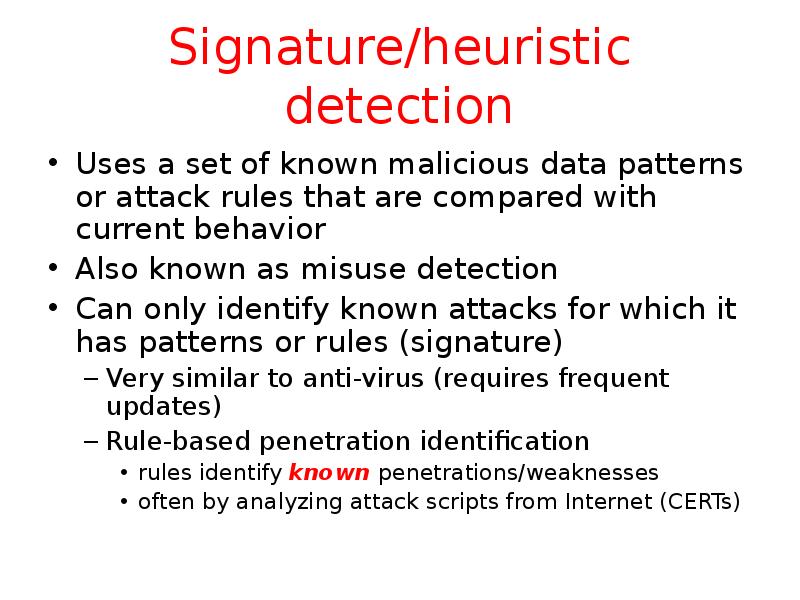
- 27. Signature/heuristic detection Uses a set of known malicious data patterns or
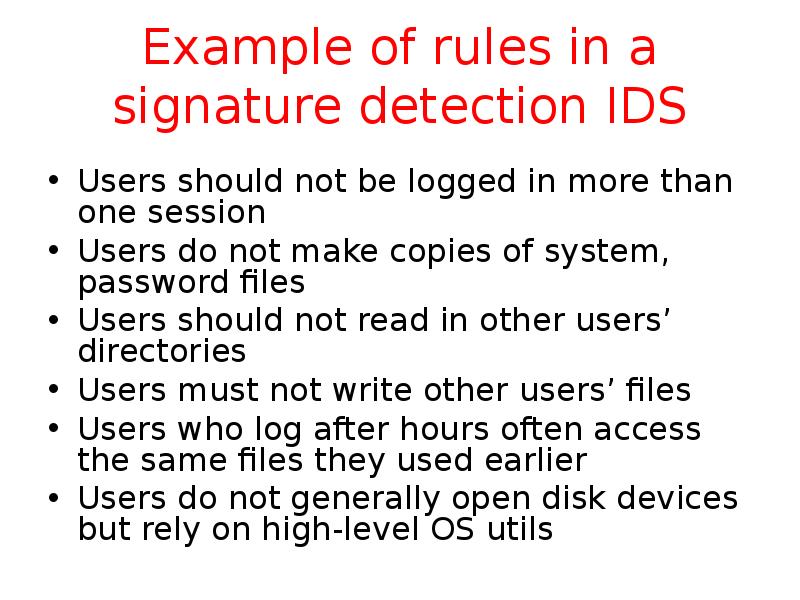
- 28. Example of rules in a signature detection IDS Users should not
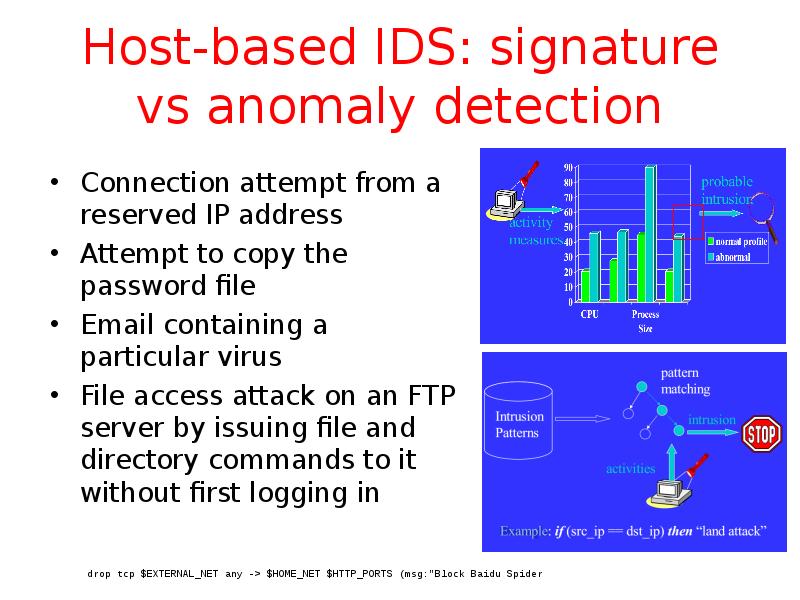
- 29. Host-based IDS: signature vs anomaly detection Connection attempt from a reserved
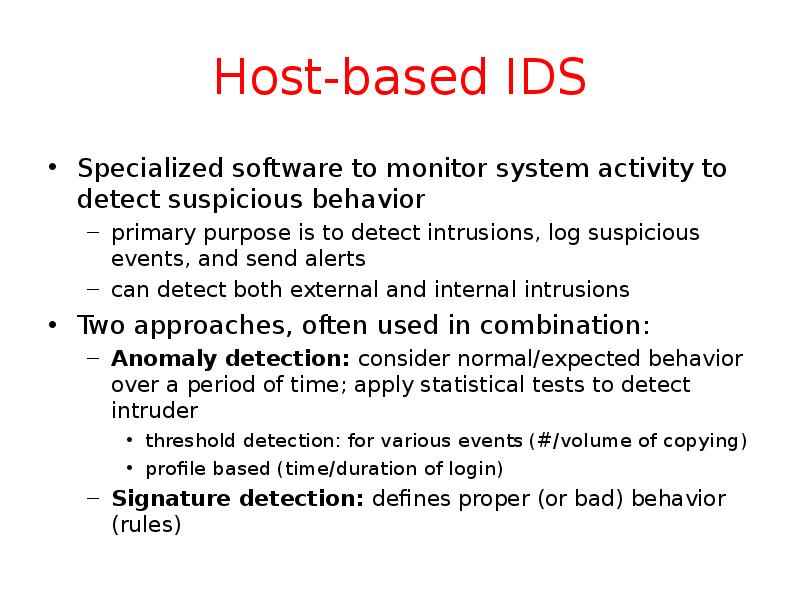
- 30. Host-based IDS Specialized software to monitor system activity to detect suspicious
- 31. Audit records A fundamental tool for intrusion detection Two variants:
- 32. Common data sources Common data sources include: System call traces Audit
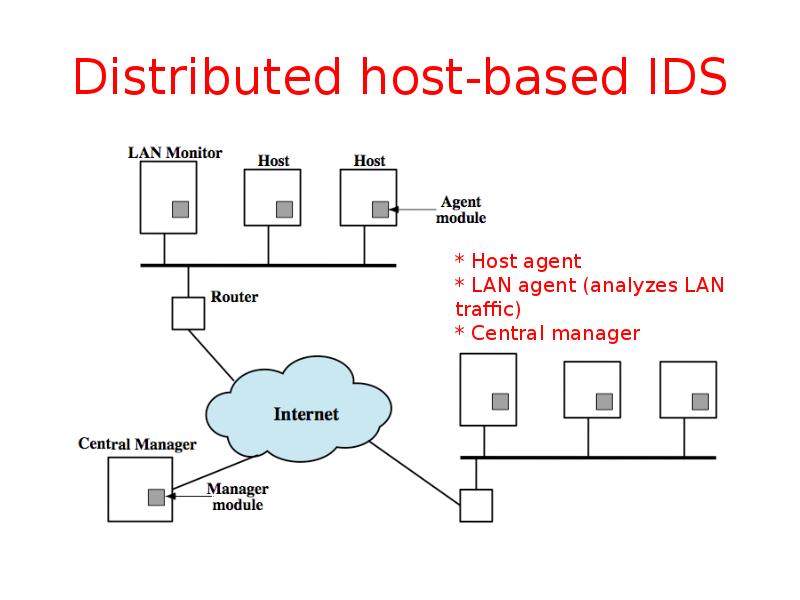
- 33. Distributed host-based IDS
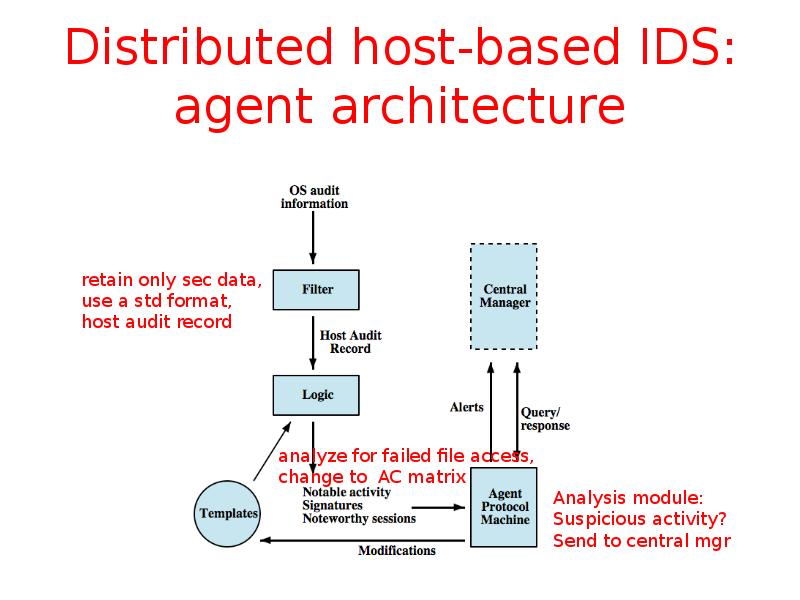
- 34. Distributed host-based IDS: agent architecture
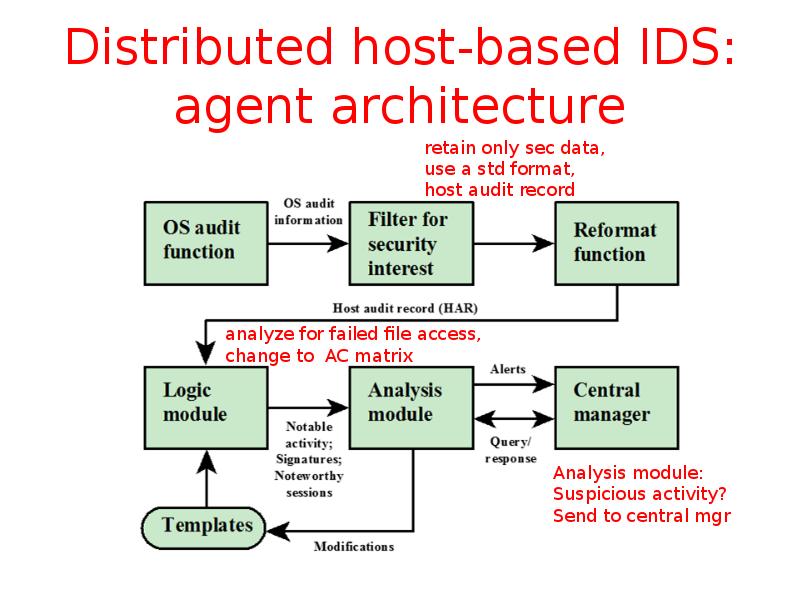
- 35. Distributed host-based IDS: agent architecture
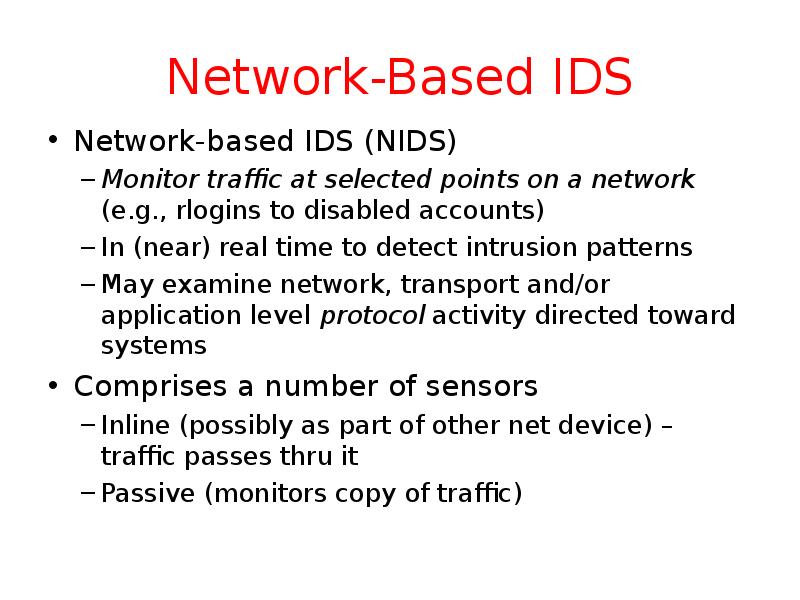
- 36. Network-Based IDS Network-based IDS (NIDS) Monitor traffic at selected points on
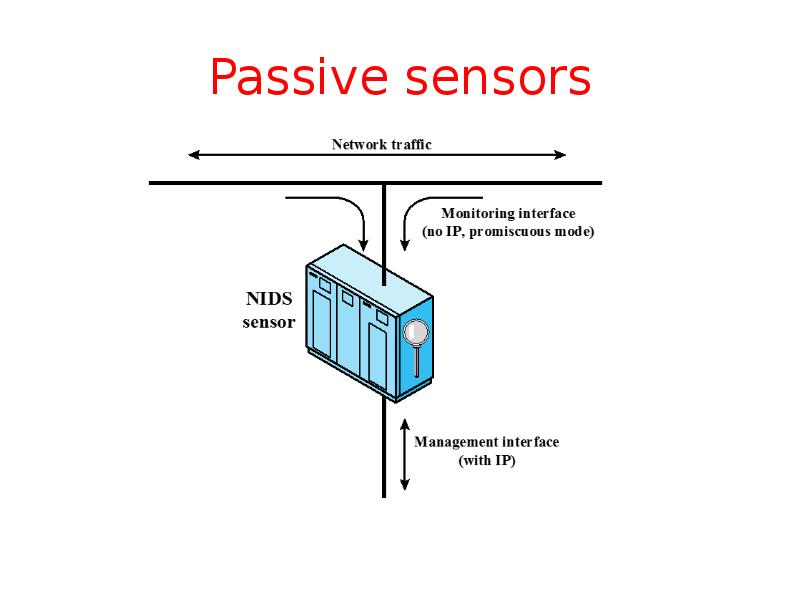
- 37. Passive sensors
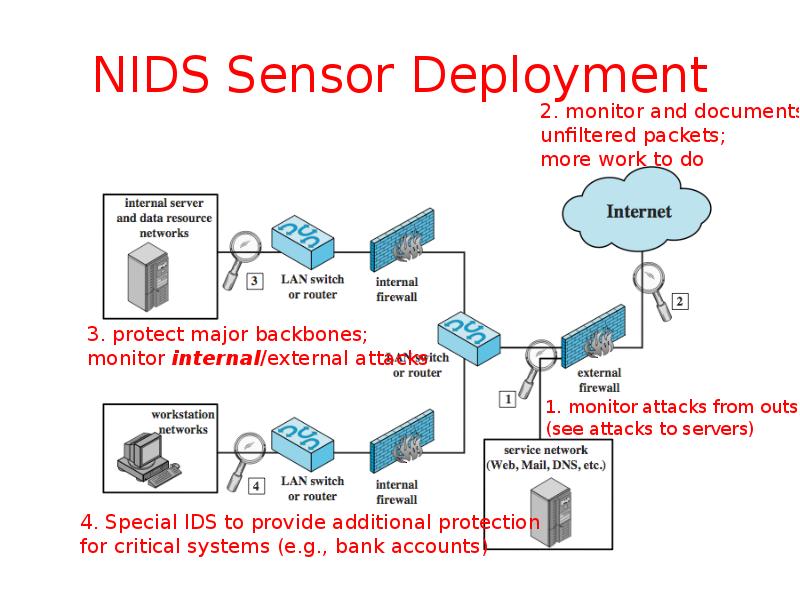
- 38. NIDS Sensor Deployment
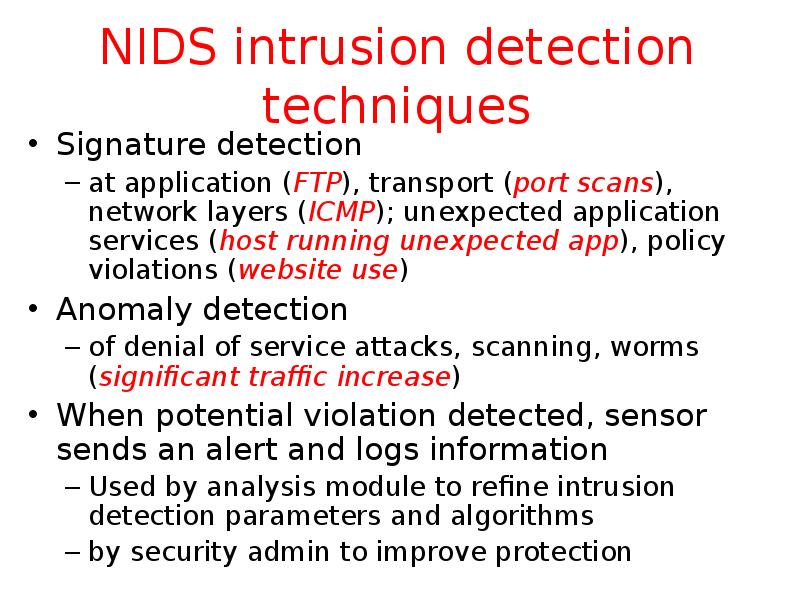
- 39. NIDS intrusion detection techniques Signature detection at application (FTP), transport (port
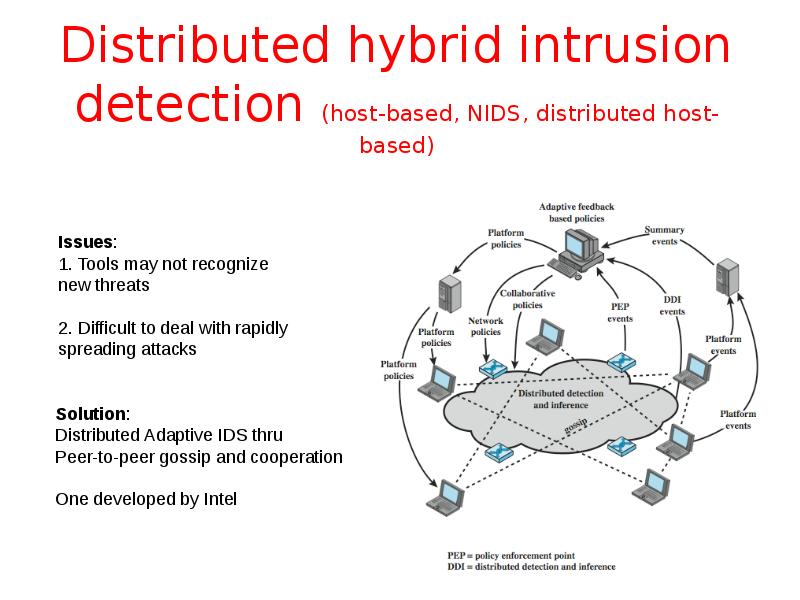
- 40. Distributed hybrid intrusion detection (host-based, NIDS, distributed host-based)
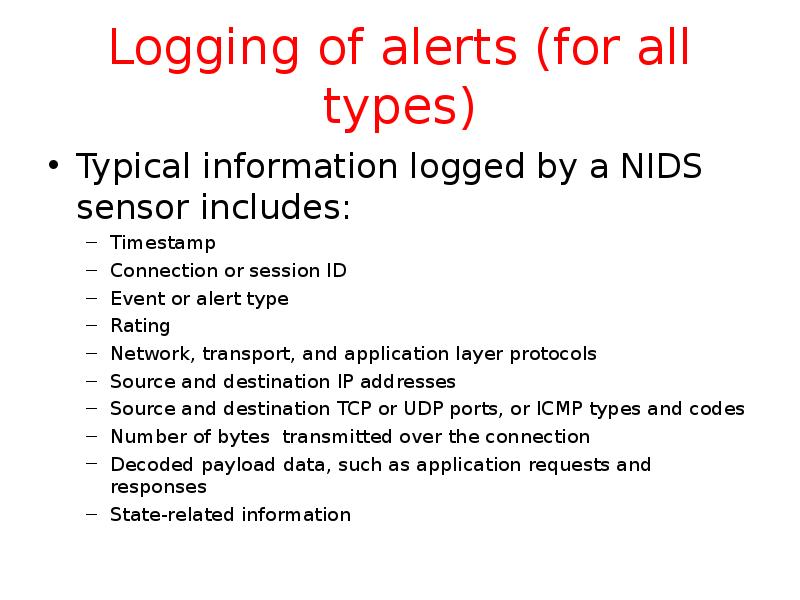
- 41. Logging of alerts (for all types) Typical information logged by a
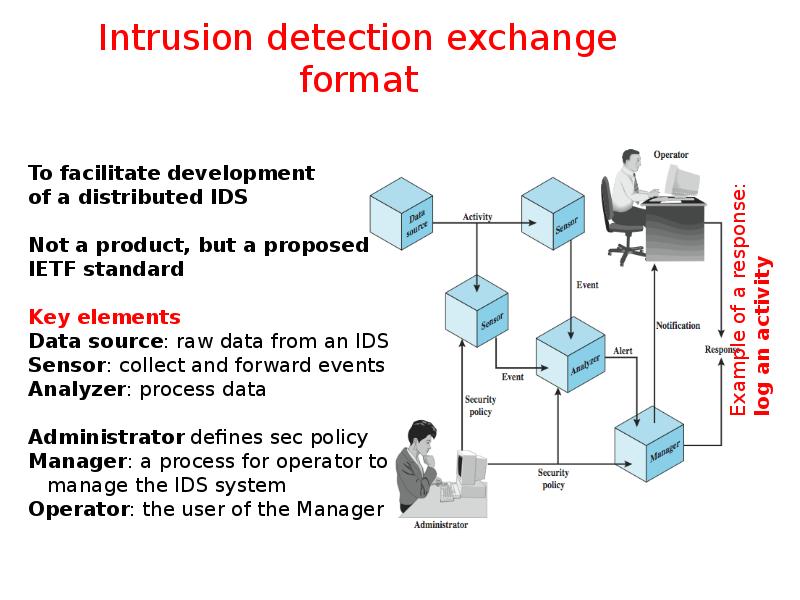
- 42. Intrusion detection exchange format
- 43. Honeypots Decoy systems Filled with fabricated info and instrumented with monitors/event
- 44. Honeypot classification Low interaction honeypot Consists of a software package that
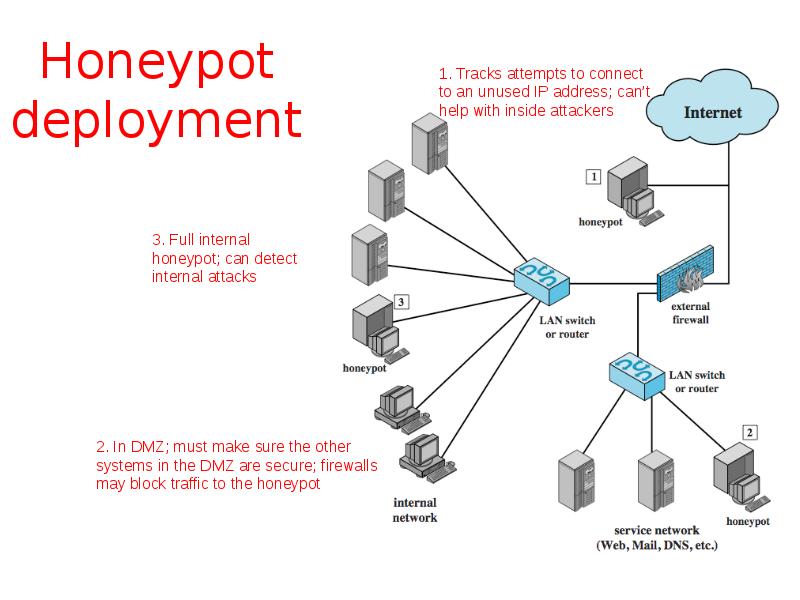
- 45. Honeypot deployment
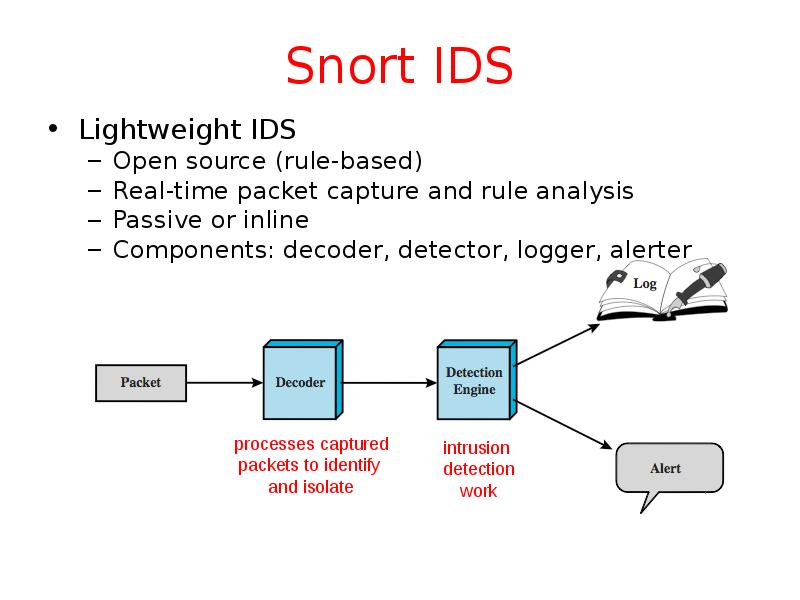
- 46. Snort IDS Lightweight IDS Open source (rule-based) Real-time packet capture and
- 47. SNORT Rules Use a simple, flexible rule definition language Fixed header
- 48. Summary Introduced intruders & intrusion detection Hackers, criminals, insiders Intrusion detection
- 49. Скачать презентацию


























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Intrusion Detection. Chapter 8. Computer Security: Principles and Practice можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























