Karmarkar Algorithm презентация
Содержание
- 2. Contents Overview Projective transformation Orthogonal projection Complexity analysis Transformation to Karmarkar’s
- 3. LP Solutions Simplex Dantzig 1947 Ellipsoid Kachian 1979 Interior Point Affine
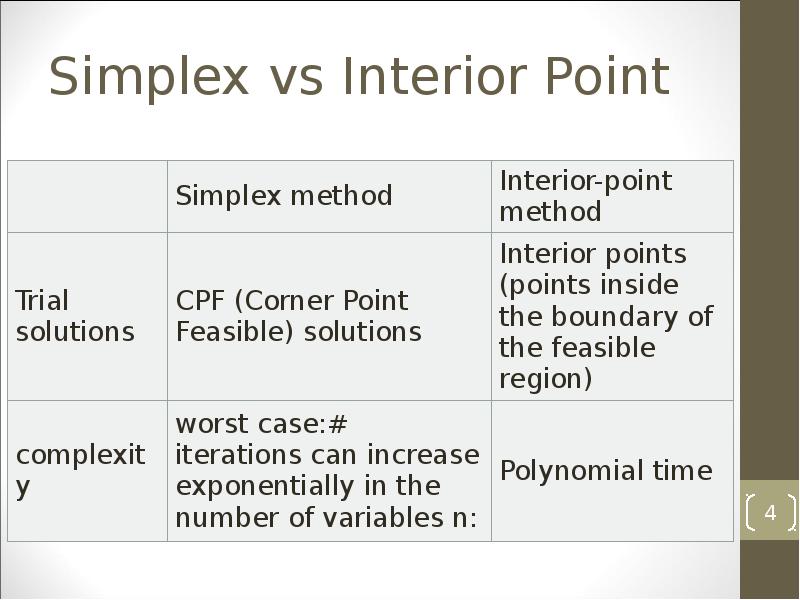
- 4. Simplex vs Interior Point
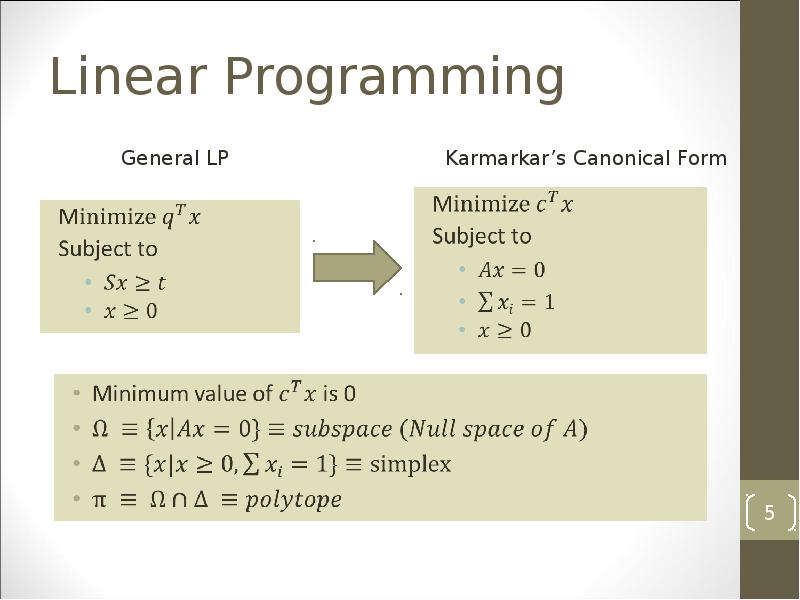
- 5. Linear Programming
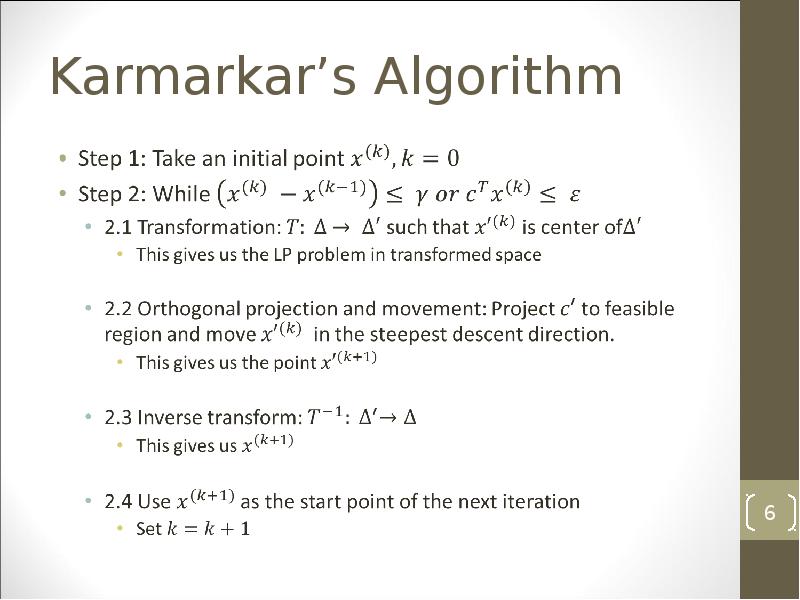
- 6. Karmarkar’s Algorithm
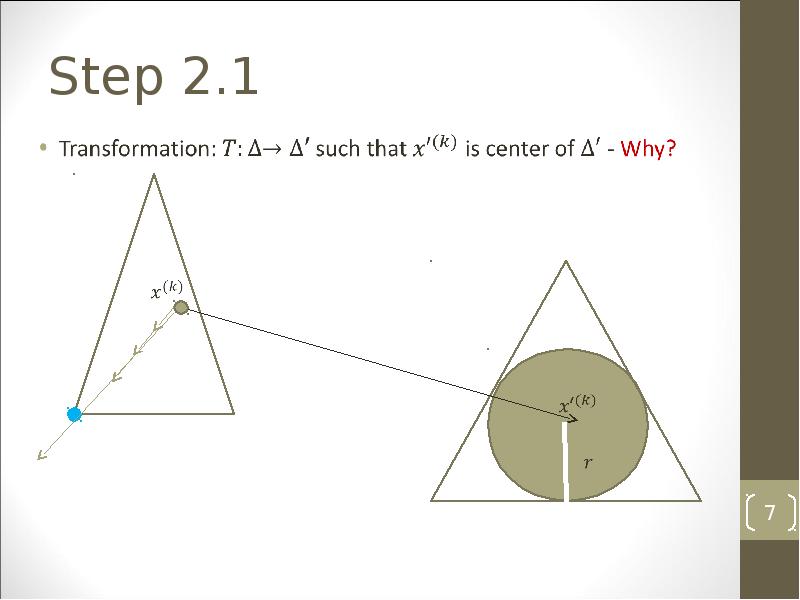
- 7. Step 2.1
- 8. Step 2.2
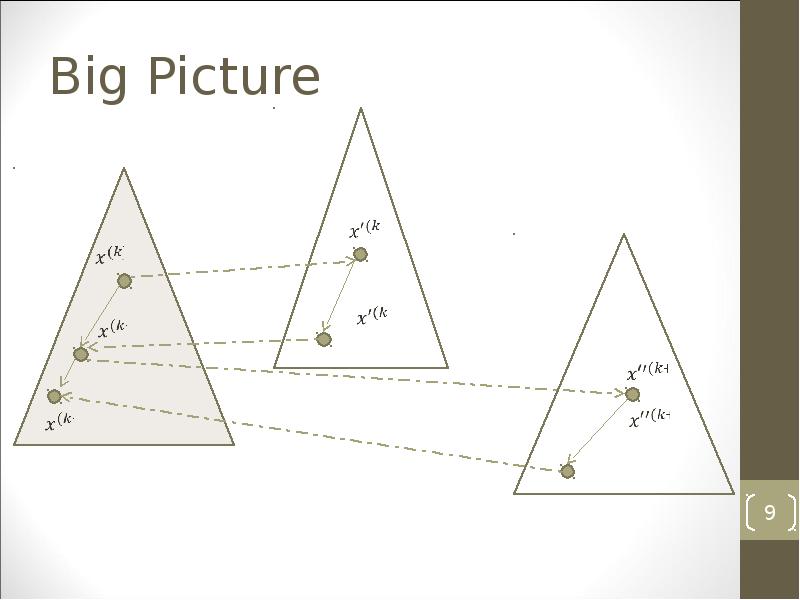
- 9. Big Picture
- 10. Contents Overview Transformation to Karmarkar’s canonical form Projective transformation Orthogonal projection
- 11. Karmarkar’s Algorithm
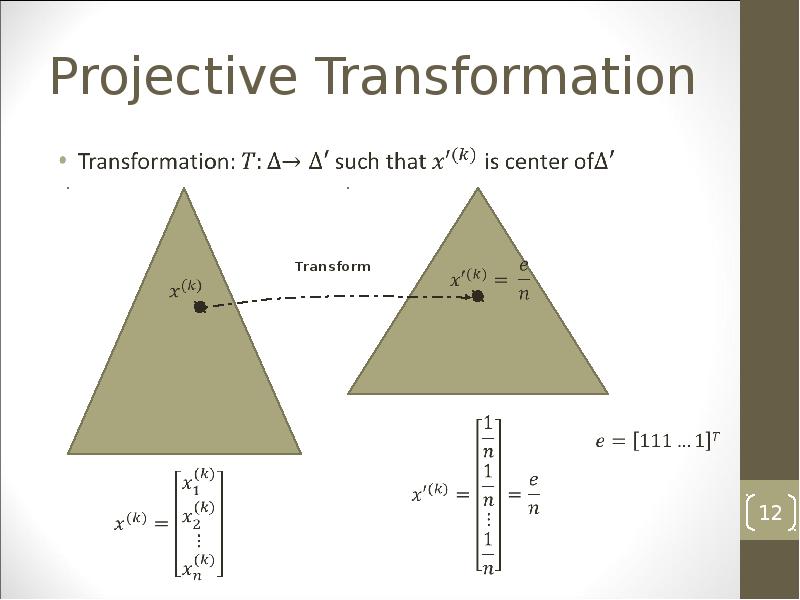
- 12. Projective Transformation
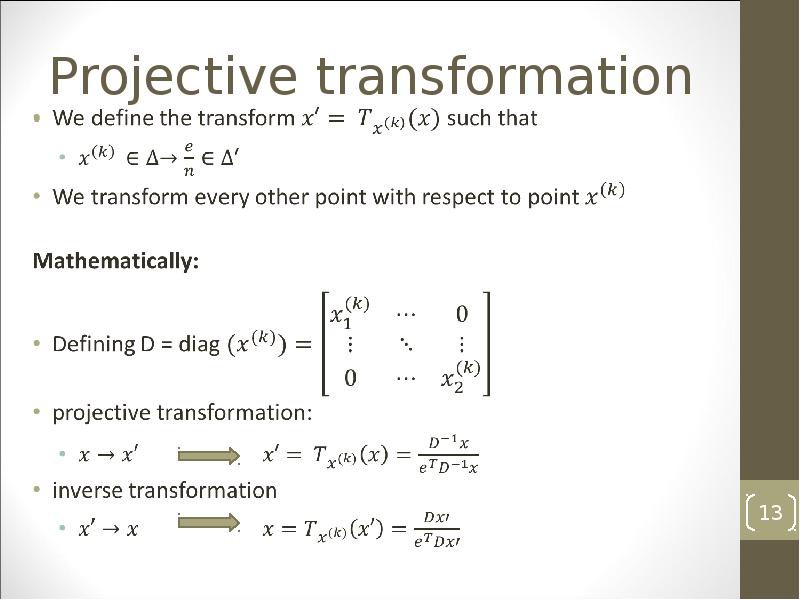
- 13. Projective transformation
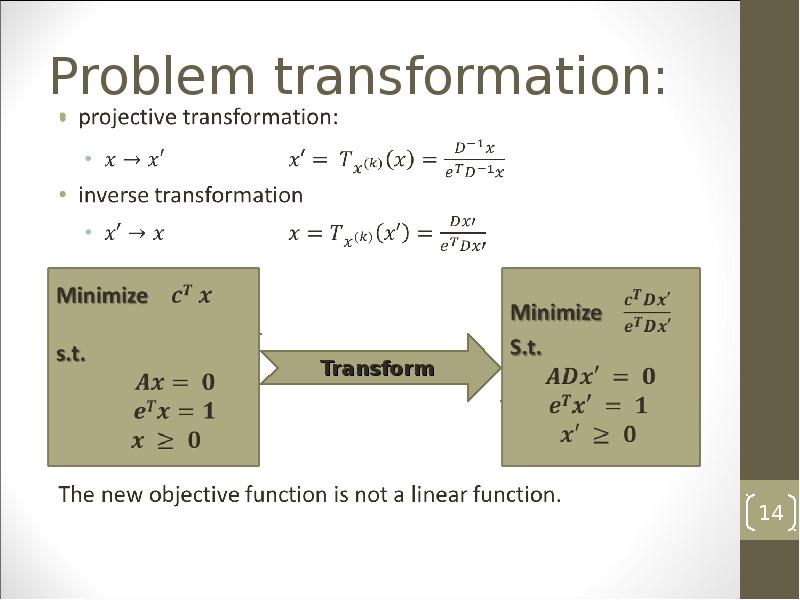
- 14. Problem transformation:
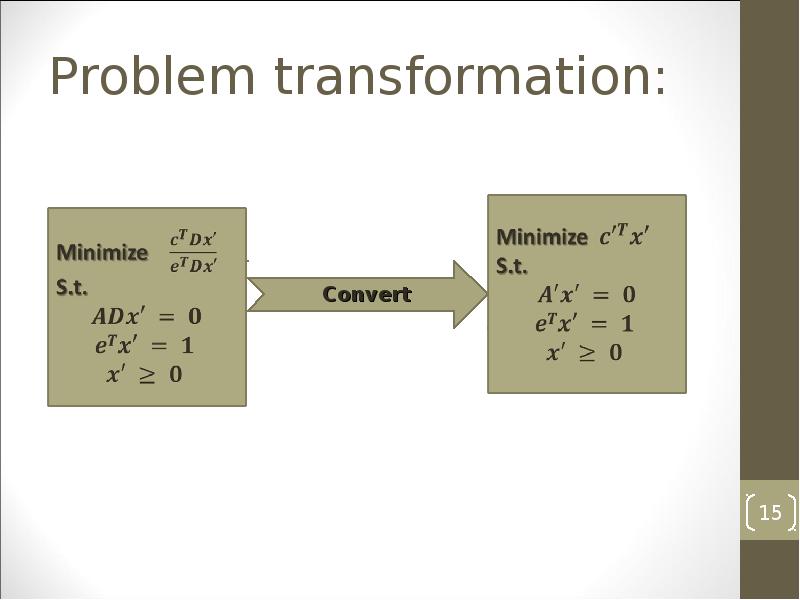
- 15. Problem transformation:
- 16. Karmarkar’s Algorithm
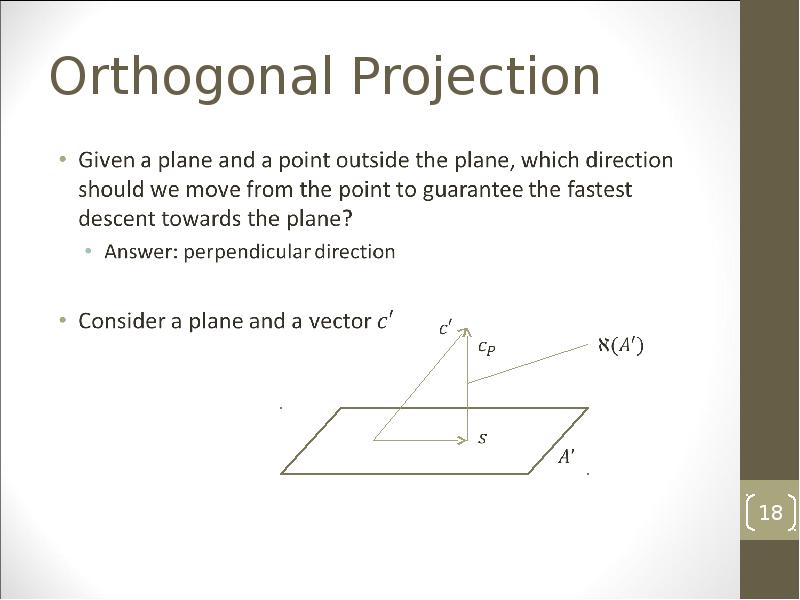
- 17. Orthogonal Projection
- 18. Orthogonal Projection
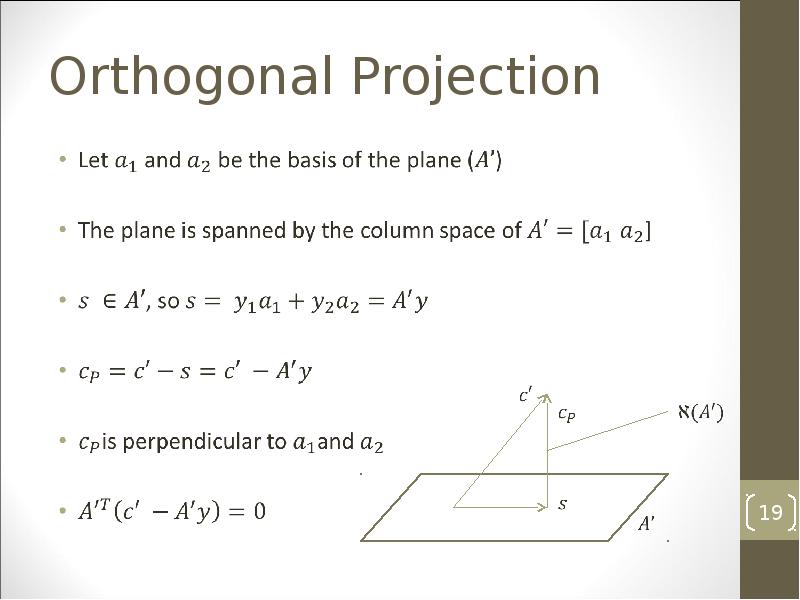
- 19. Orthogonal Projection
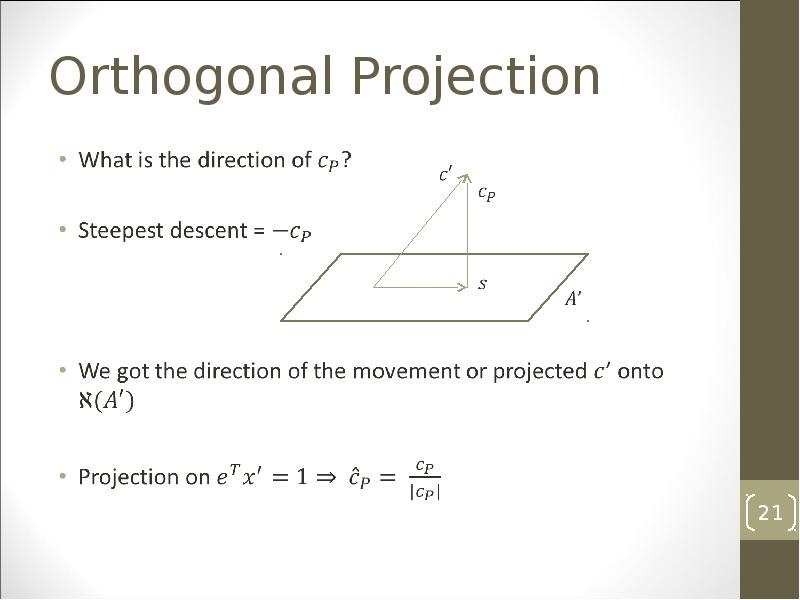
- 20. Orthogonal Projection
- 21. Orthogonal Projection
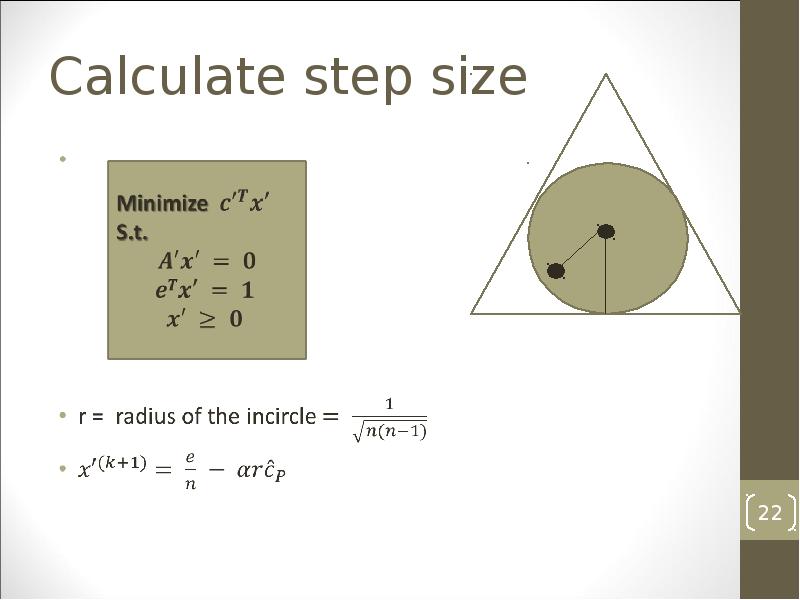
- 22. Calculate step size
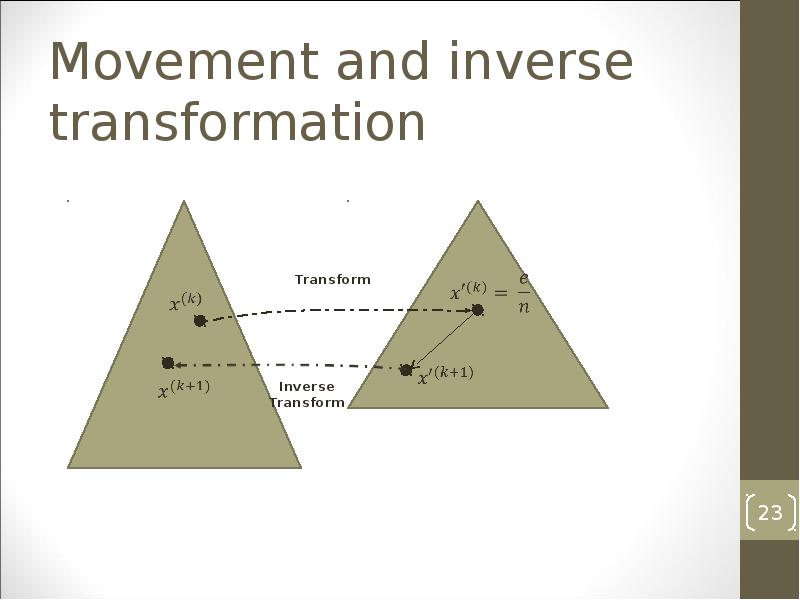
- 23. Movement and inverse transformation
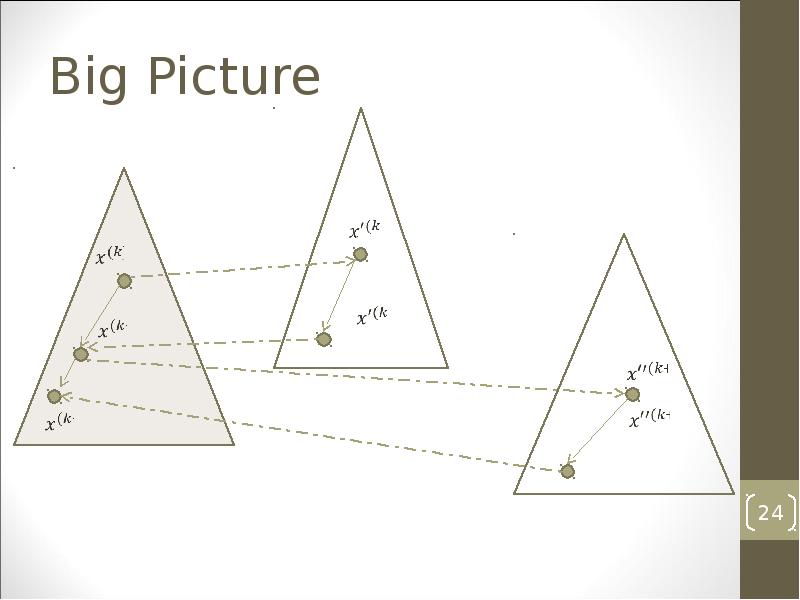
- 24. Big Picture
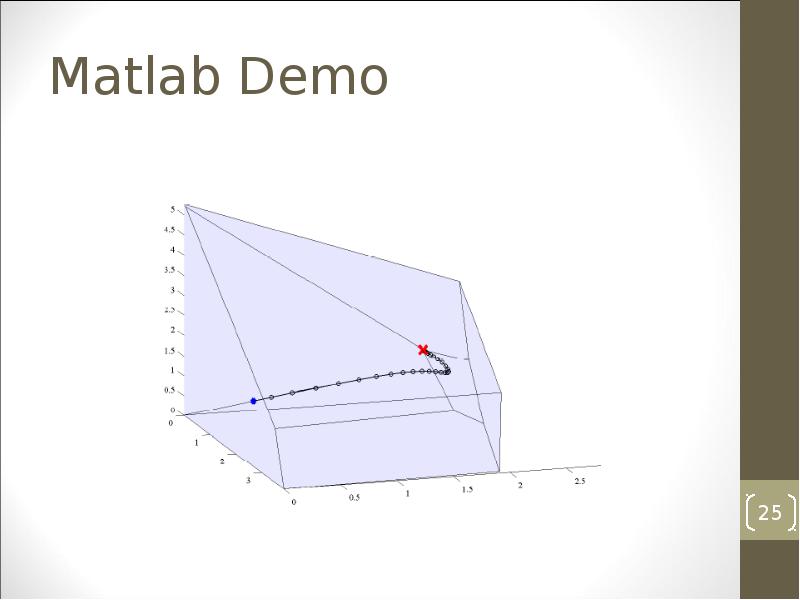
- 25. Matlab Demo
- 26. Contents Overview Projective transformation Orthogonal projection Complexity analysis Transformation to Karmarkar’s
- 27. Running Time Total complexity of iterative algorithm = (# of
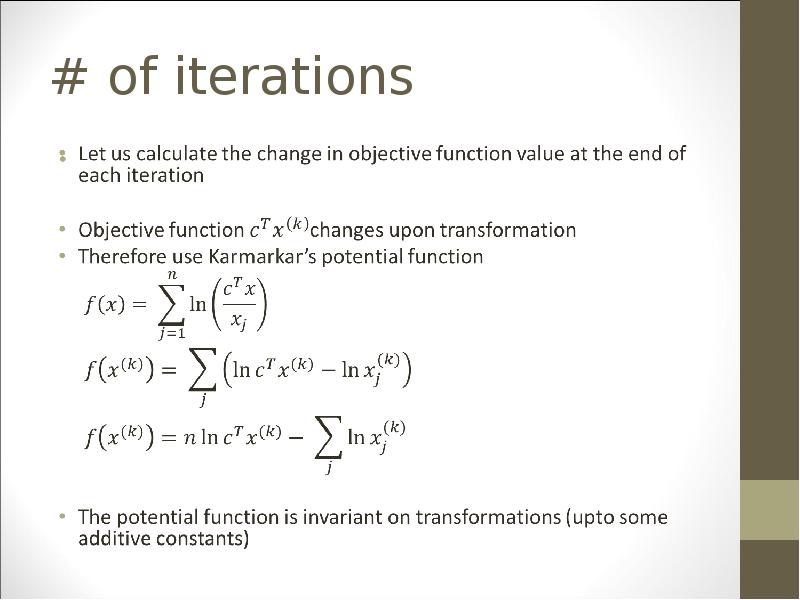
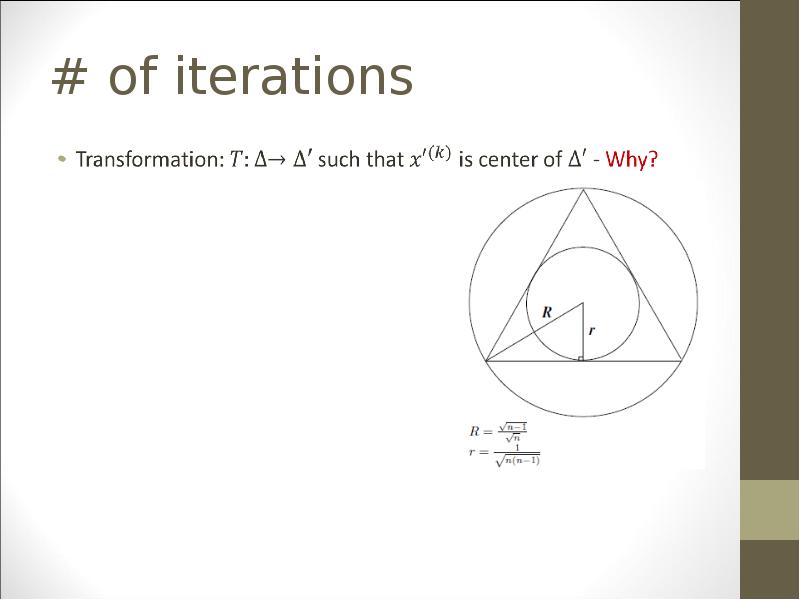
- 28. # of iterations
- 29. # of iterations
- 30. # of iterations
- 31. # of iterations
- 32. # of iterations
- 33. # of iterations
- 34. # of iterations
- 35. # of iterations
- 36. Rank-one modification
- 37. Method
- 38. Rank-one modification (cont)
- 39. Performance Analysis
- 40. Performance analysis - 2
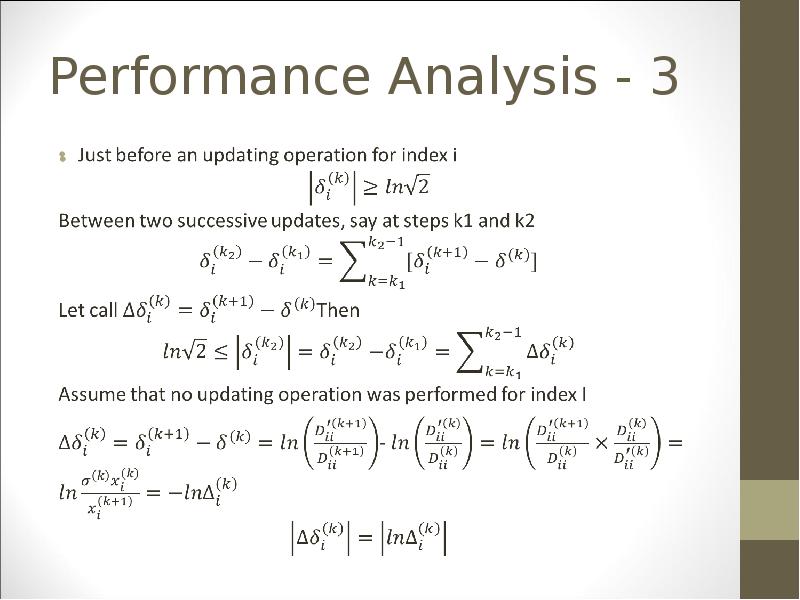
- 41. Performance Analysis - 3
- 42. Performance Analysis - 4
- 43. Performance Analysis - 5
- 44. Contents Overview Transformation to Karmarkar’s canonical form Projective transformation Orthogonal projection
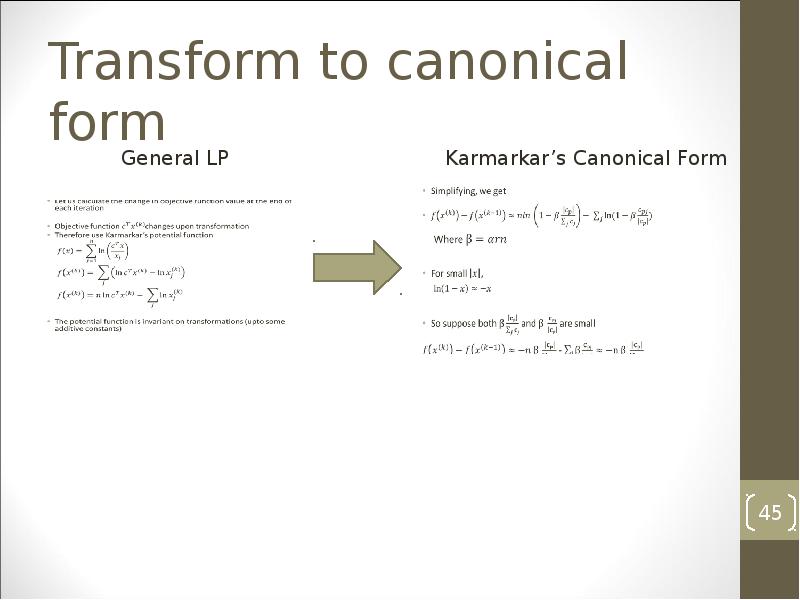
- 45. Transform to canonical form
- 46. Step 1:Convert LP to a feasibility problem Combine primal and dual
- 47. Step 2: Convert inequality to equality Introduce slack and surplus variable
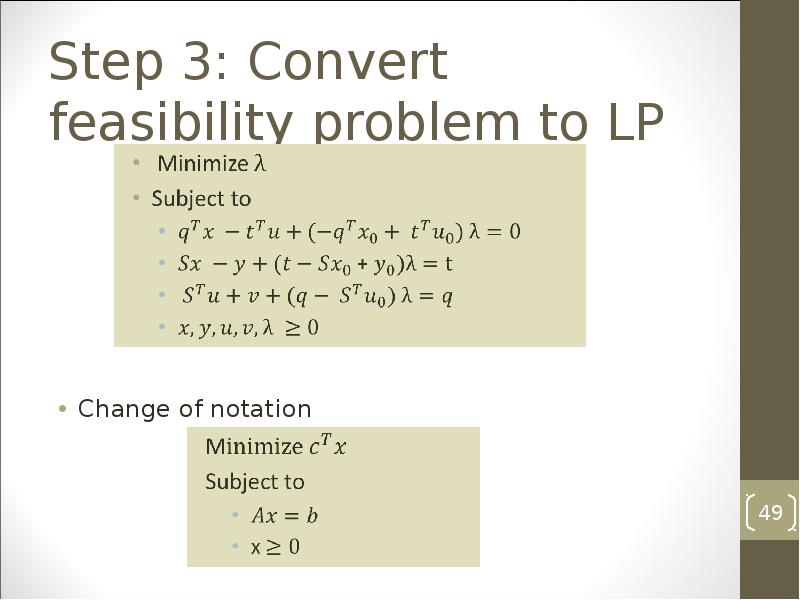
- 48. Step 3: Convert feasibility problem to LP
- 49. Step 3: Convert feasibility problem to LP Change of notation
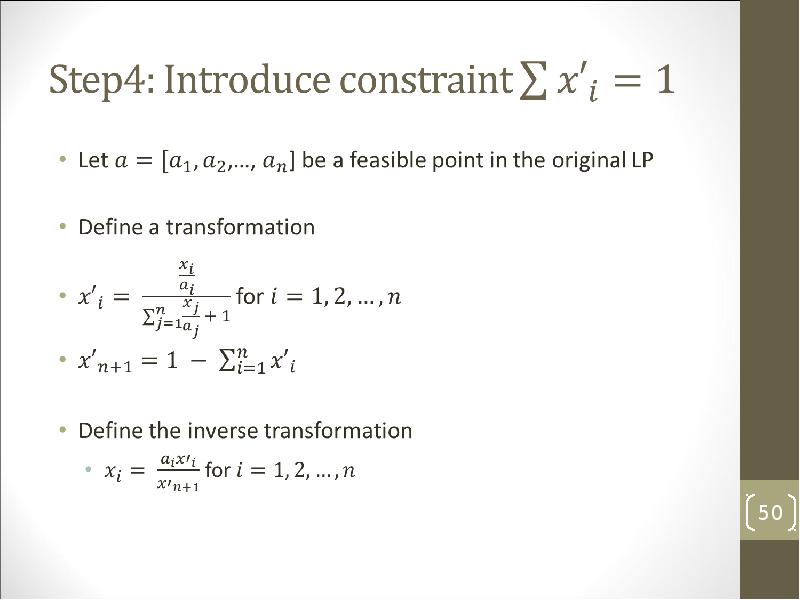
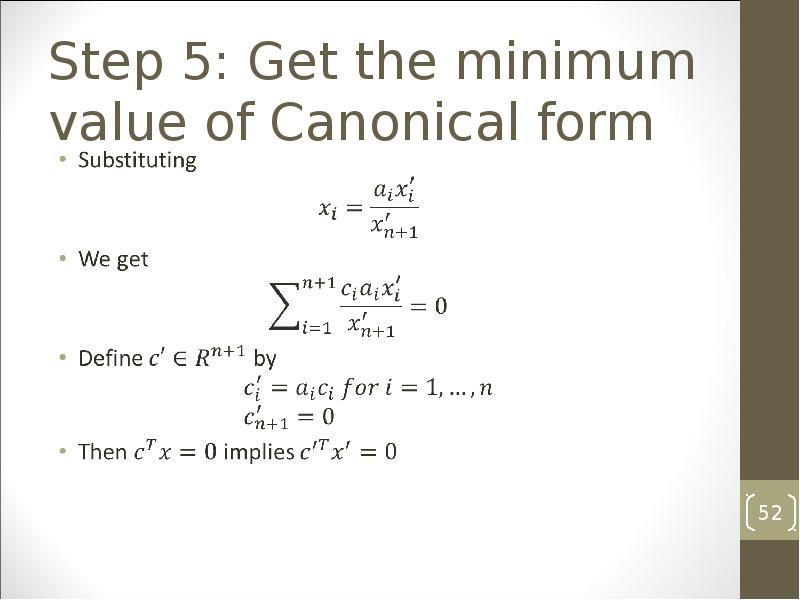
- 52. Step 5: Get the minimum value of Canonical form
- 53. Step 5: Get the minimum value of Canonical form The
- 54. References Narendra Karmarkar (1984). "A New Polynomial Time Algorithm for Linear
- 55. References Gill, Philip E.; Murray, Walter, Saunders, Michael A., Tomlin, J.
- 56. Q&A
- 57. Скачать презентацию

































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























