Lin protocol description. Automotive body network презентация
Содержание
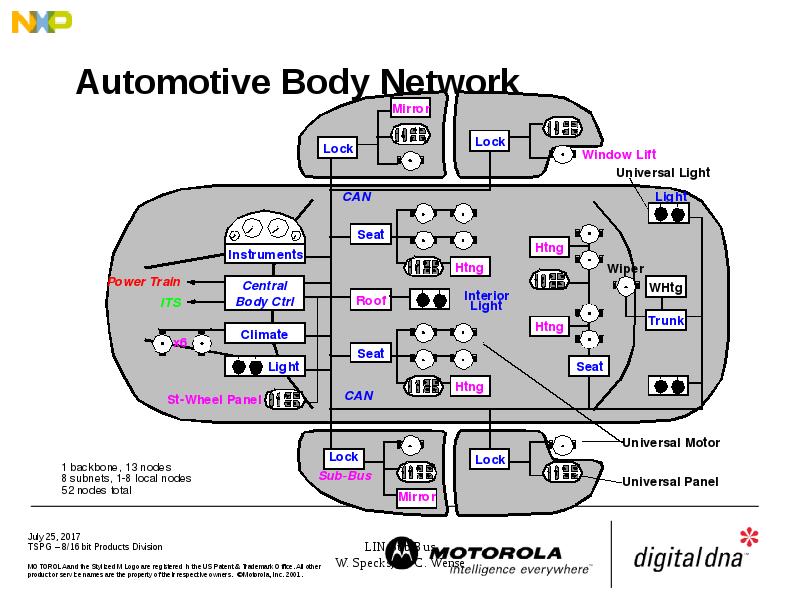
- 2. Automotive Body Network
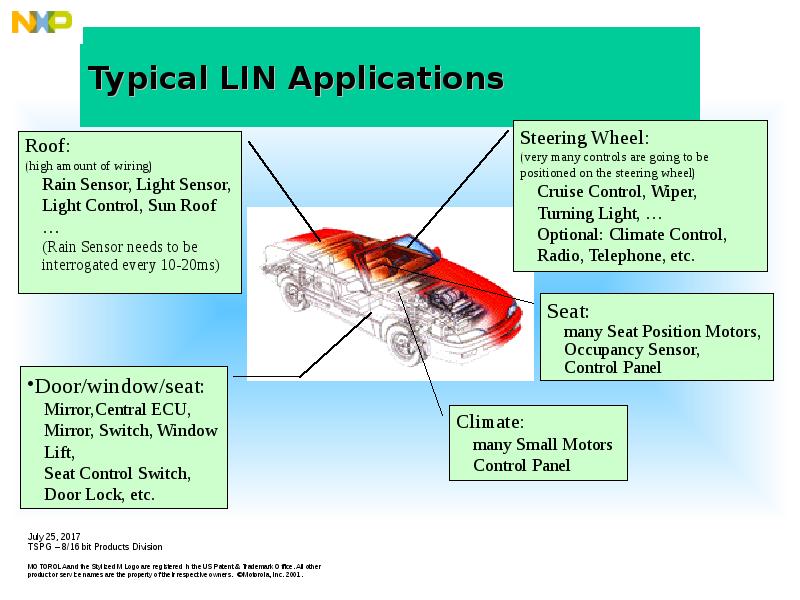
- 3. Typical LIN Applications
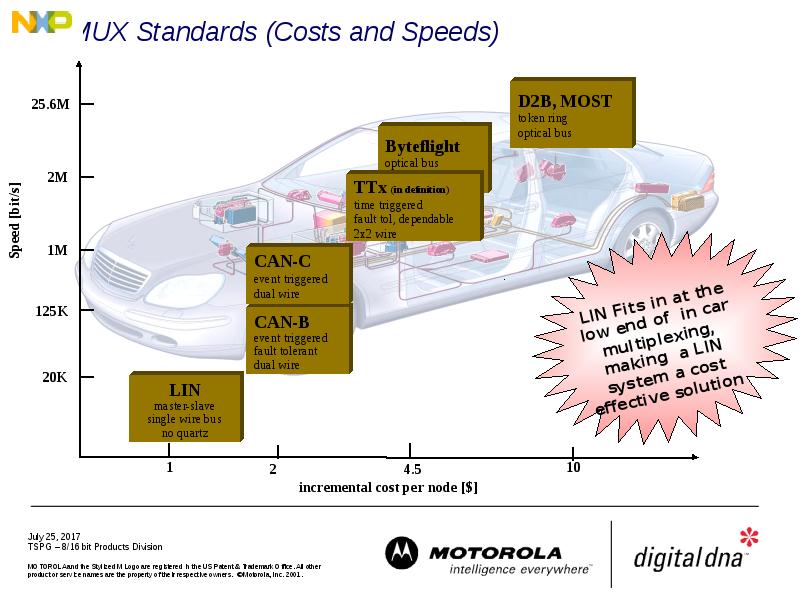
- 4. MUX Standards (Costs and Speeds)
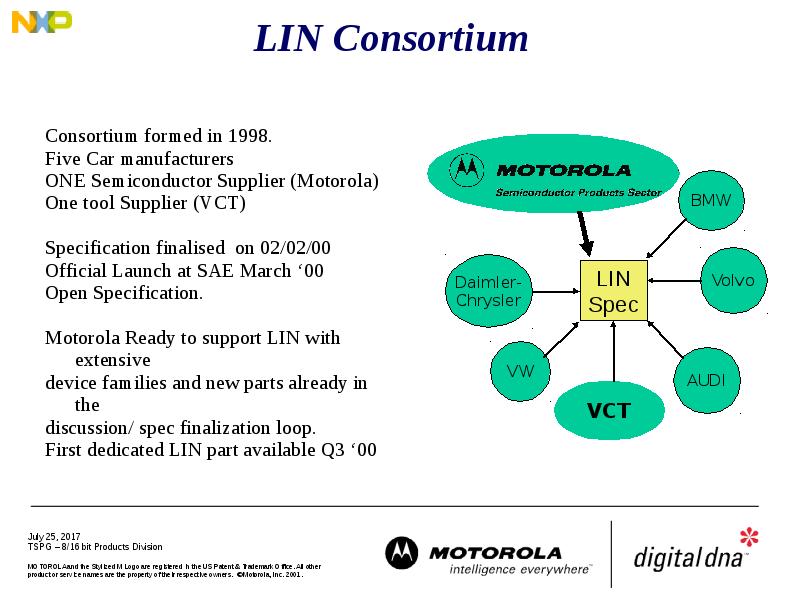
- 5. LIN Consortium Consortium formed in 1998. Five Car manufacturers ONE Semiconductor
- 6. LIN Standard - Overview
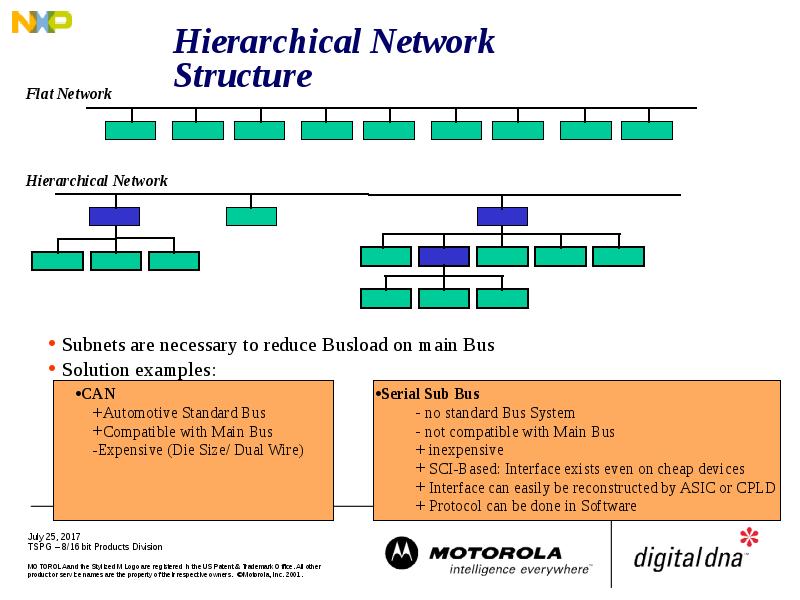
- 7. Hierarchical Network Structure
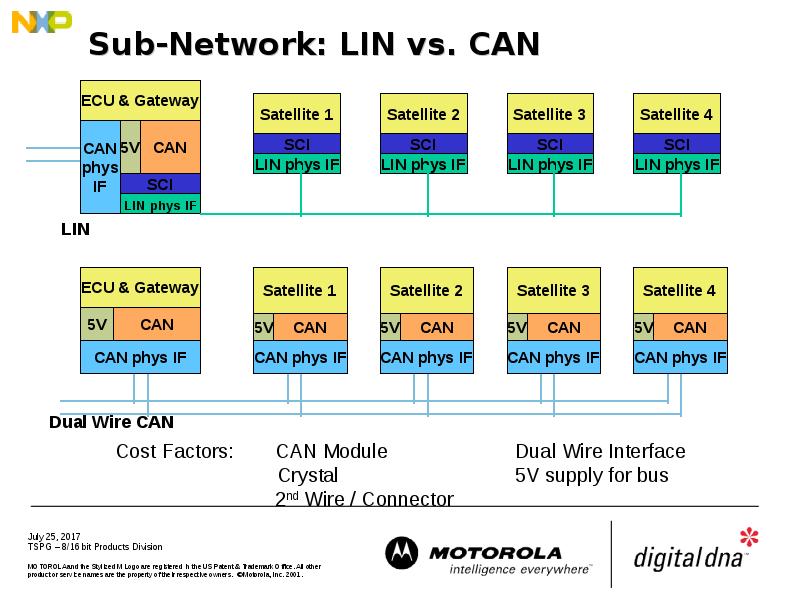
- 8. Sub-Network: LIN vs. CAN
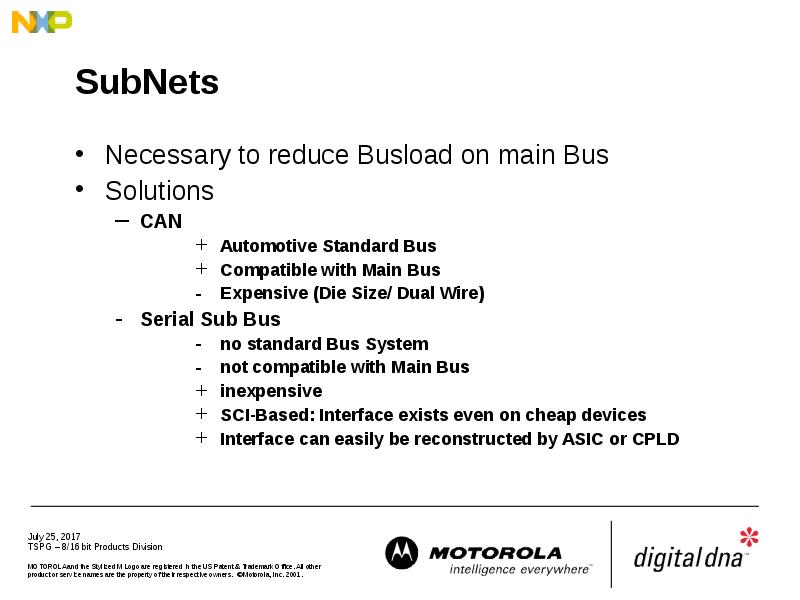
- 9. SubNets Necessary to reduce Busload on main Bus Solutions CAN Automotive
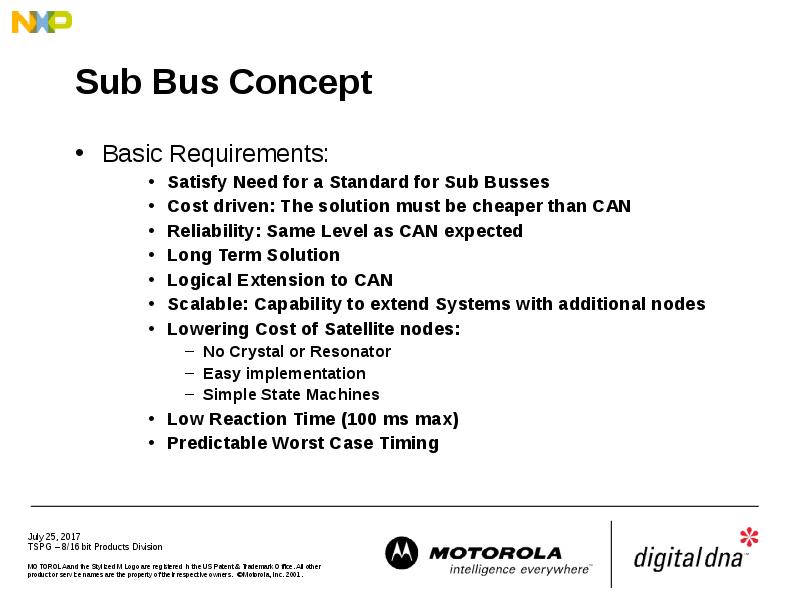
- 10. Sub Bus Concept Basic Requirements: Satisfy Need for a Standard for
- 12. Master / Slave Protocol Master Task Determines order and priority of
- 13. Master / Slave Protocol Master has control over the whole Bus
- 14. Master/Slave Protocol Slave Is one of 2-16 Members on the Bus
- 15. LIN protocol offers message timing predictability Time Triggered Approach
- 16. Data Transmission
- 17. Message Frame Synch Byte: Specific Pattern for Determination of Time Base
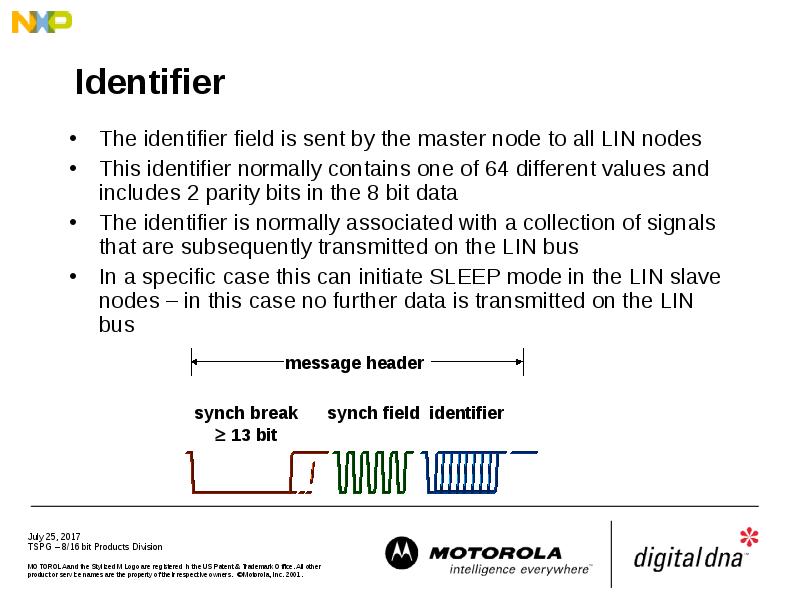
- 18. Identifier The identifier field is sent by the master node to
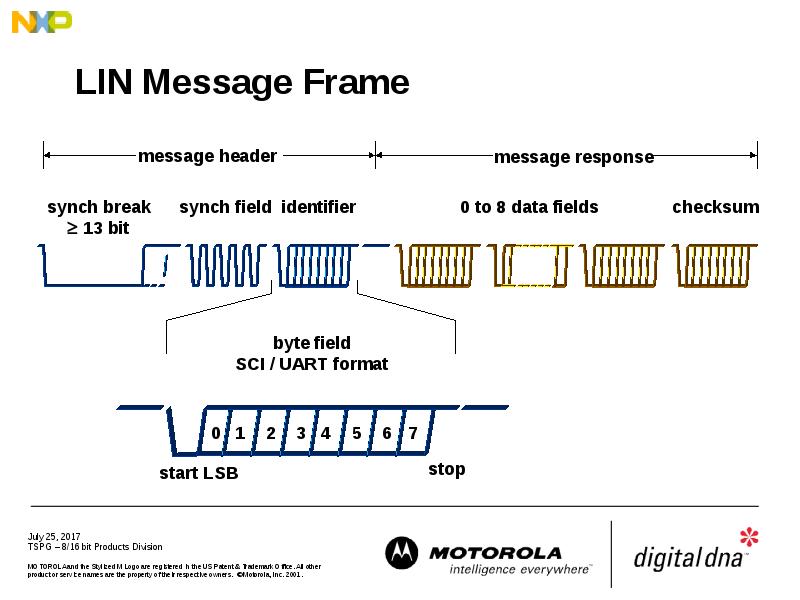
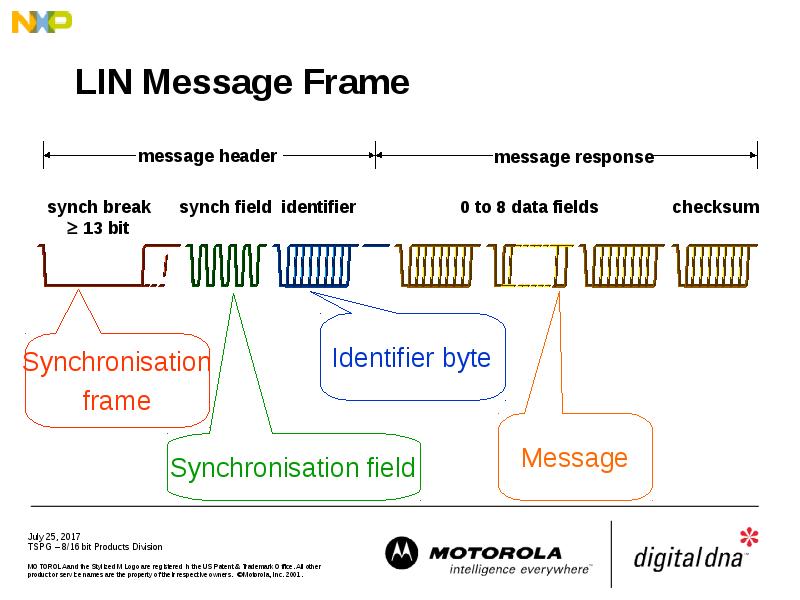
- 19. LIN Message Frame
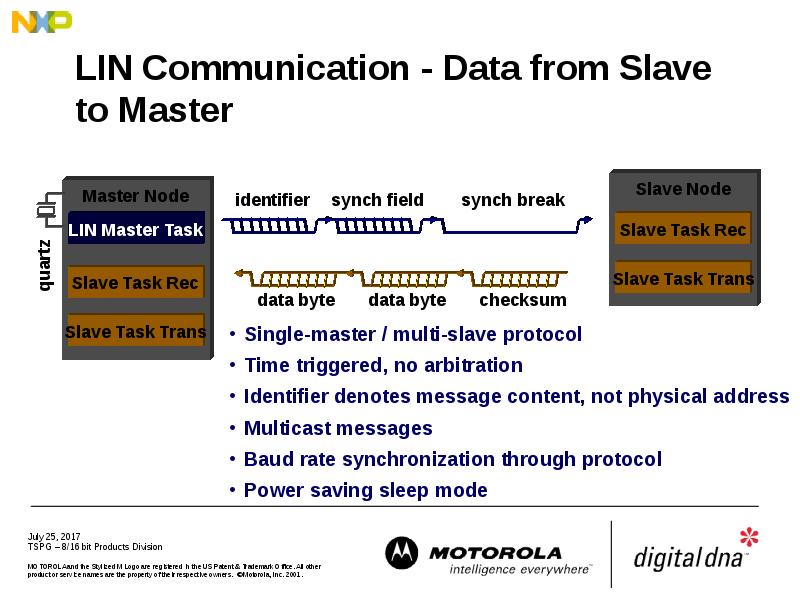
- 20. LIN Communication - Data from Slave to Master
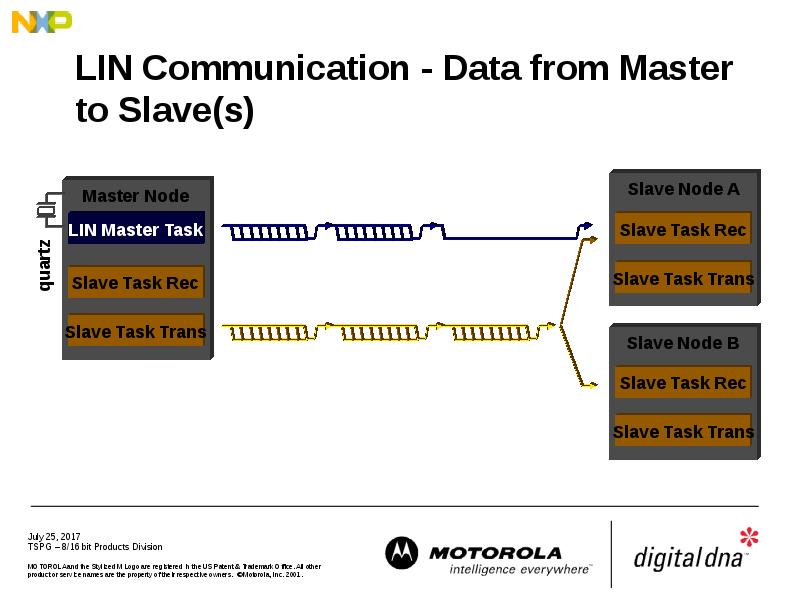
- 21. LIN Communication - Data from Master to Slave(s)
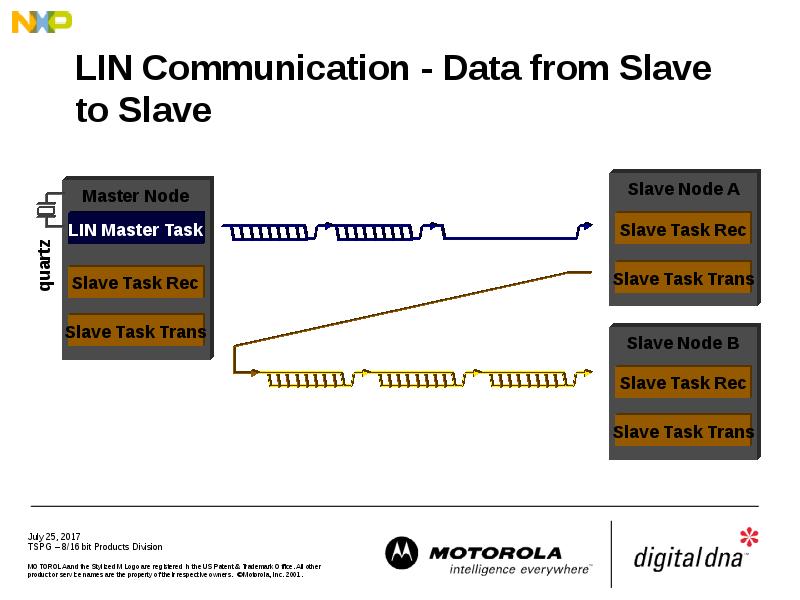
- 22. LIN Communication - Data from Slave to Slave
- 23. LIN Message Frame
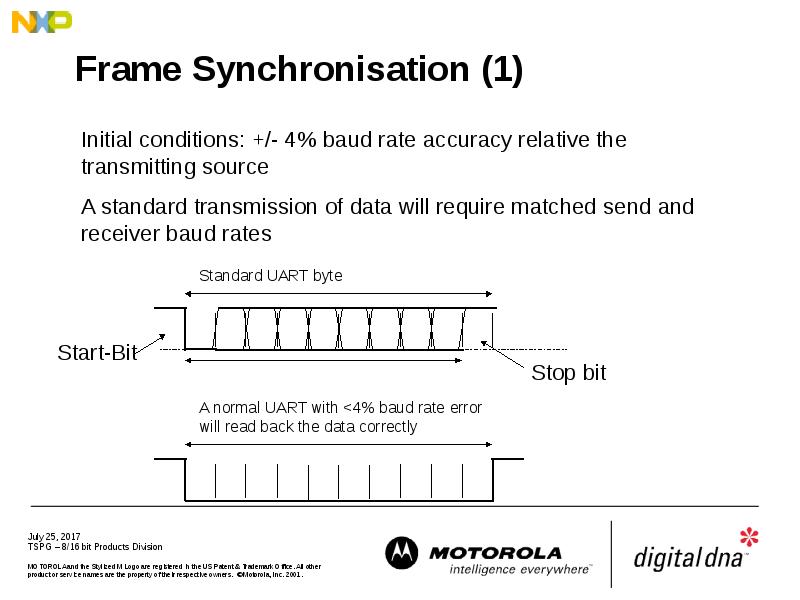
- 24. Frame Synchronisation (1)
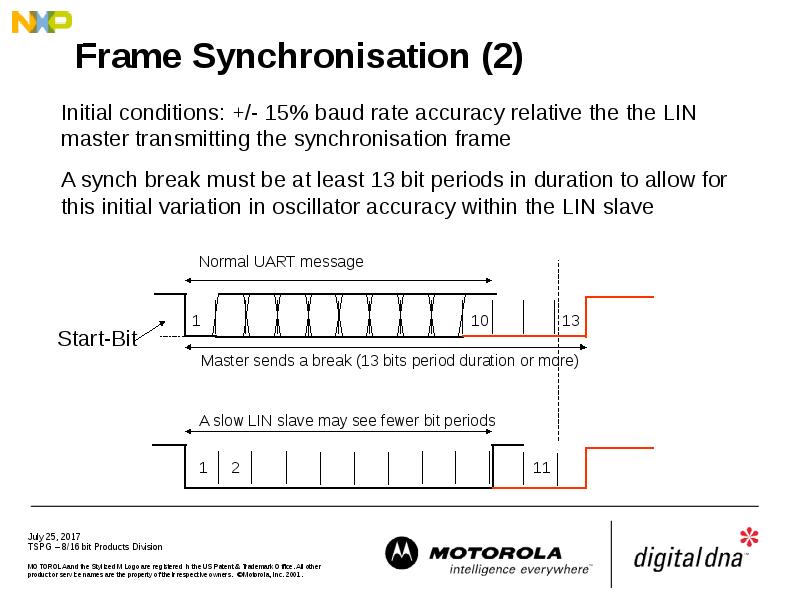
- 25. Frame Synchronisation (2)
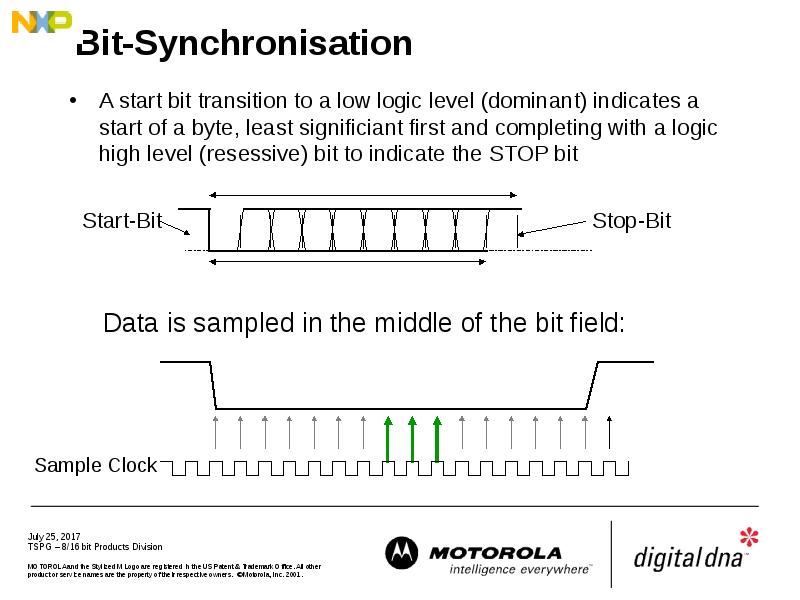
- 26. Bit-Synchronisation A start bit transition to a low logic level (dominant)
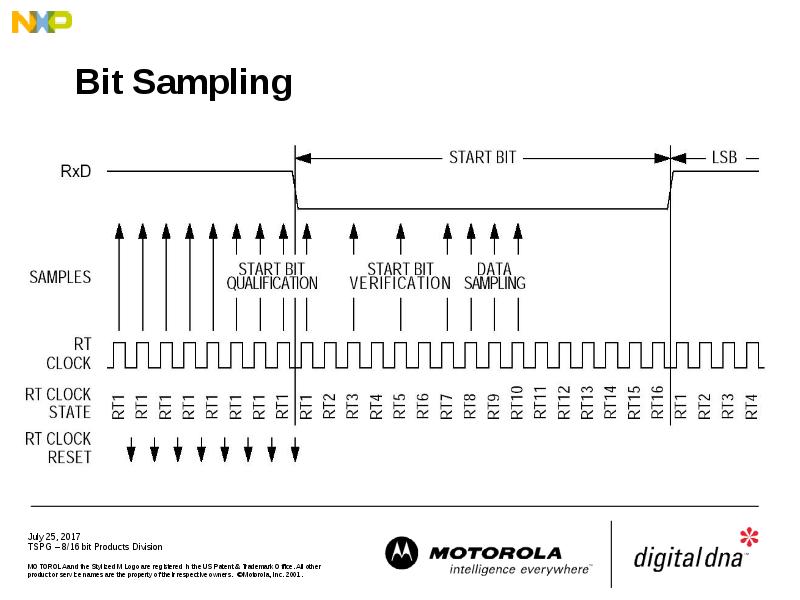
- 27. Bit Sampling
- 28. Bit-Synchronisation
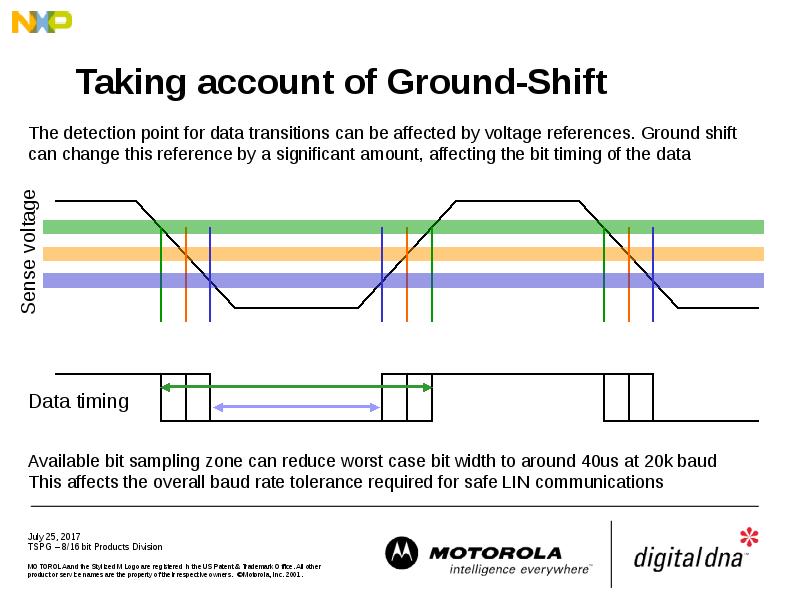
- 29. Taking account of Ground-Shift
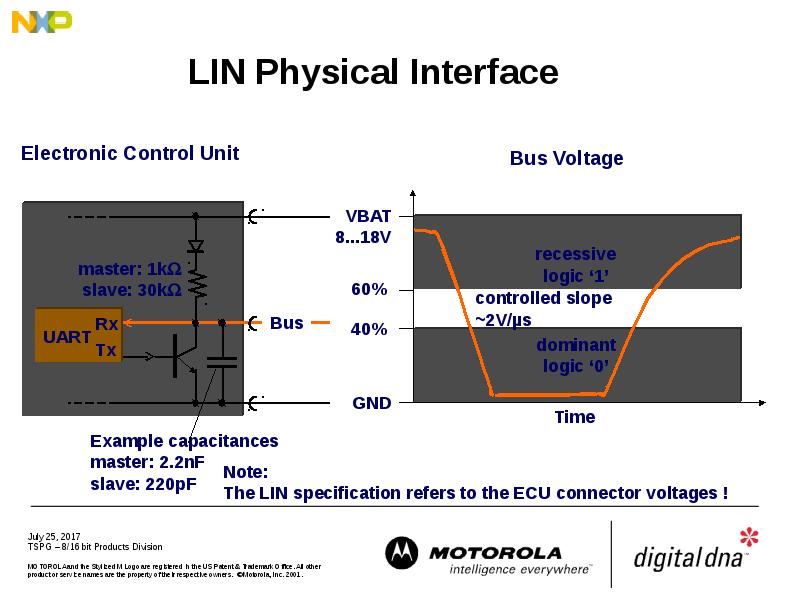
- 30. LIN Physical Interface
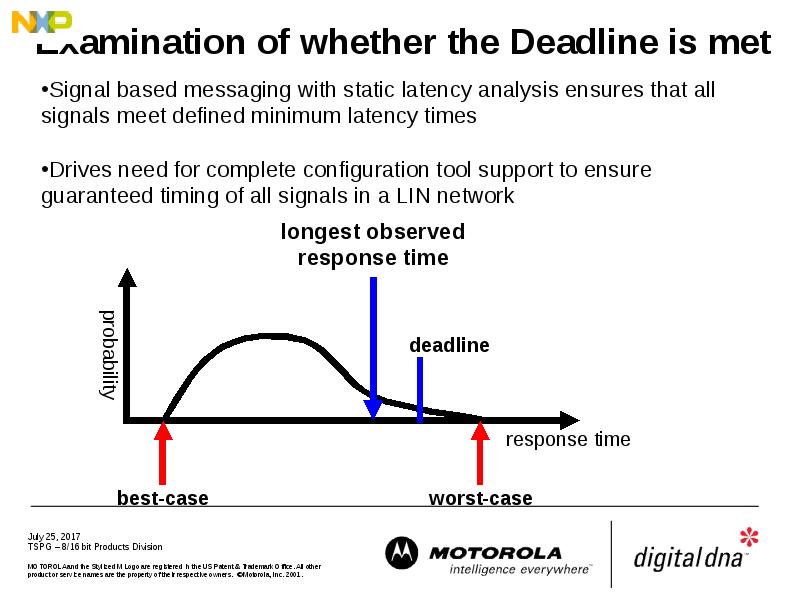
- 31. Examination of whether the Deadline is met
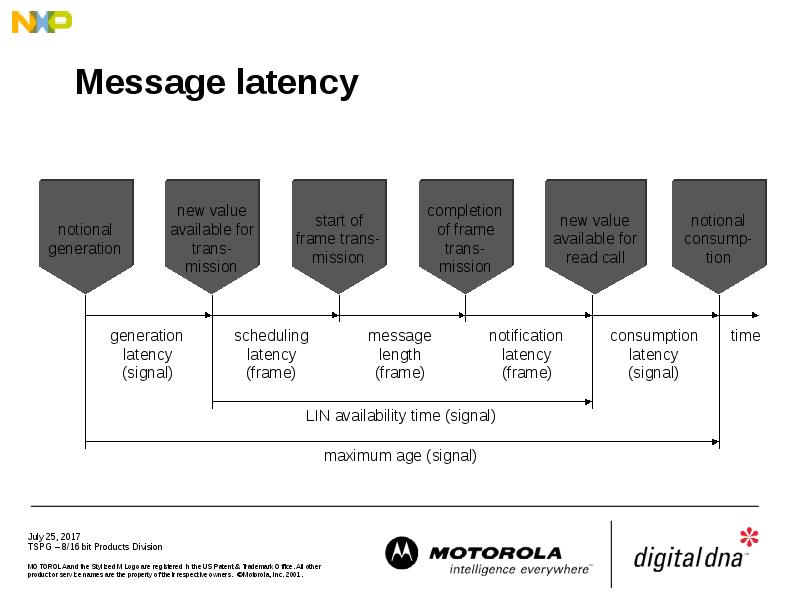
- 32. Message latency
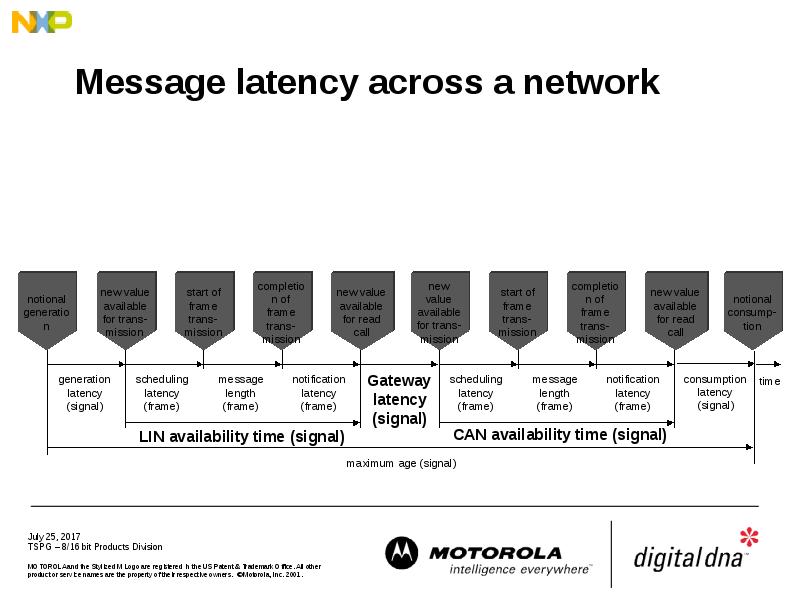
- 33. Message latency across a network
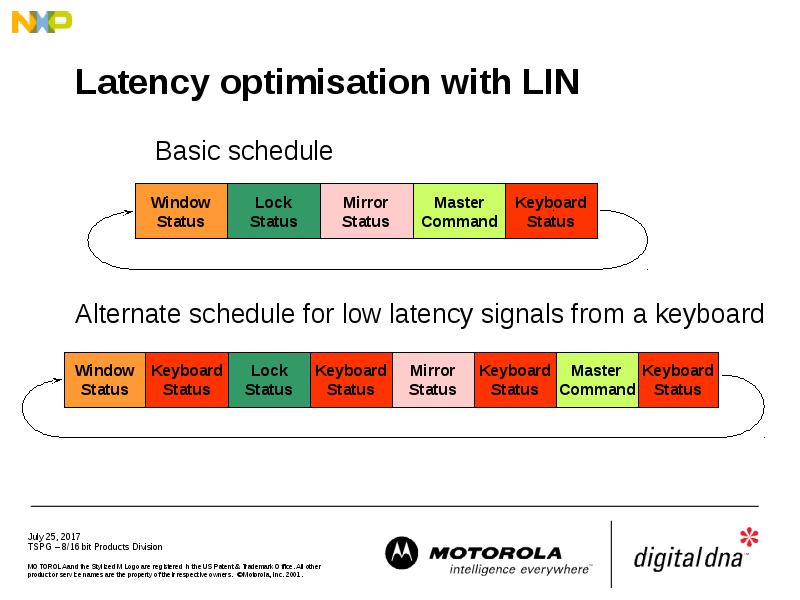
- 34. Latency optimisation with LIN
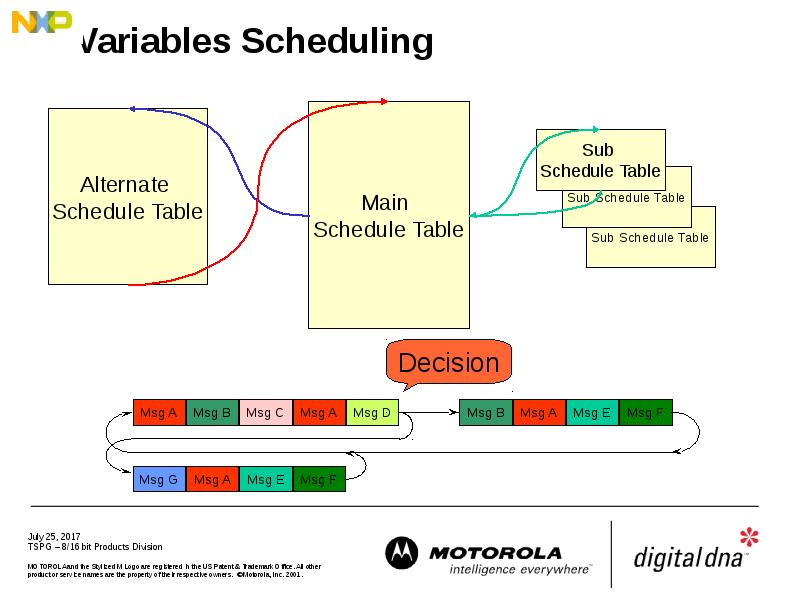
- 35. Variables Scheduling
- 36. Event Triggered Message Problem Specific node communication required but this takes
- 37. Further information http://www.lin-subbus.org
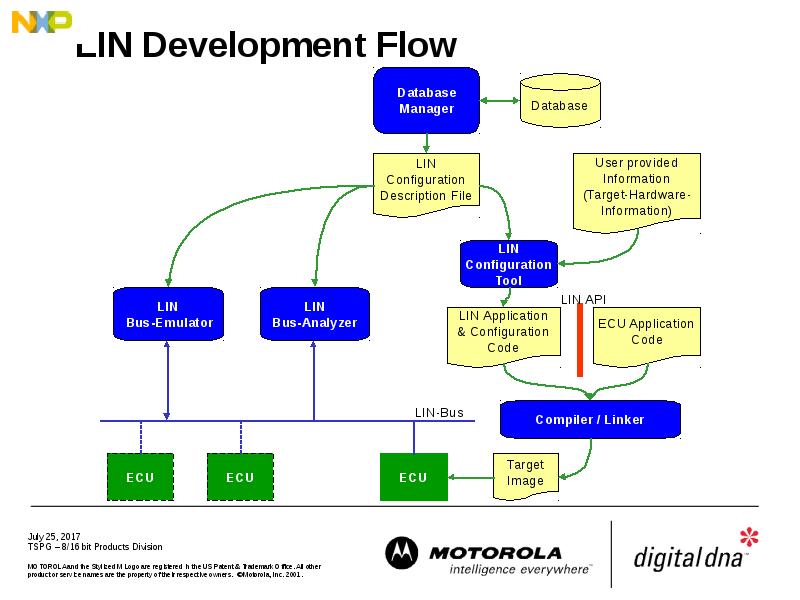
- 38. LIN Development Flow
- 39. LIN Configuration Description File Includes all essential information of network signals,
- 40. The Workflow Data Input Definition of objects Definition of relations between
- 41. Скачать презентацию











Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Lin protocol description. Automotive body network можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























