Programming Languages: Concepts and Constructs by Ravi Sethi презентация
Содержание
- 2. What is a Programming Language? a tool for instructing machines a
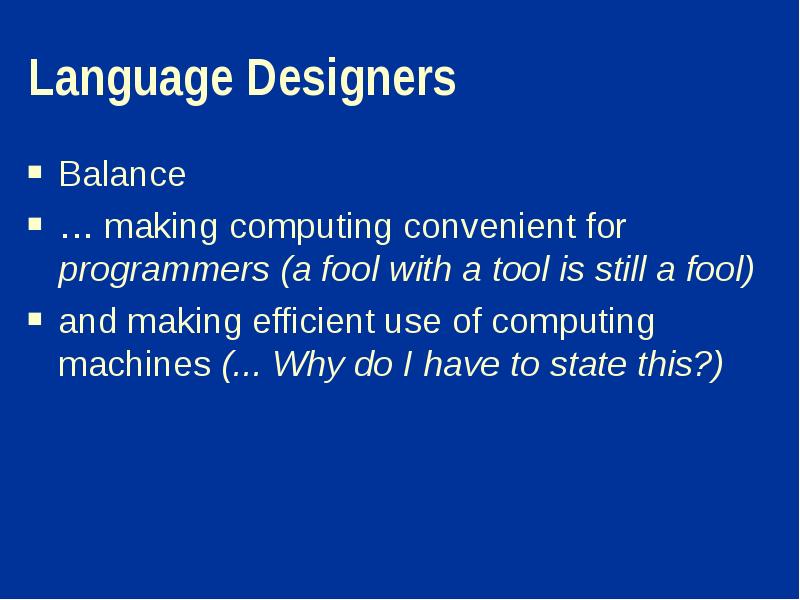
- 3. Language Designers Balance … making computing convenient for programmers (a fool
- 4. Levels Gross distinction between programming language based on readability based on
- 5. Levels Machine level language Assembly level language High-level language (3GL) sometimes
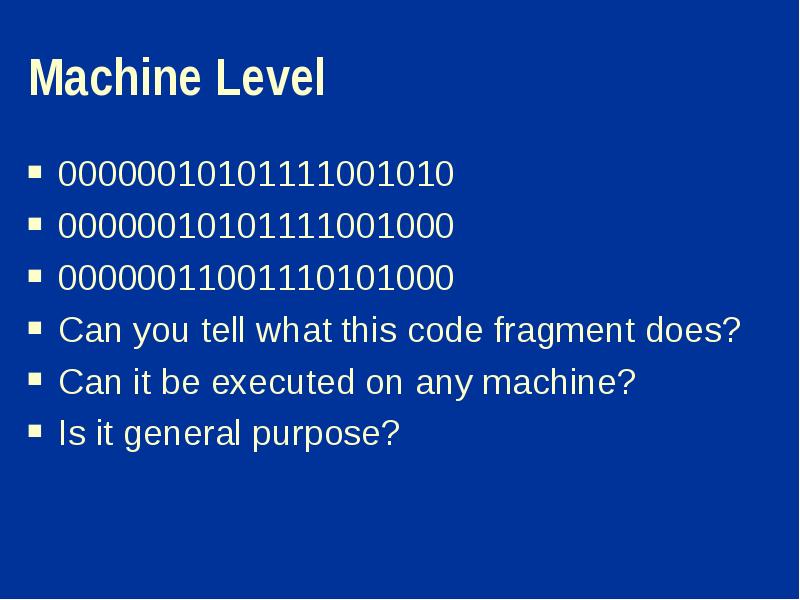
- 6. Machine Level 00000010101111001010 00000010101111001000 00000011001110101000 Can you tell what this code
- 7. Assembly Language Look at figure 1.1 LD R1,”0” LD R2, M
- 8. Assembly Language Look at page 63 in your text and figure
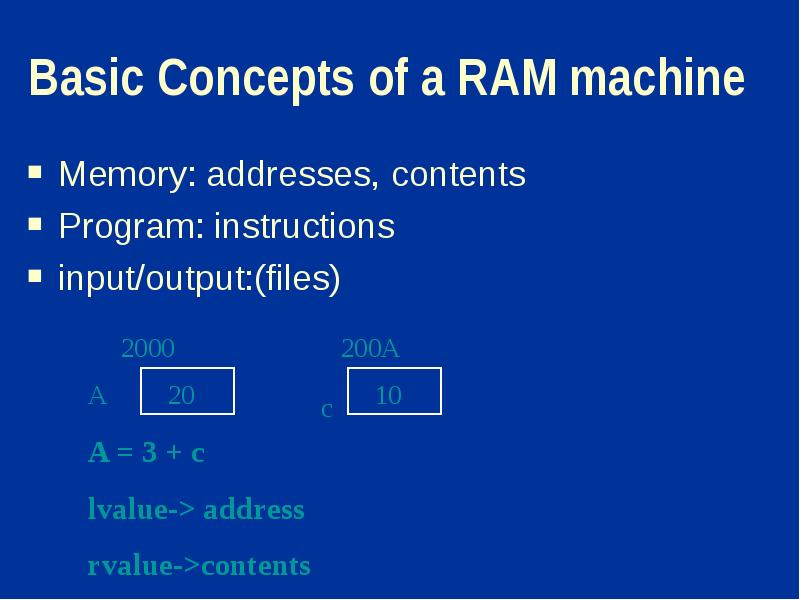
- 9. Basic Concepts of a RAM machine Memory: addresses, contents Program: instructions
- 10. High Level Readable familiar notations machine independence availability of program libraries
- 11. Problems of Scale Changes are easy to make isolated program fragments
- 12. Bugs Programming testing can be used to show the presence of
- 13. Role of Programming Languages Art (science) of programming is organizing complexity
- 14. Programming Paradigms Imperative - action oriented, sequence of actions Functional -
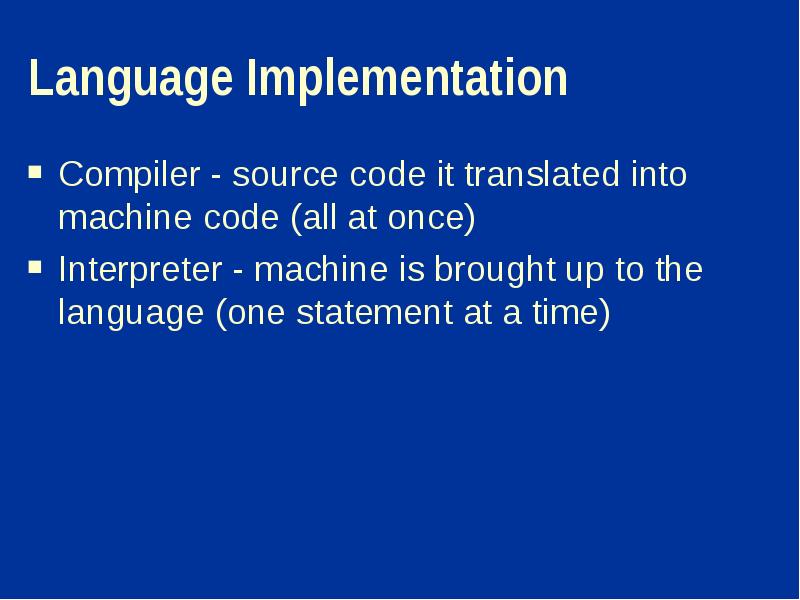
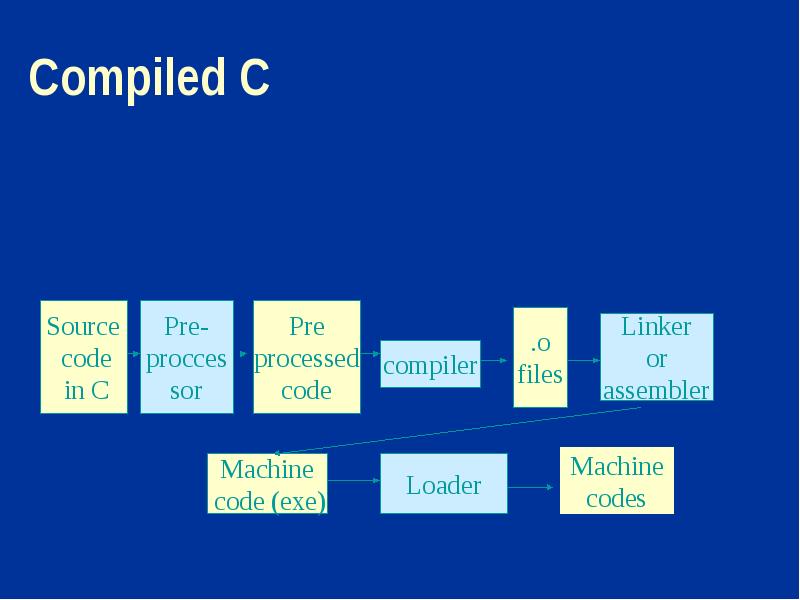
- 15. Language Implementation Compiler - source code it translated into machine code
- 16. Compiled C
- 17. Interpreted Code Each instruction is interpreted by machine interpreter does not
- 18. Comparisons Compilation more efficient interpreted more flexible
- 19. Testing your skill Do 1.4 (a,b,c) in PL book Do 1.5
- 20. Testing your skill For each module, include a module header: what
- 21. Testing your skill For the test cases, include a test header:
- 22. Скачать презентацию
















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Programming Languages: Concepts and Constructs by Ravi Sethi можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























