Programming Logic and Design, Seventh Edition презентация
Содержание
- 2. Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: The disadvantages of
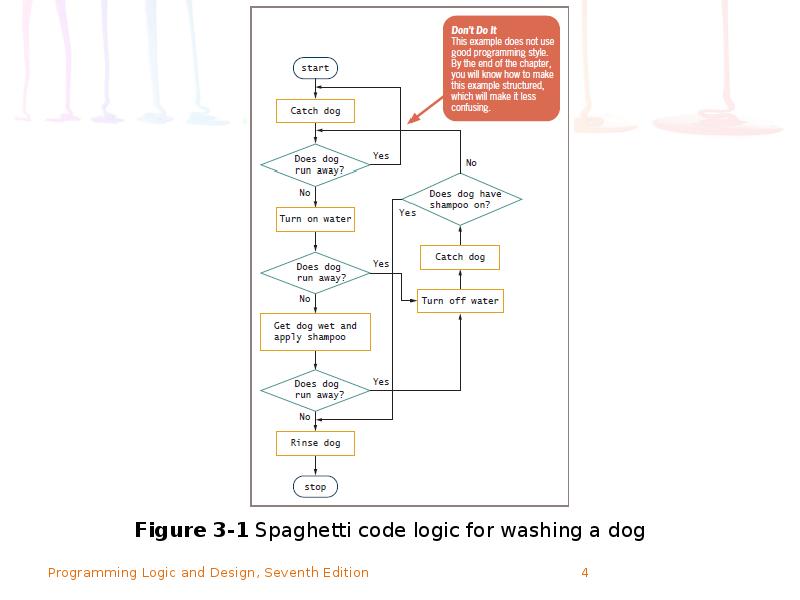
- 3. The Disadvantages of Unstructured Spaghetti Code Spaghetti code Logically snarled program
- 5. Understanding the Three Basic Structures Structure Basic unit of programming logic
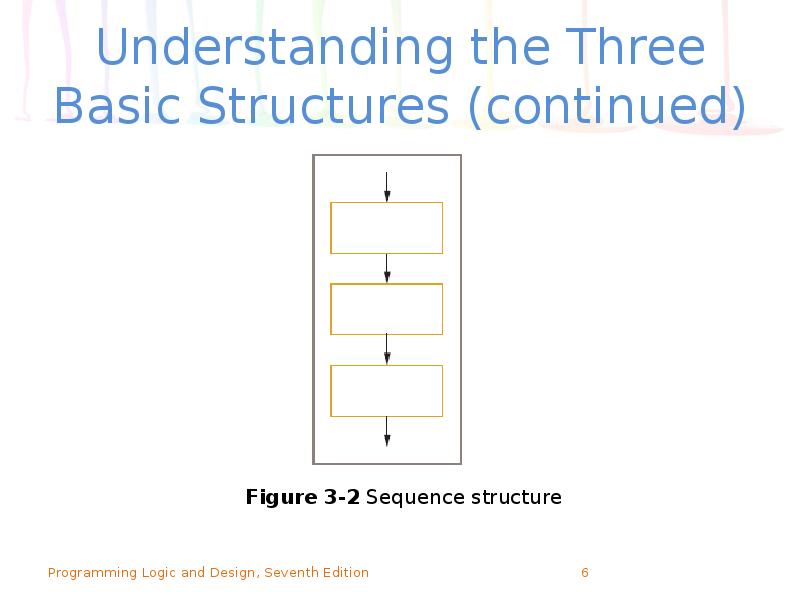
- 6. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
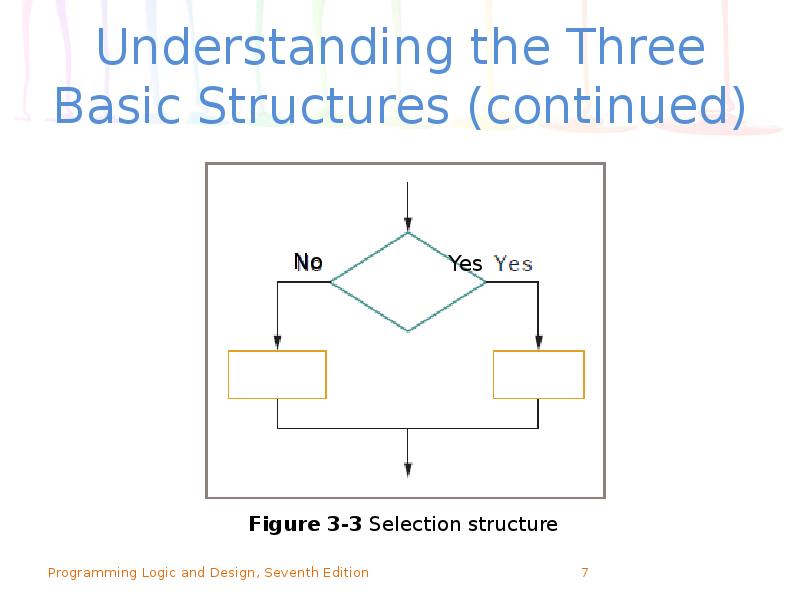
- 7. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
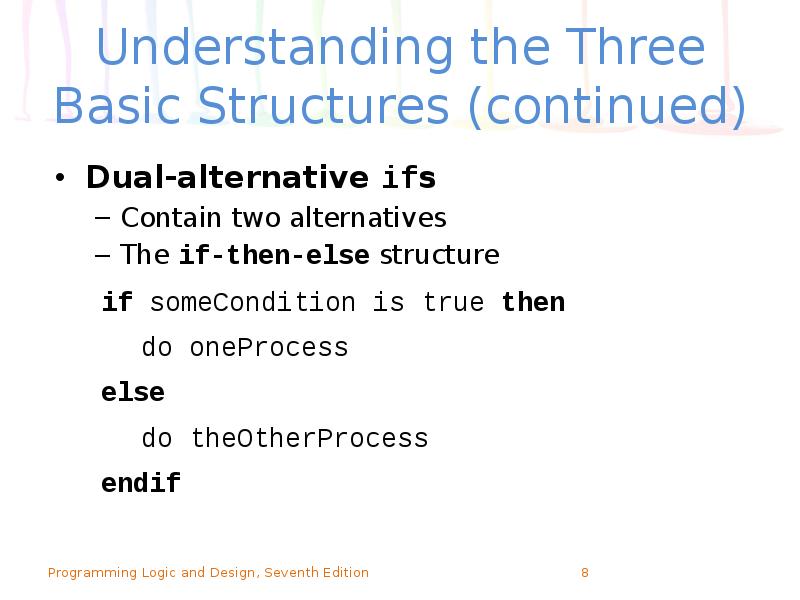
- 8. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) Dual-alternative ifs Contain two alternatives
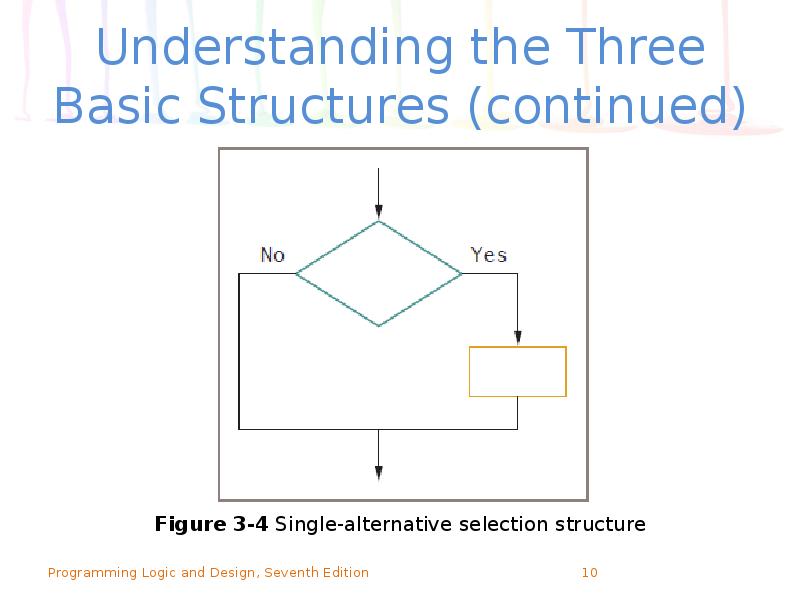
- 9. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) Single-alternative ifs An else clause
- 10. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
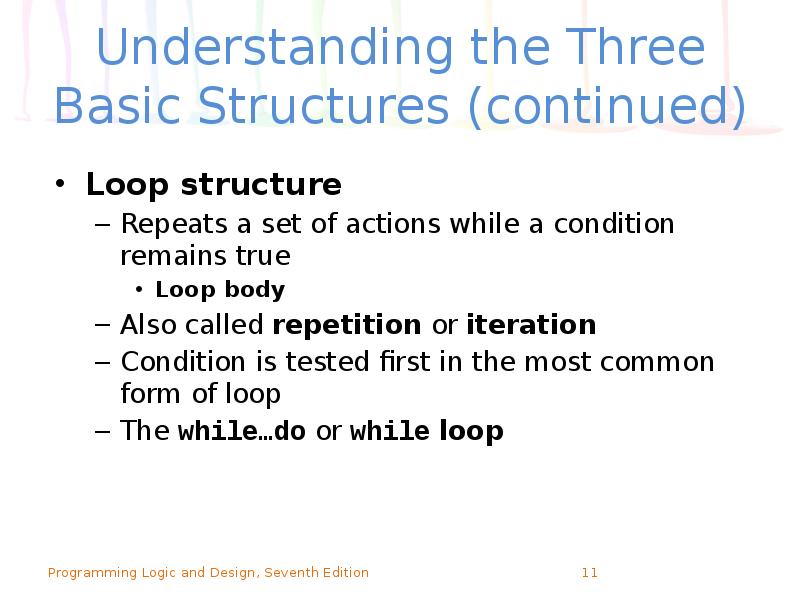
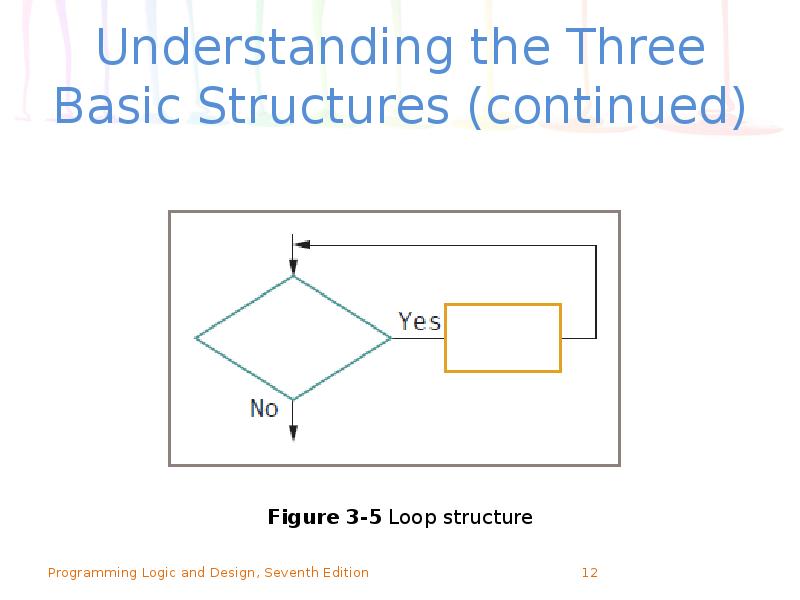
- 11. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) Loop structure Repeats a set
- 12. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
- 13. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) Loop structure
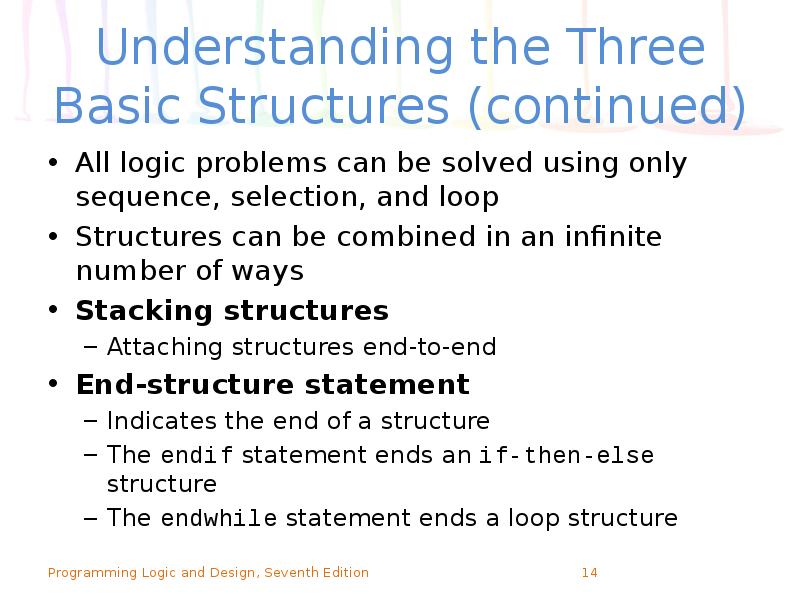
- 14. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) All logic problems can be
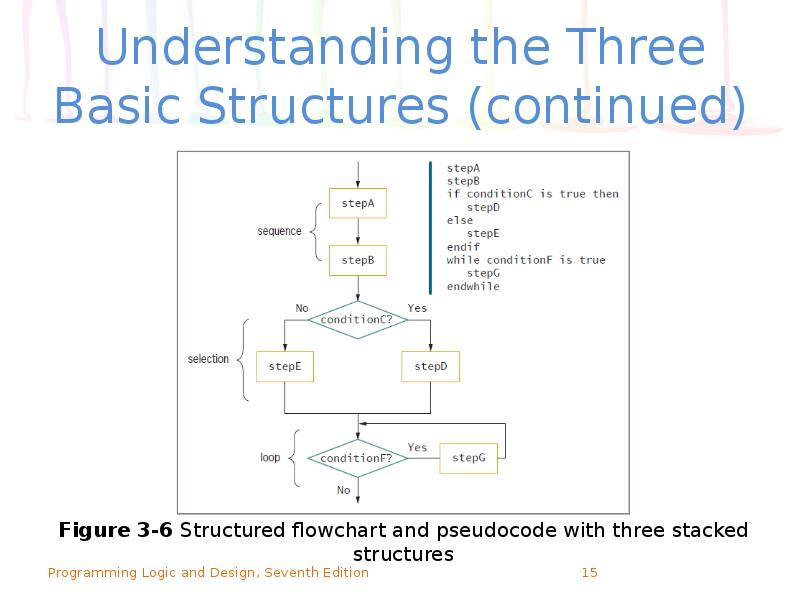
- 15. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
- 16. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) Any individual task or step
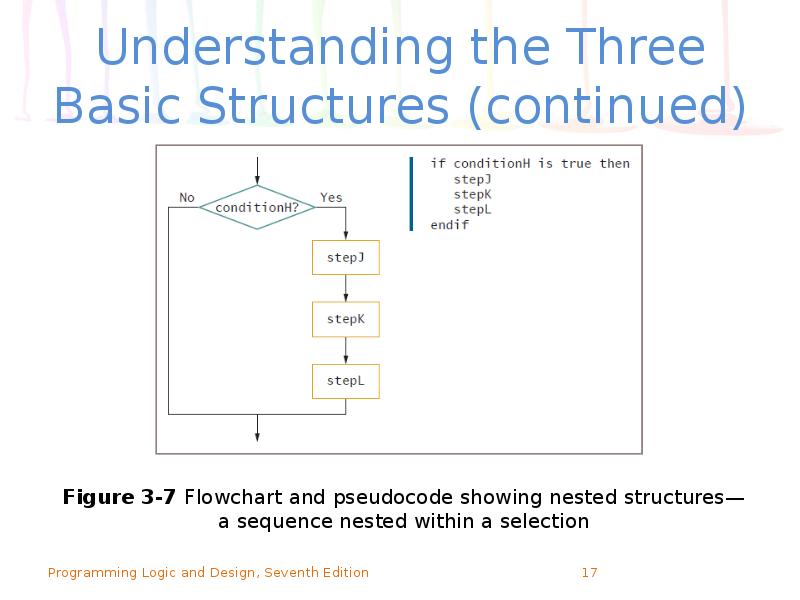
- 17. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
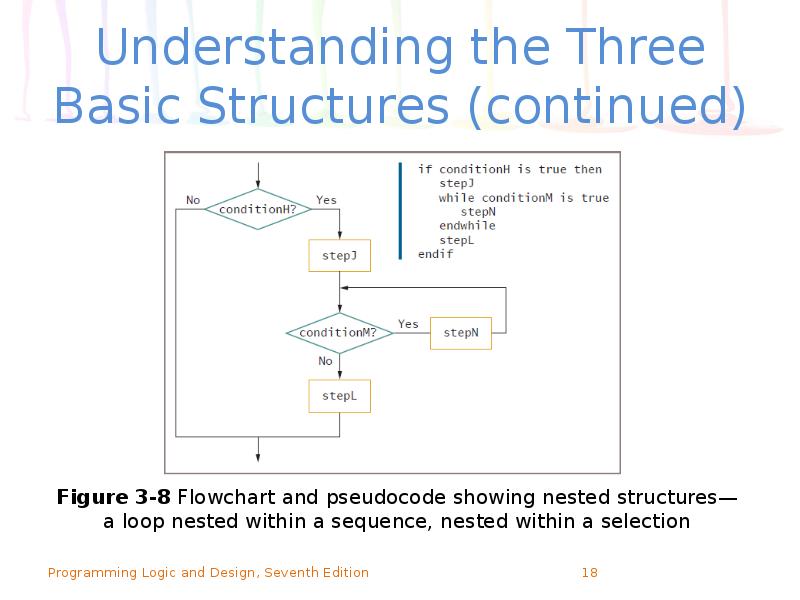
- 18. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
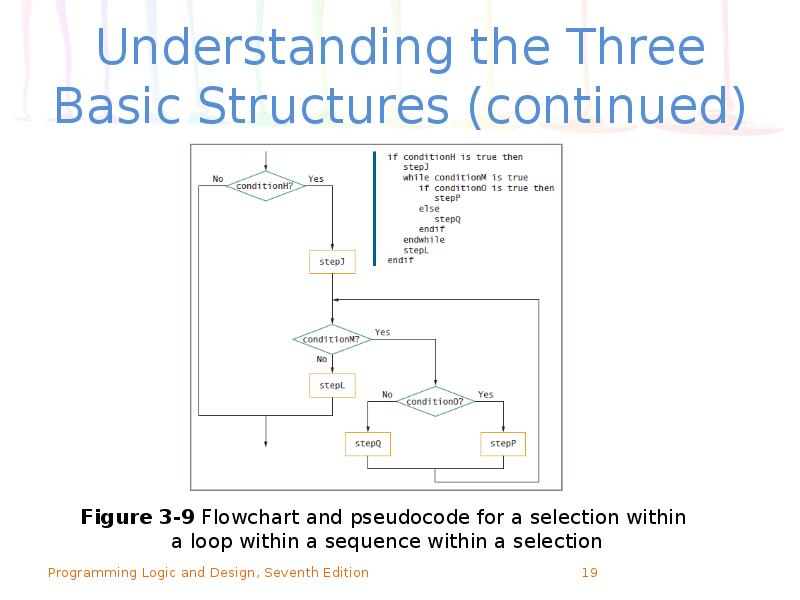
- 19. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued)
- 20. Understanding the Three Basic Structures (continued) Structured programs have the following
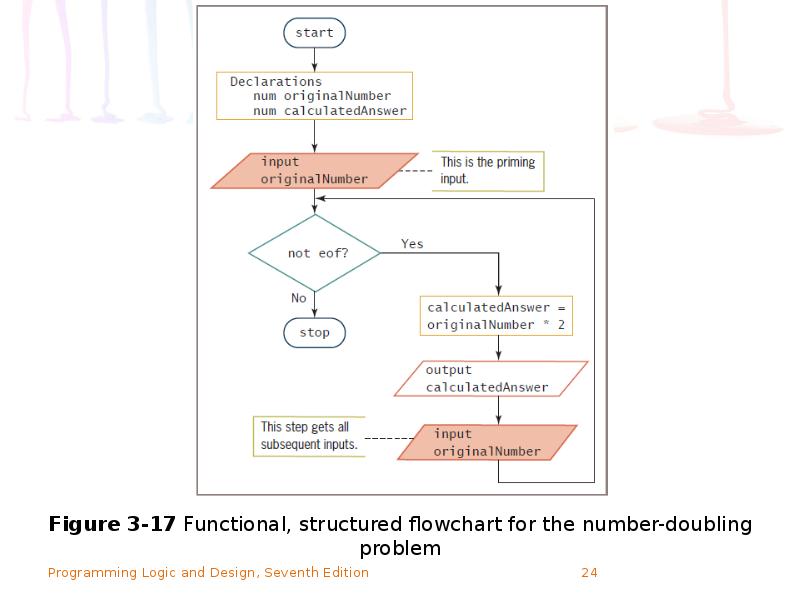
- 21. Using a Priming Input to Structure a Program Priming input (or
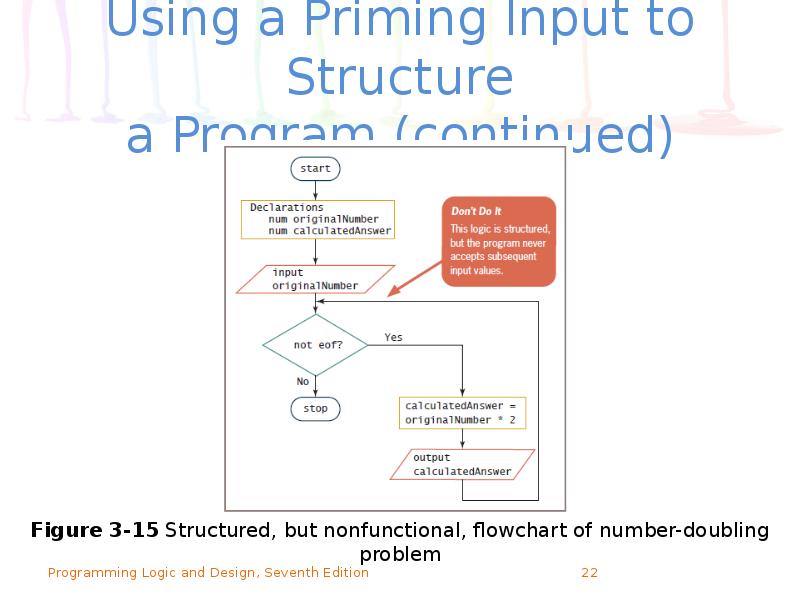
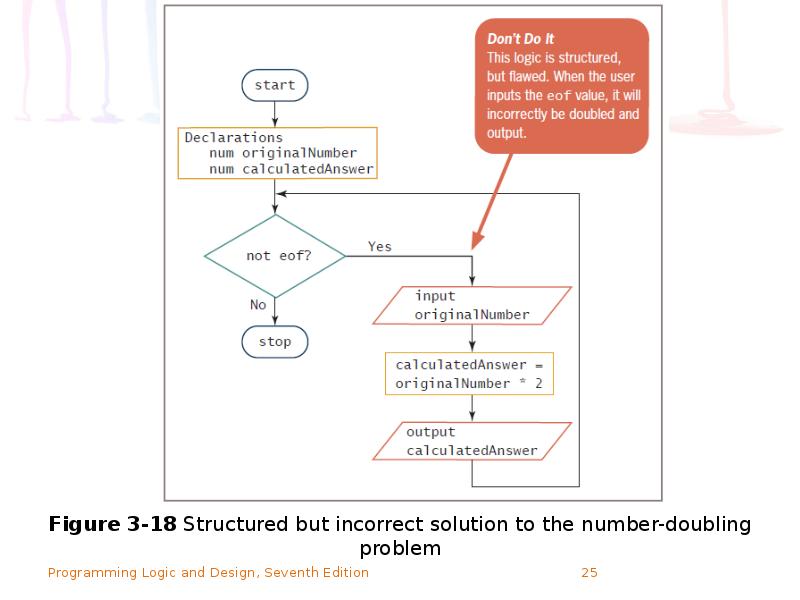
- 22. Using a Priming Input to Structure a Program (continued)
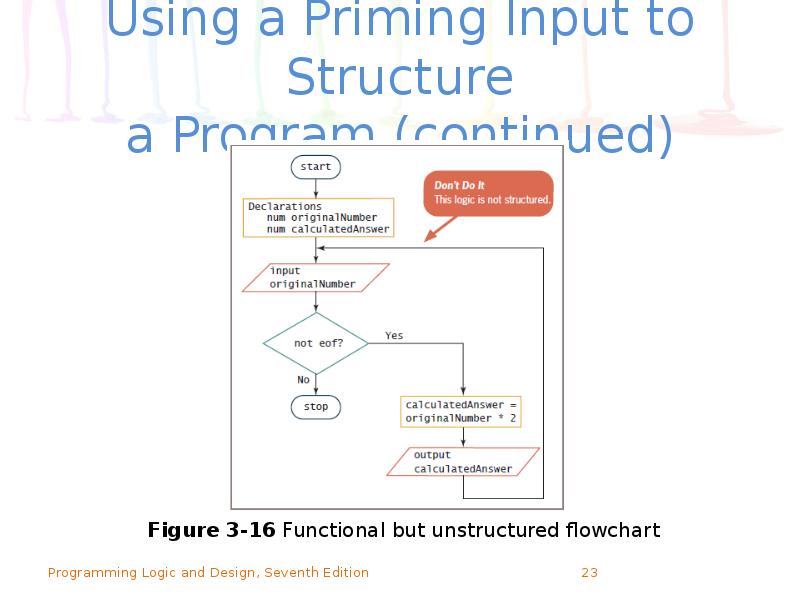
- 23. Using a Priming Input to Structure a Program (continued)
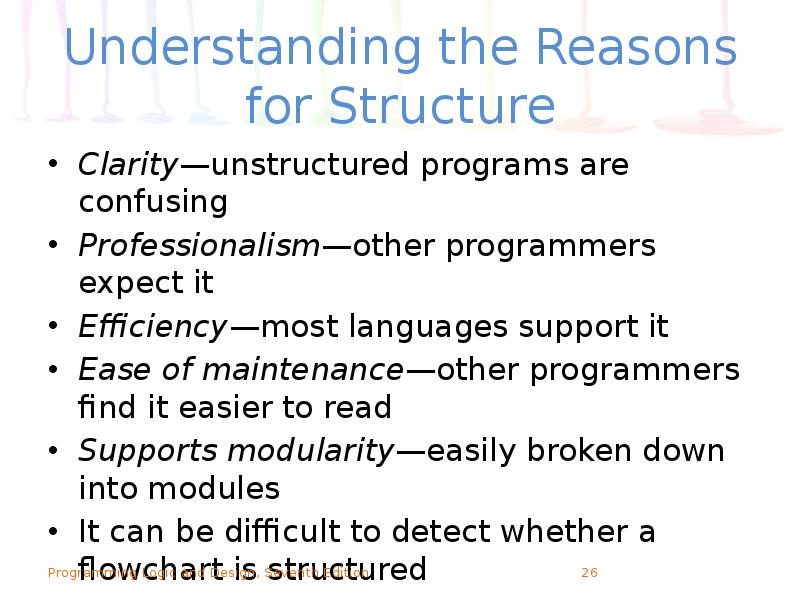
- 26. Understanding the Reasons for Structure Clarity—unstructured programs are confusing Professionalism—other programmers
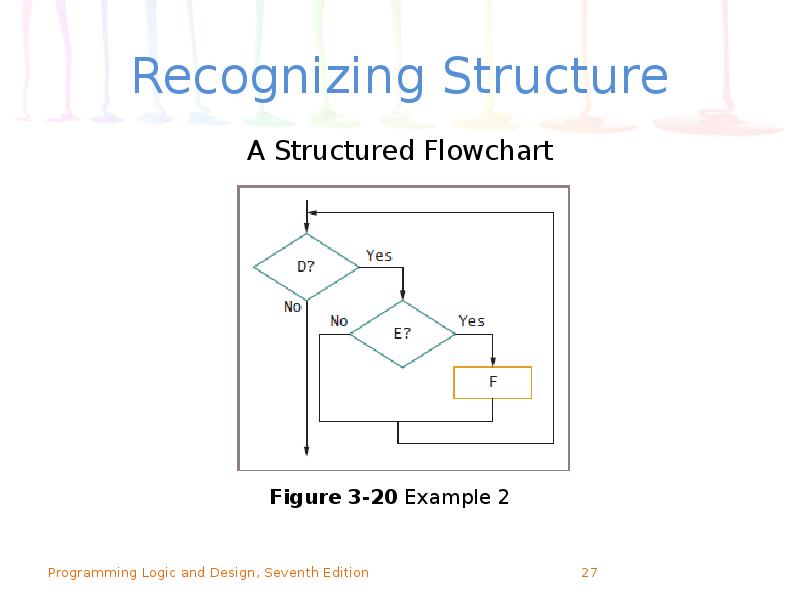
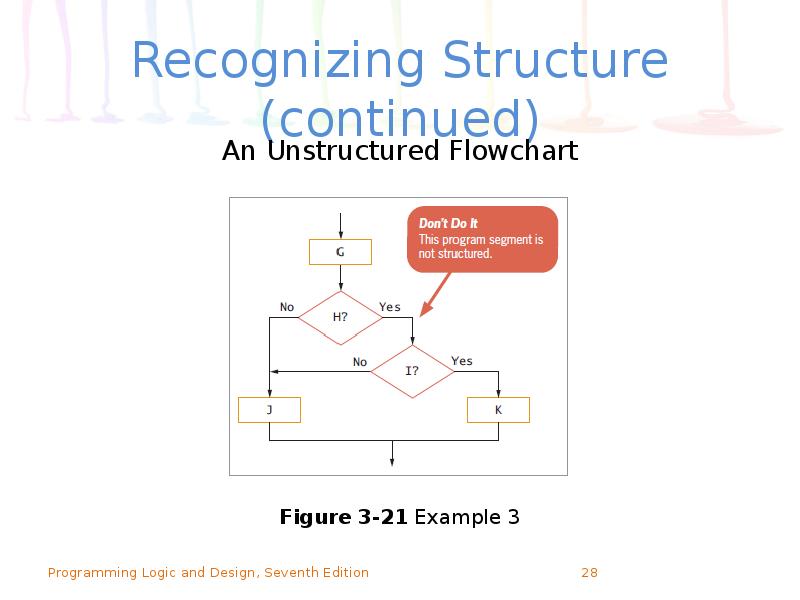
- 28. Recognizing Structure (continued)
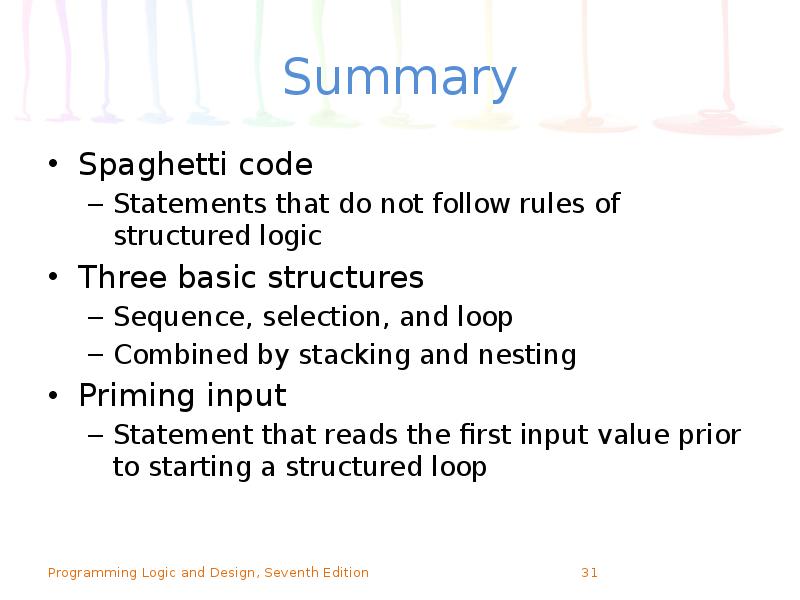
- 31. Summary Spaghetti code Statements that do not follow rules of structured
- 32. Summary (continued) Structured techniques promote: Clarity Professionalism Efficiency Modularity Flowcharts
- 33. Скачать презентацию








Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Programming Logic and Design, Seventh Edition можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























