Programming Logic and Design Seventh Edition презентация
Содержание
- 2. Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Storing data in
- 3. Objectives (continued) Searching an array for a range match Remaining within
- 4. How Arrays Occupy Computer Memory Array A series or list of
- 5. Each item has the same name and the same data type
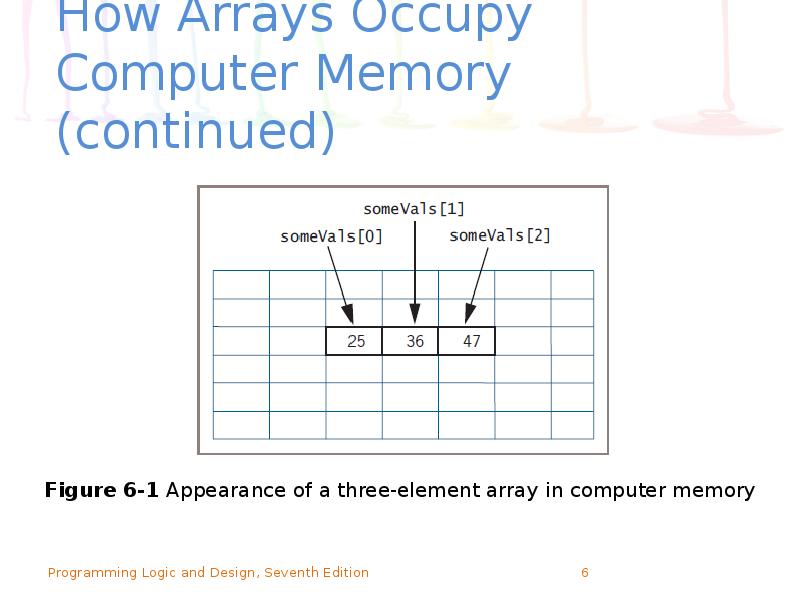
- 6. How Arrays Occupy Computer Memory (continued)
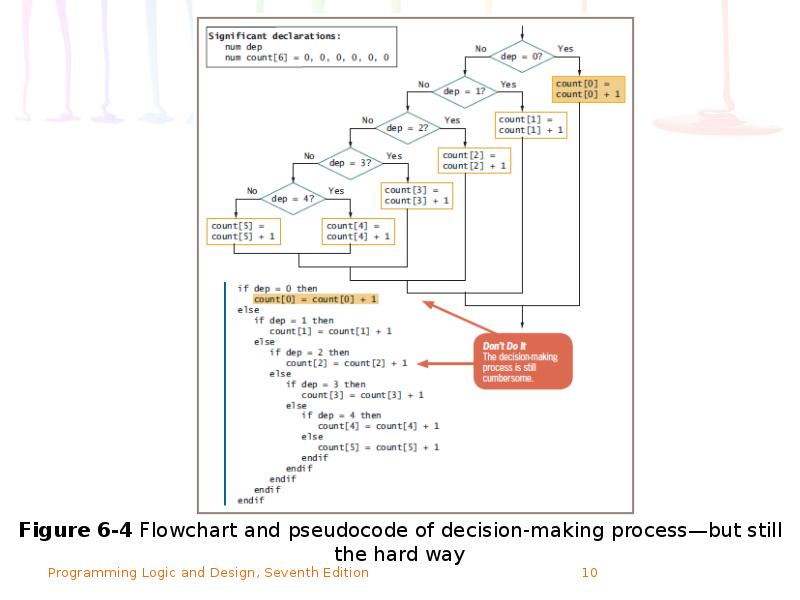
- 7. How an Array Can Replace Nested Decisions Example: Human Resources Department
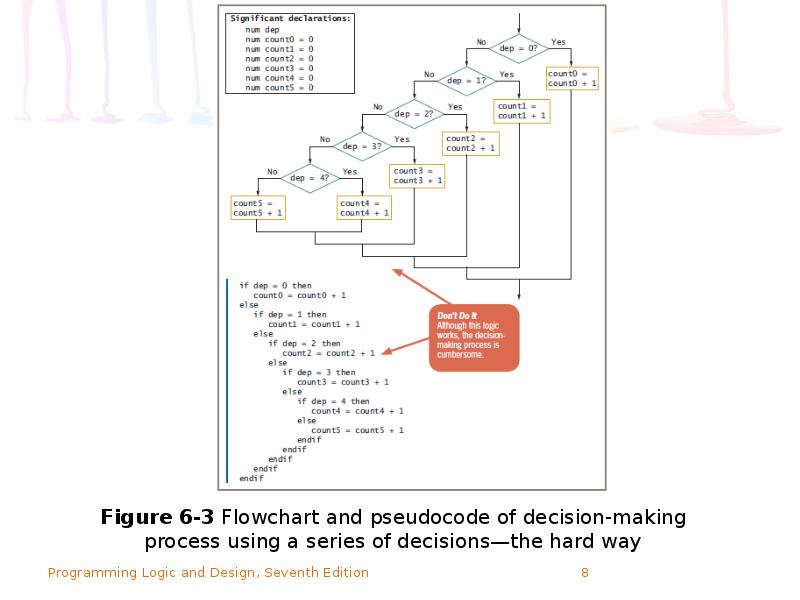
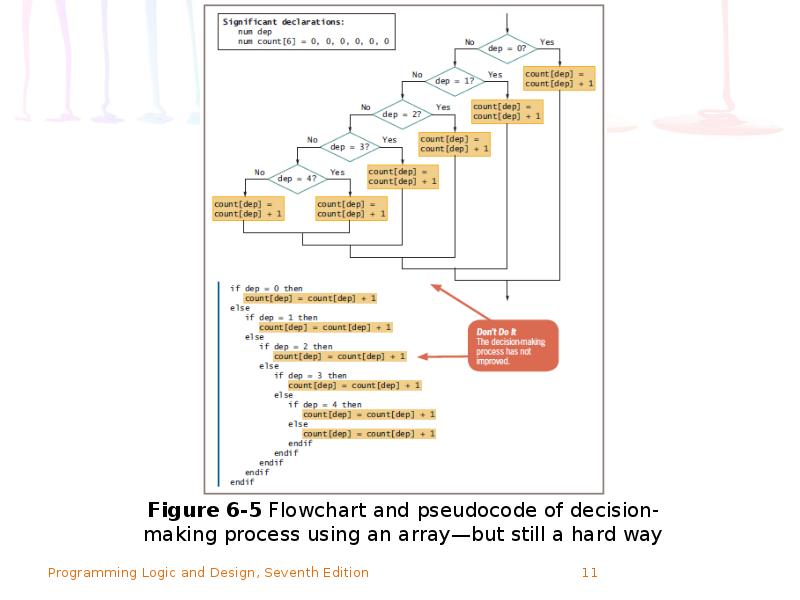
- 9. How an Array Can Replace Nested Decisions (continued) The array reduces
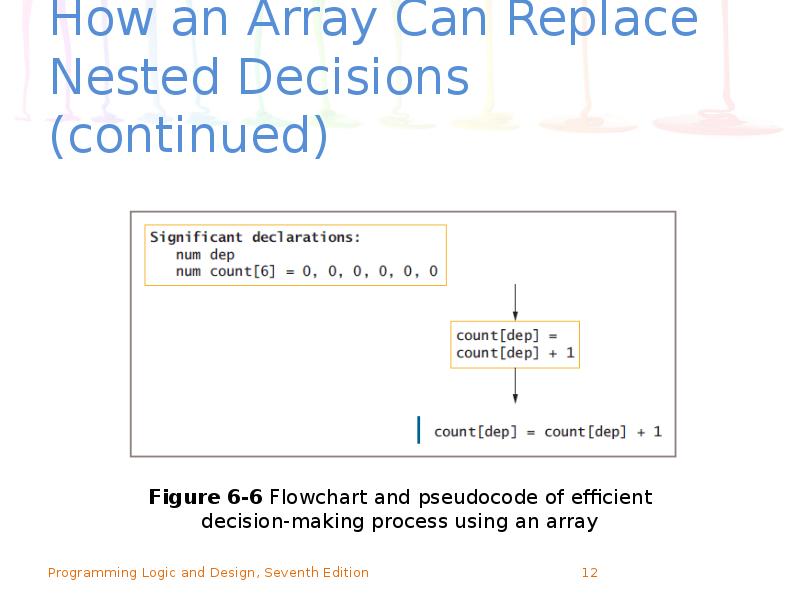
- 12. How an Array Can Replace Nested Decisions (continued)
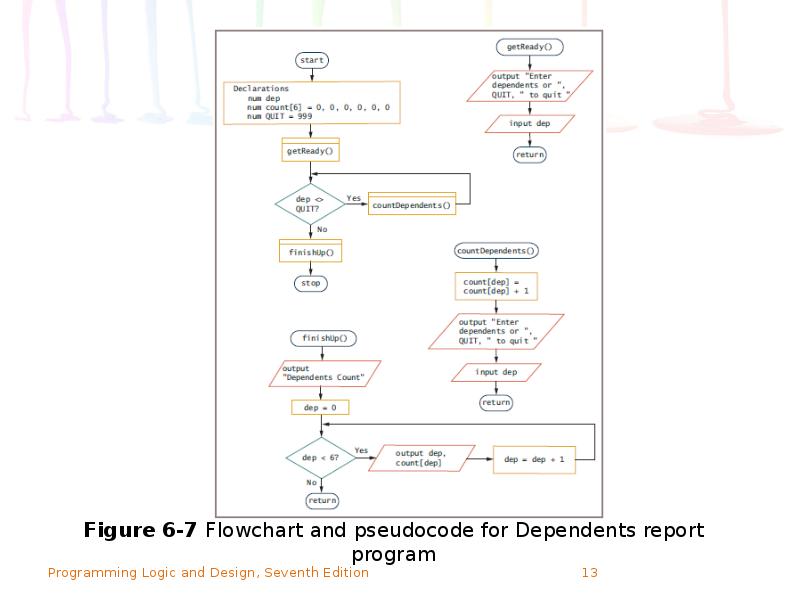
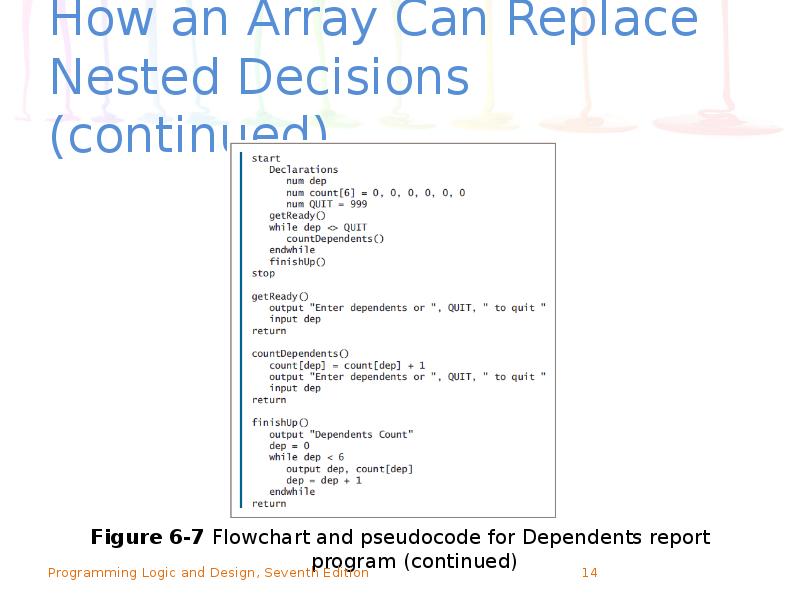
- 14. How an Array Can Replace Nested Decisions (continued) Figure 6-7 Flowchart
- 15. Using Constants with Arrays Use constants in several ways To hold
- 16. Using a Constant as the Size of an Array Avoid “magic
- 17. Using Constants as Array Element Values Sometimes the values stored in
- 18. Using a Constant as an Array Subscript Use a numeric constant
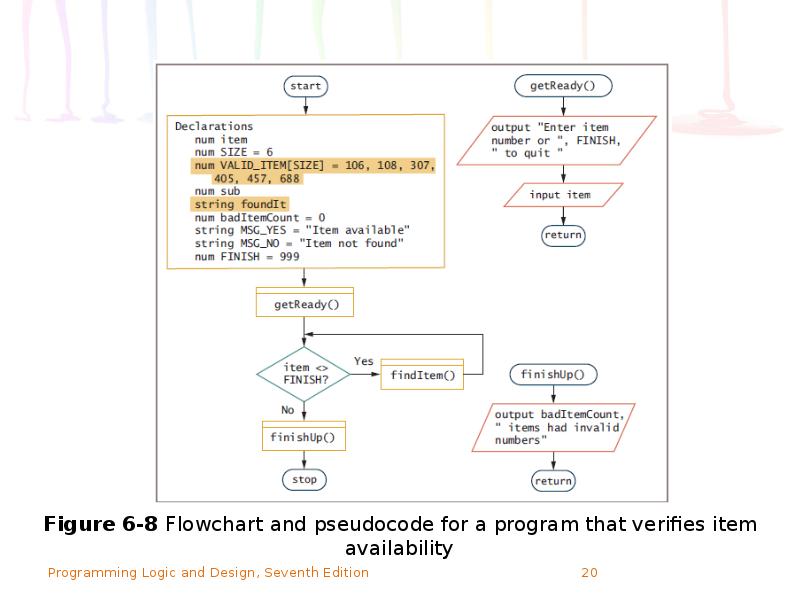
- 19. Searching an Array for an Exact Match Sometimes you must search
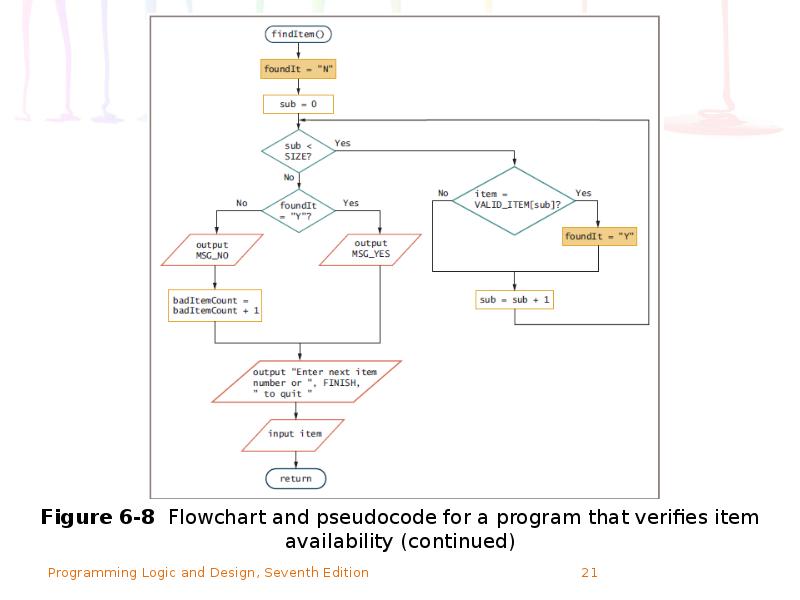
- 23. Searching an Array for an Exact Match (continued) Flag: a variable
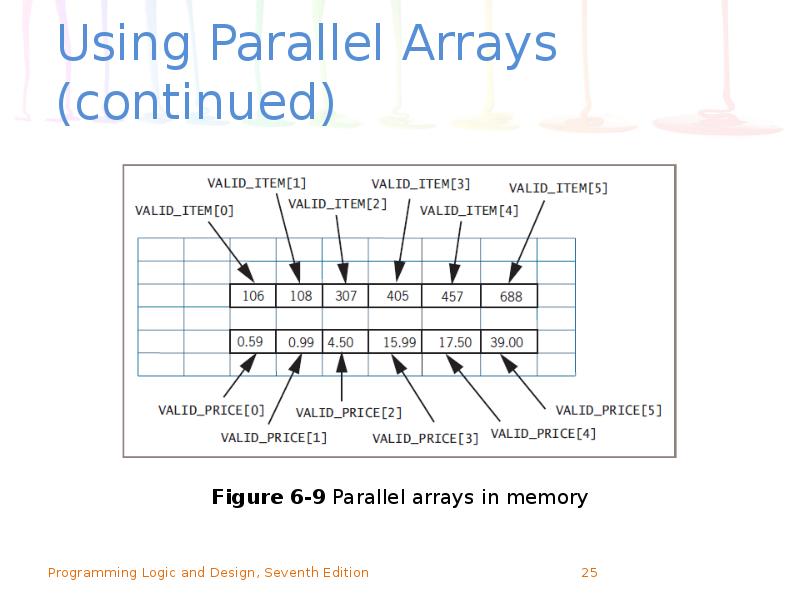
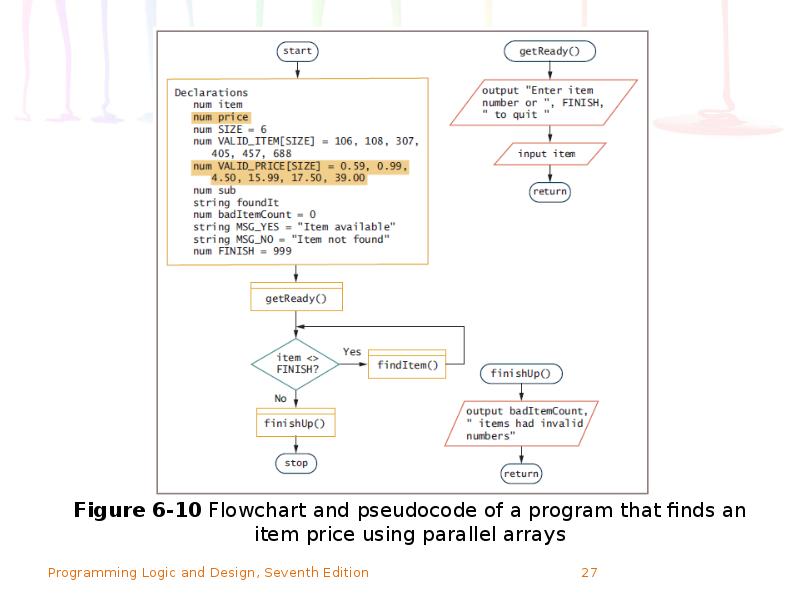
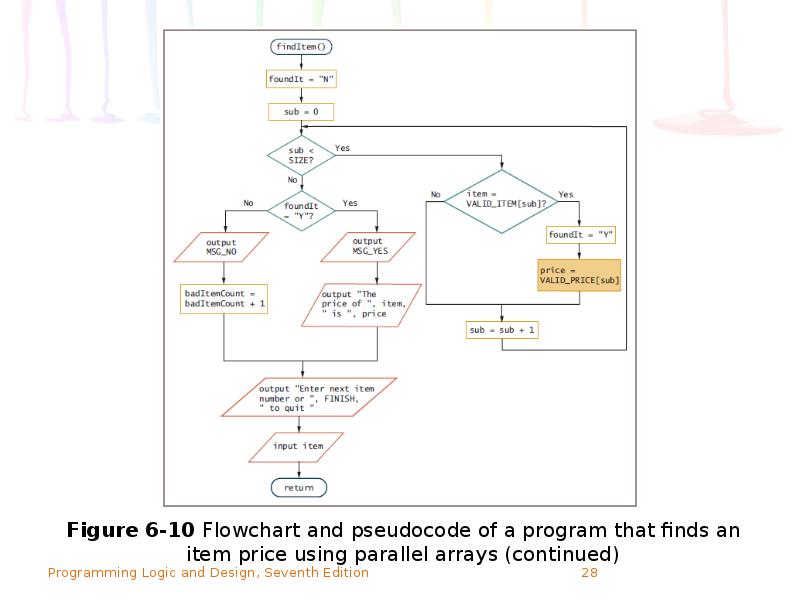
- 24. Using Parallel Arrays Example: mail-order business Two arrays, each with six
- 25. Using Parallel Arrays (continued)
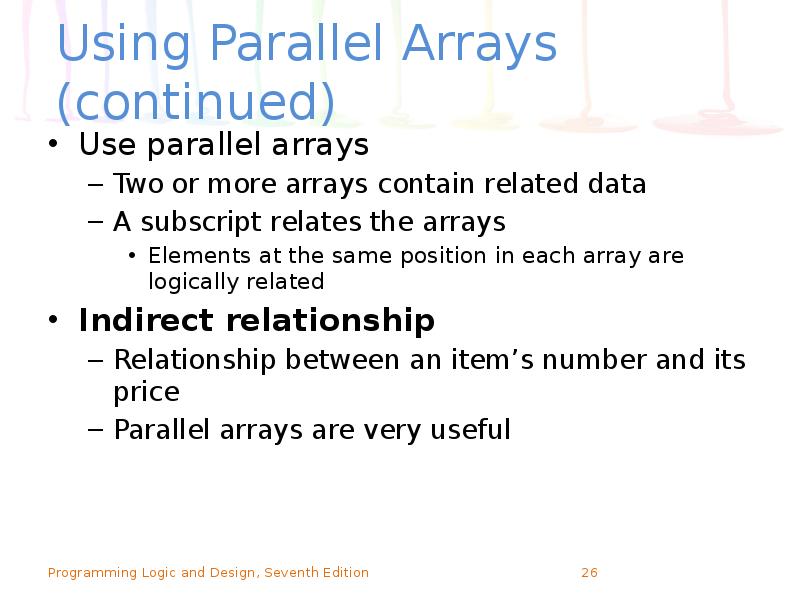
- 26. Using Parallel Arrays (continued) Use parallel arrays Two or more arrays
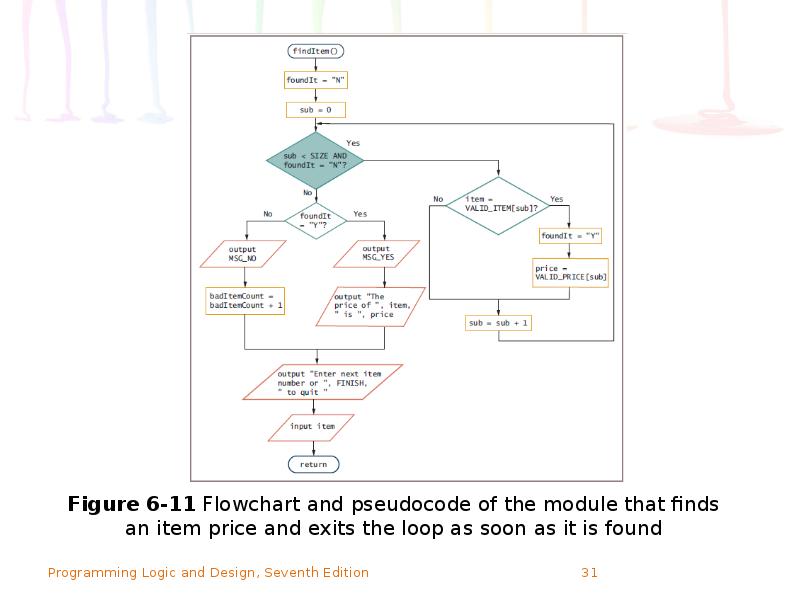
- 30. Improving Search Efficiency The program should stop searching the array when
- 32. Improving Search Efficiency (continued)
- 33. Searching an Array for a Range Match Programmers may want to
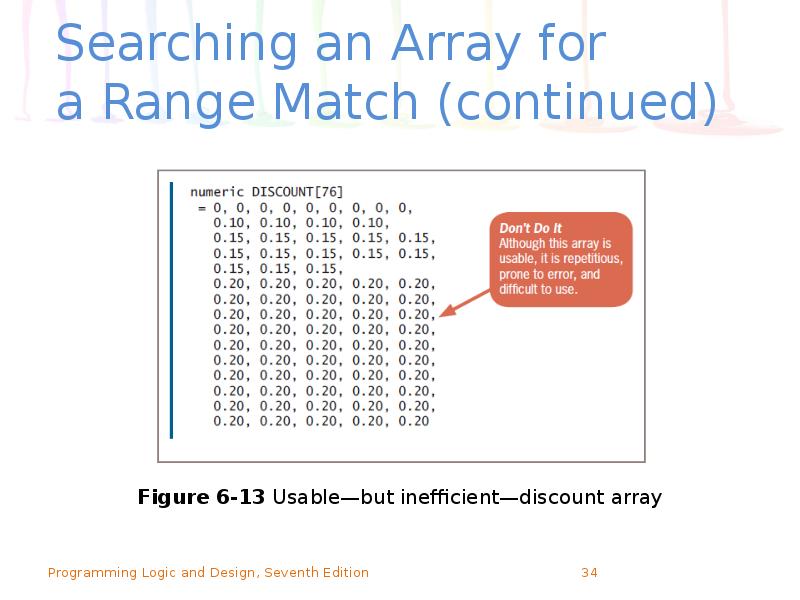
- 34. Searching an Array for a Range Match (continued)
- 35. Searching an Array for a Range Match (continued) Drawbacks of first
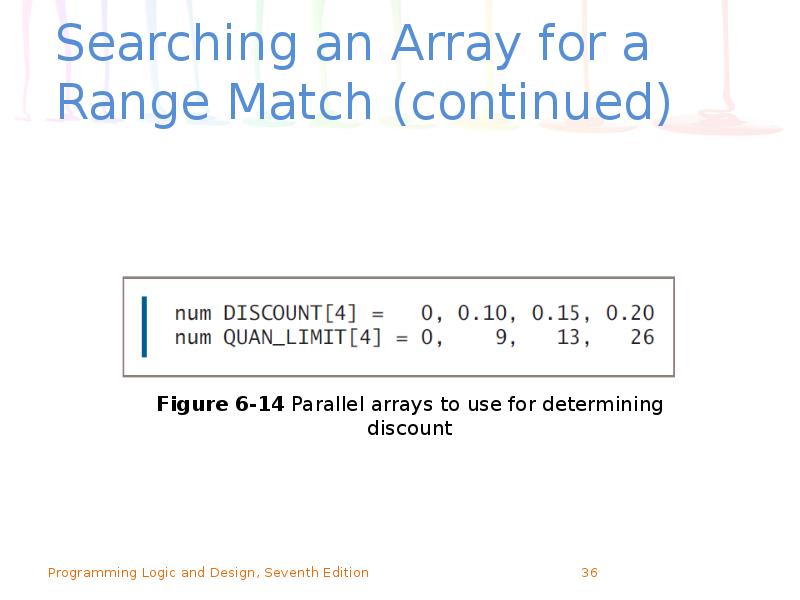
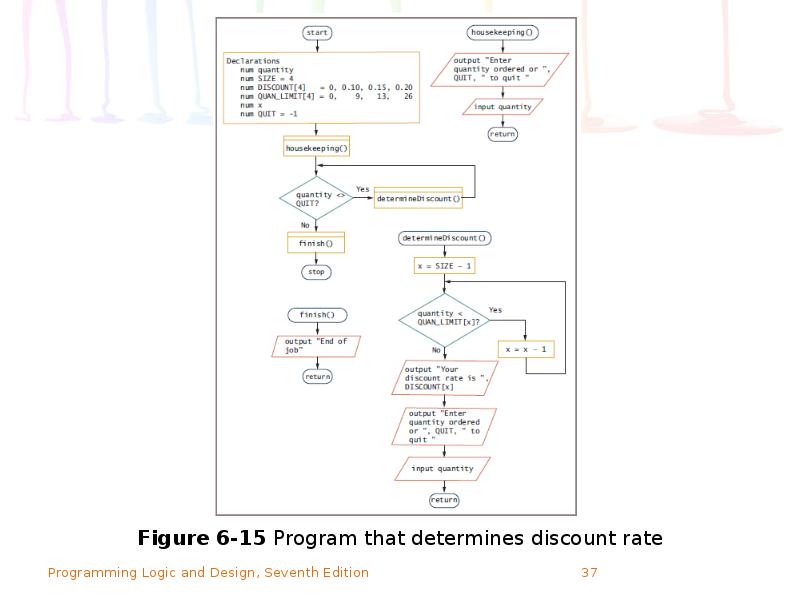
- 36. Searching an Array for a Range Match (continued)
- 38. Remaining within Array Bounds Every array has a finite size Number
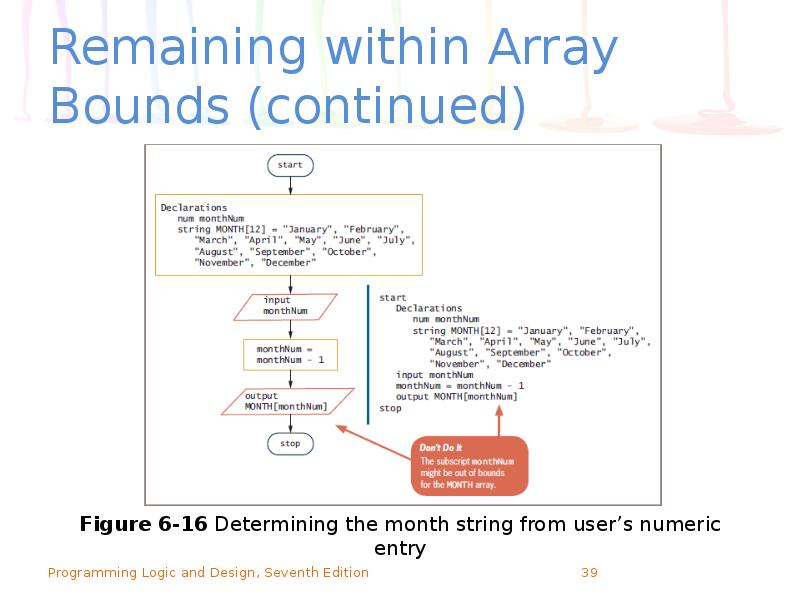
- 39. Remaining within Array Bounds (continued)
- 40. Remaining within Array Bounds (continued) Program logic assumes every number entered
- 41. Using a for Loop to Process Arrays for loop: a single
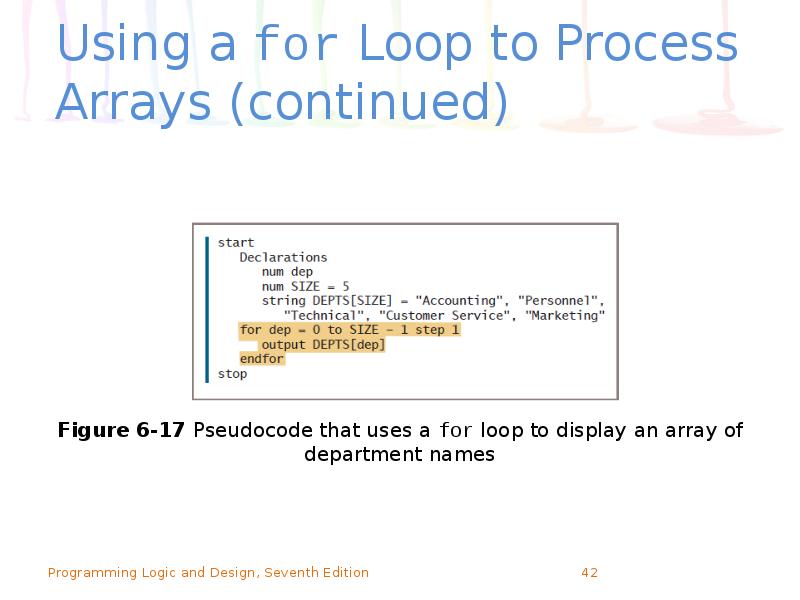
- 42. Using a for Loop to Process Arrays (continued)
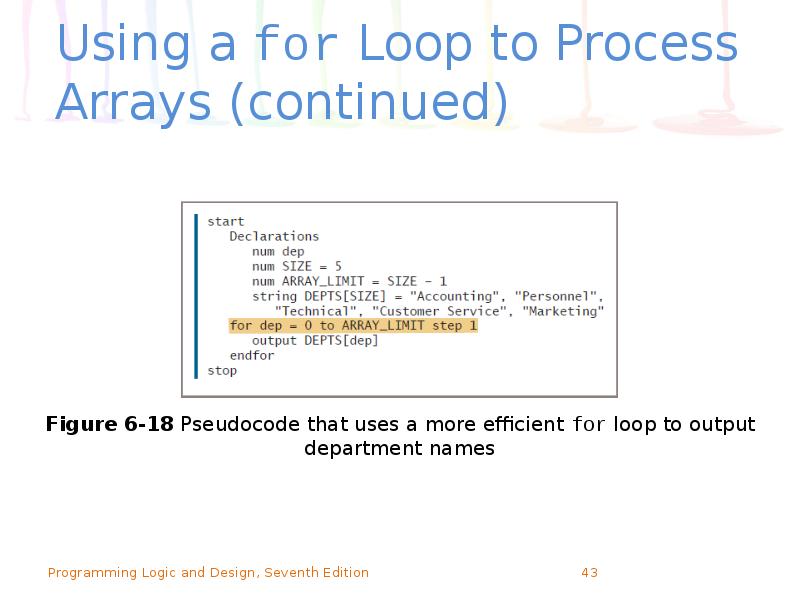
- 43. Using a for Loop to Process Arrays (continued)
- 44. Summary Array: a named series or list of values in memory
- 45. Summary (continued) Parallel arrays: each element in one array is associated
- 46. Summary (continued) Access data in an array Use a subscript containing
- 47. Скачать презентацию




















Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Programming Logic and Design Seventh Edition можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























