Programming languages презентация
Содержание
- 2. Programming Languages
- 3. Roadmap Course Schedule Programming Paradigms A Quick Tour of Programming Language
- 4. Roadmap Course Schedule Programming Paradigms A Quick Tour of Programming Language
- 5. Sources Text: Kenneth C. Louden, Programming Languages: Principles and Practice, PWS
- 6. Schedule Introduction Stack-based programming Scheme (guest lecture) Functional programming Types and
- 7. Roadmap Course Schedule Programming Paradigms A Quick Tour of Programming Language
- 8. What is a Programming Language? A formal language for describing computation?
- 9. What is a Programming Language? (II)
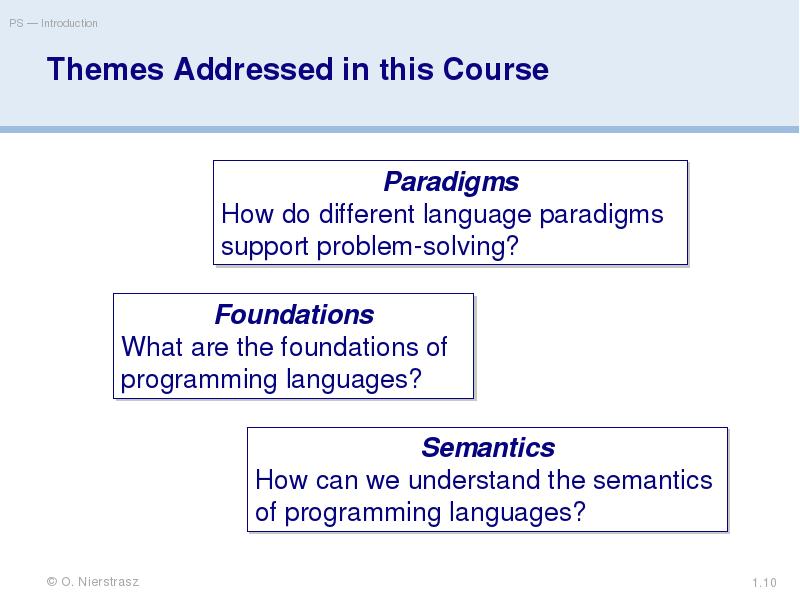
- 10. Themes Addressed in this Course
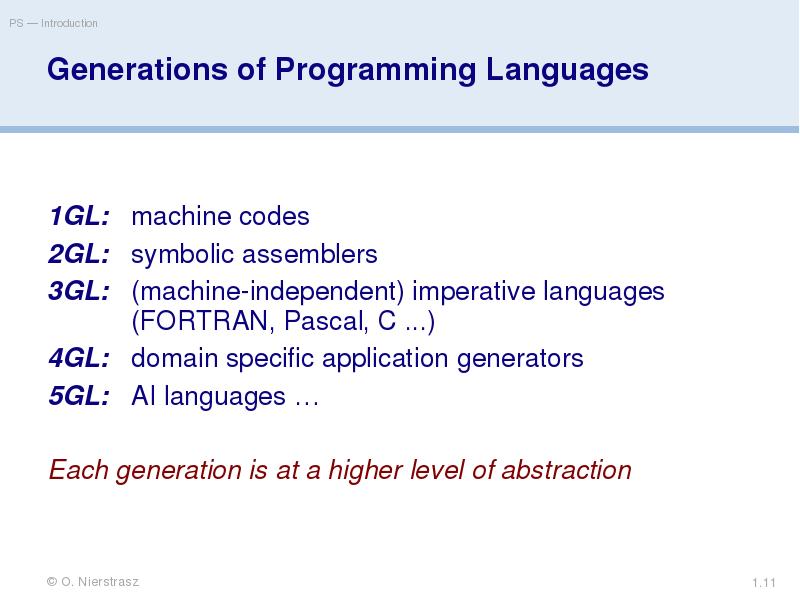
- 11. Generations of Programming Languages 1GL: machine codes 2GL: symbolic assemblers 3GL:
- 12. How do Programming Languages Differ? Common Constructs: basic data types (numbers,
- 13. Programming Paradigms
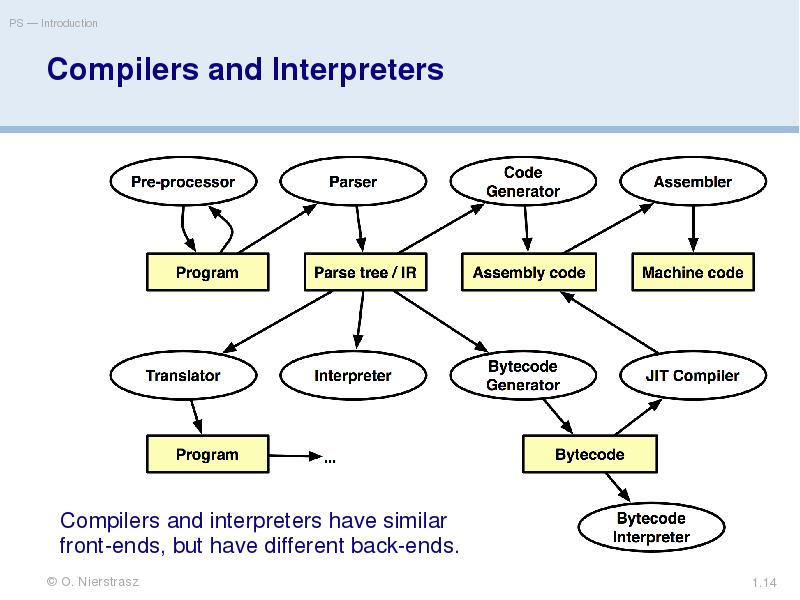
- 14. Compilers and Interpreters Compilers and interpreters have similar front-ends, but have
- 15. Roadmap Course Schedule Programming Paradigms A Quick Tour of Programming Language
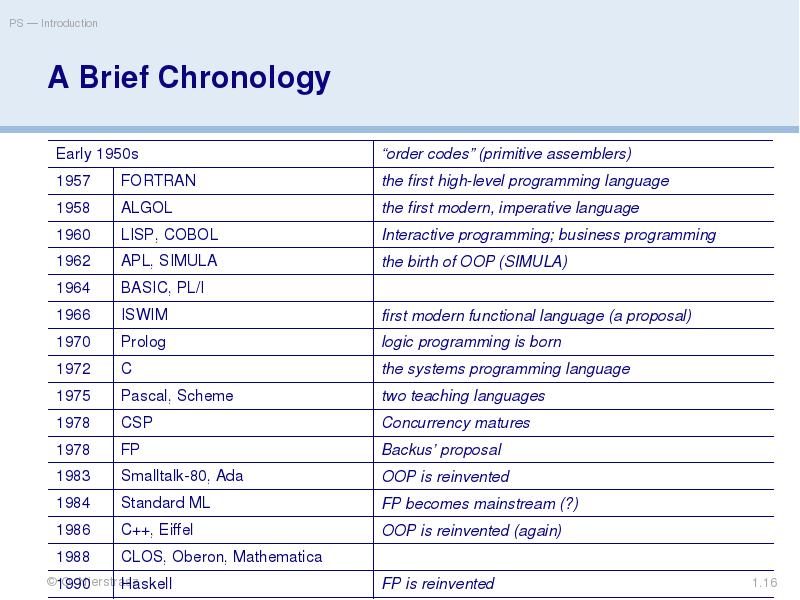
- 16. A Brief Chronology
- 17. Fortran History John Backus (1953) sought to write programs in conventional
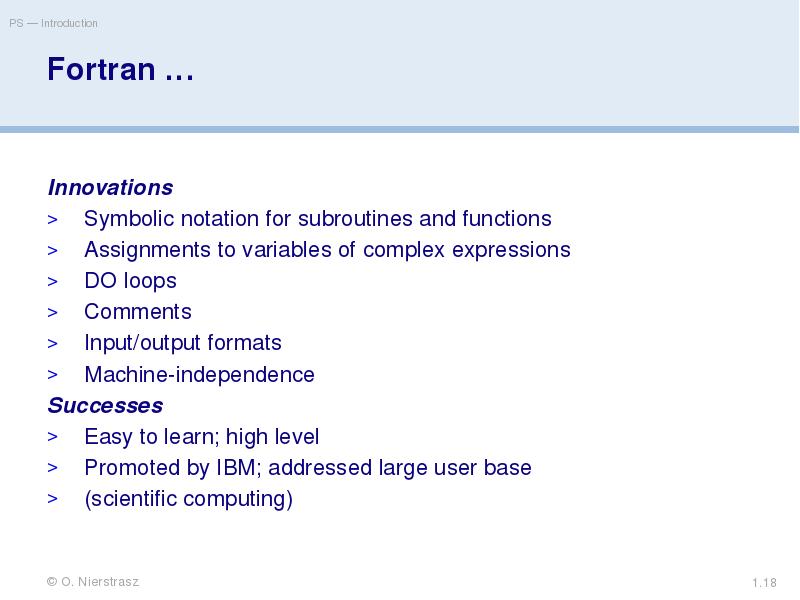
- 18. Fortran … Innovations Symbolic notation for subroutines and functions Assignments to
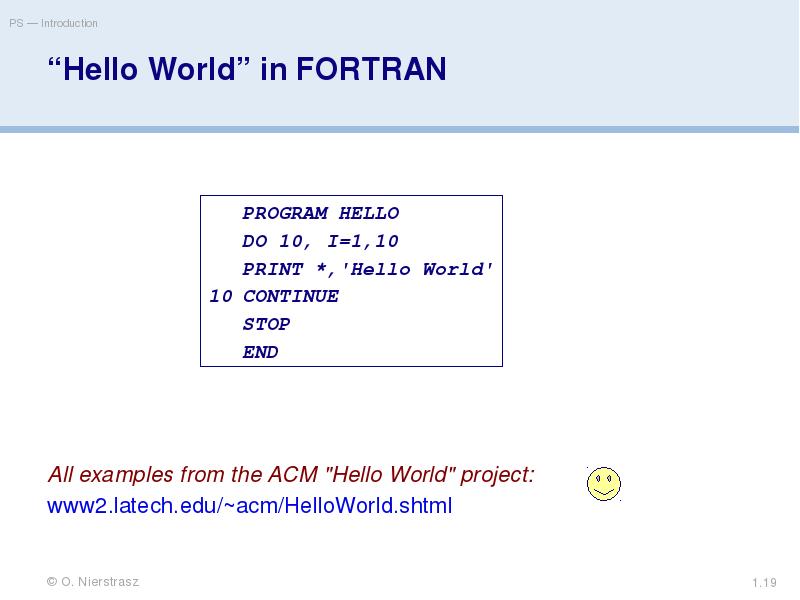
- 19. “Hello World” in FORTRAN All examples from the ACM "Hello World"
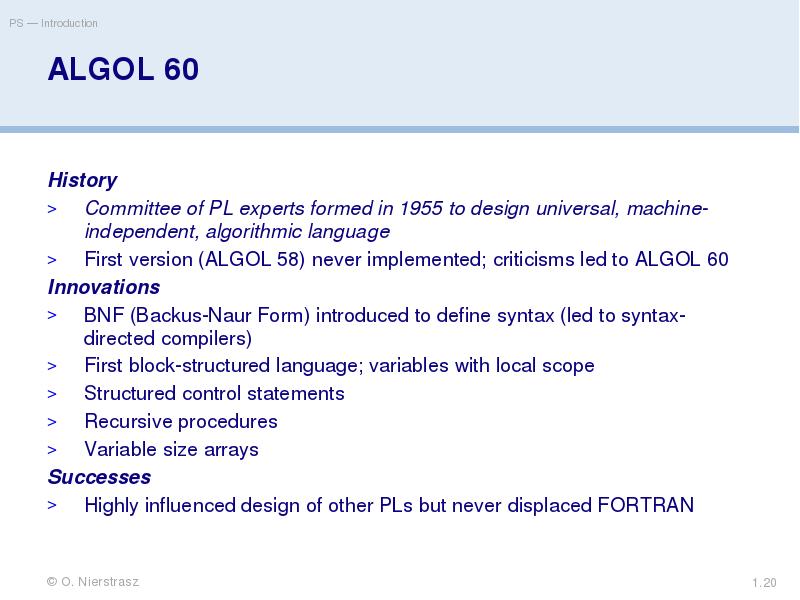
- 20. ALGOL 60 History Committee of PL experts formed in 1955 to
- 21. “Hello World” in BEALGOL
- 22. COBOL History Designed by committee of US computer manufacturers Targeted business
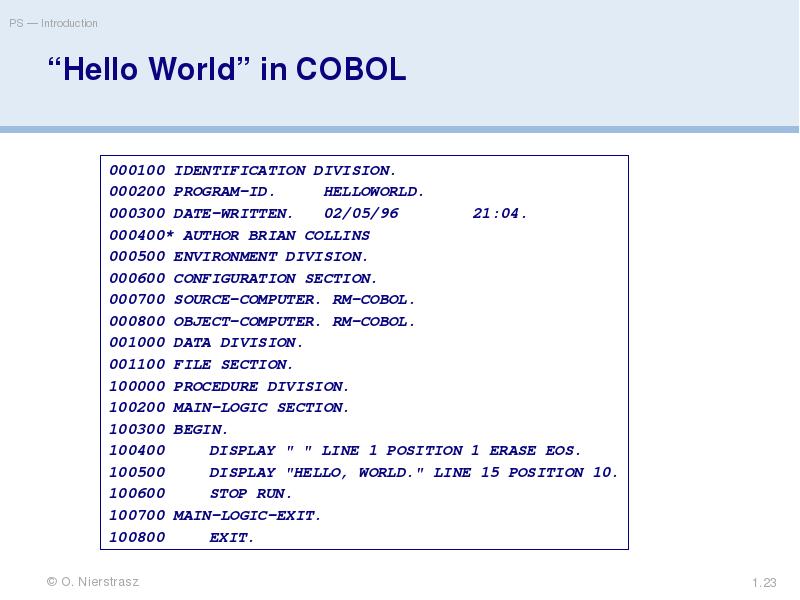
- 23. “Hello World” in COBOL
- 24. PL/1 History Designed by committee of IBM and users (early 1960s)
- 25. “Hello World” in PL/1
- 26. Functional Languages ISWIM (If you See What I Mean) Peter Landin
- 27. “Hello World” in Functional Languages SML Haskell
- 28. Prolog History Originated at U. Marseilles (early 1970s), and compilers developed
- 29. “Hello World” in Prolog
- 30. Object-Oriented Languages History Simula was developed by Nygaard and Dahl (early
- 31. Object-Oriented Languages Innovations Encapsulation of data and operations (contrast ADTs) Inheritance
- 32. Interactive Languages Made possible by advent of time-sharing systems (early 1960s
- 33. Interactive Languages ... APL Developed by Ken Iverson for concise description
- 34. Special-Purpose Languages SNOBOL First successful string manipulation language Influenced design of
- 35. Symbolic Languages ... Lisp Performs computations on symbolic expressions Symbolic expressions
- 36. 4GLs “Problem-oriented” languages PLs for “non-programmers” Very High Level (VHL) languages
- 37. “Hello World” in RPG
- 38. “Hello World” in SQL
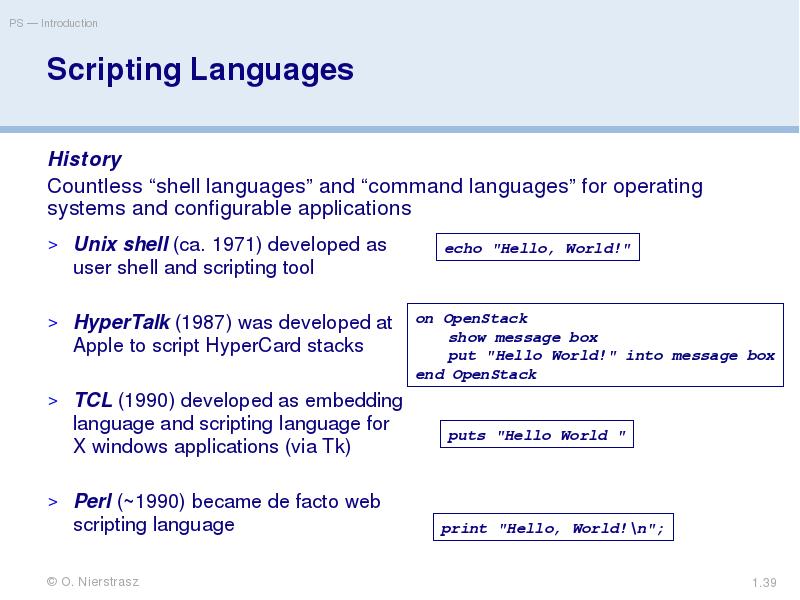
- 39. Scripting Languages History Countless “shell languages” and “command languages” for operating
- 40. Scripting Languages ... Innovations Pipes and filters (Unix shell) Generalized embedding/command
- 41. The future? Dynamic languages very active Domain-specific languages very active Visual
- 42. What you should know! What, exactly, is a programming language? How
- 43. Can you answer these questions? Why are there so many programming
- 44. License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
- 45. Скачать презентацию


































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























