Programming paradigms презентация
Содержание
- 2. Specifying the WHAT Describe the Inputs Specific values Properties Describe the
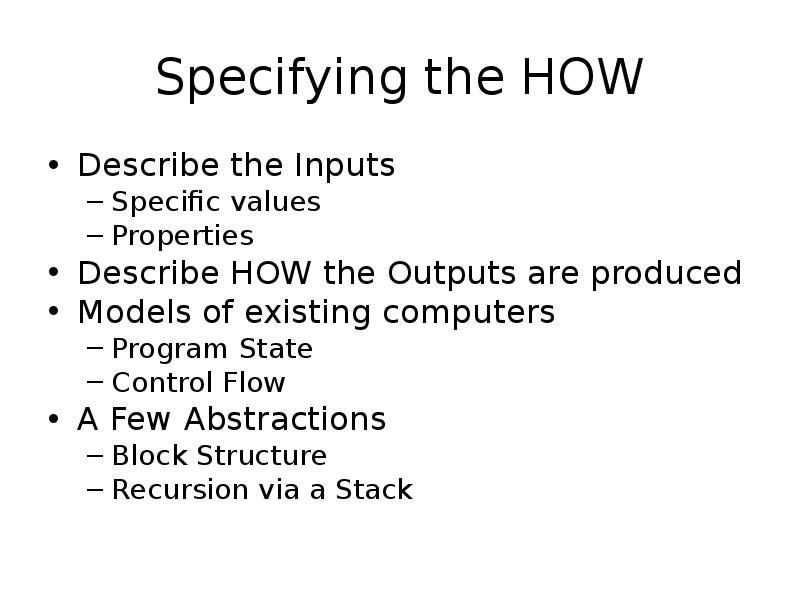
- 3. Specifying the HOW Describe the Inputs Specific values Properties Describe HOW
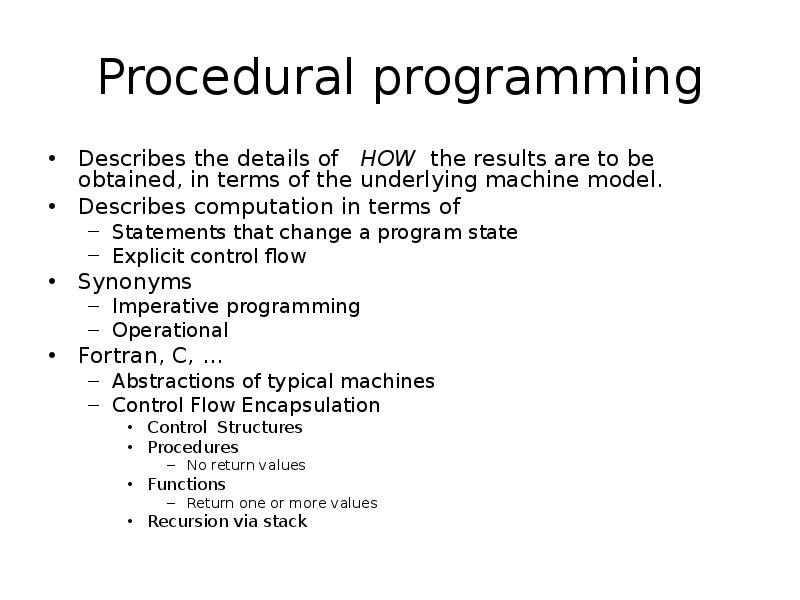
- 4. Procedural programming Describes the details of HOW the results are to
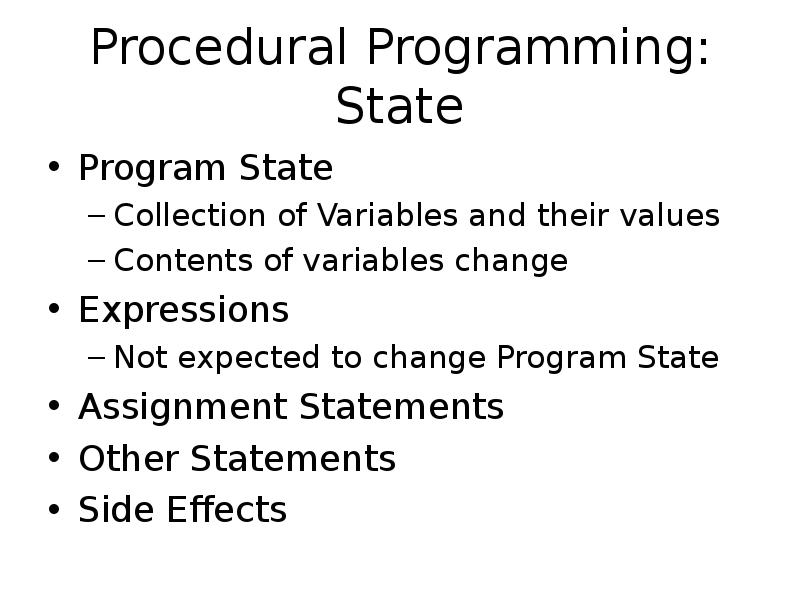
- 5. Procedural Programming: State Program State Collection of Variables and their values
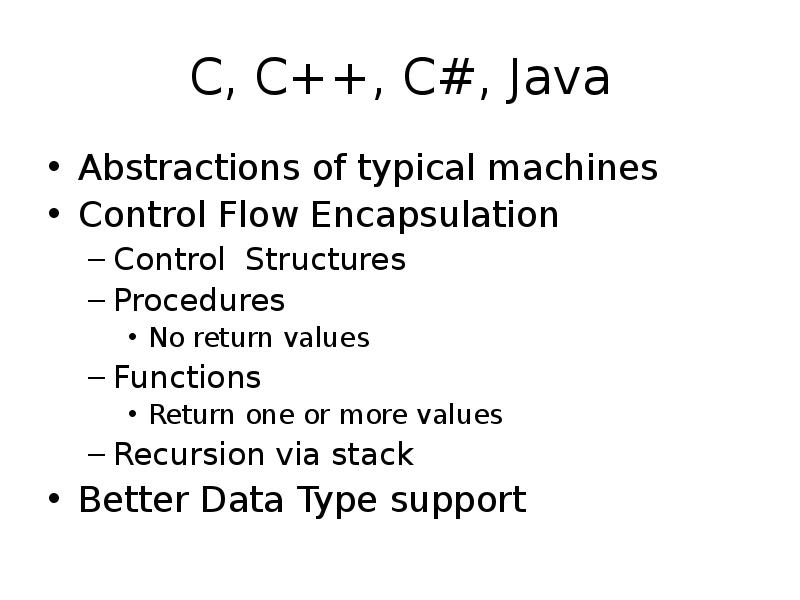
- 6. C, C++, C#, Java Abstractions of typical machines Control Flow Encapsulation
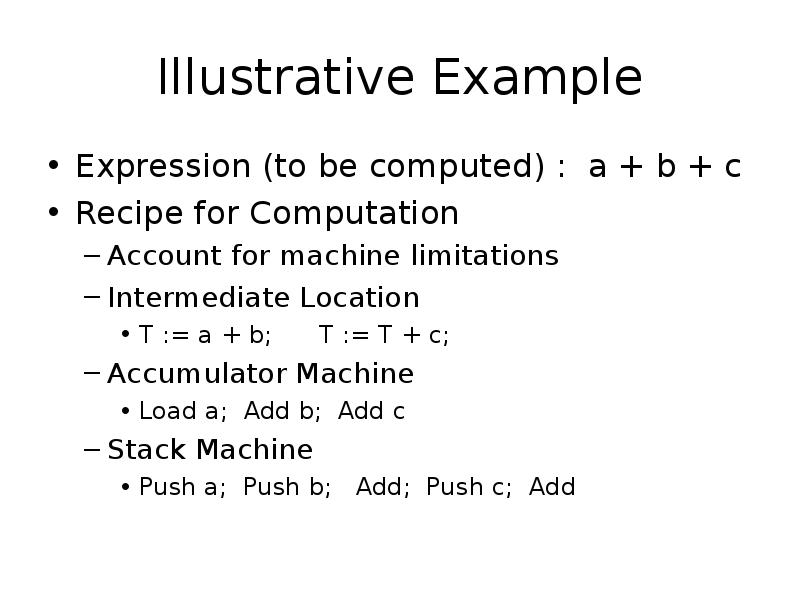
- 7. Illustrative Example Expression (to be computed) : a + b +
- 8. Declarative Programming Specifies WHAT is to be computed abstractly Expresses the
- 9. Imperative vs Non-Imperative Functional/Logic style clearly separates WHAT aspects of a
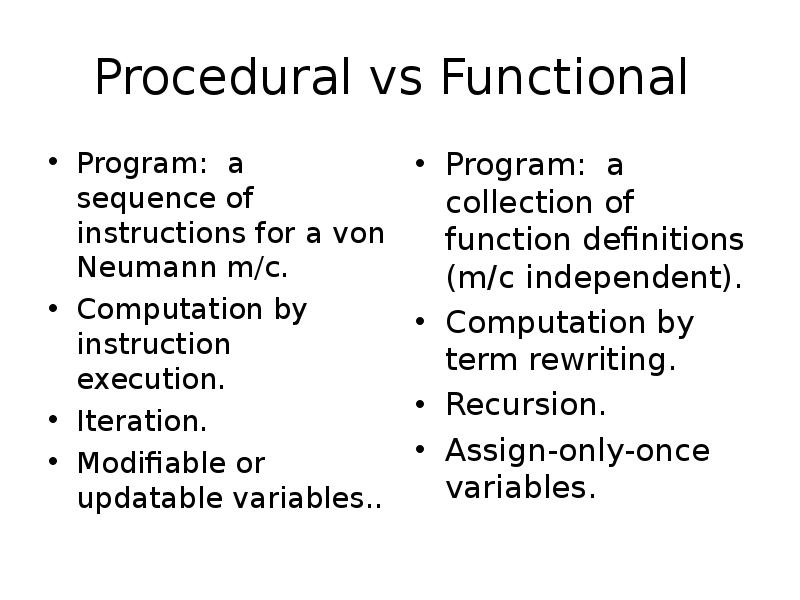
- 10. Procedural vs Functional Program: a sequence of instructions for a
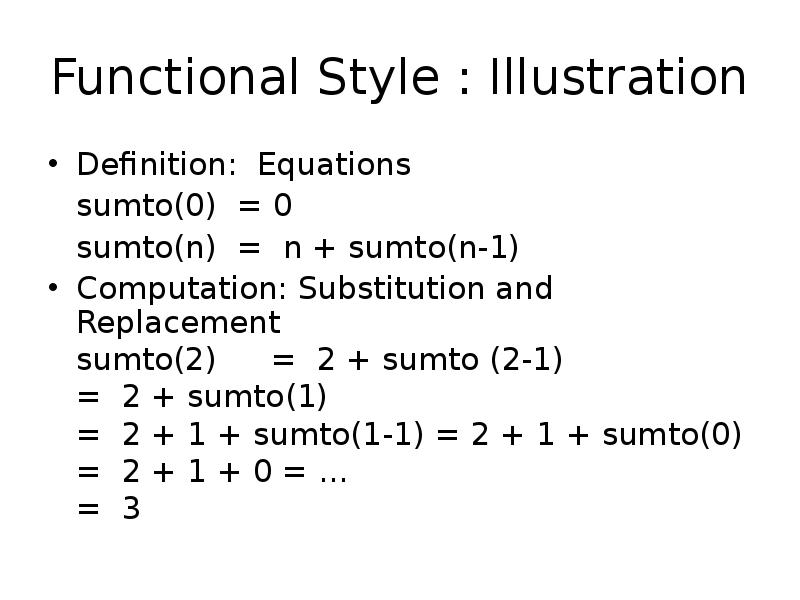
- 11. Functional Style : Illustration Definition: Equations sumto(0) = 0 sumto(n)
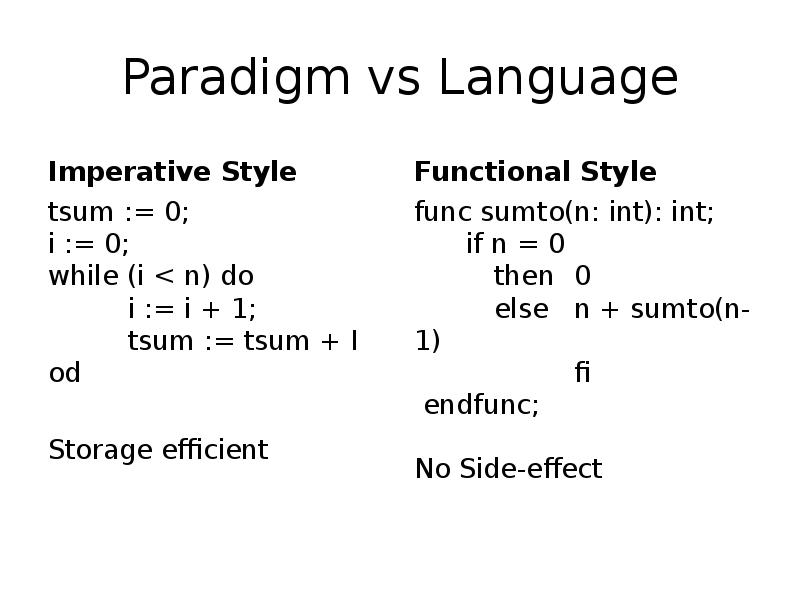
- 12. Paradigm vs Language Imperative Style
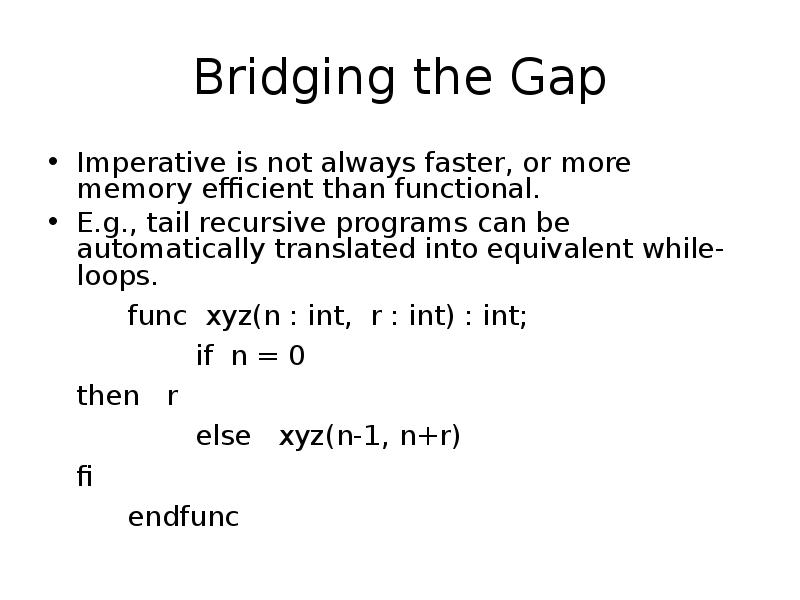
- 13. Bridging the Gap Imperative is not always faster, or more memory
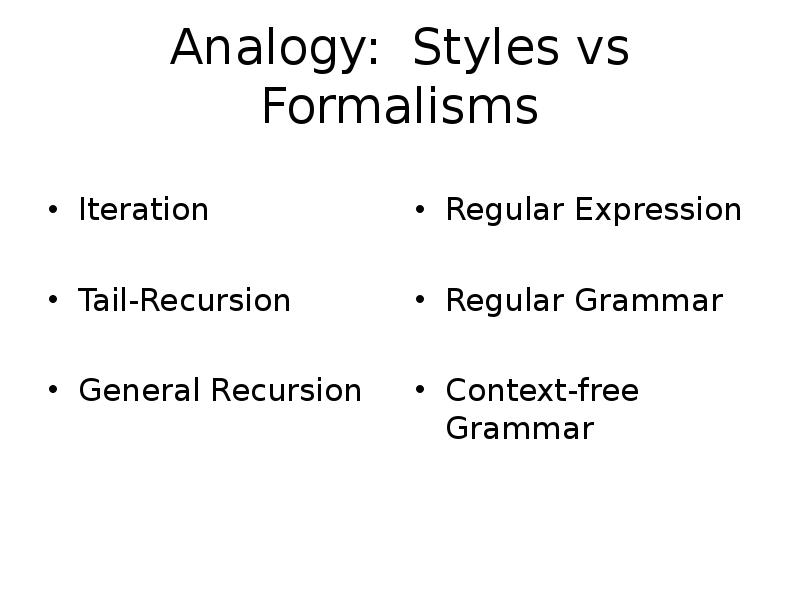
- 14. Analogy: Styles vs Formalisms Iteration Tail-Recursion General Recursion
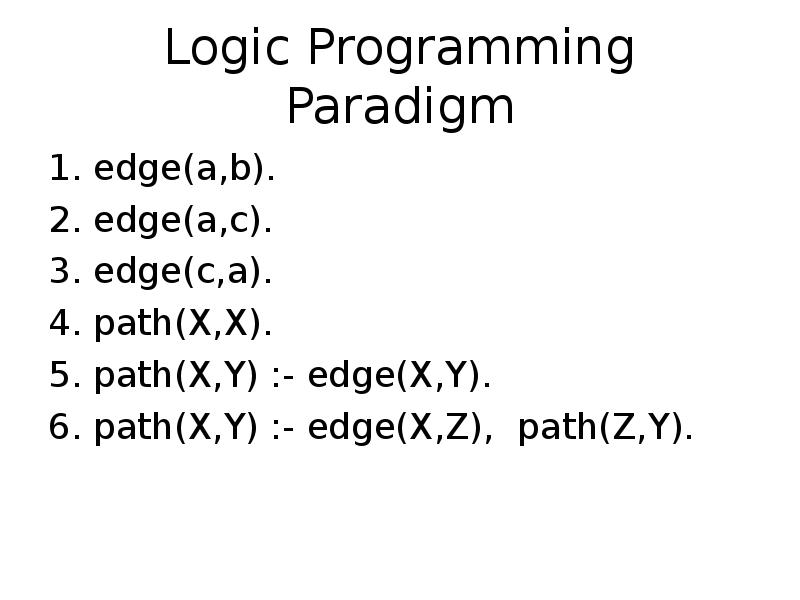
- 15. Logic Programming Paradigm edge(a,b). edge(a,c). edge(c,a). path(X,X). path(X,Y) :- edge(X,Y). path(X,Y)
- 16. Logic Programming A logic program defines a set of relations.
- 17. Append in Prolog append([], L, L). append([ H | T ],
- 18. Different Kinds of Queries Verification append: list x list x list
- 19. More Queries Constraint solving append: list x list -> list
- 20. Object-Oriented Style Programming with Abstract Data Types ADTs specify/describe behaviors. Basic
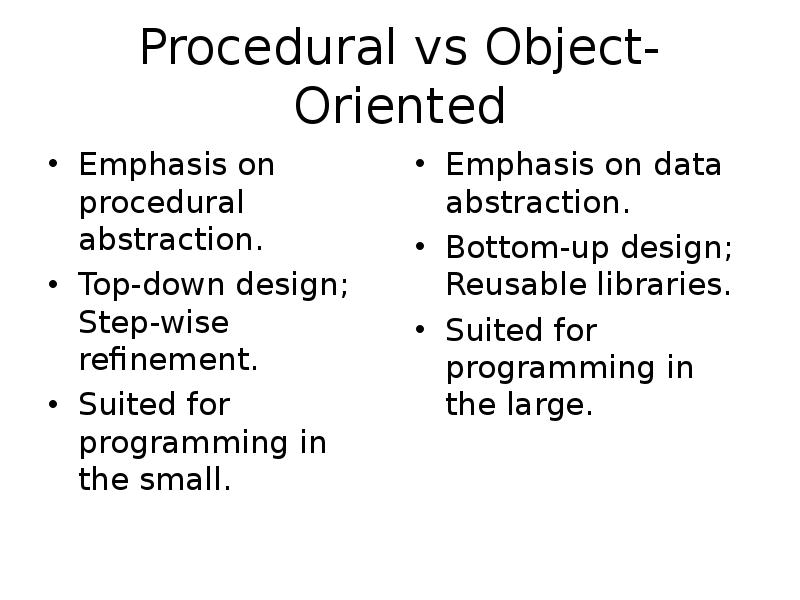
- 21. Procedural vs Object-Oriented Emphasis on procedural abstraction. Top-down design; Step-wise refinement.
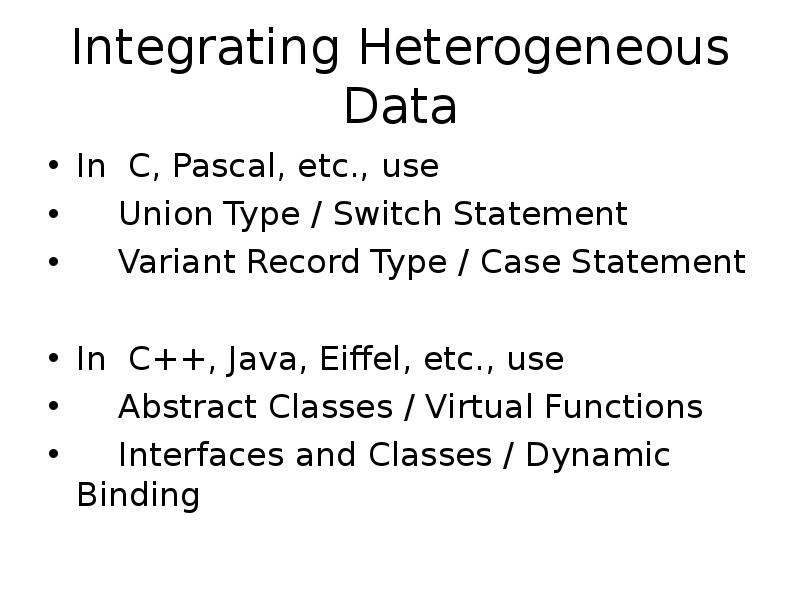
- 22. Integrating Heterogeneous Data In C, Pascal, etc., use Union Type
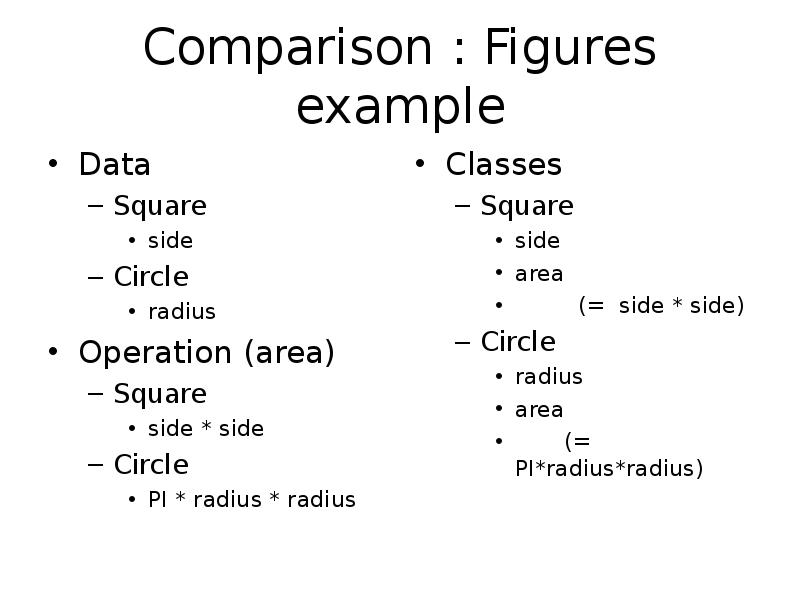
- 23. Comparison : Figures example Data Square side Circle radius Operation (area)
- 24. Adding a new operation Data ... Operation (area) Operation
- 25. Adding a new data representation
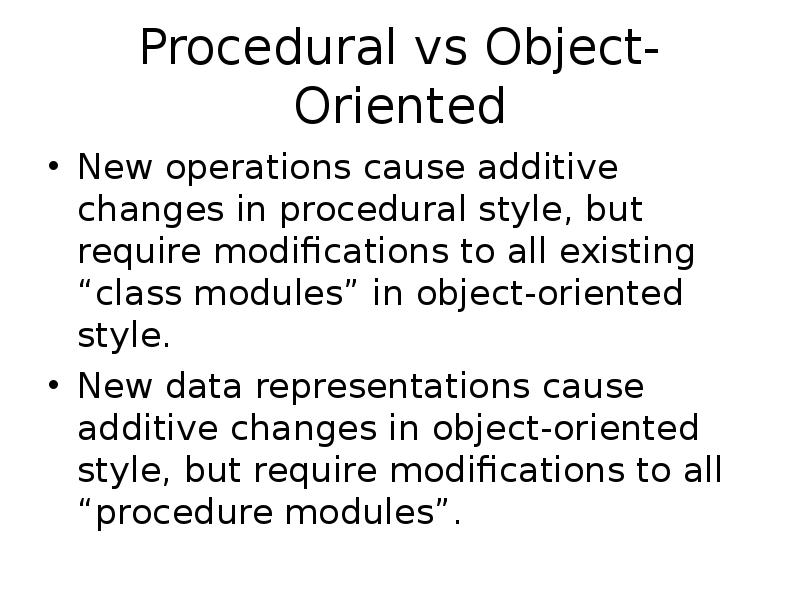
- 26. Procedural vs Object-Oriented New operations cause additive changes in procedural style,
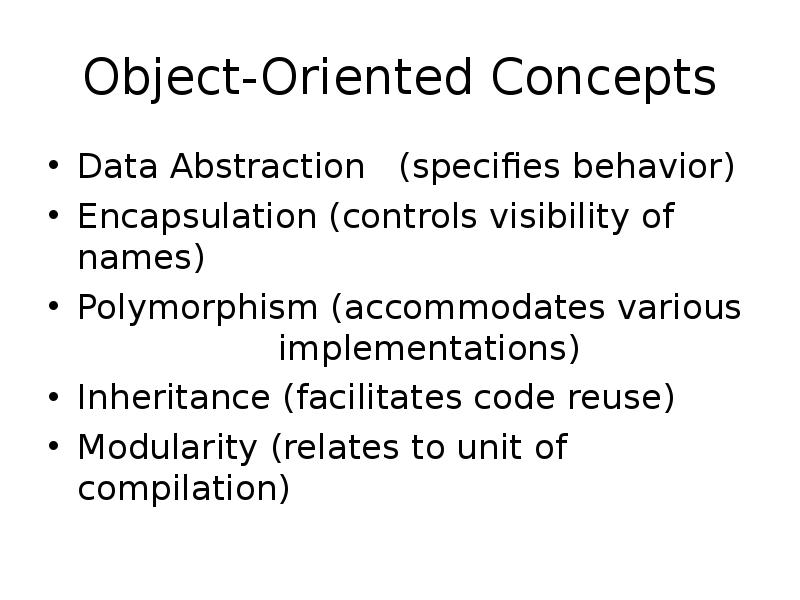
- 27. Object-Oriented Concepts Data Abstraction (specifies behavior) Encapsulation (controls visibility of names)
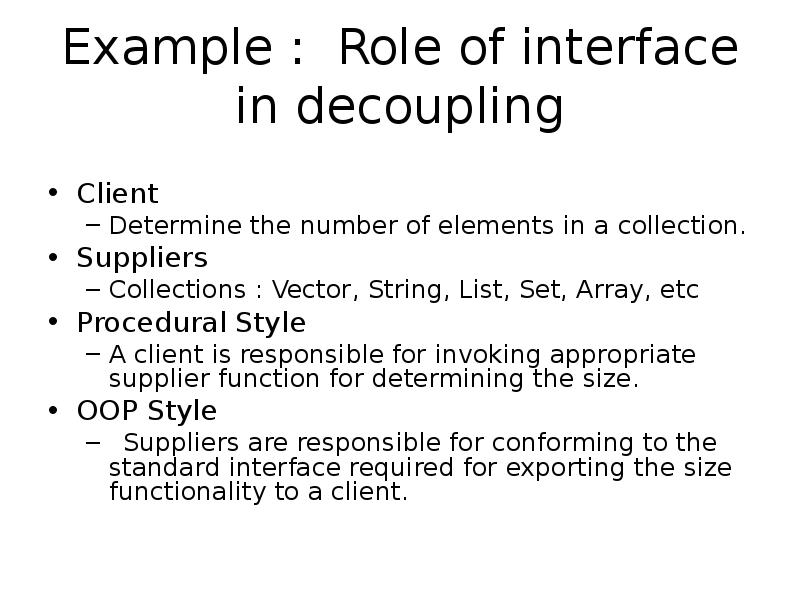
- 28. Example : Role of interface in decoupling Client Determine the number
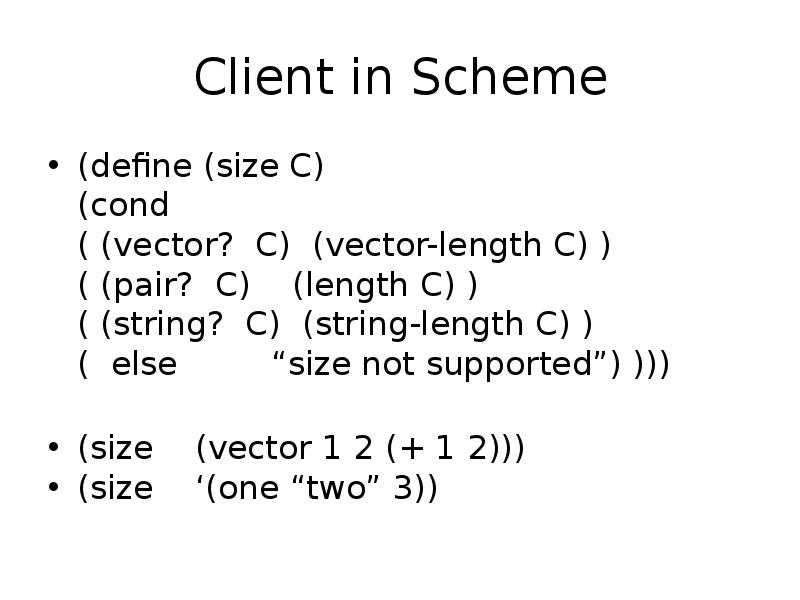
- 29. Client in Scheme (define (size C) (cond ( (vector?
- 30. Suppliers and Client in Java Interface Collection {int size(); } class
- 31. Скачать презентацию





![Append in Prolog
append([], L, L).
append([ H | T ], Append in Prolog
append([], L, L).
append([ H | T ],](/documents_3/748335ab45bc6ee6339916887663ce43/img16.jpg)






Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























