Troubleshooting JavaScript сode. (Module 6) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Agenda Exception Handling Debugging Code in Browser Using Console API Useful
- 3. Exception Handling
- 4. Errors are Natural Any software solution faces errors: invalid user input,
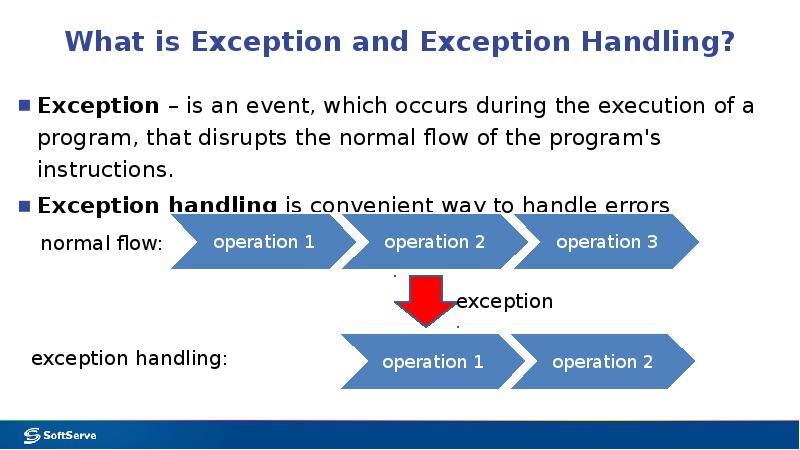
- 5. What is Exception and Exception Handling? Exception – is an event,
- 6. Exception Syntax To make exception handling possible we should use two
- 7. Throwing Exceptions To raise an exception we use throw keyword. Throwing
- 8. Exception Handling Sample In a sample below we ask the user
- 9. Using finally keyword Keyword finally is used in try..catch construction to
- 10. Method .onerror() Method window.onerror() called each time when unhandled exception occurs.
- 11. Sample .onerror() handler In a sample below we assign .onerror() event
- 12. Debugging Code in Browser
- 13. What is Debugging?
- 14. Using Developers Tools Press F12 to access Developers Tools in most
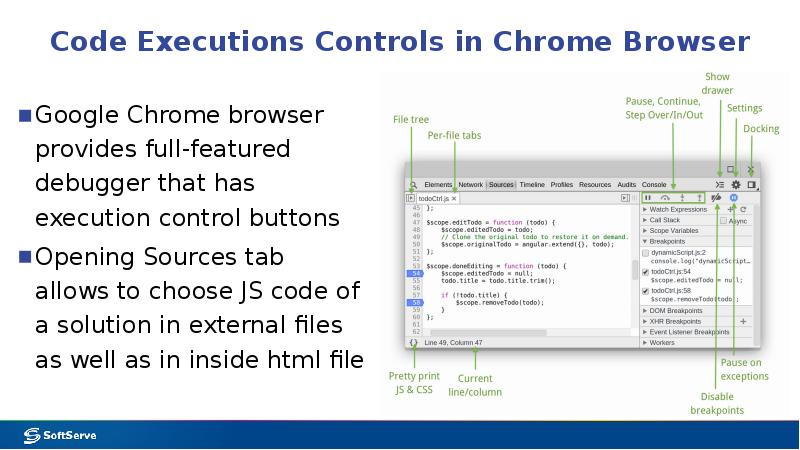
- 15. Code Executions Controls in Chrome Browser Google Chrome browser provides full-featured
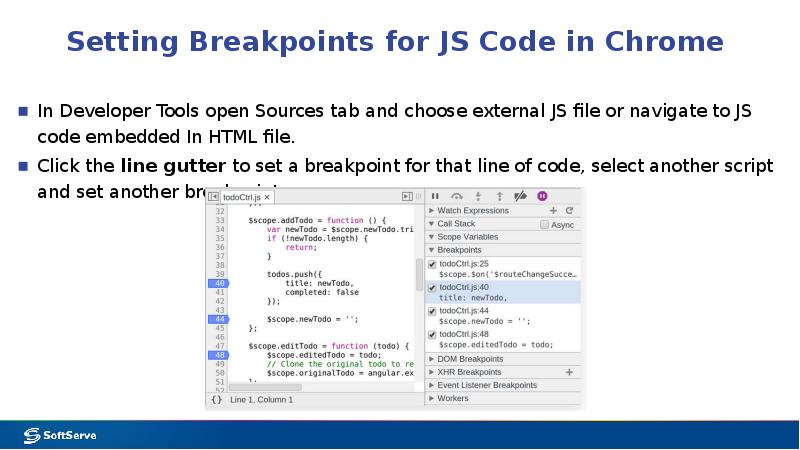
- 16. Setting Breakpoints for JS Code in Chrome In Developer Tools
- 17. Execution Control Buttons in Chrome Continue: continues code execution to another breakpoint.
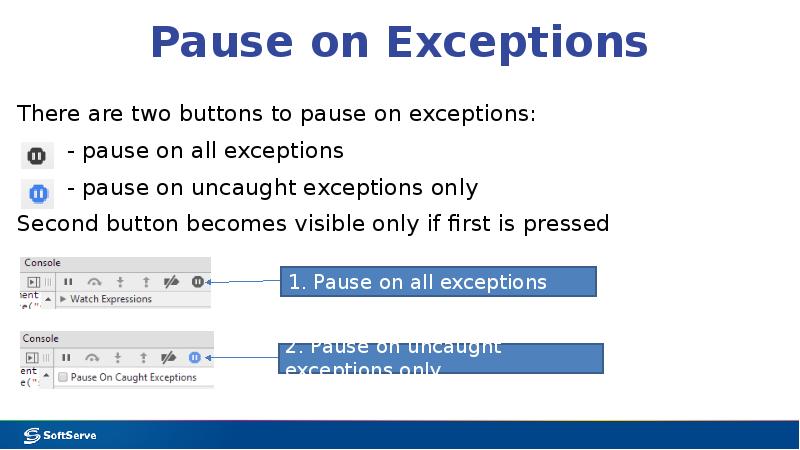
- 18. Pause on Exceptions There are two buttons to pause on exceptions:
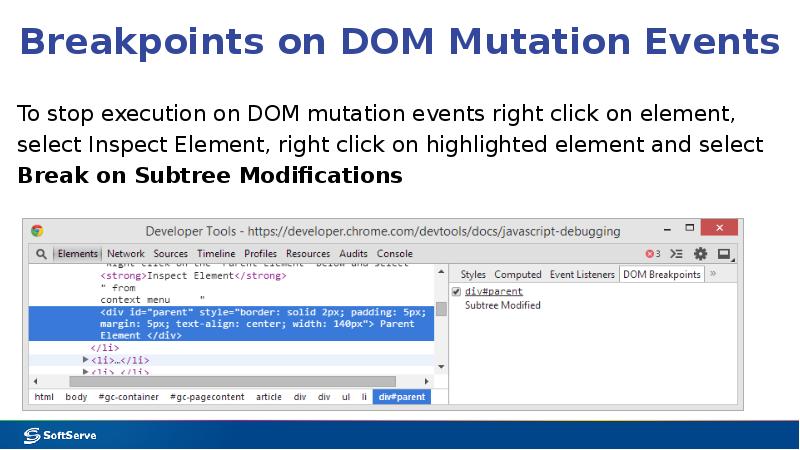
- 19. Breakpoints on DOM Mutation Events To stop execution on DOM mutation
- 20. Breakpoints on XMLHttpRequest Events XMLHttpRequest object is used to make Ajax
- 21. Breakpoints on JavaScript Event Listeners To set breakpoint on Event Listeners:
- 22. Using Console API
- 23. Console object The console object provides access to the browser's debugging
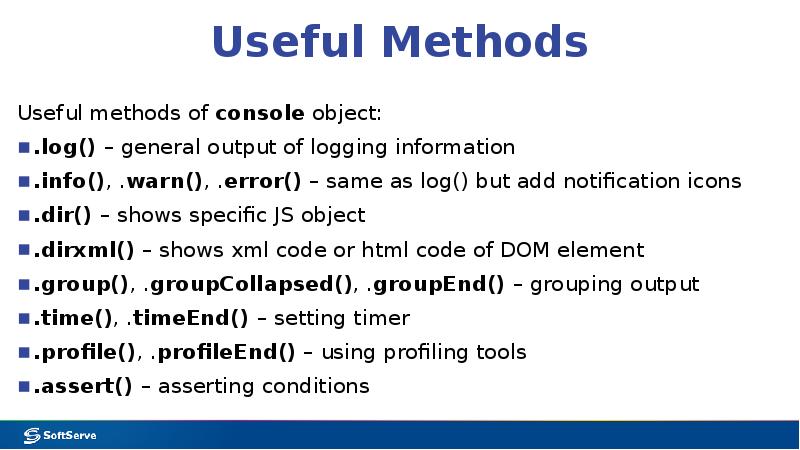
- 24. Useful Methods Useful methods of console object: .log() – general output
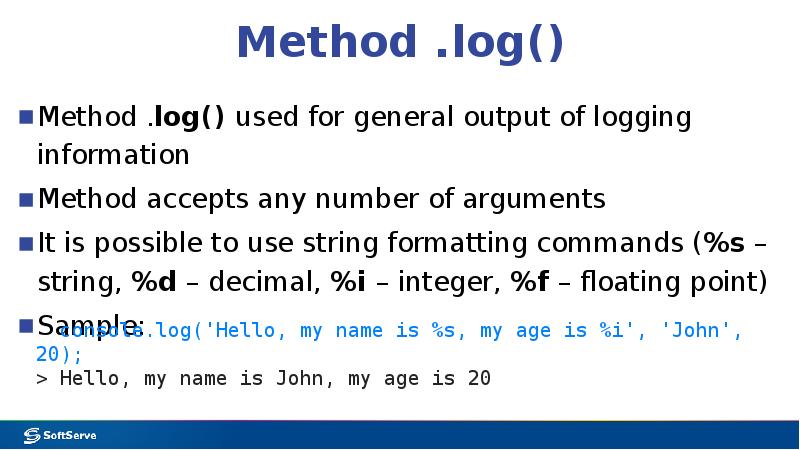
- 25. Method .log() Method .log() used for general output of logging information
- 26. Methods .info(), .warn(), .error() Methods .info(), .warn(), .error() act almost
- 27. Methods .dirxml() and .dir() Method .dirxml() – shows xml code or
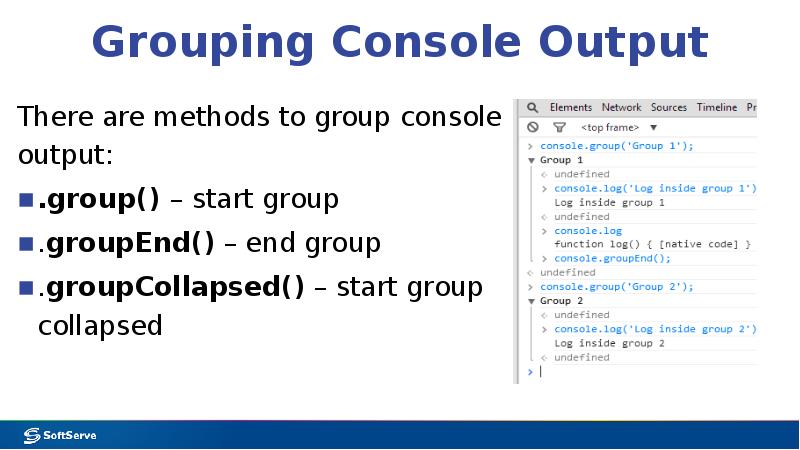
- 28. Grouping Console Output There are methods to group console output: .group()
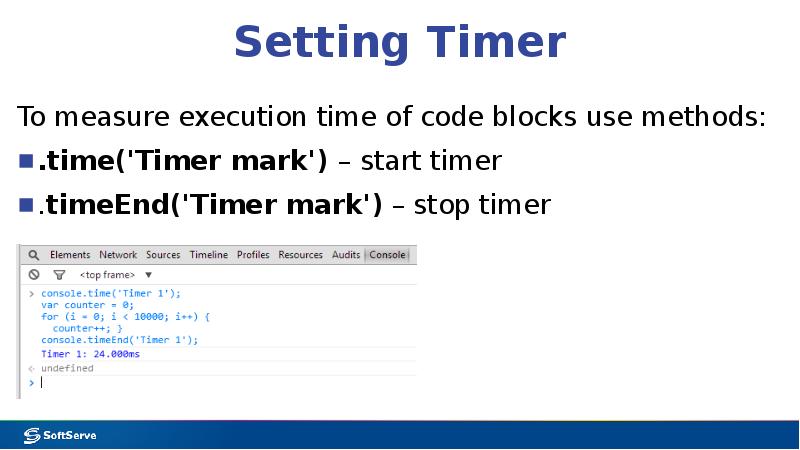
- 29. Setting Timer To measure execution time of code blocks use methods:
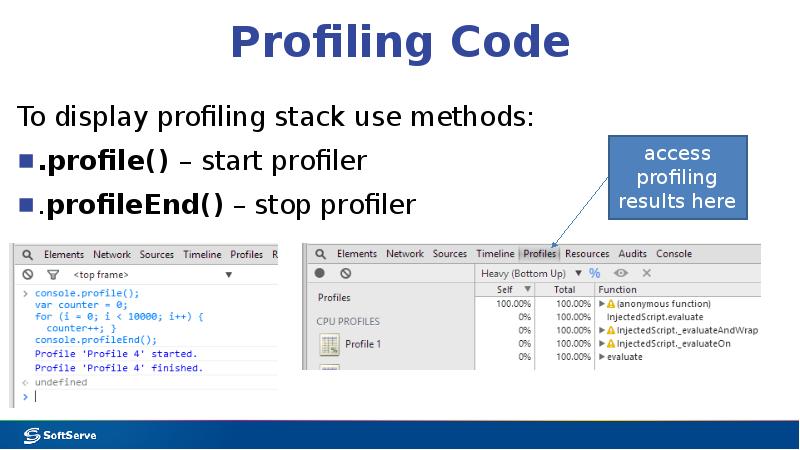
- 30. Profiling Code To display profiling stack use methods: .profile() – start
- 31. Making Assertions Method .assert() allows to make assertions about conditions in
- 32. Best Practices Assume your code will fail Log errors to the
- 33. Useful links
- 34. Links JavaScript Errors on W3Schools.com: http://www.w3schools.com/js/js_errors.asp Error object on MDN:
- 35. Thank you!
- 36. Скачать презентацию
























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Troubleshooting JavaScript сode. (Module 6) можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























