Ancient Indian and Chinese philosophy. (Lecture 2) презентация
Содержание
- 2. In the West, the term Eastern (Oriental) philosophy refers very broadly
- 3. One must take into account that this term ignores that these
- 4. Ancient eastern philosophy developed mainly in India and China. The Indian
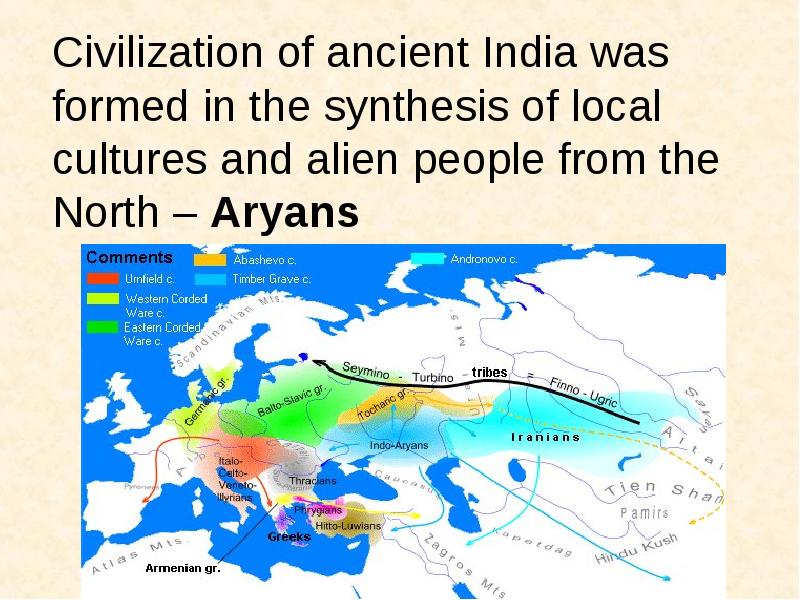
- 5. Ancient Indian philosophy Ancient Indian philosophy
- 9. The development of ancient Indian philosophy consists of two periods: the
- 10. Rig-Veda (Sanskrit ऋग्वेद, «Veda hymns») is a collection of religious hymns,
- 11. The word «veda» means «knowledge» and comes from the root «vid-»,
- 12. Rig-Veda contains an extreme pluralism: the gods, people, animals, plants, elements,
- 13. At the heart of cosmos there is an eternal substance –
- 14. The world and its phenomena are considered as the improvement of
- 15. Head corresponds to the caste of Brahmins (priests). Head corresponds
- 16. Feet – Vaisya caste (merchants, artisans). Feet – Vaisya caste
- 17. Universal law, which operates in the past, present and future called
- 18. If a person adheres to a strict asceticism, his samsara ceases
- 19. According to a traditional principle of classification, the schools or systems
- 20. These are regarded as orthodox, not because they believe in god,
- 21. To the first group belong the six chief philosophical systems (popularly
- 22. Mimamsa (Prabhakara), the tradition of Vedic exegesis (толкование) of sacrifice (жертвоприношения)
- 23. Samkhya (Kapila), the school of enumeration or “reasonable deliberation” (разумное взвешивание,
- 24. Yoga (Patanjali), practice of contemplation, theoretical basis is the Samkhya, but
- 25. Vaisesika (Kanada), the atomistic school, looking for identify the differences among
- 26. During next classical period, there appears an interest in ethical issues.
- 27. Buddhism (Pali बुद्ध धम्म, Buddha Dhamma, “Teaching of Awakening (Пробужденный)”) is
- 28. At the core of Buddhism is the doctrine of the Four
- 29. In Buddhism it’s proposed median (срединный), or the Eightfold Path (Восьмеричный
- 30. Eightfold Path Eightfold Path Righteous faith. The true determination (решимость).
- 31. 5. Saintliness (Праведная жизнь). 5. Saintliness (Праведная жизнь). 6.
- 32. Jainism preaches non-violence to all living beings in this world. Philosophy
- 33. Lokayata (also Charvaq, Skt. चार्वाक) is a materialist doctrine of ancient
- 34. Ancient Chinese philosophy Ancient Chinese philosophy
- 36. Considering all things as a unity of opposites (Yang – Yin),
- 37. Yin and yang is a Chinese symbol of balance and harmony,
- 38. Basically, this symbol represents the Positive and Negative forces in the
- 39. In Chinese mythology, it is allocated the highest principle, which rules
- 40. During this period, freely and creatively there were six major philosophical
- 41. 1) School of Confucians; 1) School of Confucians; 2) School of
- 42. Confucianism is the philosophy based on the teachings of Confucius, who
- 43. Confucianism focuses on the ethical rules, social norms and regulation control.
- 44. Confucianism was made to stop the fall of Chinese society. After
- 45. People slowly started to believe in it, because they wanted to
- 46. The teachings of Confucius focus largely on the respect of one’s
- 47. Also, he taught that humans 'can never stop learning'; meaning that
- 48. Confucianism can be considered as the oldest school of philosophy in
- 49. Ethics of Confucius explaned human in connection with his social functions,
- 50. The social order (Li) Confucius had established through the ideal of
- 54. Moists school was named after the founder Moe Dee (479-391 BC).
- 55. The whole meaning was to the ideas of universal love (Jiang
- 56. School of Names examined the relations of things and expression of
- 57. Legism (Bu Hei Shen, Han Feng-tzu) is formed almost as a
- 58. It is political philosophy which say that people are bad by
- 59. One of the most important contributors to Legalism was Han Fei
- 60. 2. Shu (method, tactic or art): These are methods the ruler has to
- 61. One of the major directions in China, along with Confucianism, was
- 62. The world is in constant motion and change, evolving, living and
- 63. Lao Tzu (old teacher) is a senior contemporary of Confucius. Lao
- 64. Скачать презентацию






























































Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Ancient Indian and Chinese philosophy. (Lecture 2) можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























