Bluetooth 101. Training for Plantronics презентация
Содержание
- 3. Contact Info Roger Garvert Field Application Engineer
- 4. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
- 5. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
- 6. What is Bluetooth? Robust unlicensed short range wireless standard It is
- 7. What does Bluetooth provide? Provides point-to-point connections Provides ad-hoc networking capabilities
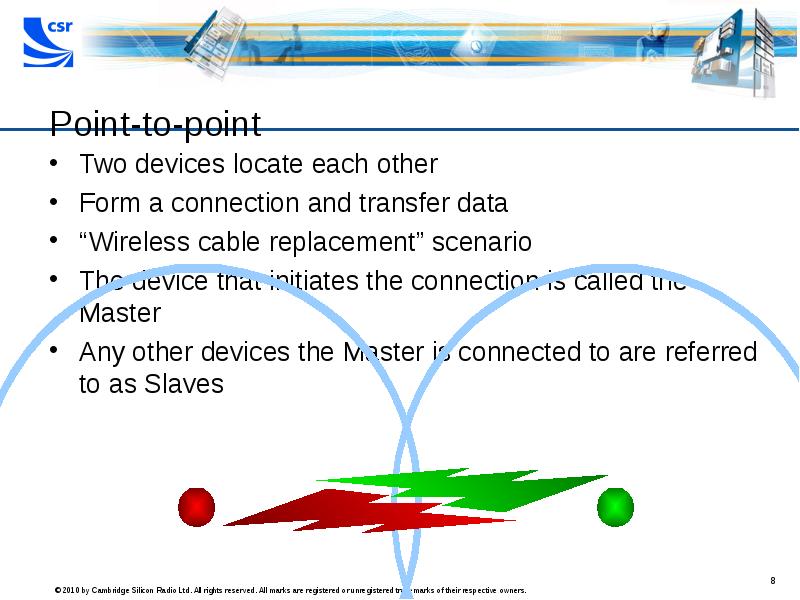
- 8. Point-to-point Two devices locate each other Form a connection and transfer
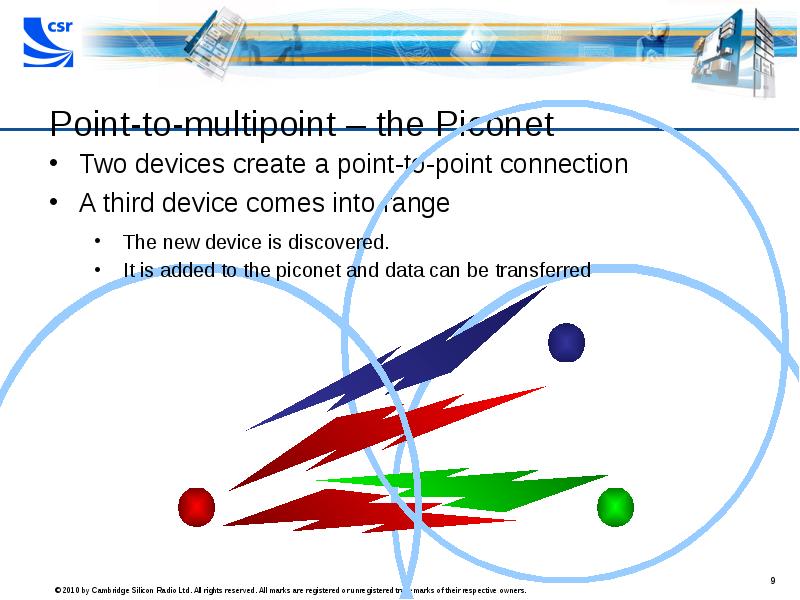
- 9. Point-to-multipoint – the Piconet Two devices create a point-to-point connection A
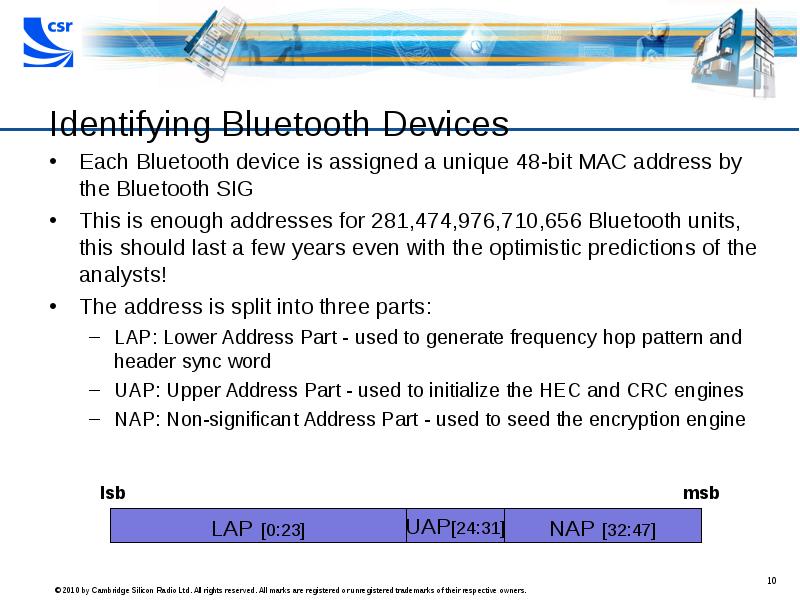
- 10. Identifying Bluetooth Devices Each Bluetooth device is assigned a unique 48-bit
- 11. Bluetooth Channels A master can create two types of logical channel
- 12. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
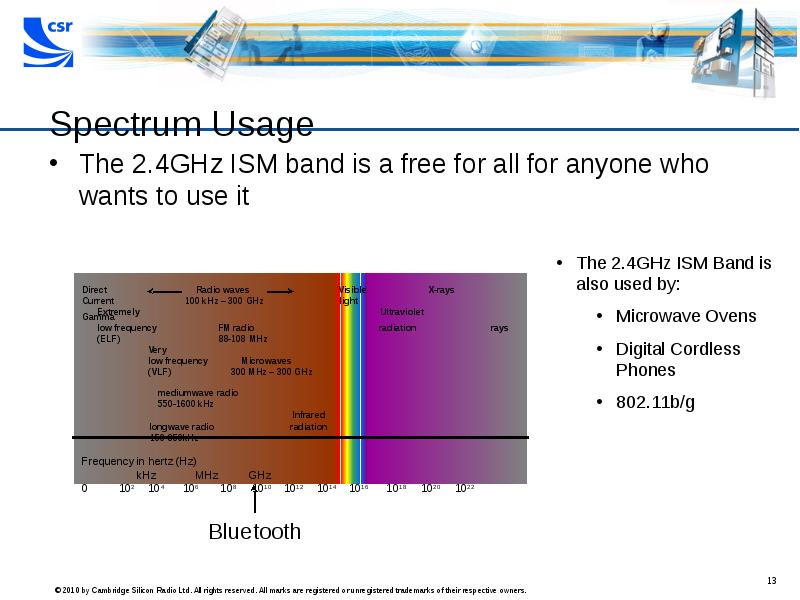
- 13. Spectrum Usage The 2.4GHz ISM band is a free for all
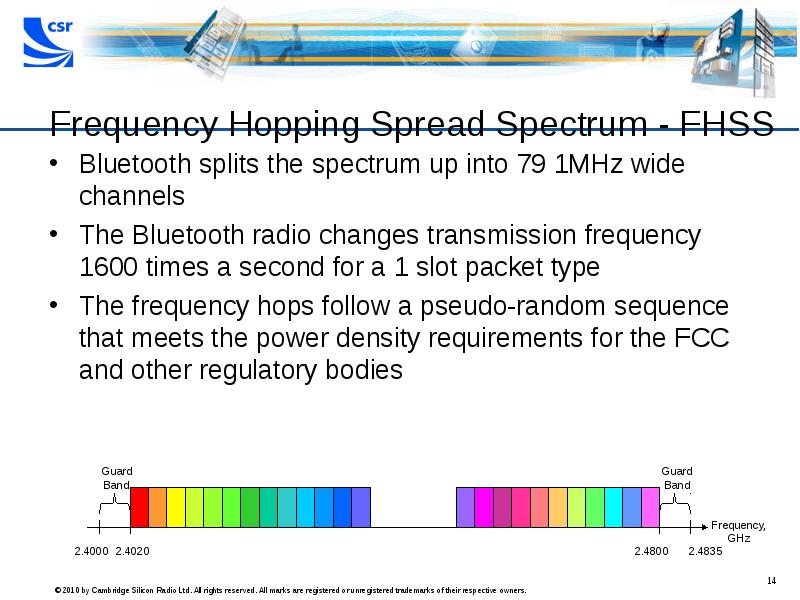
- 14. Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum - FHSS Bluetooth splits the spectrum up
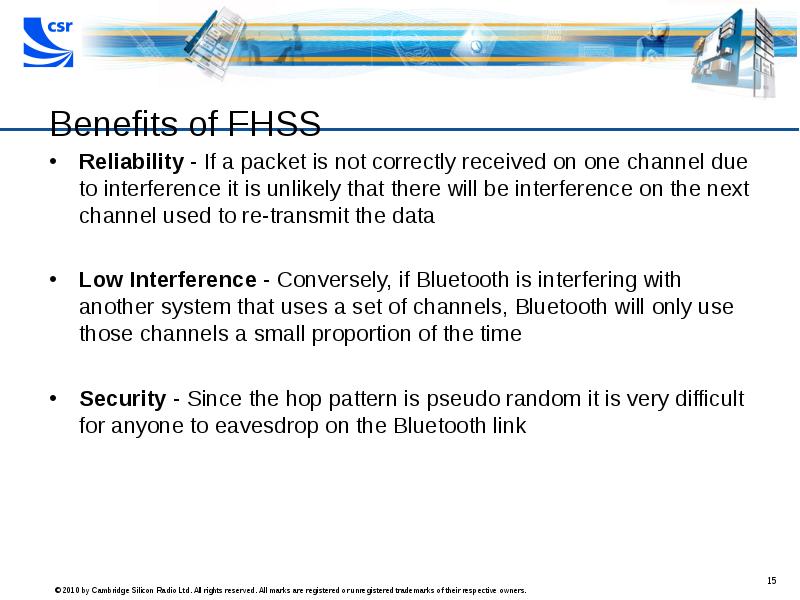
- 15. Benefits of FHSS Reliability - If a packet is not correctly
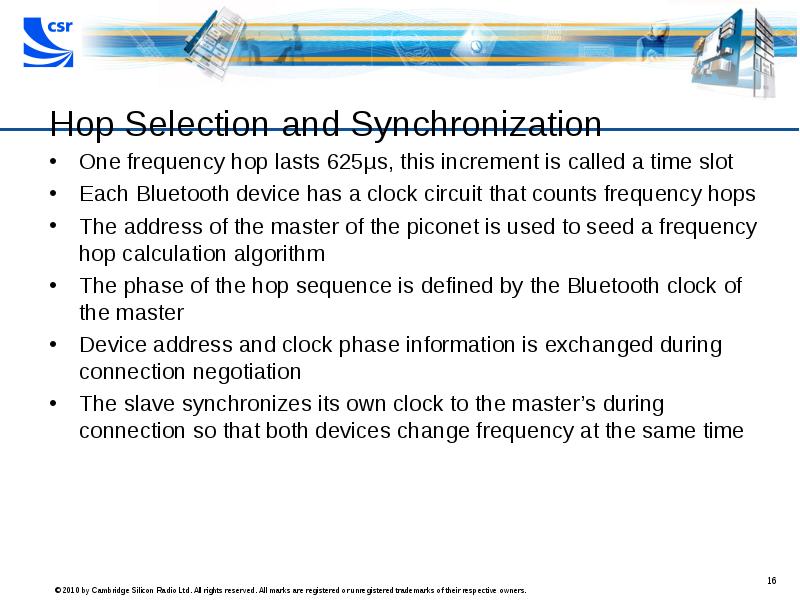
- 16. Hop Selection and Synchronization One frequency hop lasts 625µs, this increment
- 17. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Introduced in Bluetooth v1.2 Bluetooth shares the 2.4GHz
- 18. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Three steps
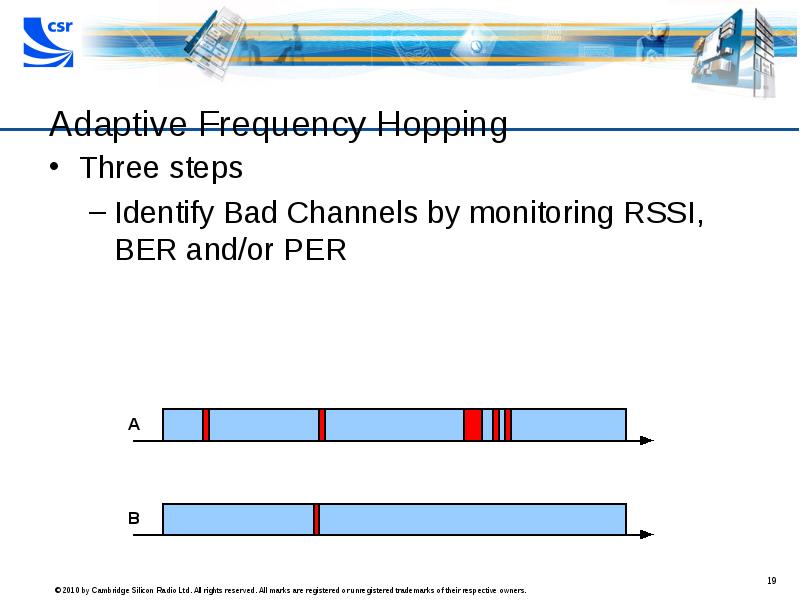
- 19. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Three steps Identify Bad Channels by monitoring RSSI,
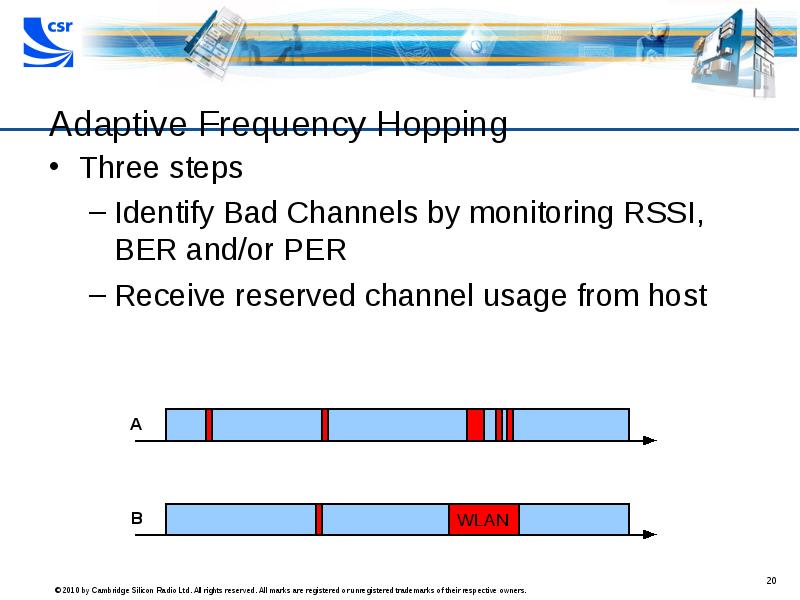
- 20. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Three steps Identify Bad Channels by monitoring RSSI,
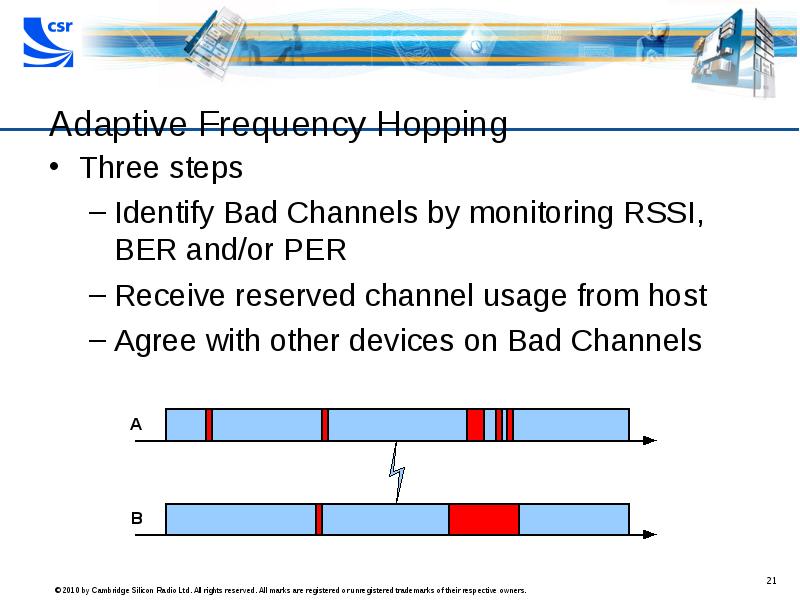
- 21. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Three steps Identify Bad Channels by monitoring RSSI,
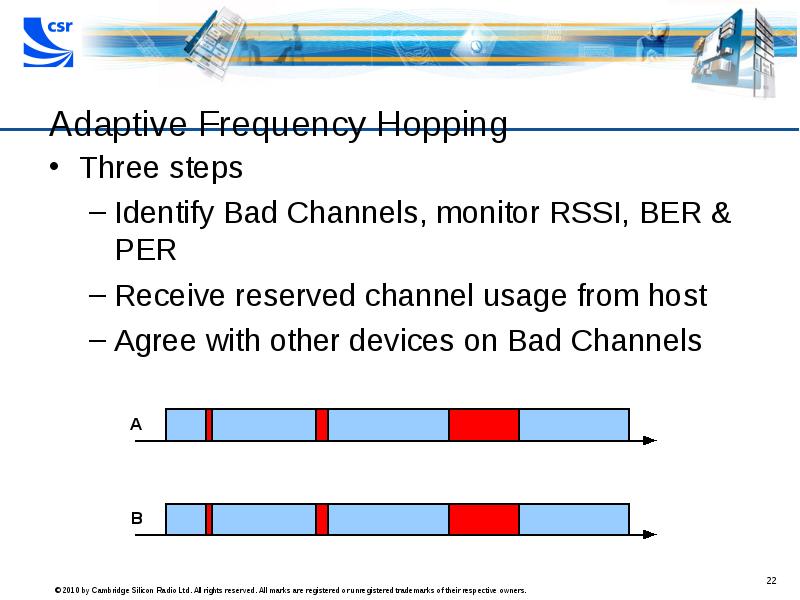
- 22. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Three steps Identify Bad Channels, monitor RSSI, BER
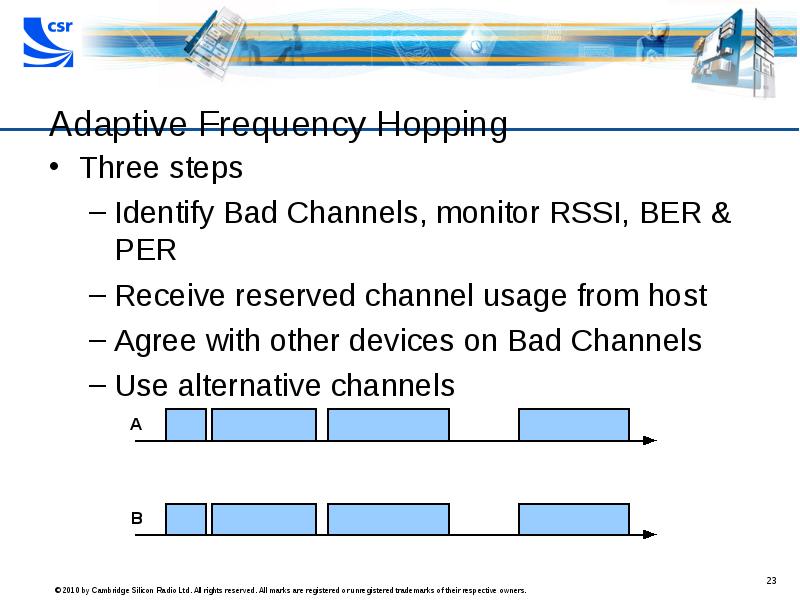
- 23. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Three steps Identify Bad Channels, monitor RSSI, BER
- 24. Adaptive Frequency Hopping Benefits: Fewer lost packets = better audio quality
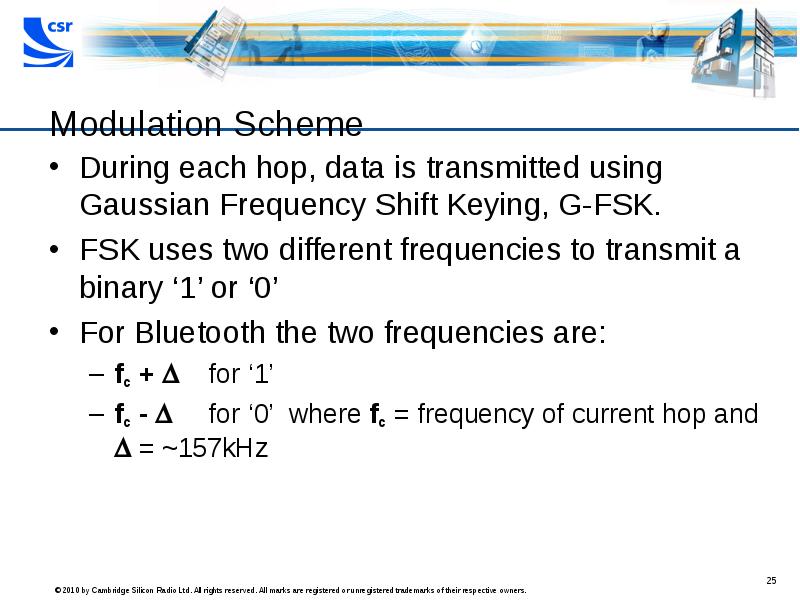
- 25. Modulation Scheme During each hop, data is transmitted using Gaussian Frequency
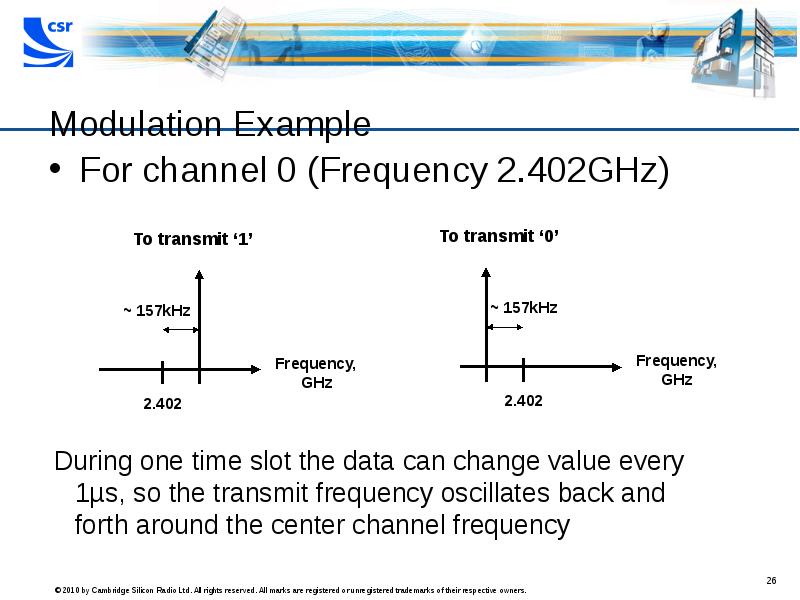
- 26. Modulation Example For channel 0 (Frequency 2.402GHz)
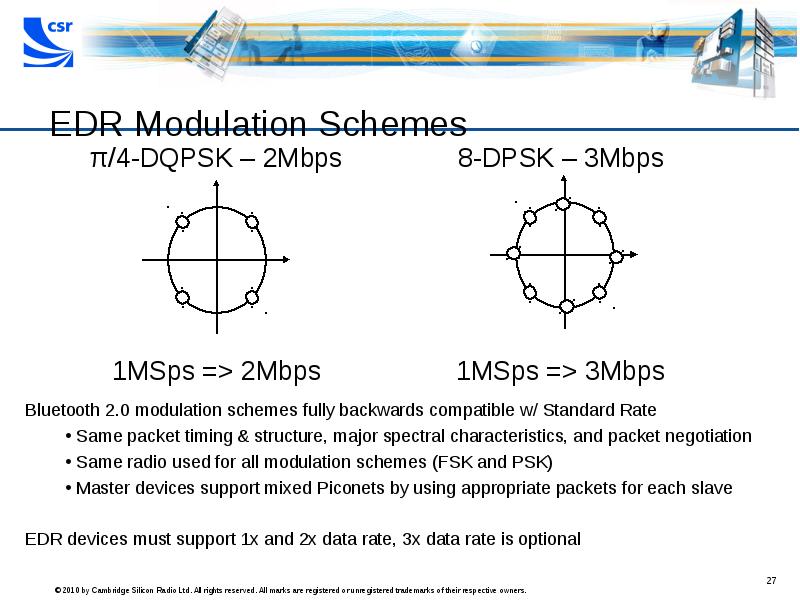
- 27. EDR Modulation Schemes π/4-DQPSK – 2Mbps 1MSps => 2Mbps
- 28. EDR Packets v1.2 Packets: v2.0 EDR Packets:
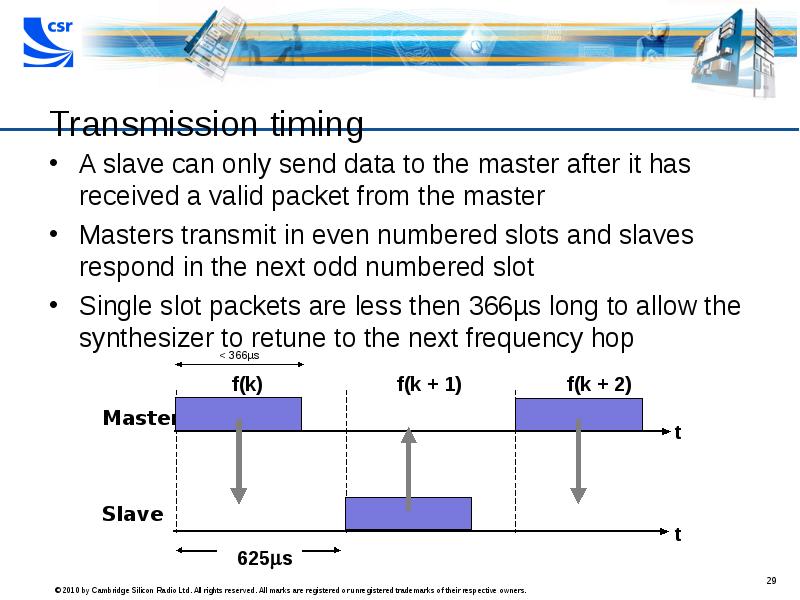
- 29. Transmission timing A slave can only send data to the master
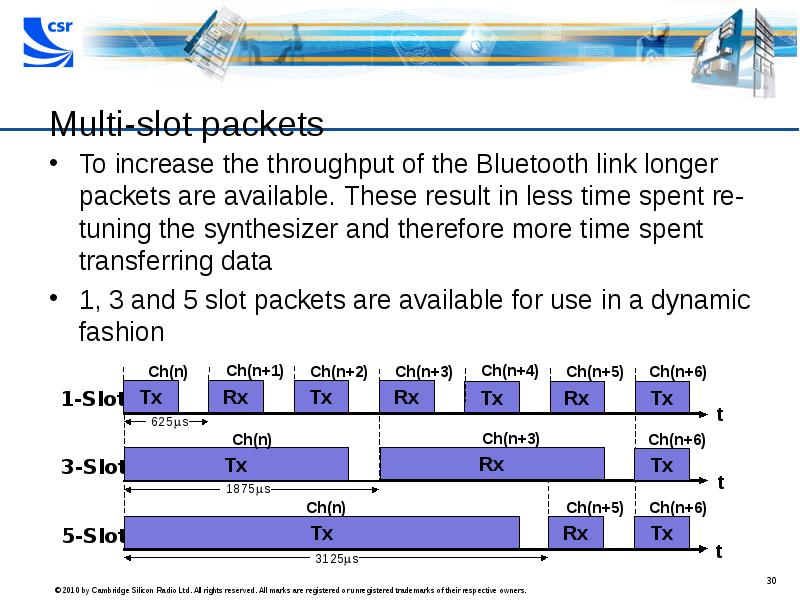
- 30. Multi-slot packets To increase the throughput of the Bluetooth link longer
- 31. Packet Types There are 14 basic rate packet types defined, split
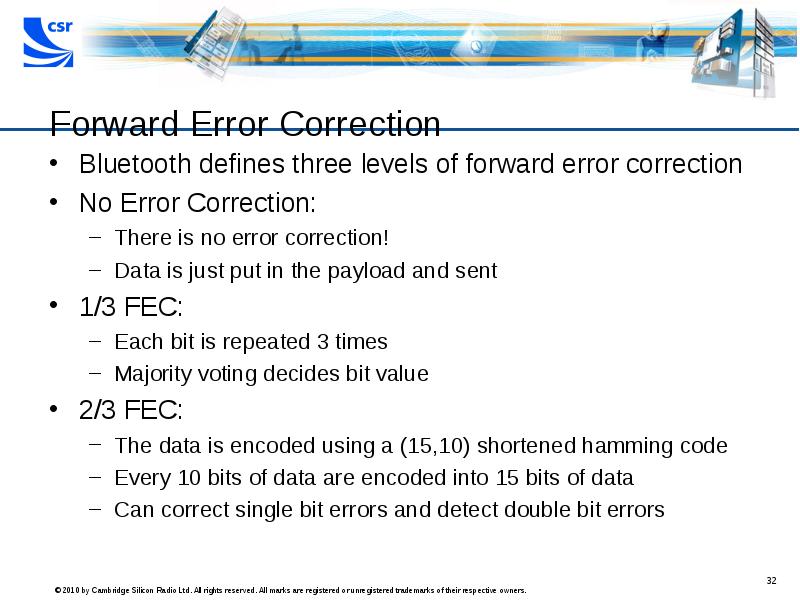
- 32. Forward Error Correction Bluetooth defines three levels of forward error correction
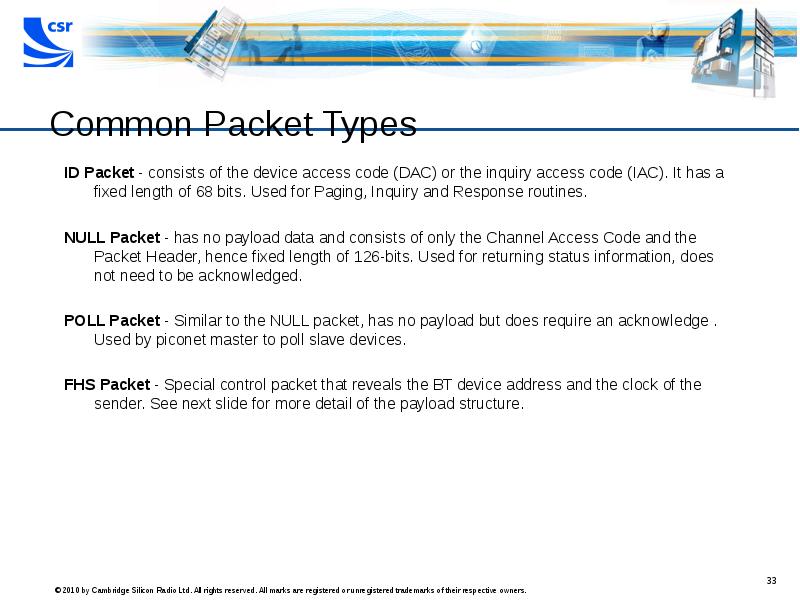
- 33. Common Packet Types
- 34. SCO Packets
- 35. ACL Packets
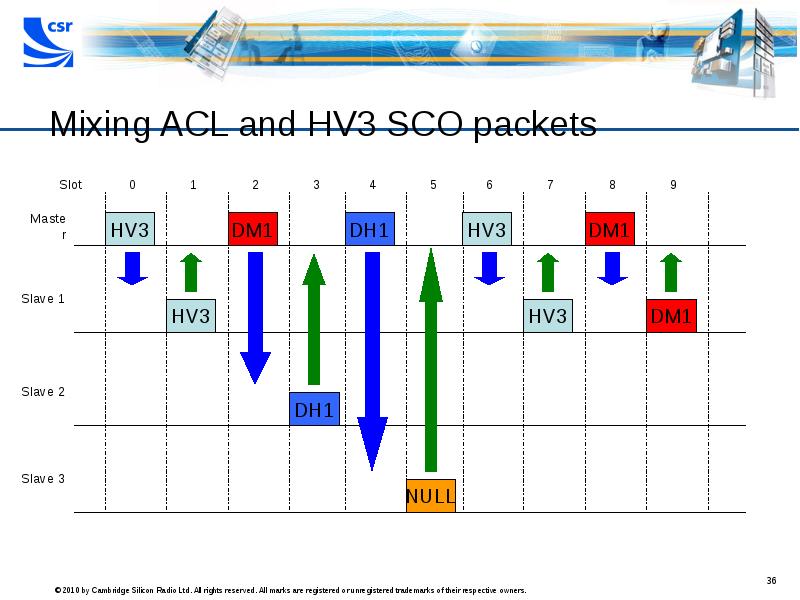
- 36. Mixing ACL and HV3 SCO packets
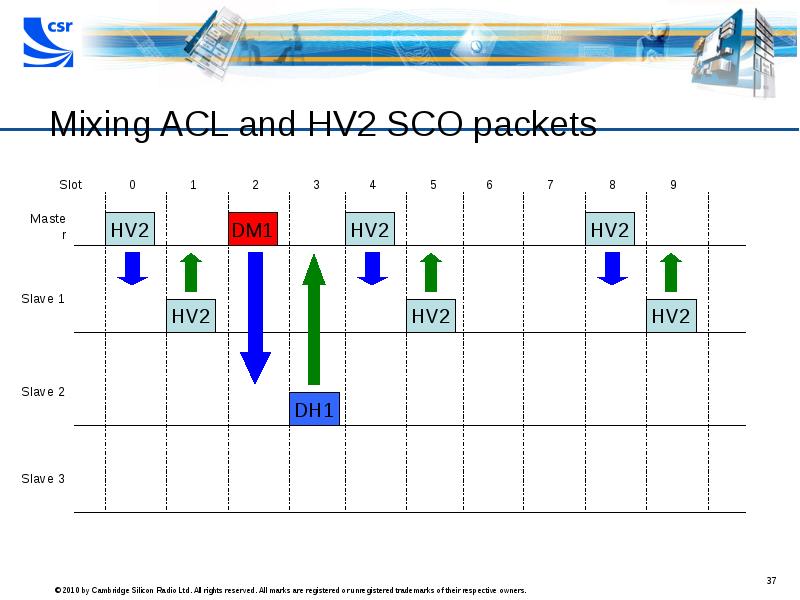
- 37. Mixing ACL and HV2 SCO packets
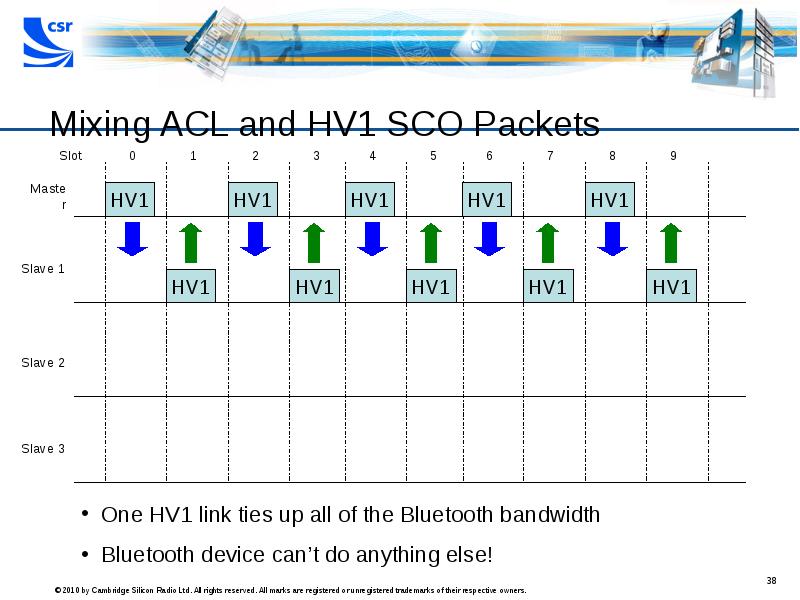
- 38. Mixing ACL and HV1 SCO Packets
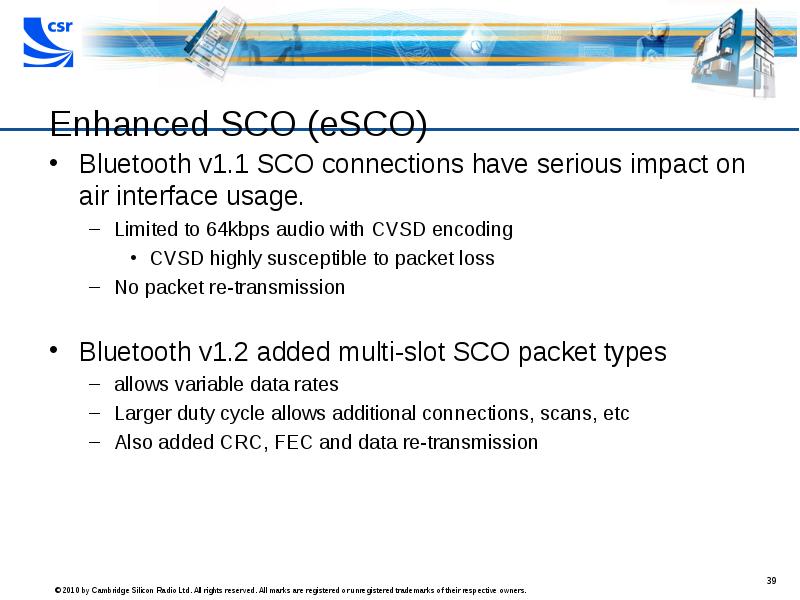
- 39. Enhanced SCO (eSCO) Bluetooth v1.1 SCO connections have serious impact on
- 40. Bluetooth 1.2 eSCO Packets
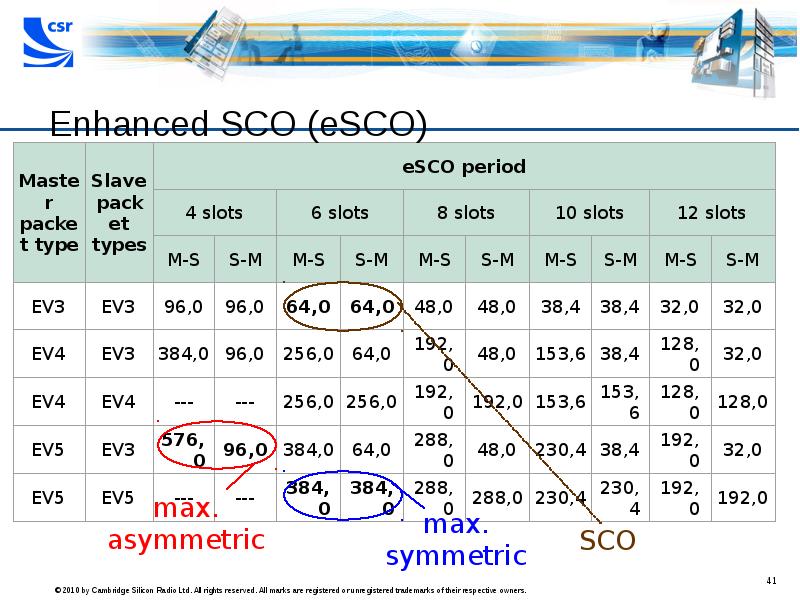
- 41. Enhanced SCO (eSCO)
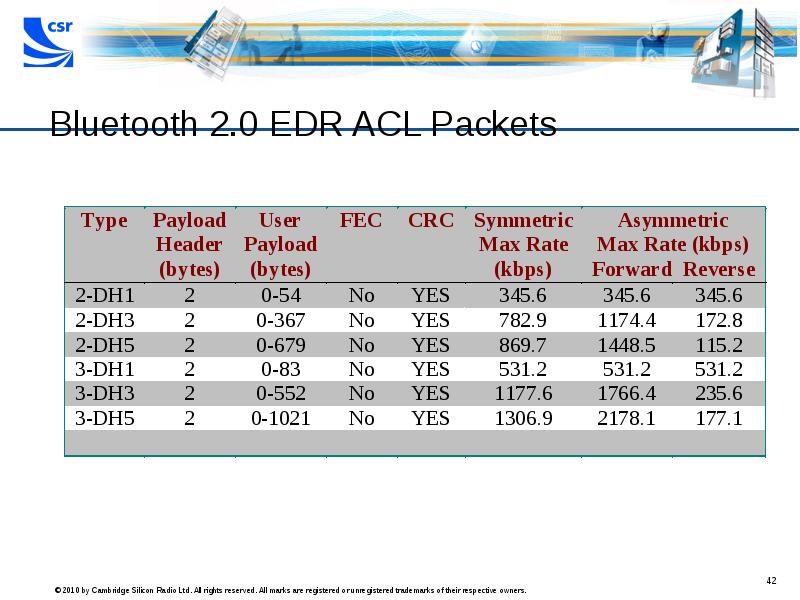
- 42. Bluetooth 2.0 EDR ACL Packets
- 43. Bluetooth 2.0 EDR eSCO Packets
- 44. Power Classes Bluetooth defines 3 power classes for devices: Class 1:
- 45. Discovering and Connecting to Other Devices For a Bluetooth device to
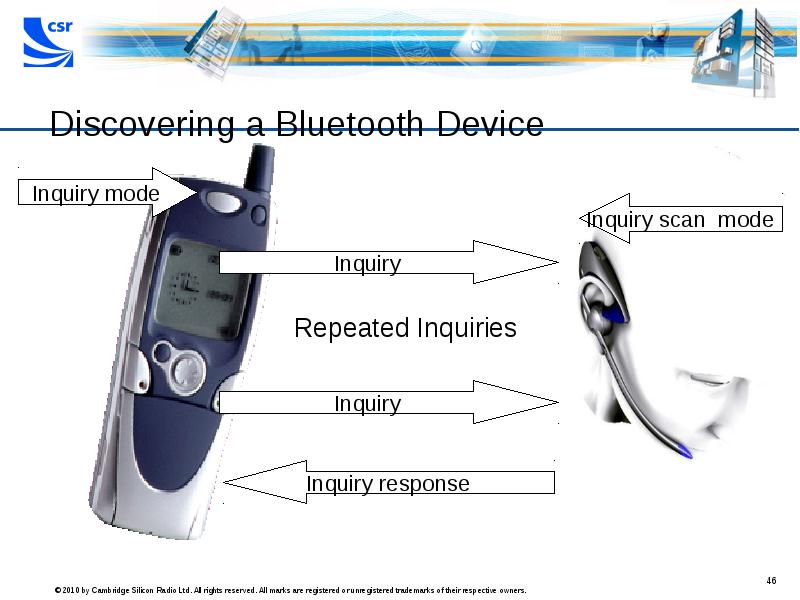
- 46. Discovering a Bluetooth Device
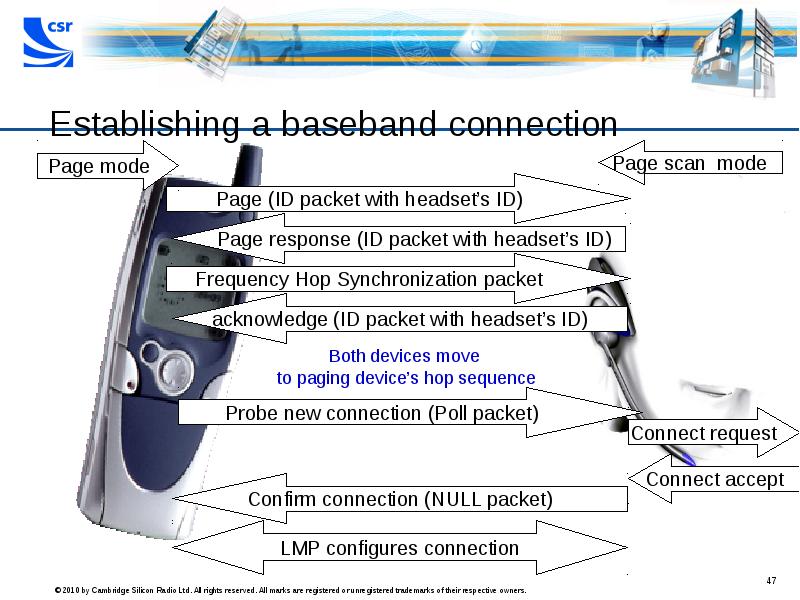
- 47. Establishing a baseband connection
- 48. Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) Feature of Bluetooth 2.1 Enables easier connectivity
- 49. Input/Output Capabilities Four I/O capabilities defined Display Only Display Yes/No Keyboard
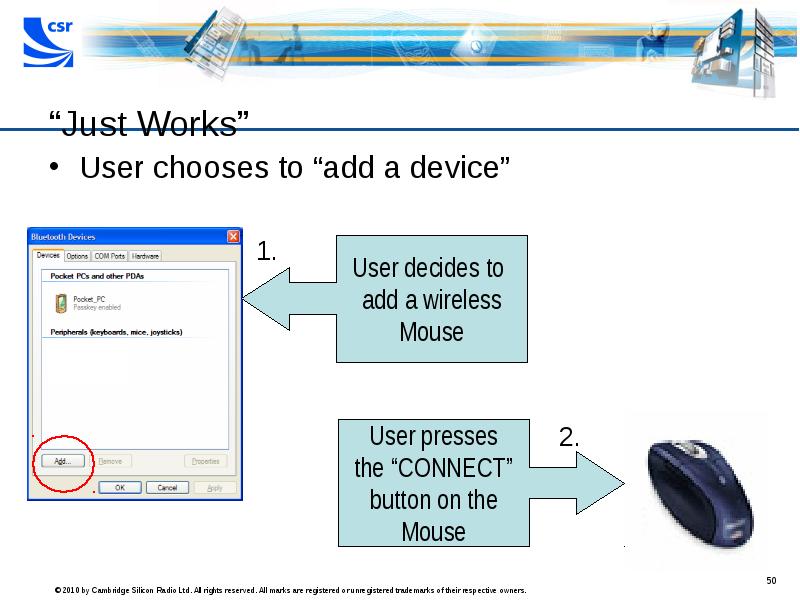
- 50. “Just Works” User chooses to “add a device”
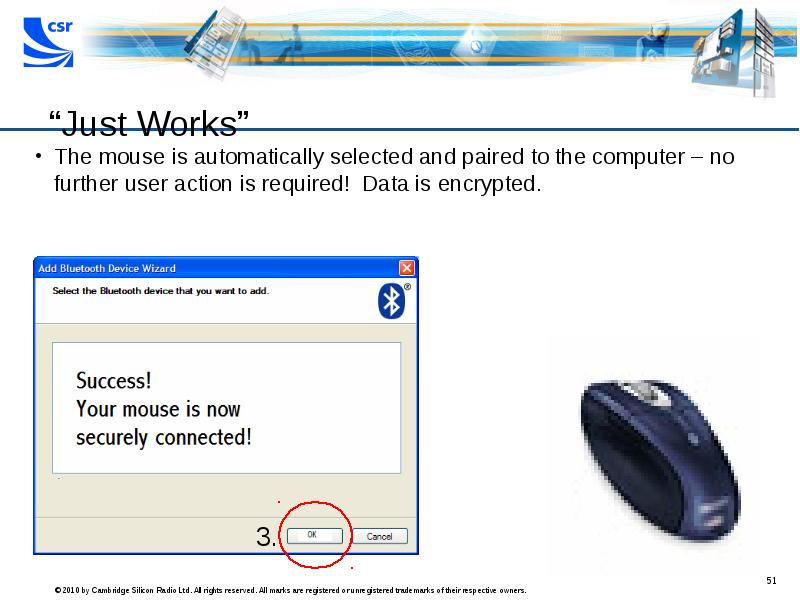
- 51. “Just Works”
- 52. Numeric Comparison Step 1 – User enables technology on PC and
- 53. Passkey Entry Step 1 – User powers on keyboard and activates
- 54. Extended Inquiry Response Feature of Bluetooth 2.1 Problem: Takes a long
- 55. Low Power Modes To help reduce power consumption, there are three
- 56. Sniff Subrating Feature of Bluetooth 2.1 Problem: HID devices want low
- 57. Sniff Mode Devices agree upon a time delay during which no
- 58. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
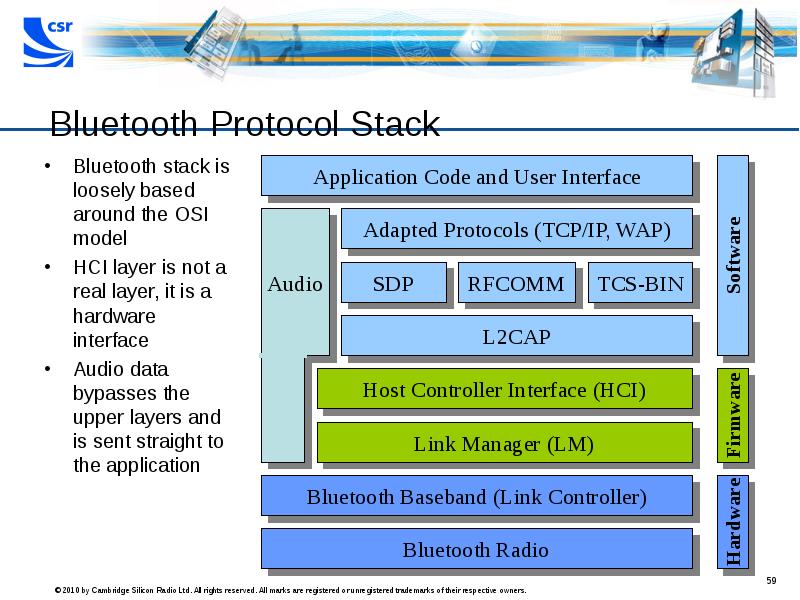
- 59. Bluetooth Protocol Stack Bluetooth stack is loosely based around the OSI
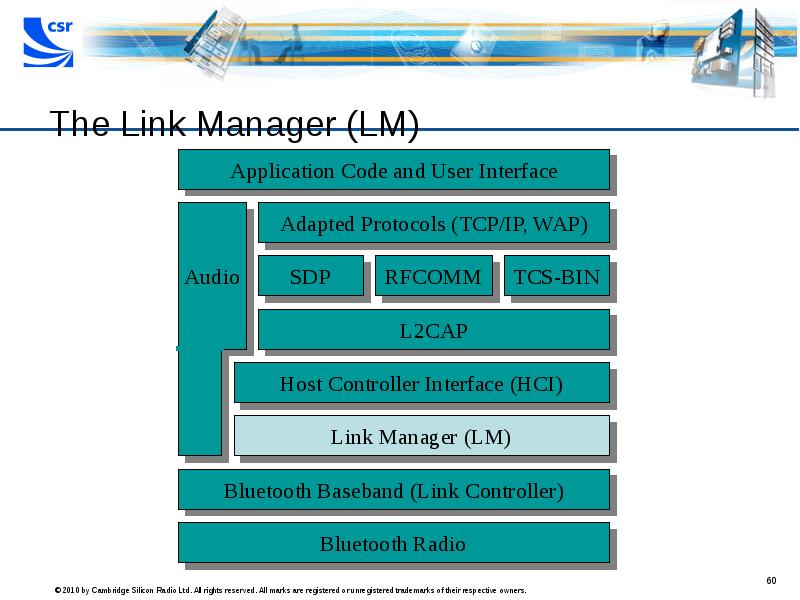
- 60. The Link Manager (LM)
- 61. The Link Manager (LM) Manages link set-up Manages security Manages piconet
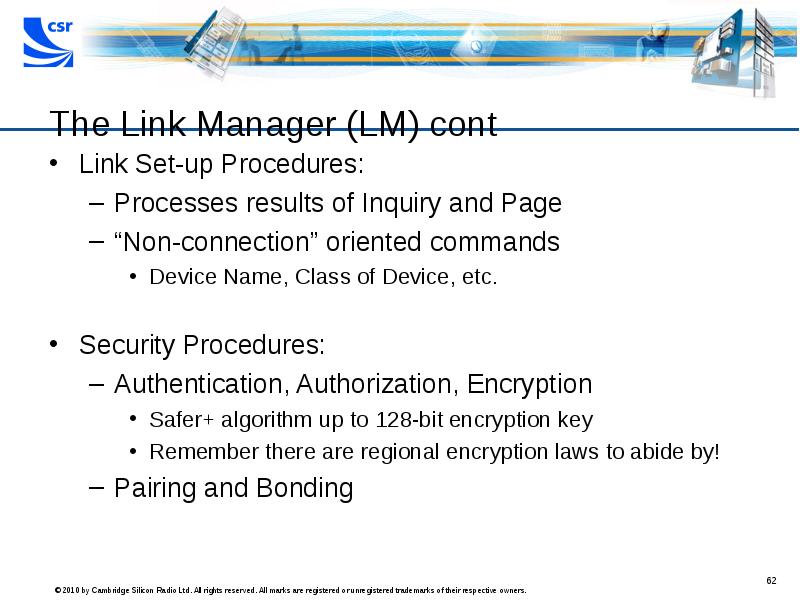
- 62. The Link Manager (LM) cont Link Set-up Procedures: Processes results of
- 63. The Link Manager (LM) cont. Piconet Connection Management: Packet type adjustment
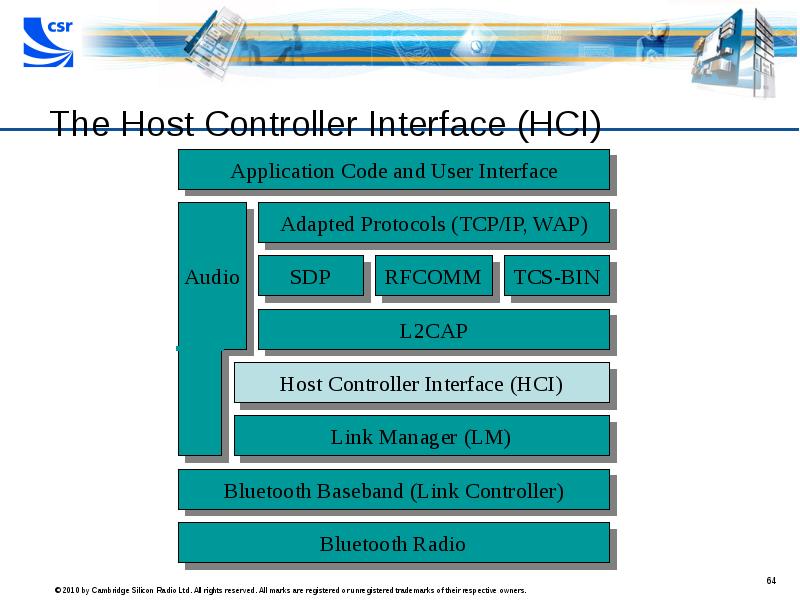
- 64. The Host Controller Interface (HCI)
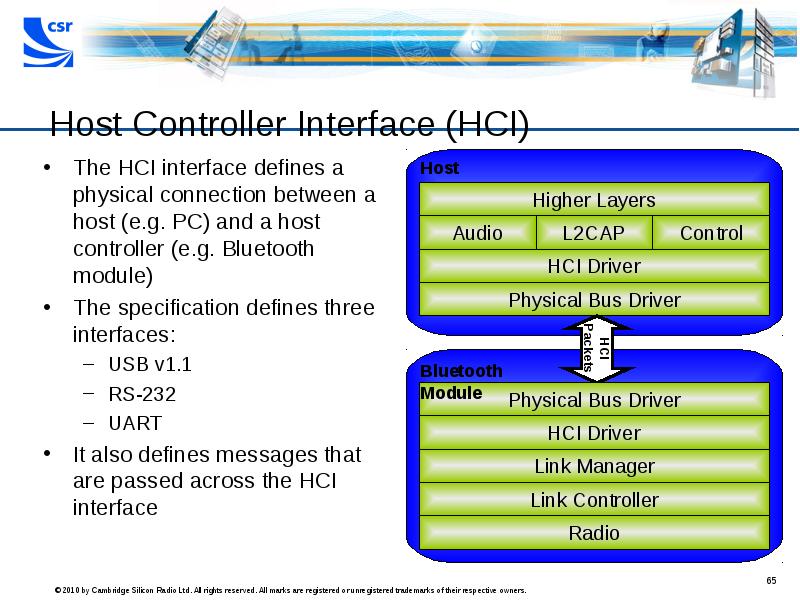
- 65. Host Controller Interface (HCI) The HCI interface defines a physical connection
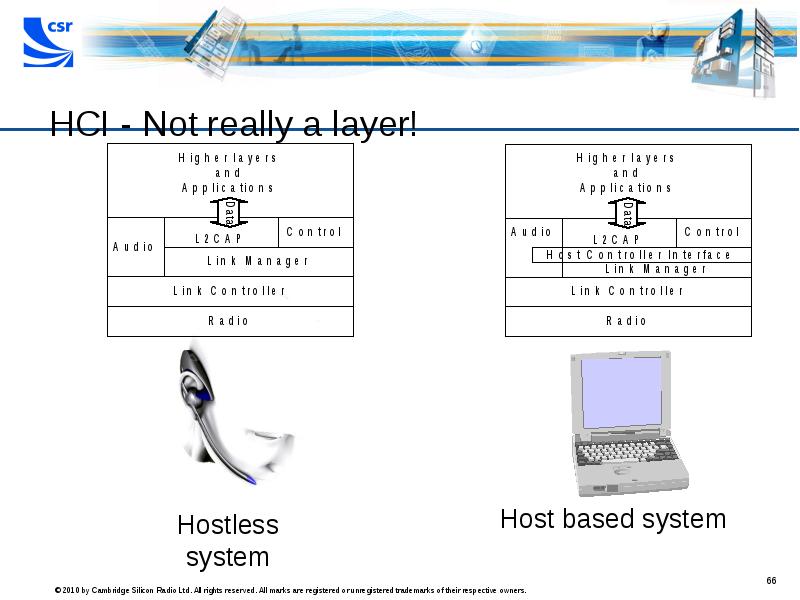
- 66. HCI - Not really a layer!
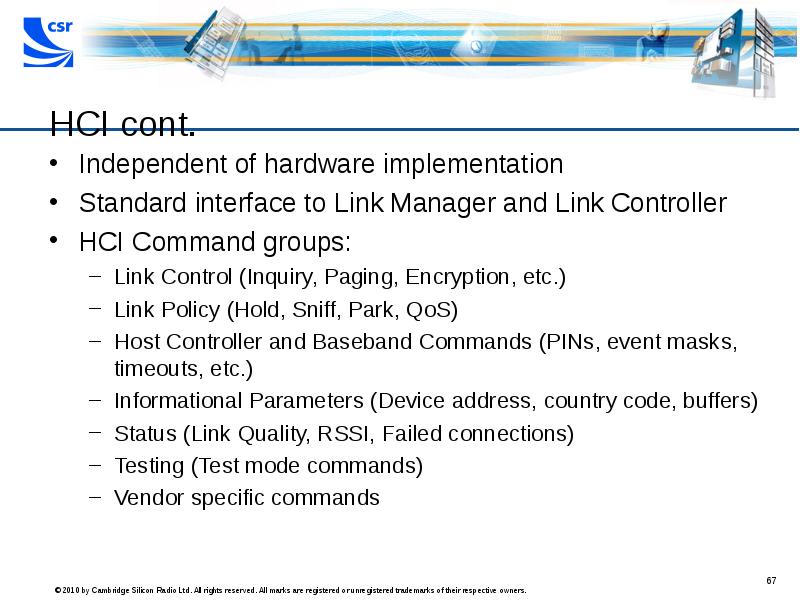
- 67. HCI cont. Independent of hardware implementation Standard interface to Link Manager
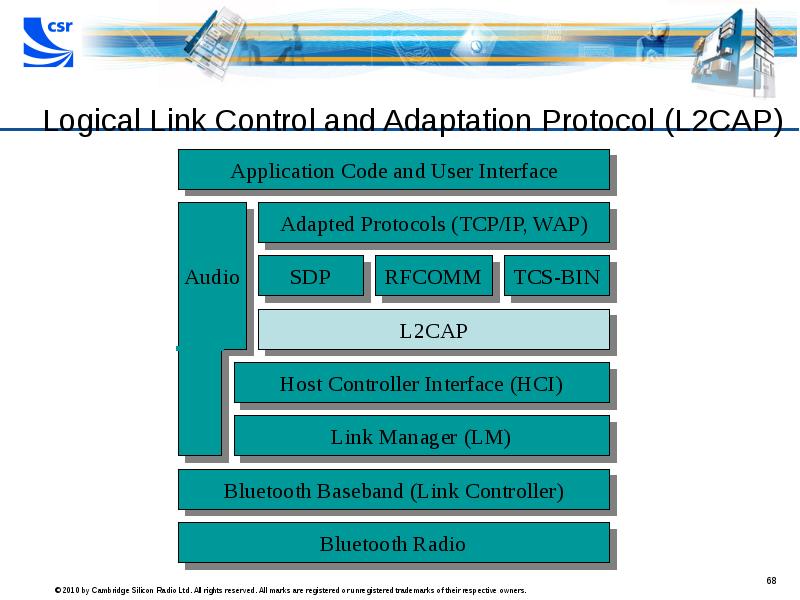
- 68. Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP)
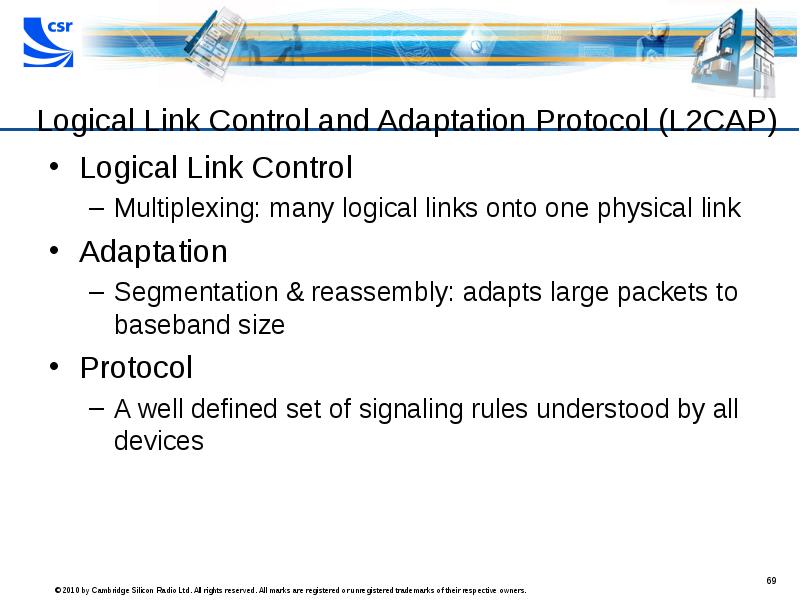
- 69. Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) Logical Link Control Multiplexing:
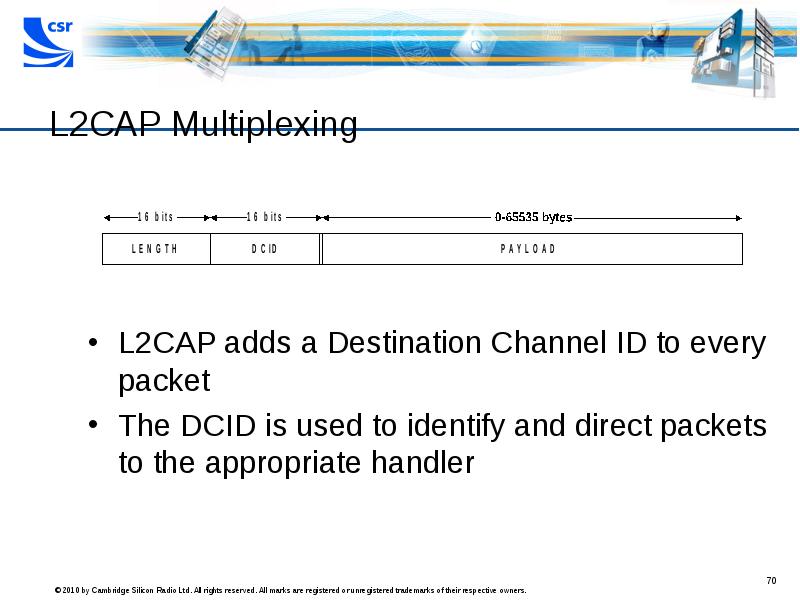
- 70. L2CAP Multiplexing L2CAP adds a Destination Channel ID to every packet
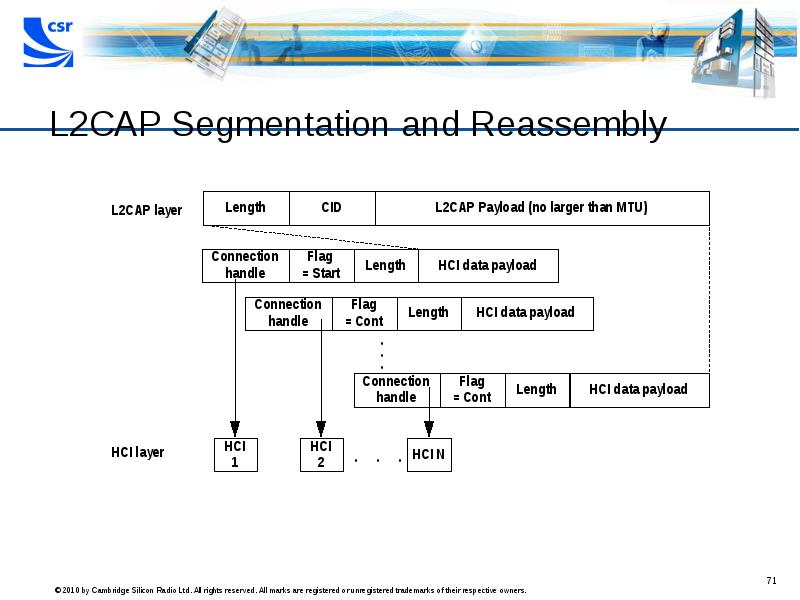
- 71. L2CAP Segmentation and Reassembly
- 72. L2CAP Quality of Service No Traffic This level indicates that no
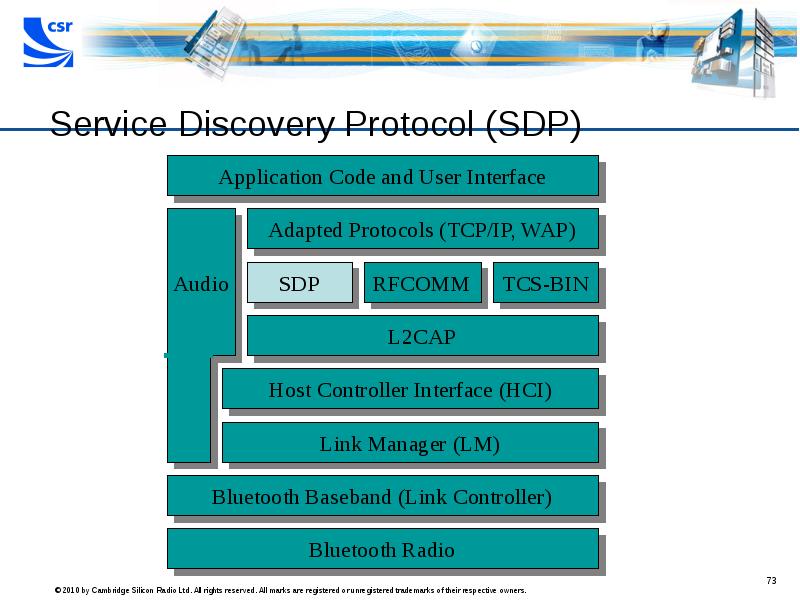
- 73. Service Discovery Protocol (SDP)
- 74. Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) SDP servers maintain a database on services
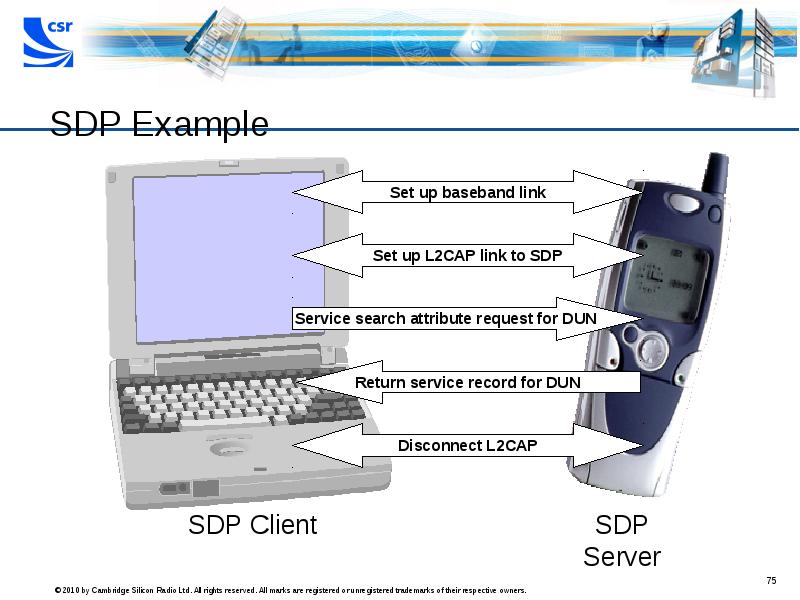
- 75. SDP Example
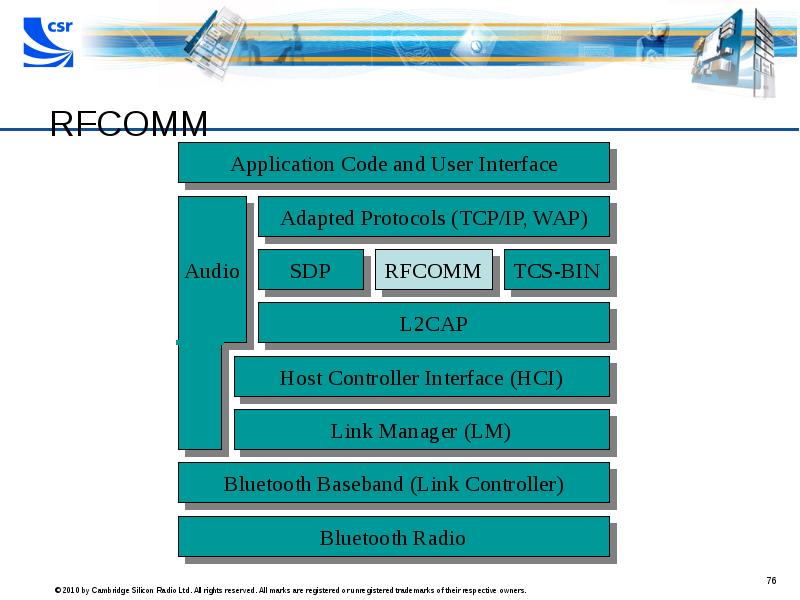
- 76. RFCOMM
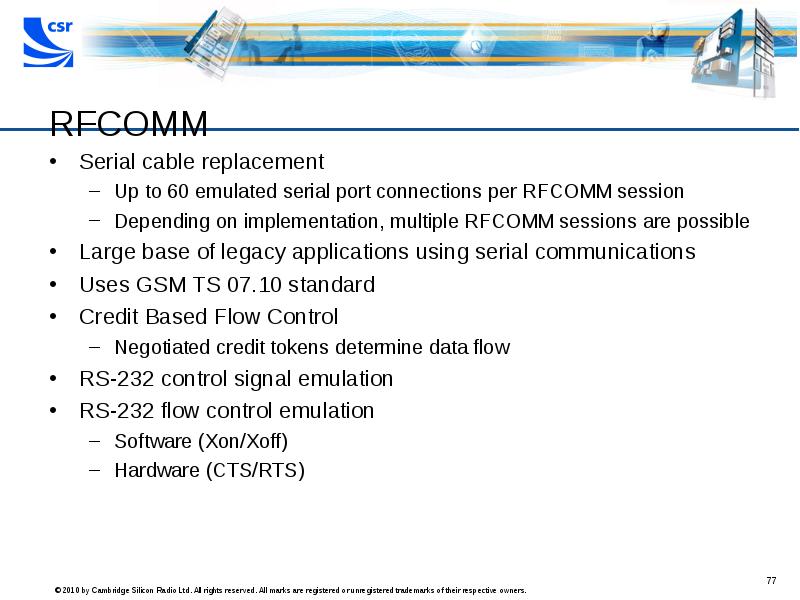
- 77. RFCOMM Serial cable replacement Up to 60 emulated serial port connections
- 78. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
- 79. Bluetooth Profiles Basic set of standards for common usage models. Reduces
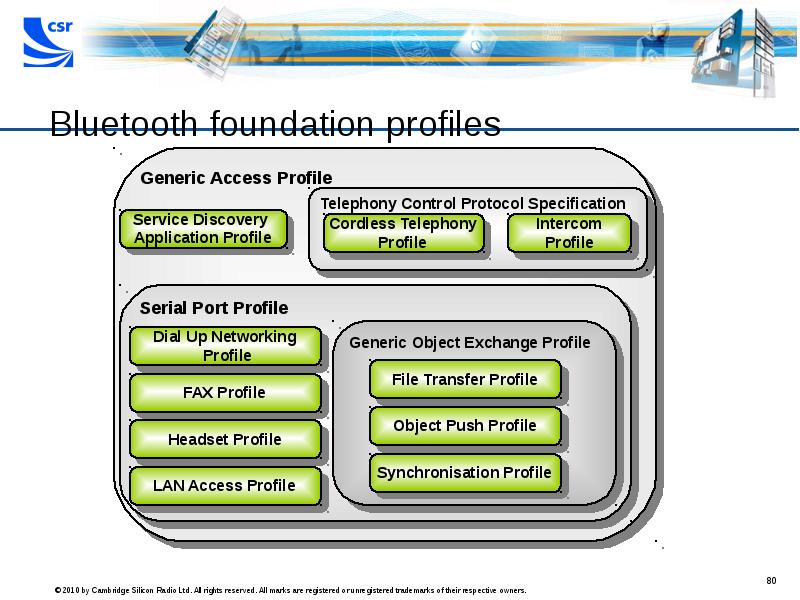
- 80. Bluetooth foundation profiles
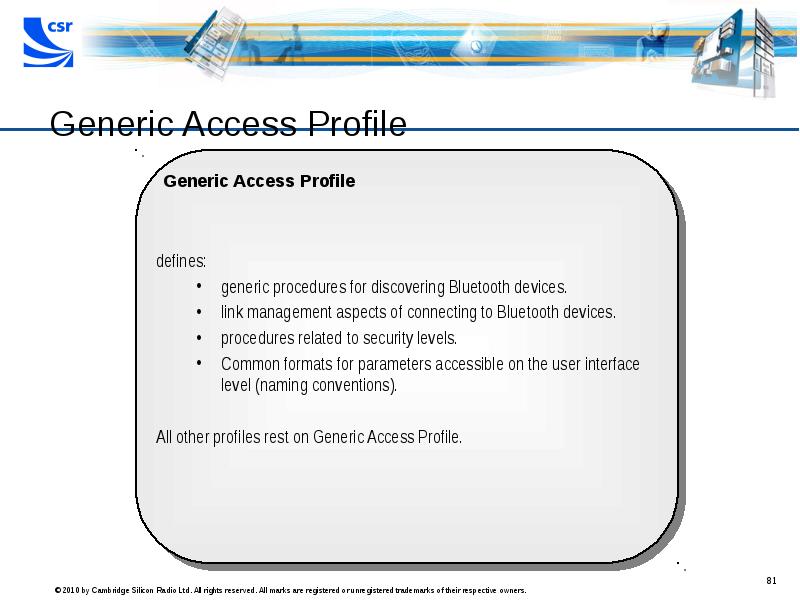
- 81. Generic Access Profile
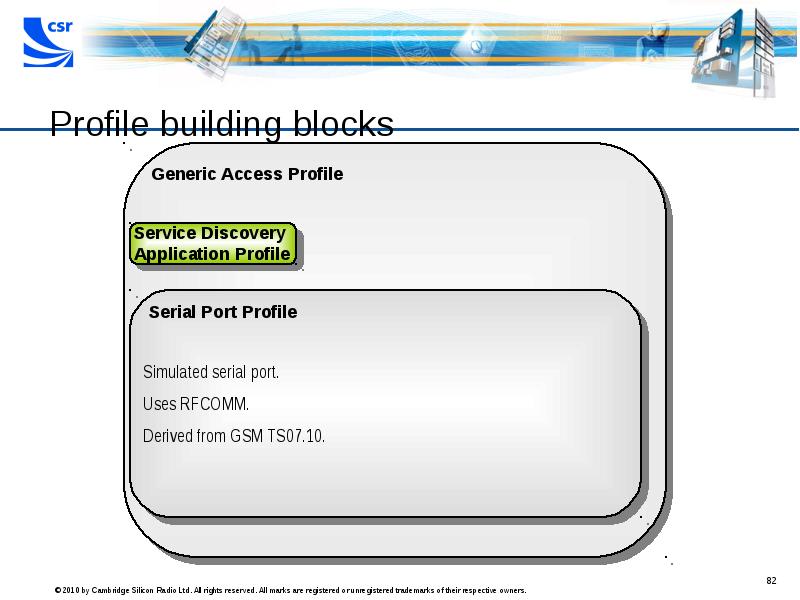
- 82. Profile building blocks
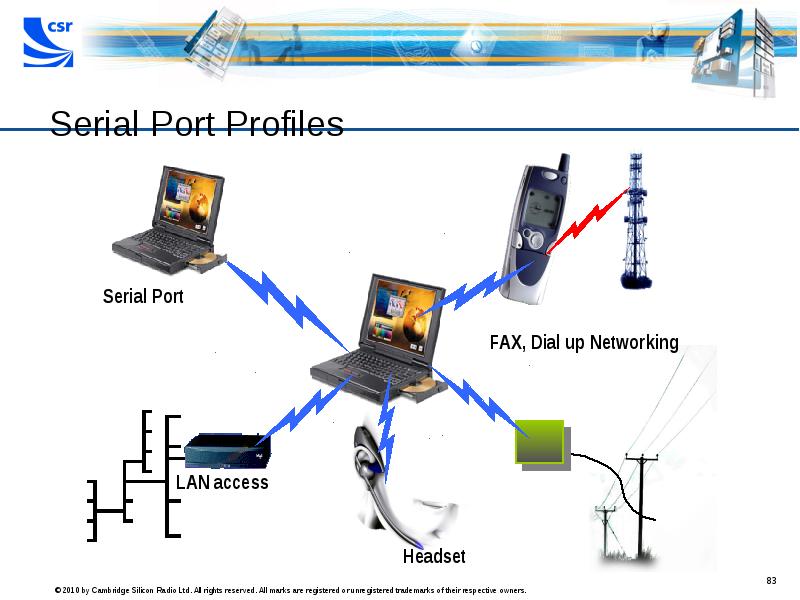
- 83. Serial Port Profiles
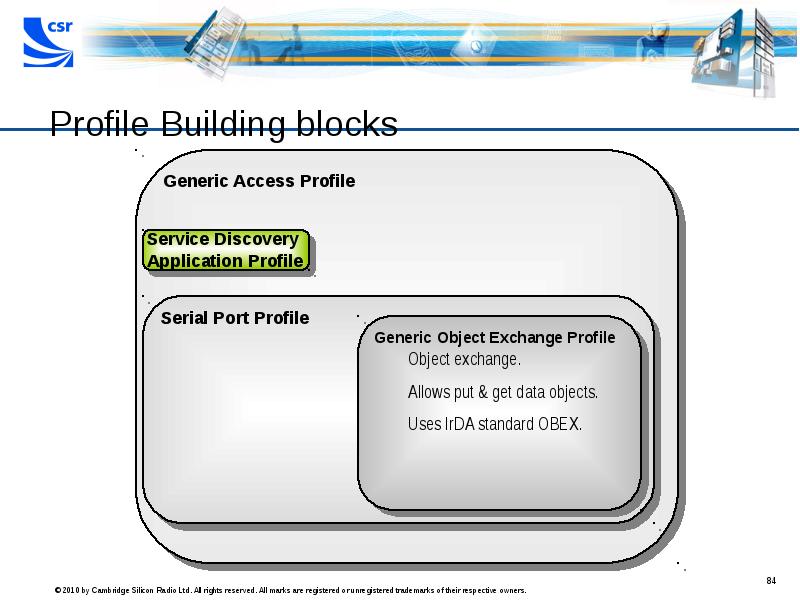
- 84. Profile Building blocks
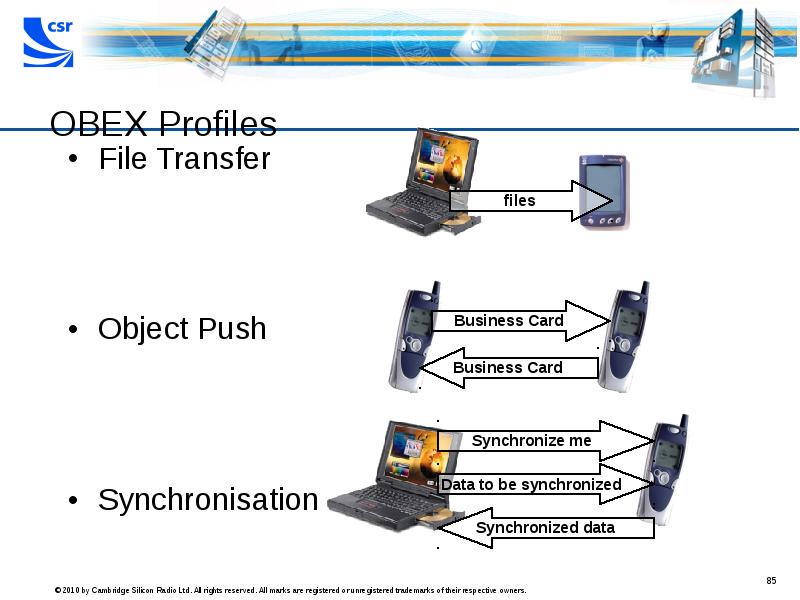
- 85. OBEX Profiles File Transfer Object Push Synchronisation
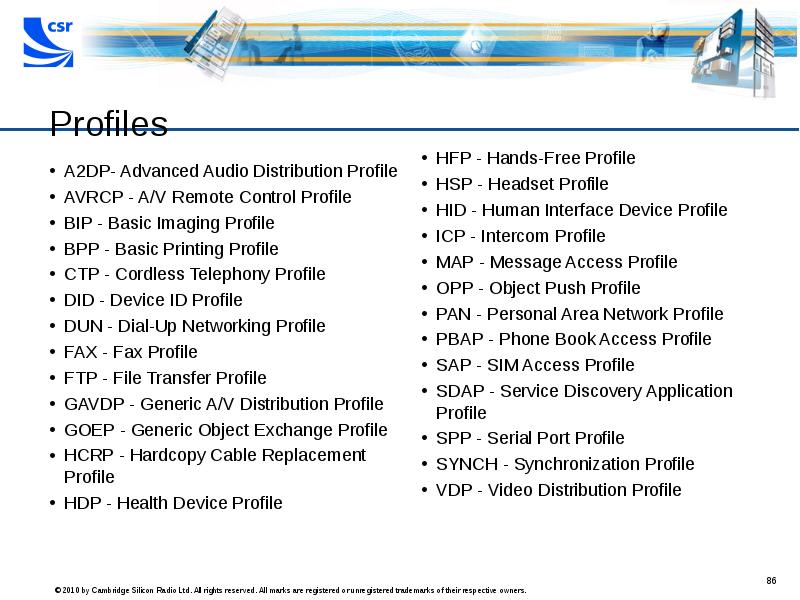
- 86. Profiles A2DP- Advanced Audio Distribution Profile AVRCP - A/V Remote Control
- 87. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
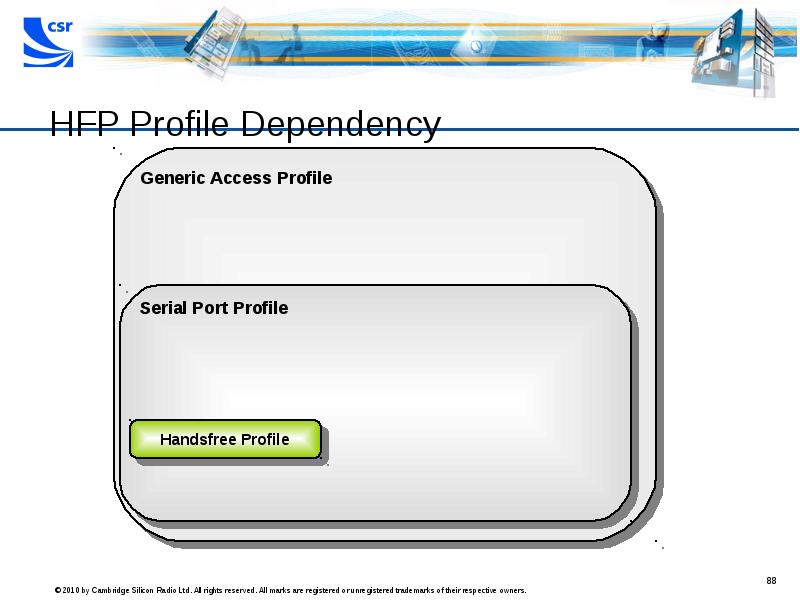
- 88. HFP Profile Dependency
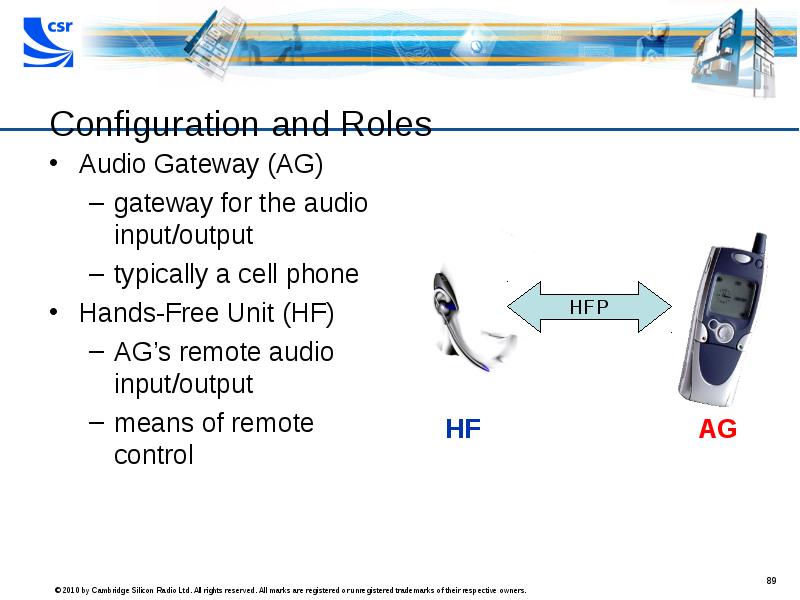
- 89. Configuration and Roles Audio Gateway (AG) gateway for the audio input/output
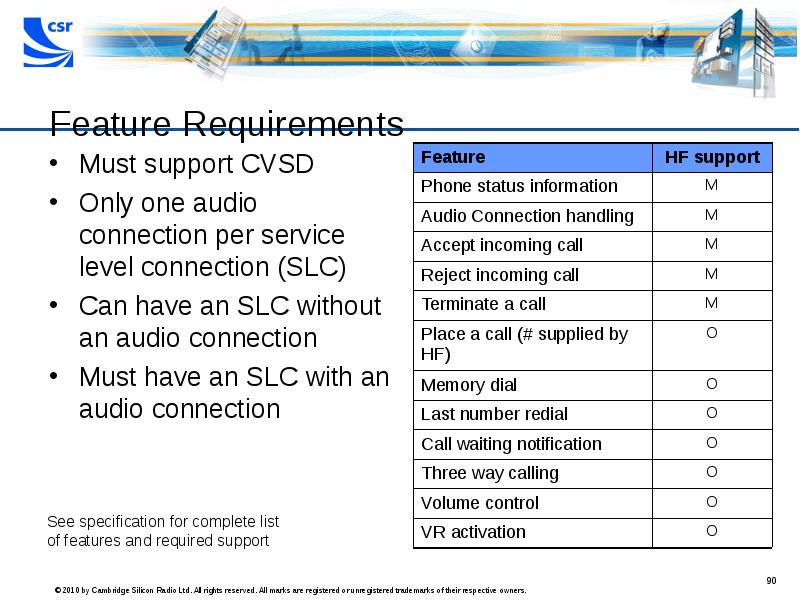
- 90. Feature Requirements Must support CVSD Only one audio connection per service
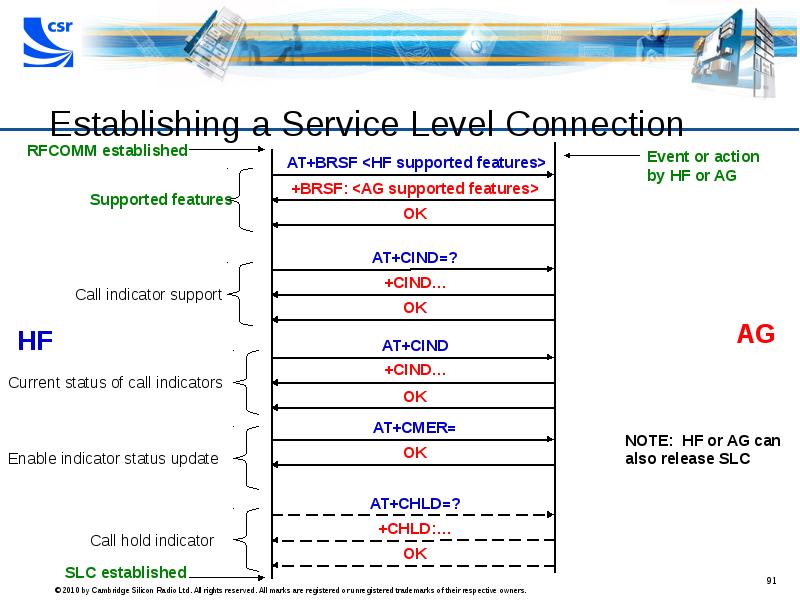
- 91. Establishing a Service Level Connection
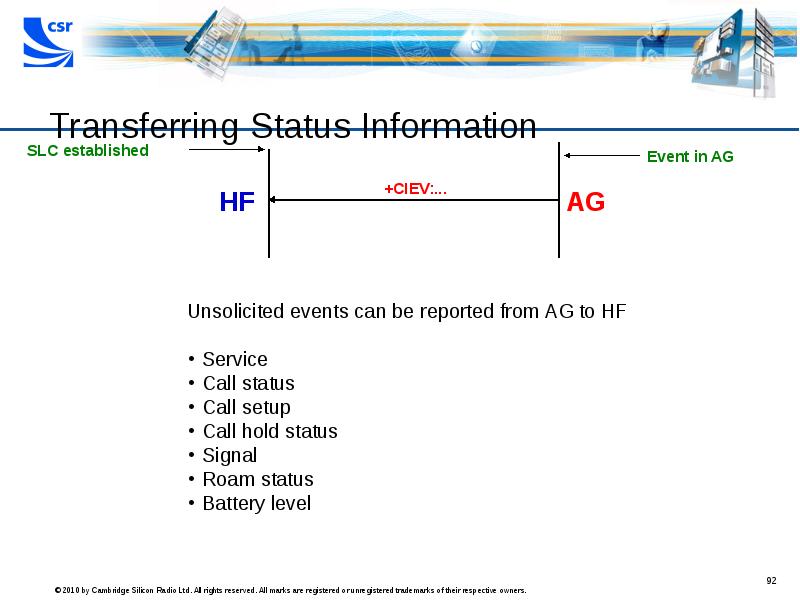
- 92. Transferring Status Information
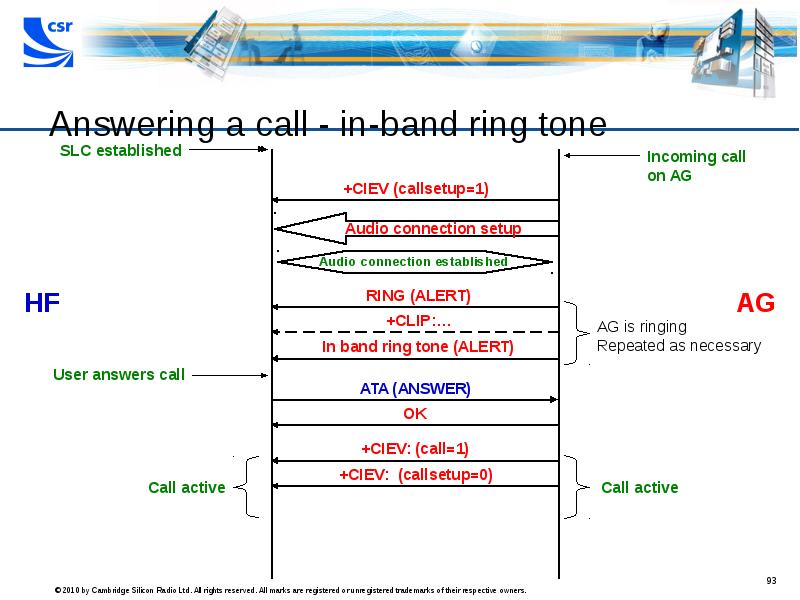
- 93. Answering a call - in-band ring tone
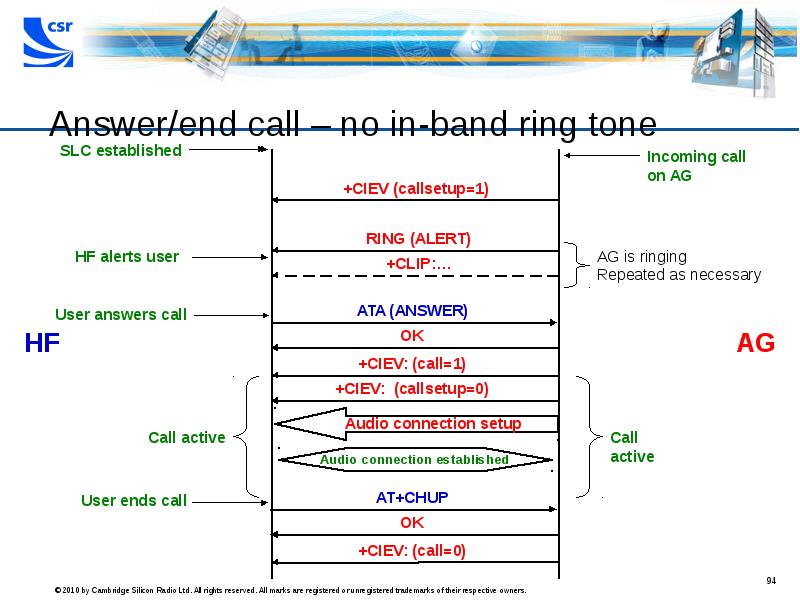
- 94. Answer/end call – no in-band ring tone
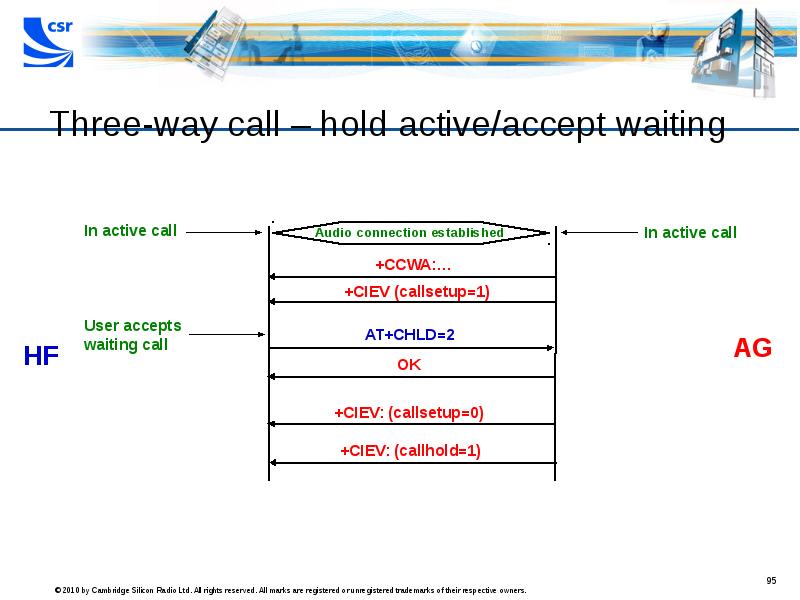
- 95. Three-way call – hold active/accept waiting
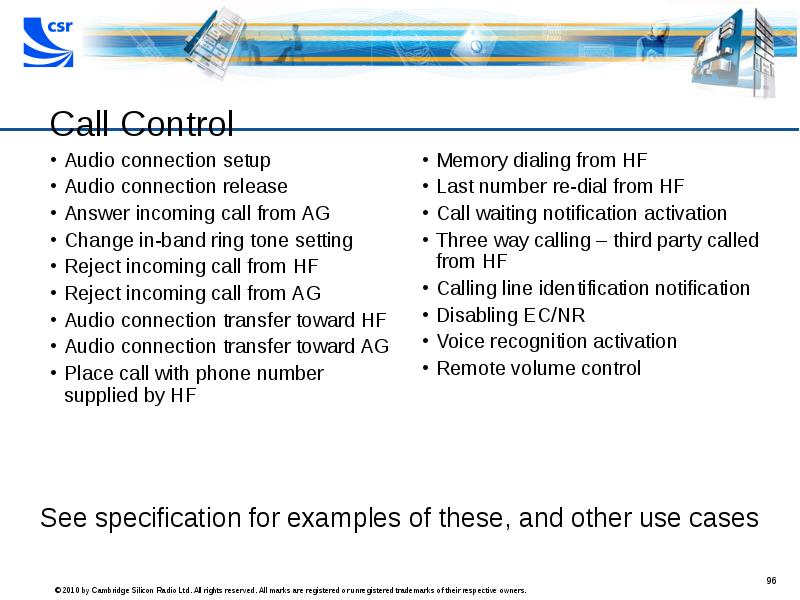
- 96. Call Control Audio connection setup Audio connection release Answer incoming call
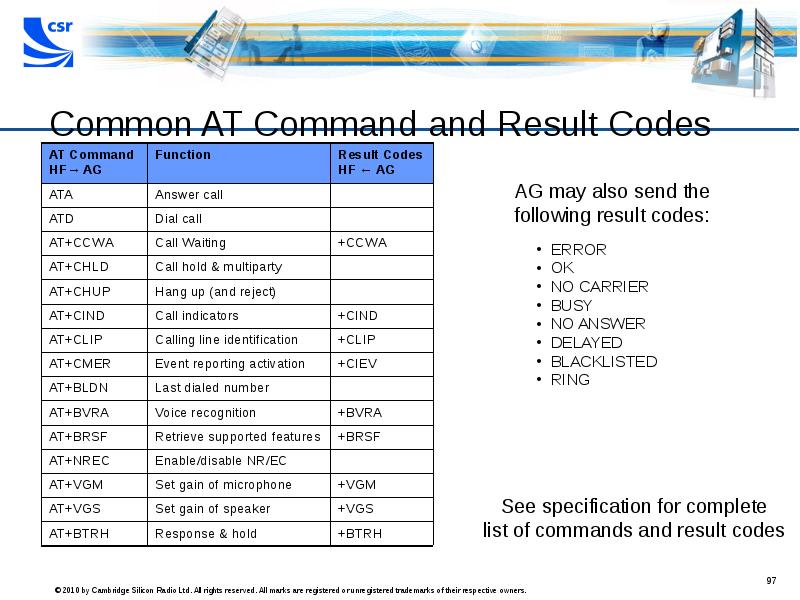
- 97. Common AT Command and Result Codes
- 98. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
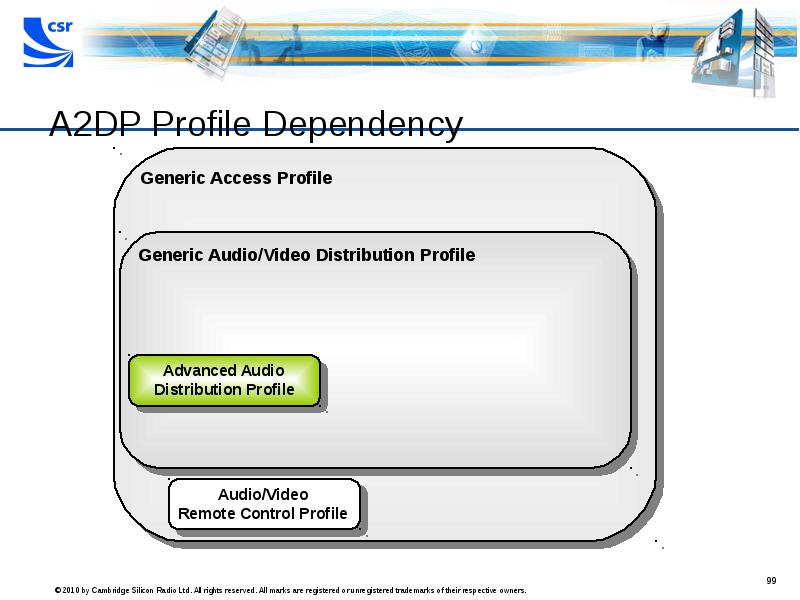
- 99. A2DP Profile Dependency
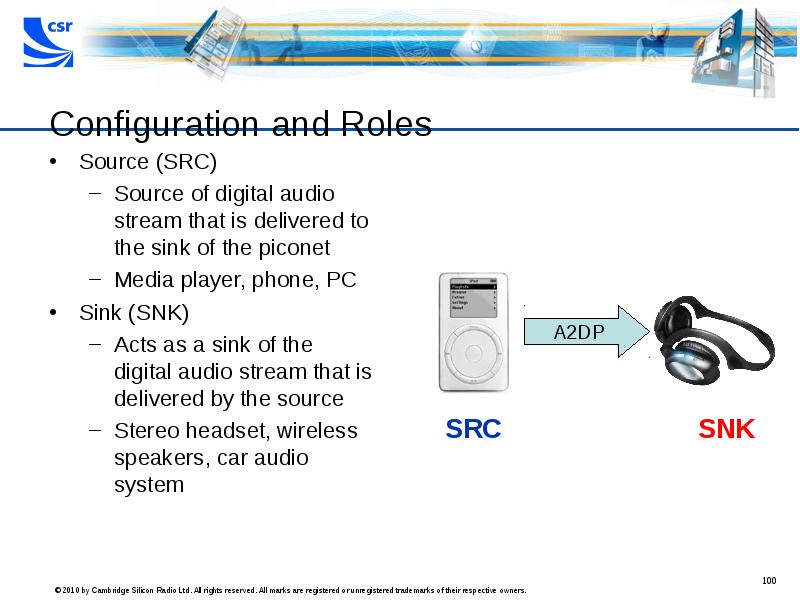
- 100. Configuration and Roles Source (SRC) Source of digital audio stream that
- 101. Audio Codec Interoperability Requirements Must support SBC Optional support for MP3,
- 102. Codec Specific Information Elements AVDTP signaling procedure negotiates codec parameters Parameters
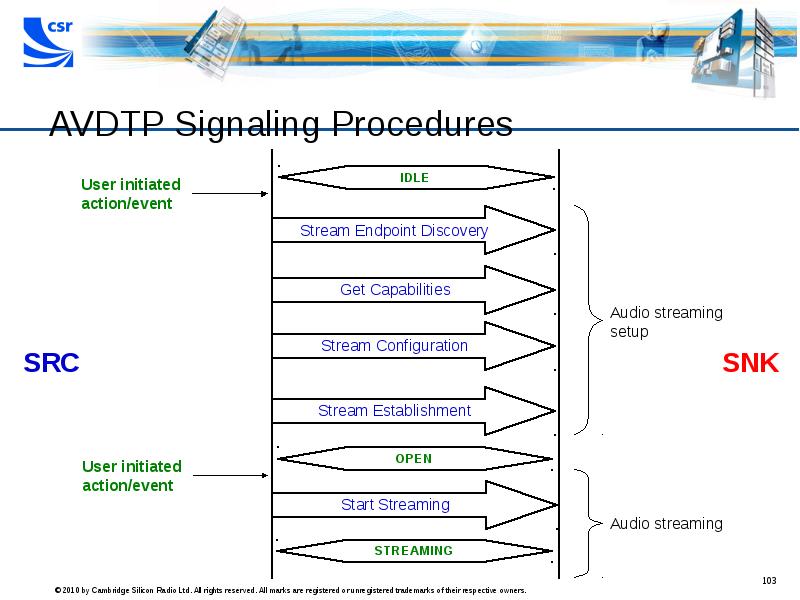
- 103. AVDTP Signaling Procedures
- 104. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
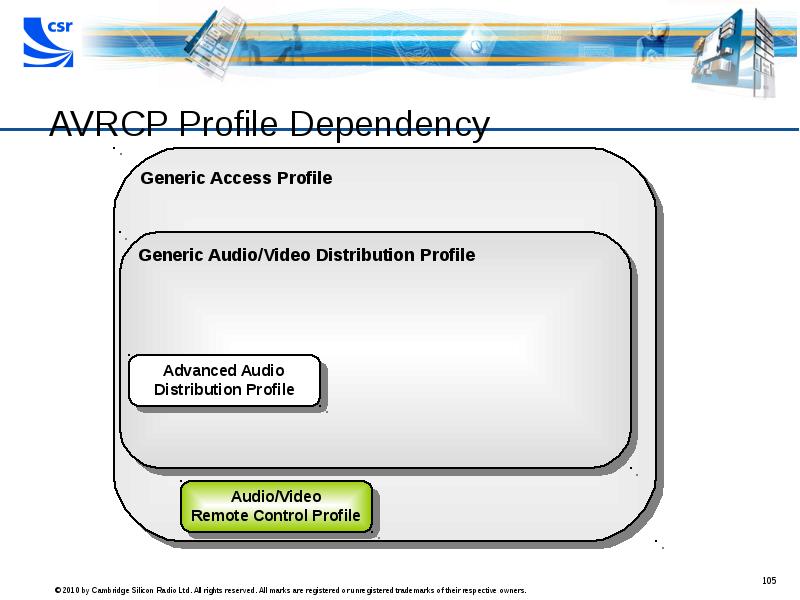
- 105. AVRCP Profile Dependency
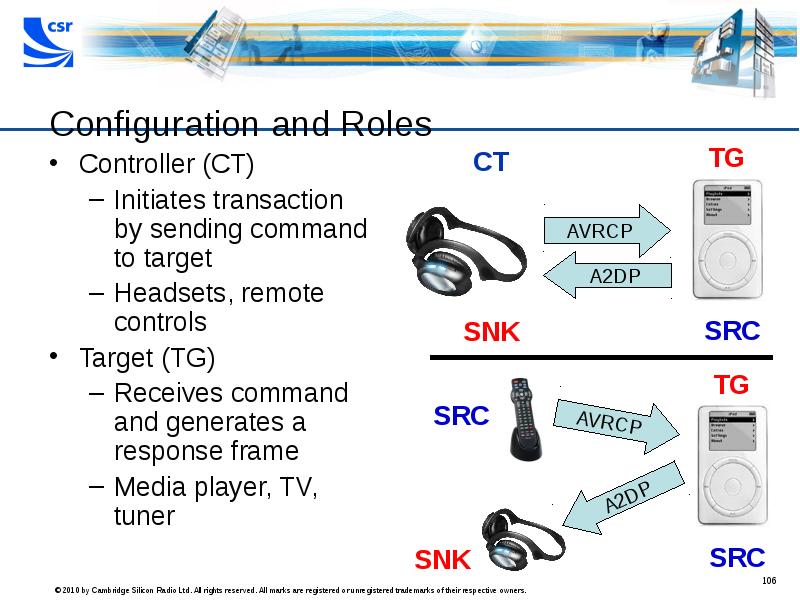
- 106. Configuration and Roles Controller (CT) Initiates transaction by sending command to
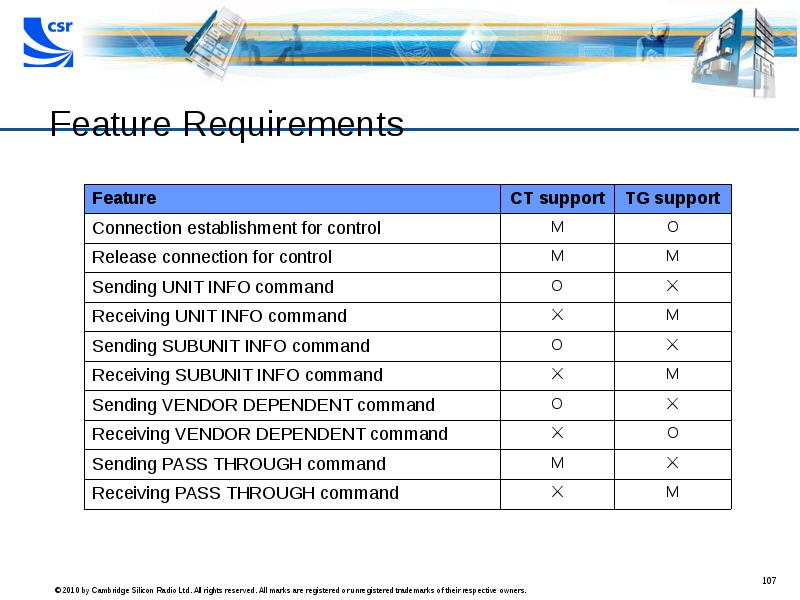
- 107. Feature Requirements
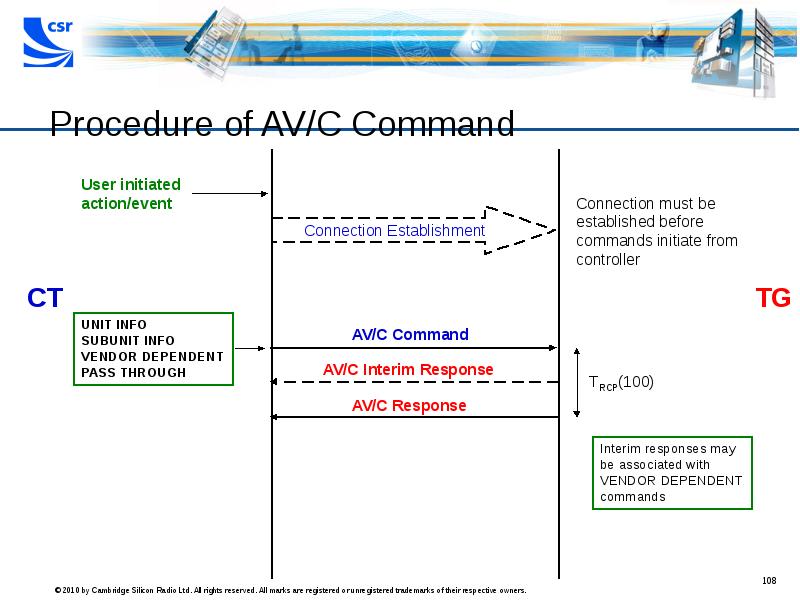
- 108. Procedure of AV/C Command
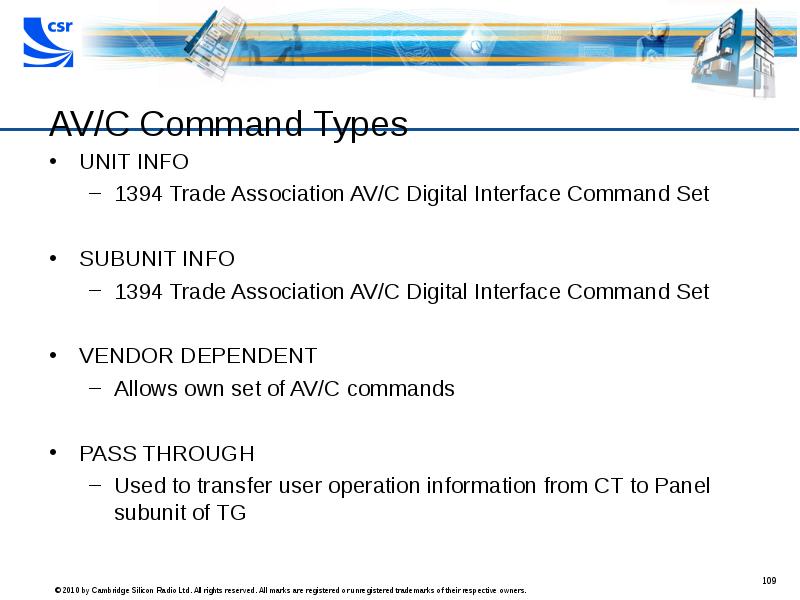
- 109. AV/C Command Types UNIT INFO 1394 Trade Association AV/C Digital Interface
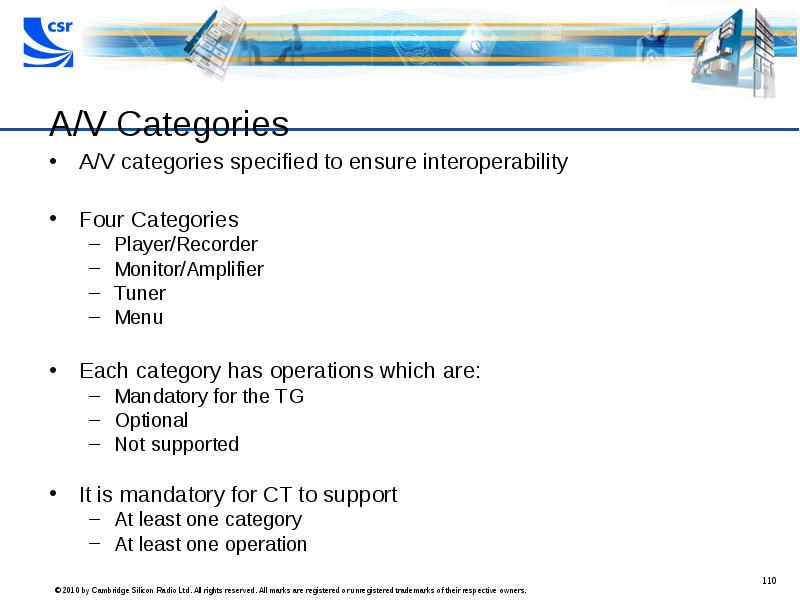
- 110. A/V Categories A/V categories specified to ensure interoperability Four Categories Player/Recorder
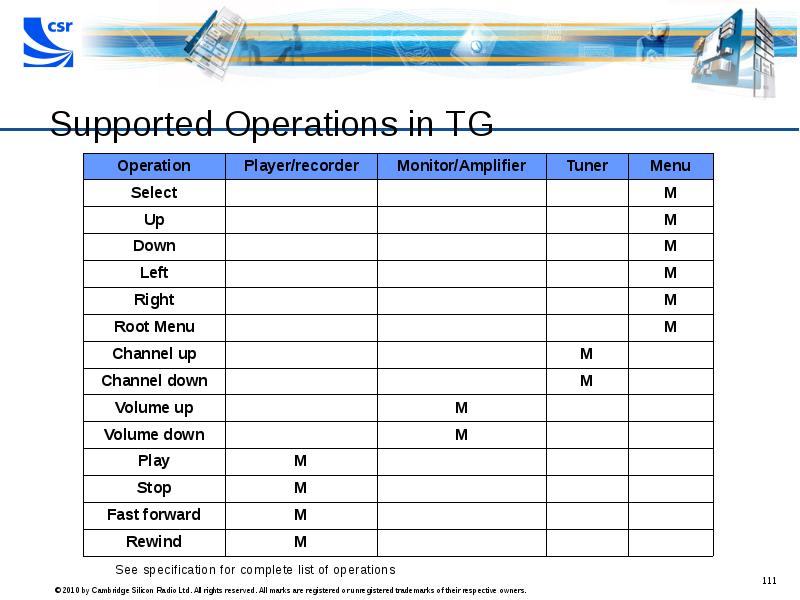
- 111. Supported Operations in TG
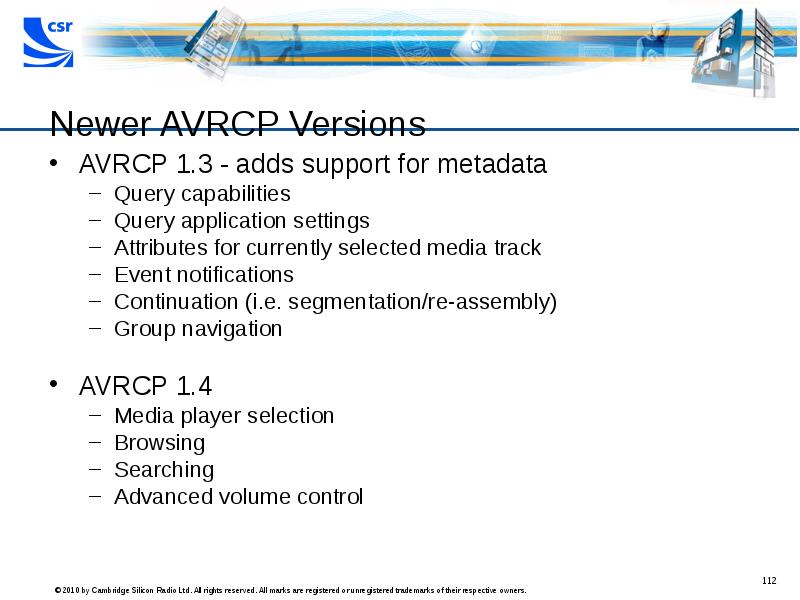
- 112. Newer AVRCP Versions AVRCP 1.3 - adds support for metadata Query
- 113. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
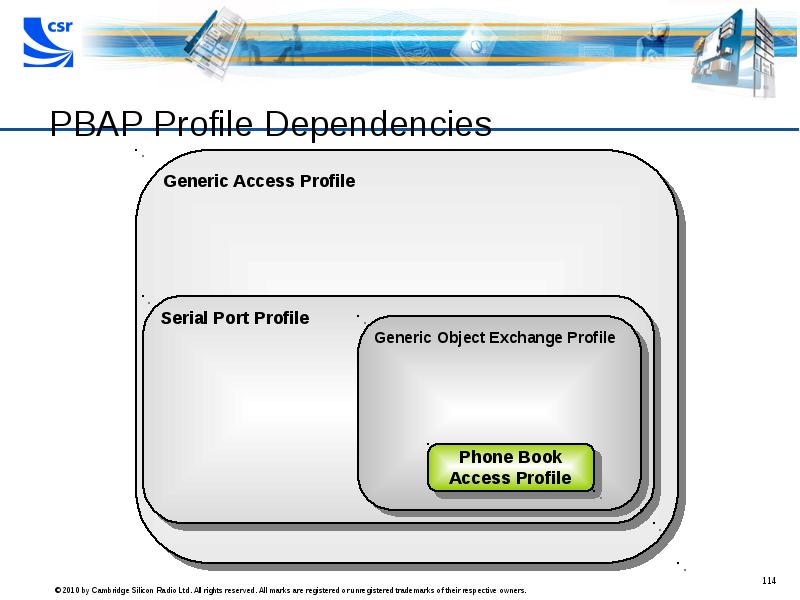
- 114. PBAP Profile Dependencies
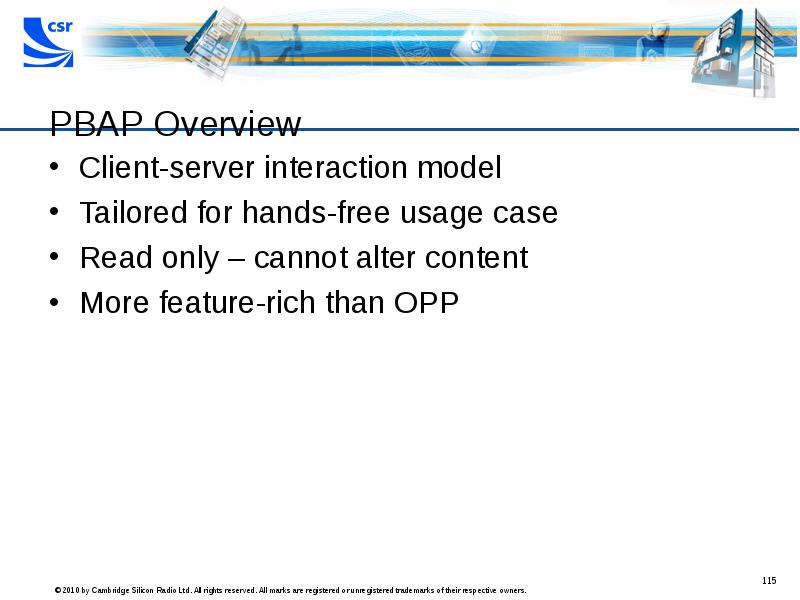
- 115. PBAP Overview Client-server interaction model Tailored for hands-free usage case Read
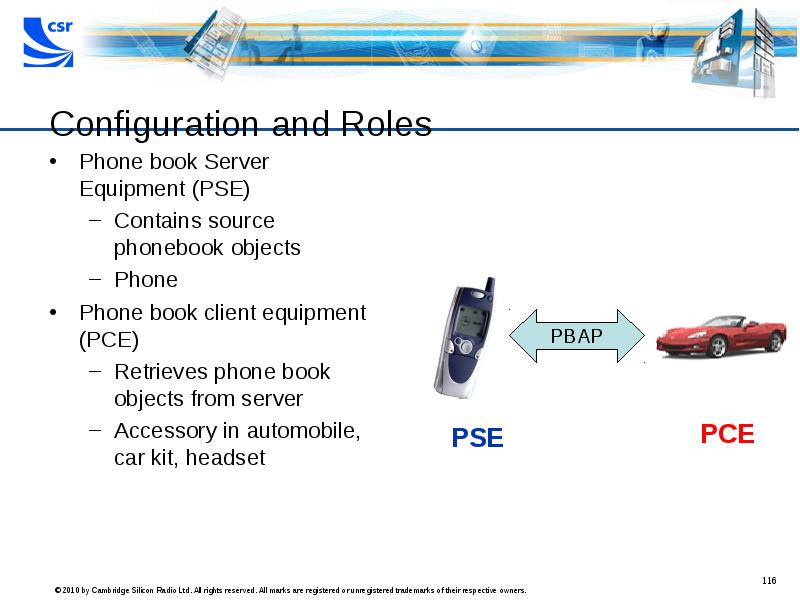
- 116. Configuration and Roles Phone book Server Equipment (PSE) Contains source phonebook
- 117. Phone Book Objects and Representations Based upon IR Mobile Communications specification
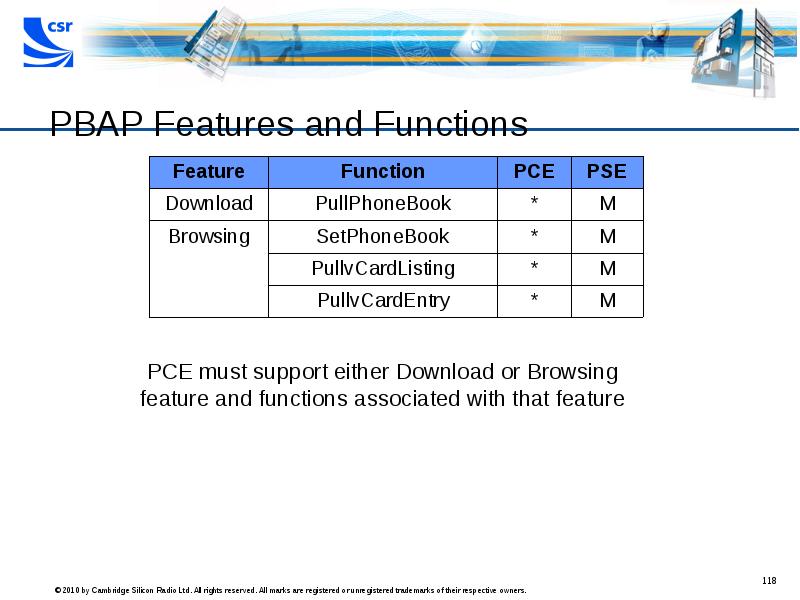
- 118. PBAP Features and Functions
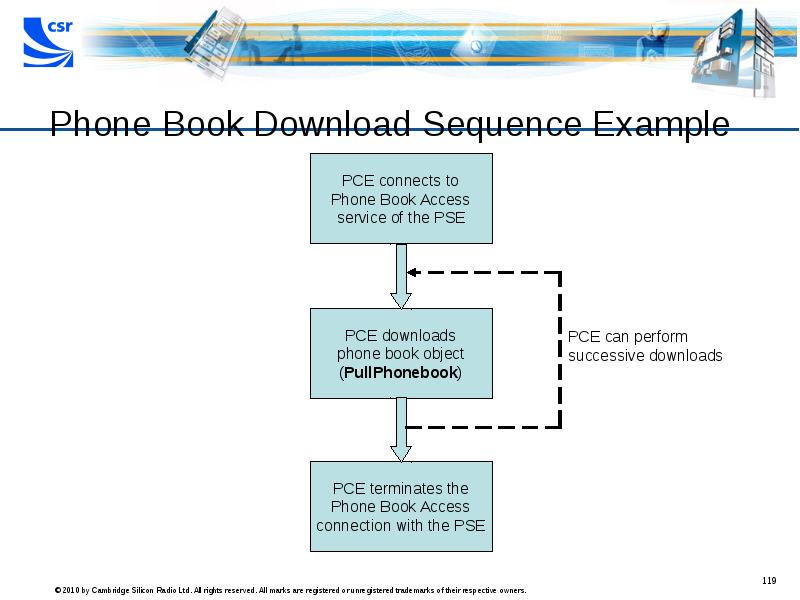
- 119. Phone Book Download Sequence Example
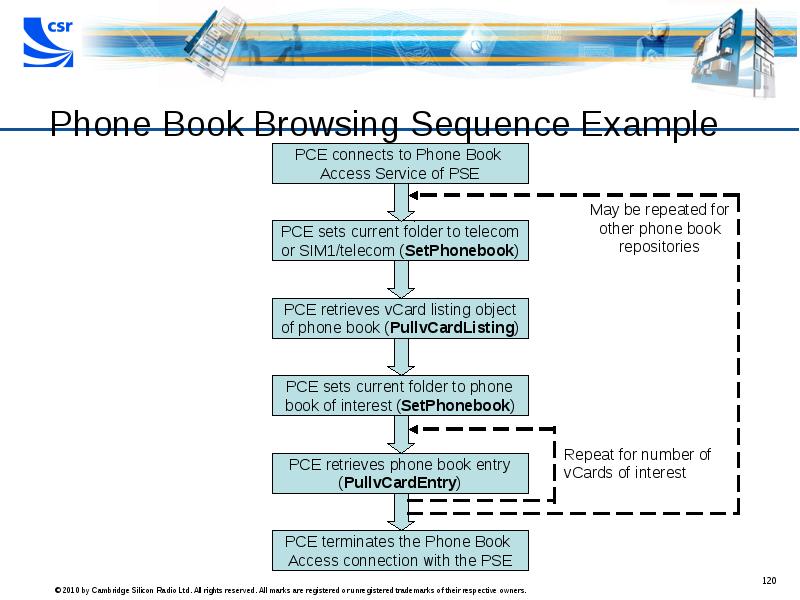
- 120. Phone Book Browsing Sequence Example
- 121. Agenda Bluetooth Overview Bluetooth Air Interface & Baseband Bluetooth Protocol Stack
- 122. Bluetooth 3.0+HS Alternate MAC/PHY (AMP) Enables high speed using other radio
- 123. Bluetooth 4.0 (BTle) Used to transfer simple data sets between compact
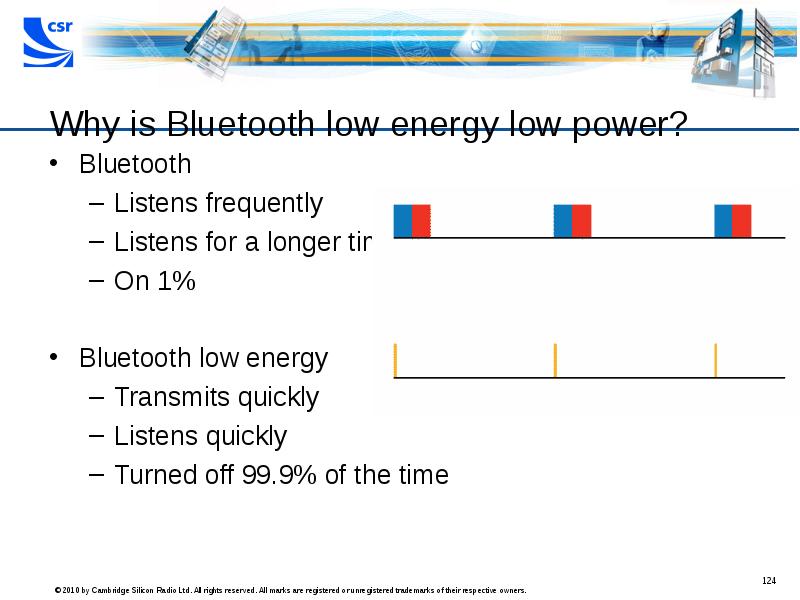
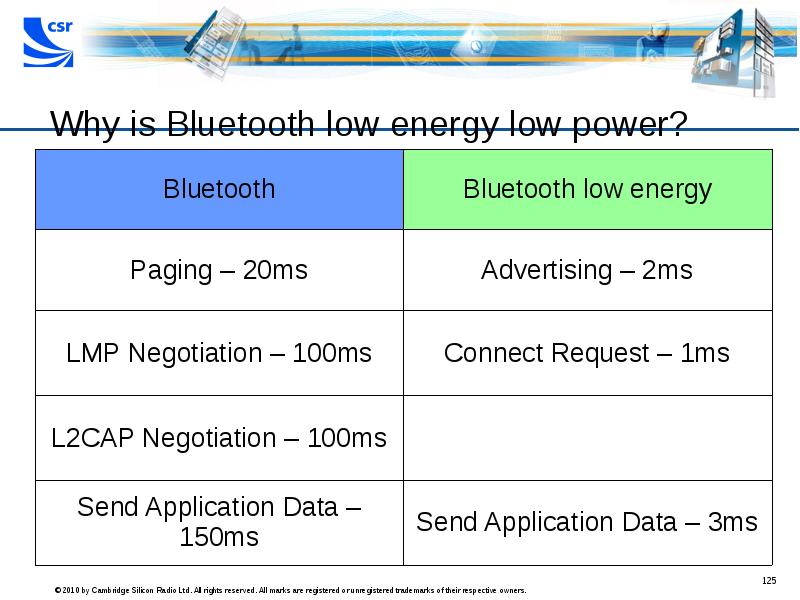
- 124. Why is Bluetooth low energy low power? Bluetooth Listens frequently Listens
- 125. Why is Bluetooth low energy low power?
- 127. Скачать презентацию

























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Bluetooth 101. Training for Plantronics можно ниже:
Похожие презентации





























