Graph theory irina prosvirnina. Definitions and examples. Paths and cycles презентация
Содержание
- 2. Definitions and examples Although generally regarded as one of the more
- 3. Definitions and examples Euler (1707 – 1783) was born in Switzerland
- 4. Definitions and examples Like many of the very great mathematicians of
- 5. Definitions and examples What is a ‘graph’? Intuitively, a graph is
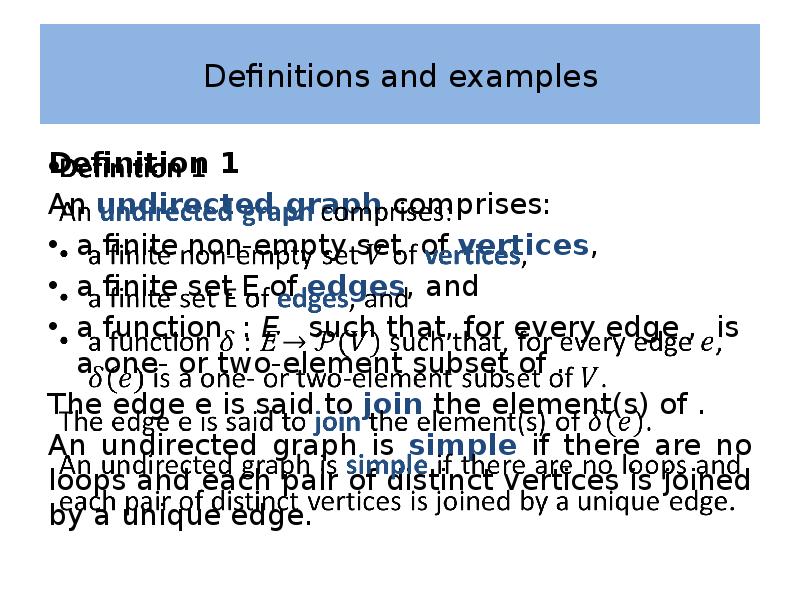
- 6. Definitions and examples Definition 1 An undirected graph comprises: a finite
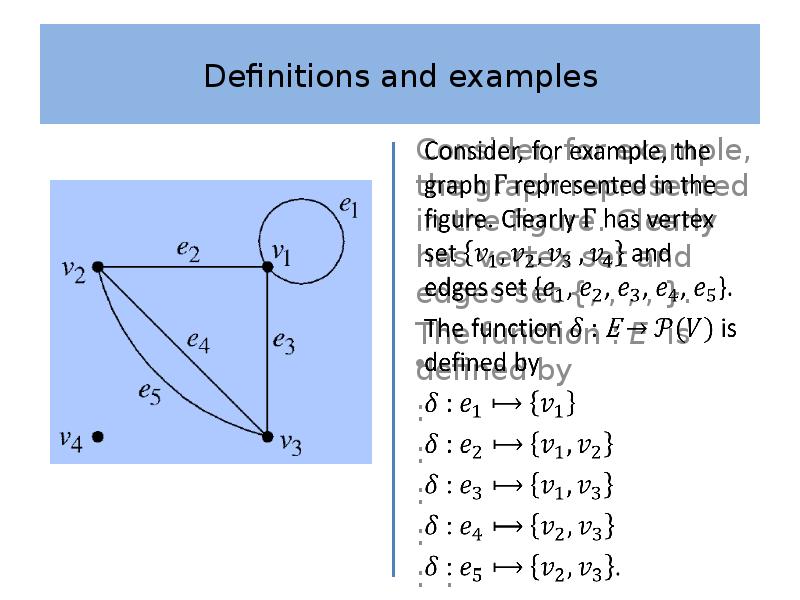
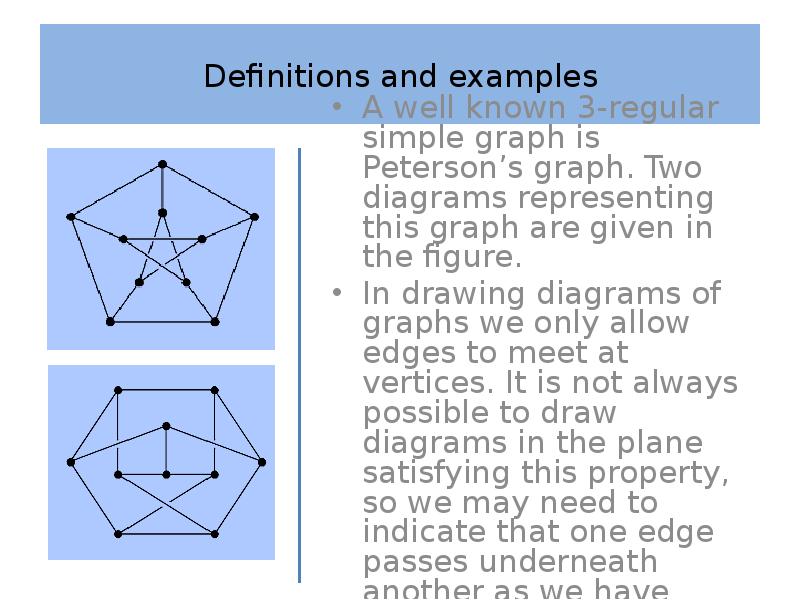
- 7. Definitions and examples
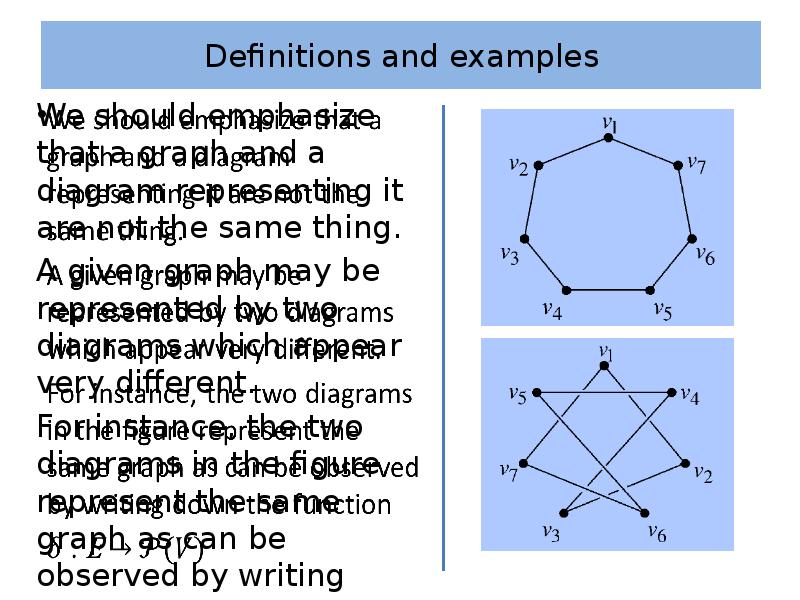
- 8. Definitions and examples We should emphasize that a graph and a
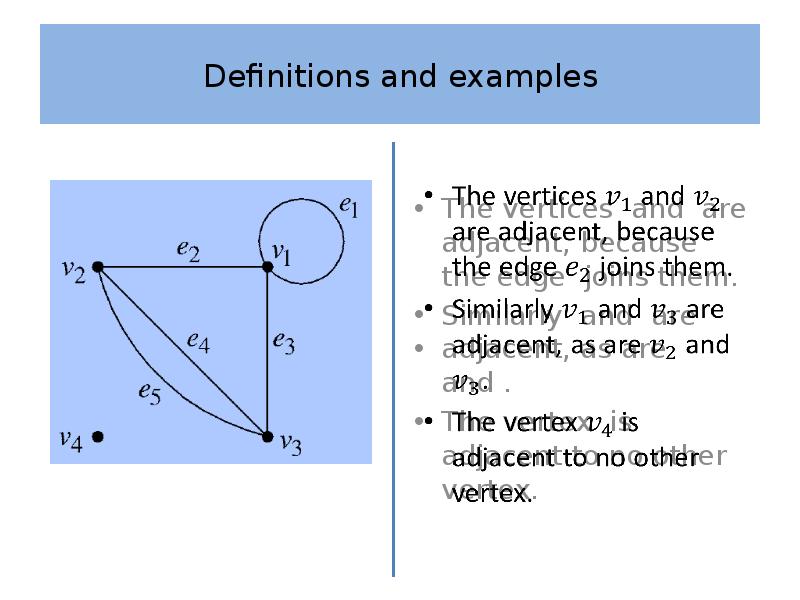
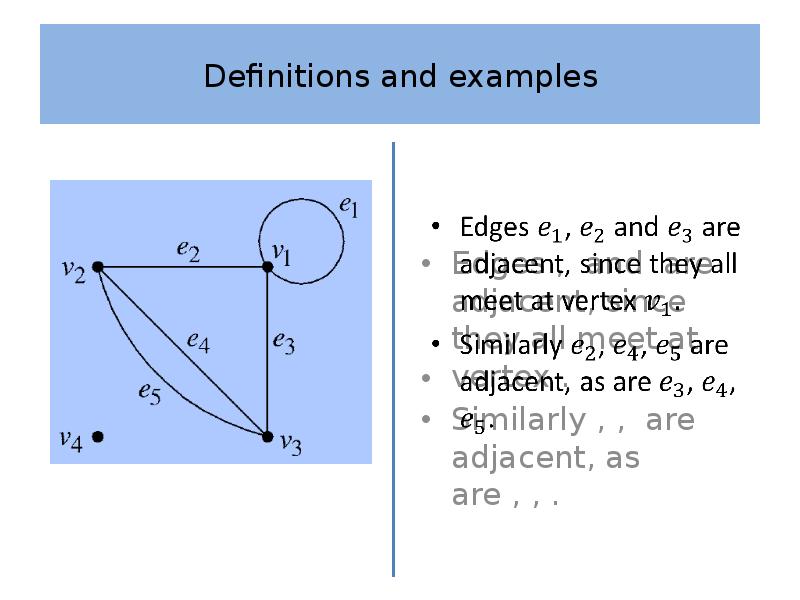
- 9. Definitions and examples Definition 2 A pair of vertices and are
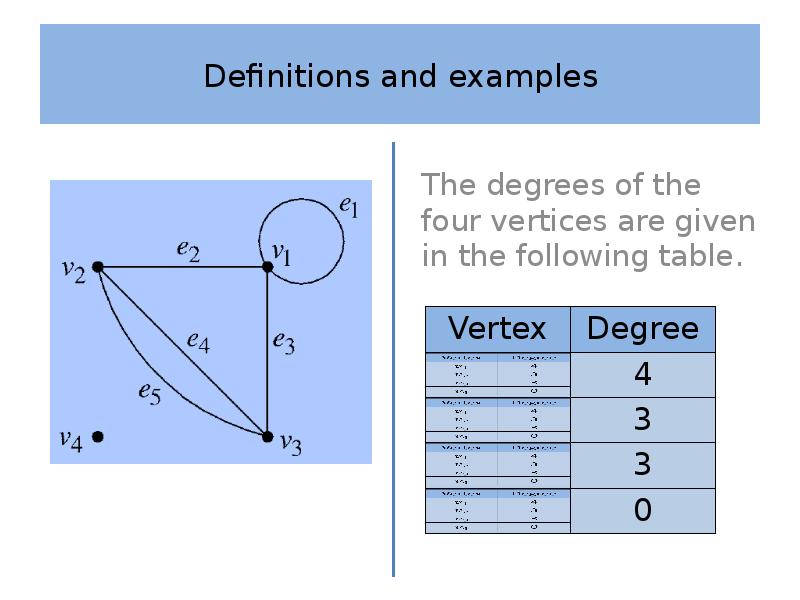
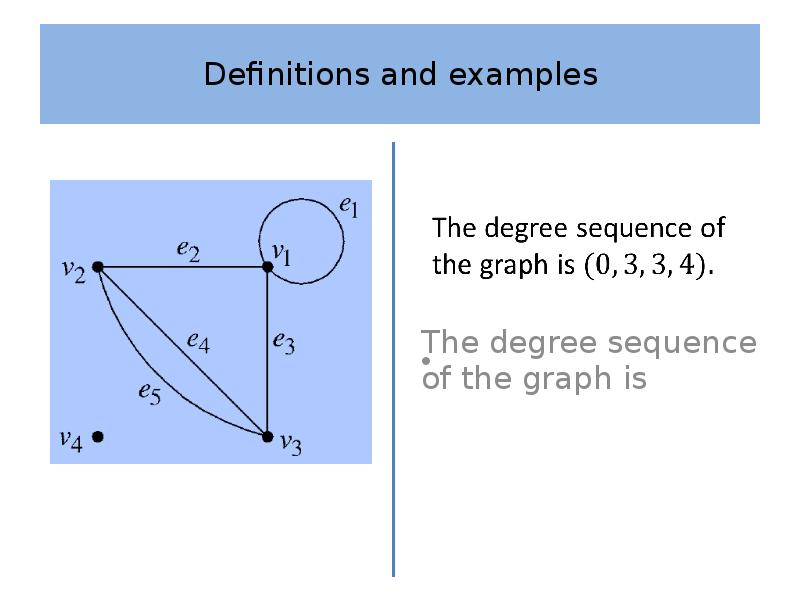
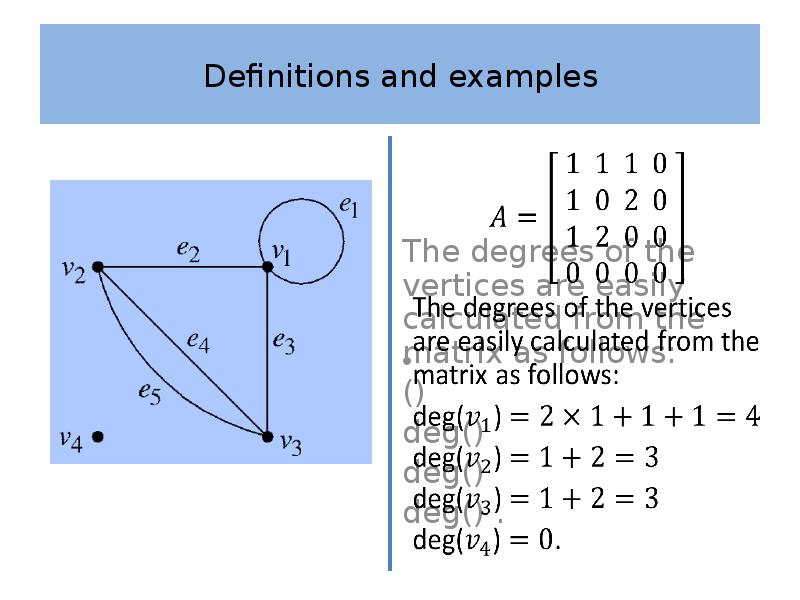
- 10. Definitions and examples Definition 2 The degree or valency, deg(), of
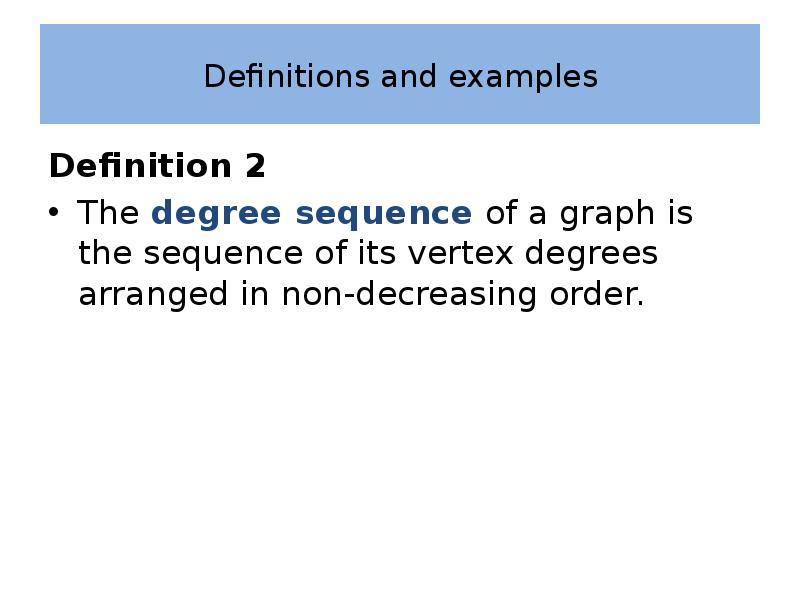
- 11. Definitions and examples Definition 2 The degree sequence of a graph
- 12. Definitions and examples
- 13. Definitions and examples
- 14. Definitions and examples
- 15. Definitions and examples
- 16. Definitions and examples
- 17. Definitions and examples Definition 3 A null graph (or totally disconnected
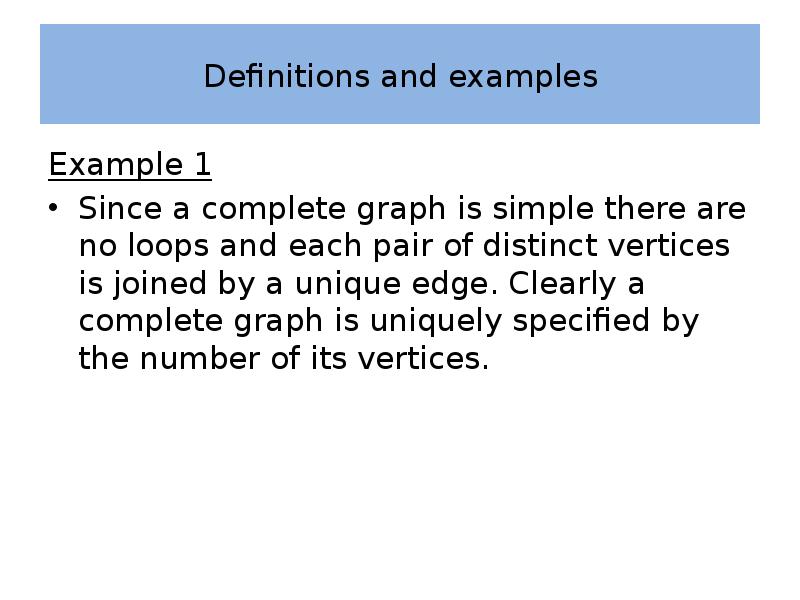
- 18. Definitions and examples Example 1 Since a complete graph is simple
- 19. Definitions and examples Example 1 The complete graph with vertices can
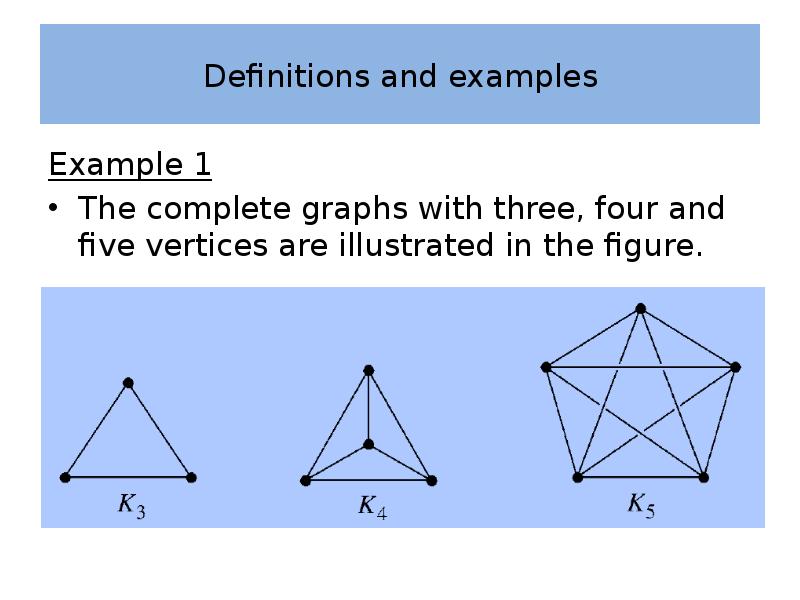
- 20. Definitions and examples Example 1 The complete graphs with three, four
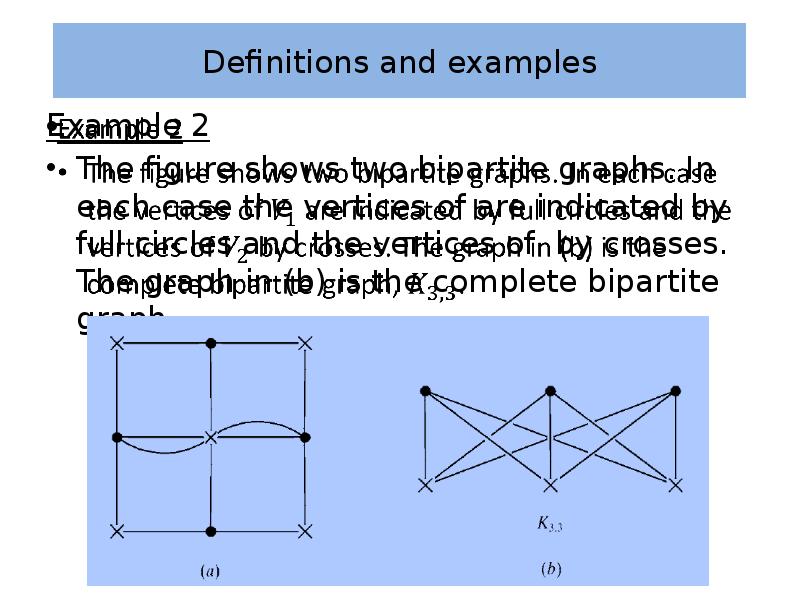
- 21. Definitions and examples Example 2 Let be a bipartite graph where
- 22. Definitions and examples Example 2 A complete bipartite graph is completely
- 23. Definitions and examples Example 2 The figure shows two bipartite graphs.
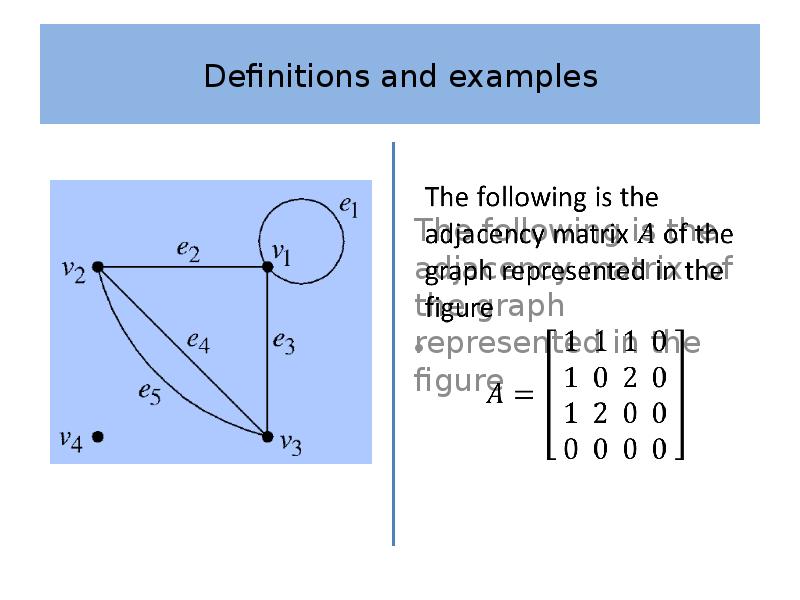
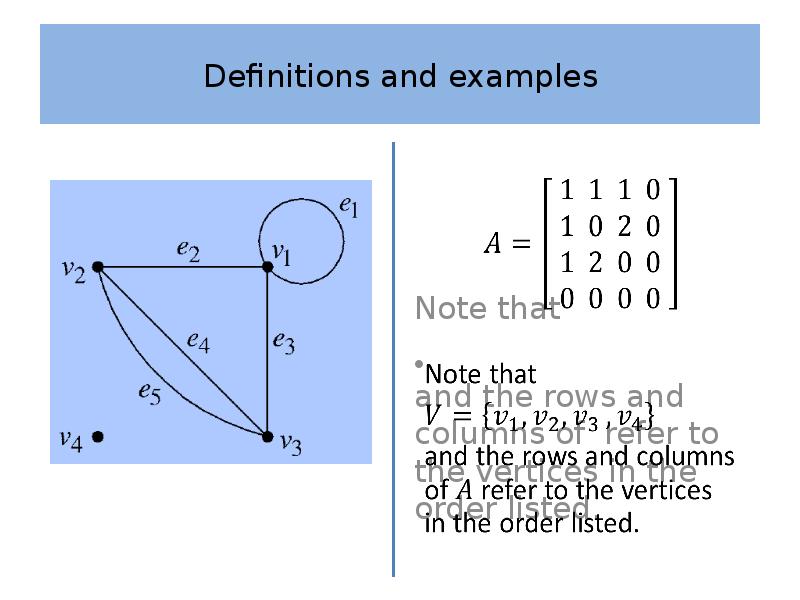
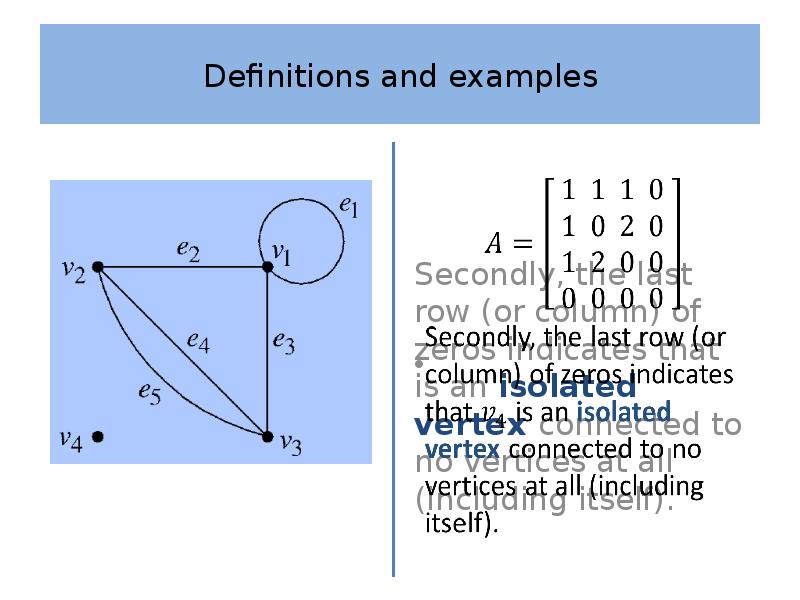
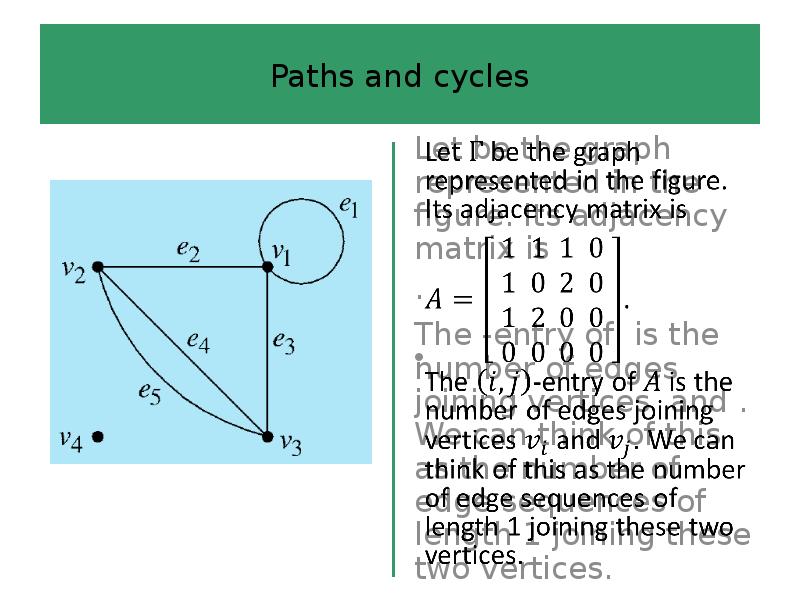
- 24. Definitions and examples Definition 4 Let be a graph with vertex
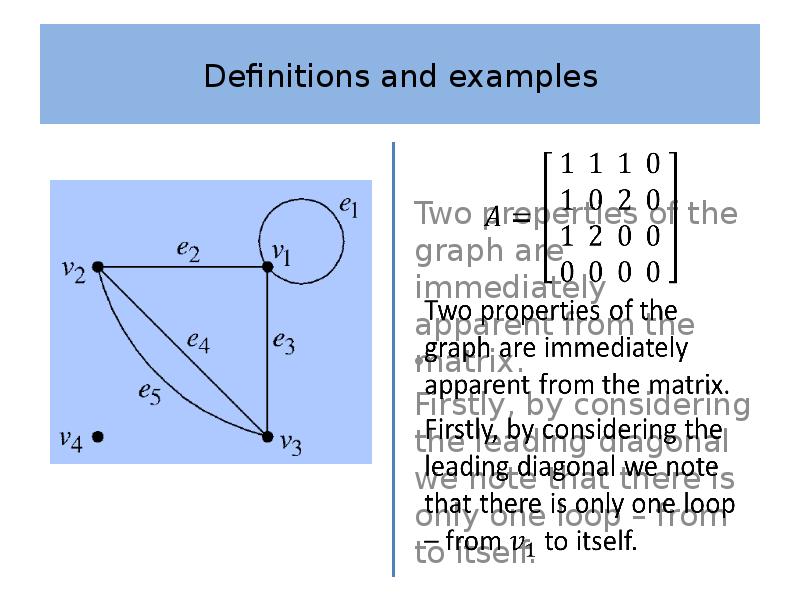
- 25. Definitions and examples The adjacency matrix is necessarily symmetric as the
- 26. Definitions and examples
- 27. Definitions and examples
- 28. Definitions and examples
- 29. Definitions and examples
- 30. Definitions and examples
- 31. Definitions and examples Example 3 The null graph with vertices has
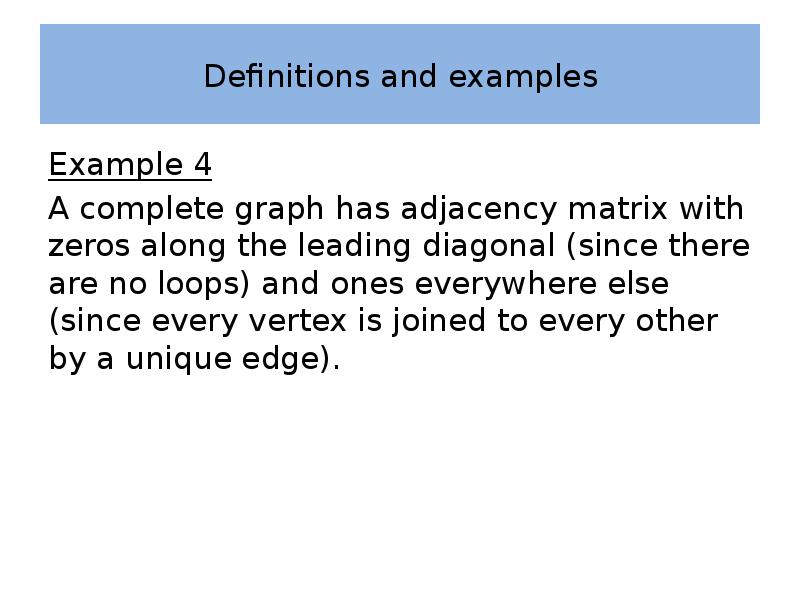
- 32. Definitions and examples Example 4 A complete graph has adjacency matrix
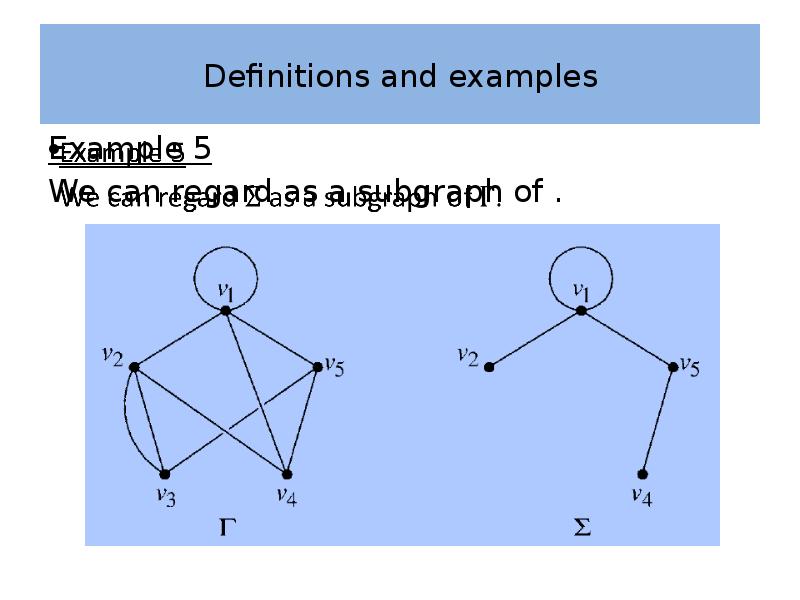
- 33. Definitions and examples Definition 5 A graph is a subgraph of
- 34. Definitions and examples Example 5 We can regard as a subgraph
- 35. Paths and cycles Using the analogy of a road map, we
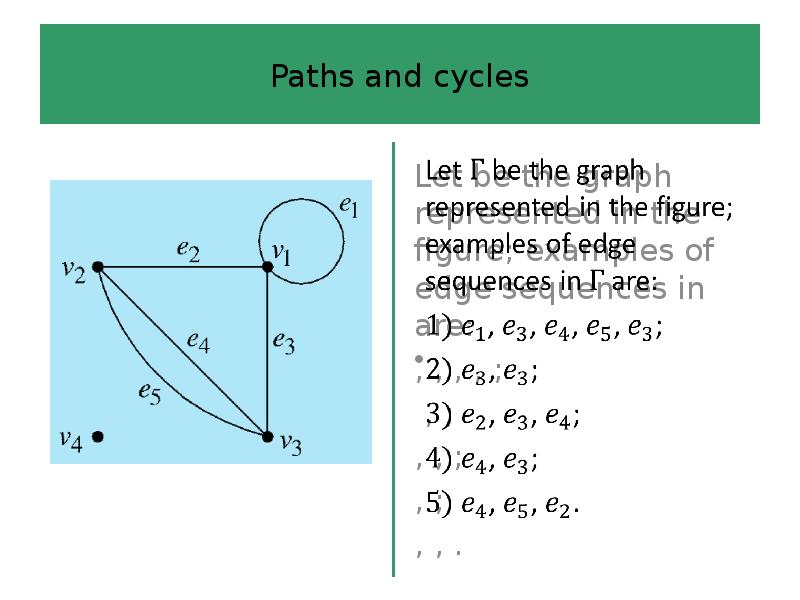
- 36. Paths and cycles Definition 6 An edge sequence of length in
- 37. Paths and cycles Definition 6 A path is an edge sequence
- 38. Paths and cycles Definition 6 An edge sequence is closed if
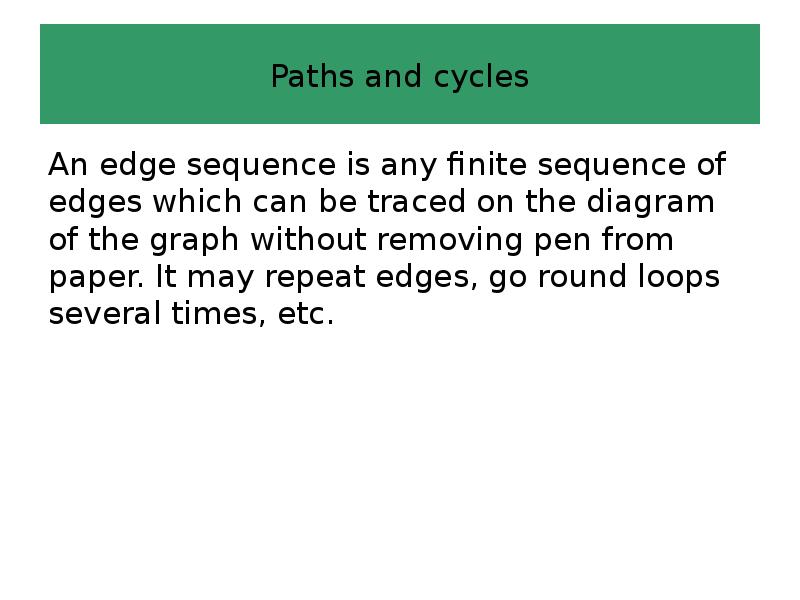
- 39. Paths and cycles An edge sequence is any finite sequence of
- 40. Paths and cycles Edge sequences are too general to be of
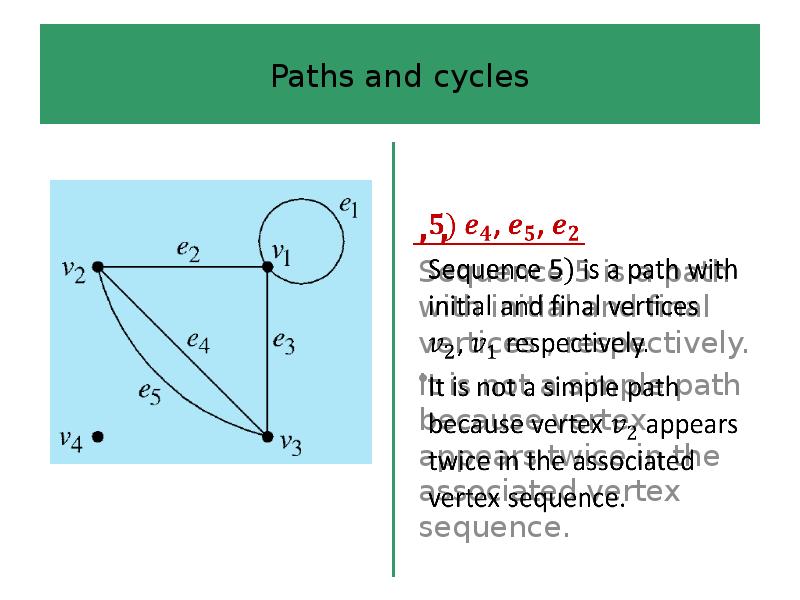
- 41. Paths and cycles In a path we are not allowed to
- 42. Paths and cycles If, in addition, we do not ‘visit’ the
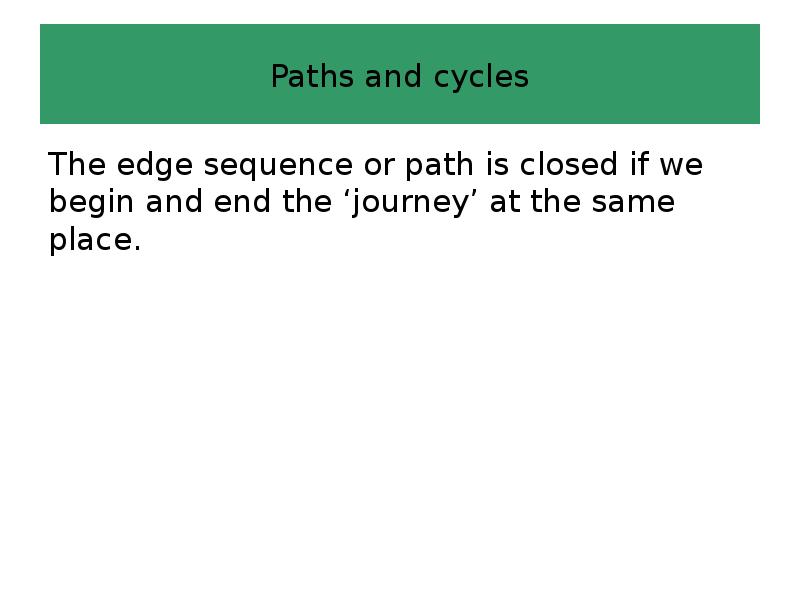
- 43. Paths and cycles The edge sequence or path is closed if
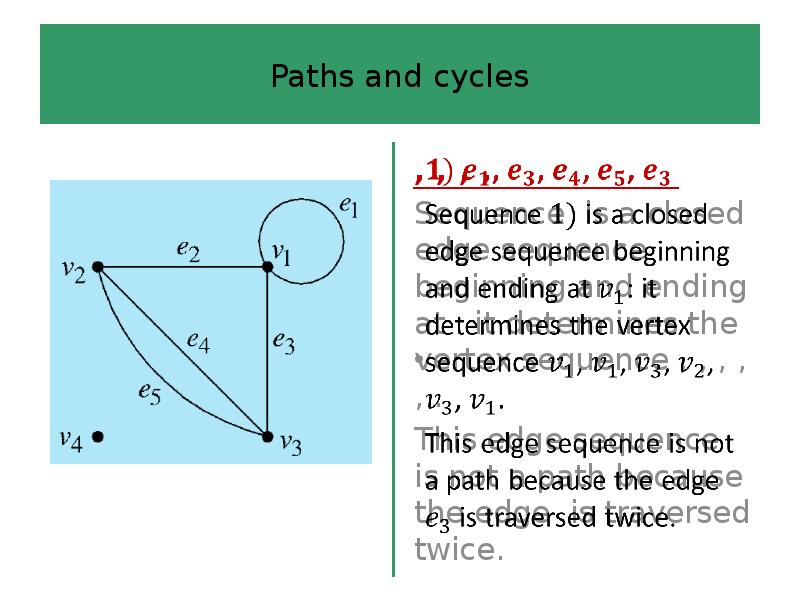
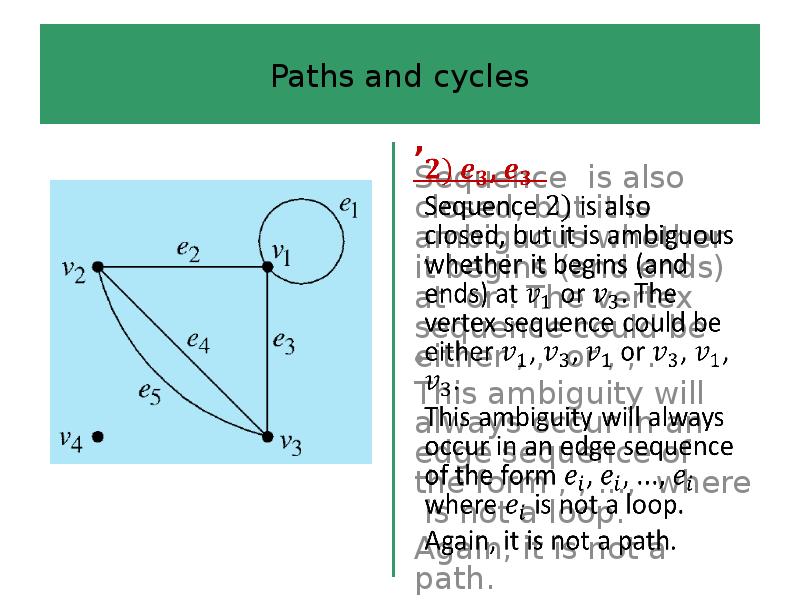
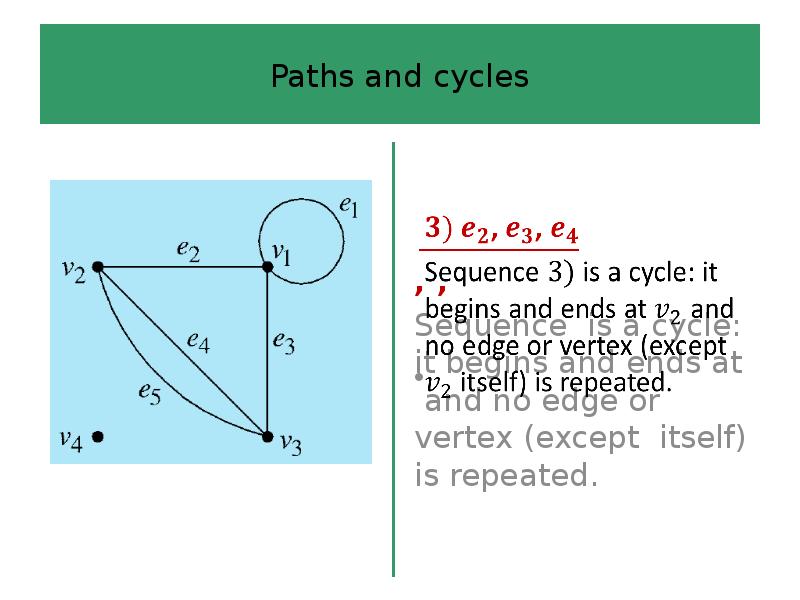
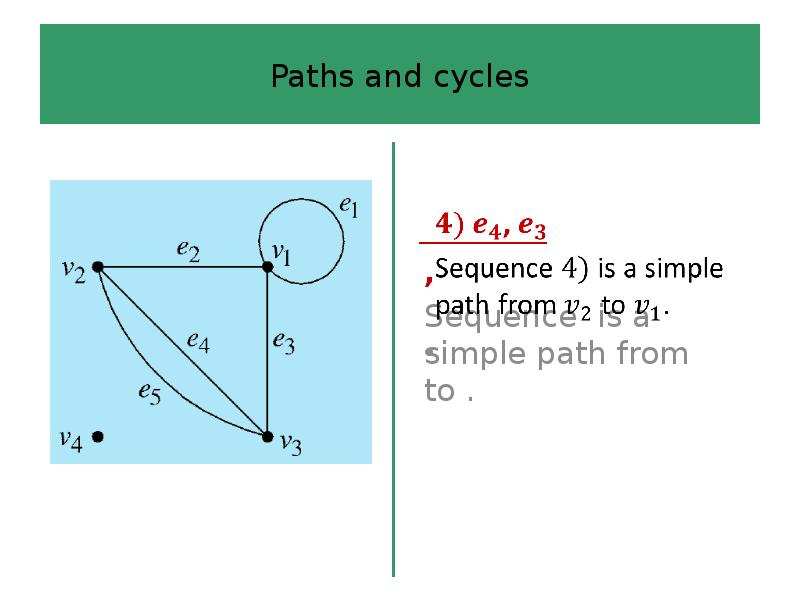
- 44. Paths and cycles
- 45. Paths and cycles
- 46. Paths and cycles
- 47. Paths and cycles
- 48. Paths and cycles
- 49. Paths and cycles
- 50. Paths and cycles
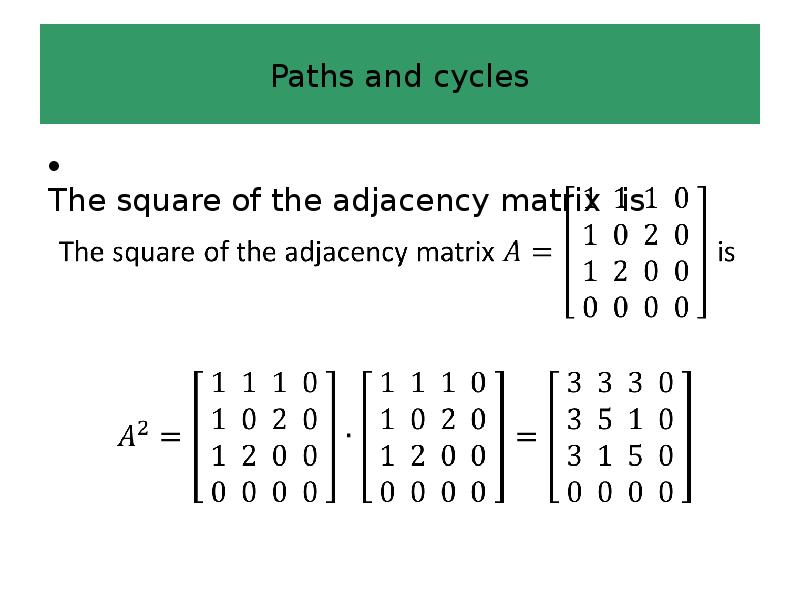
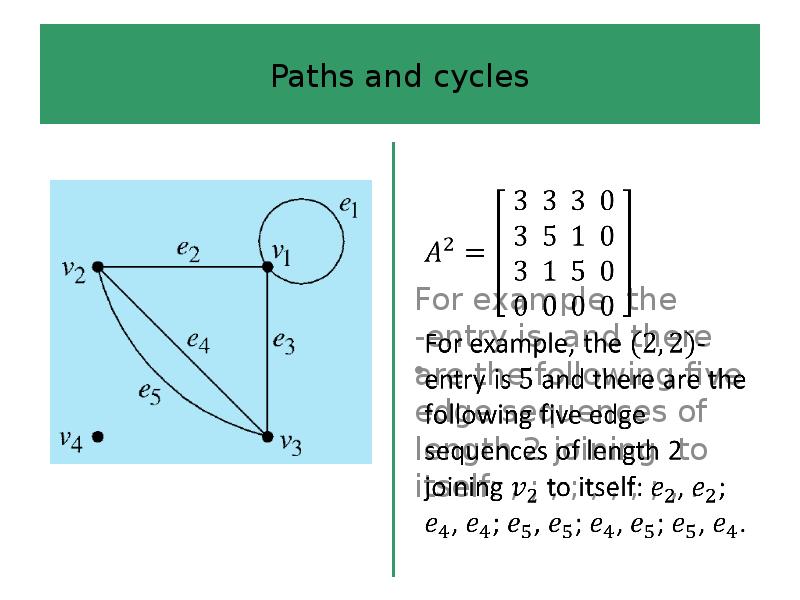
- 51. Paths and cycles The square of the adjacency matrix is
- 52. Paths and cycles
- 53. Paths and cycles
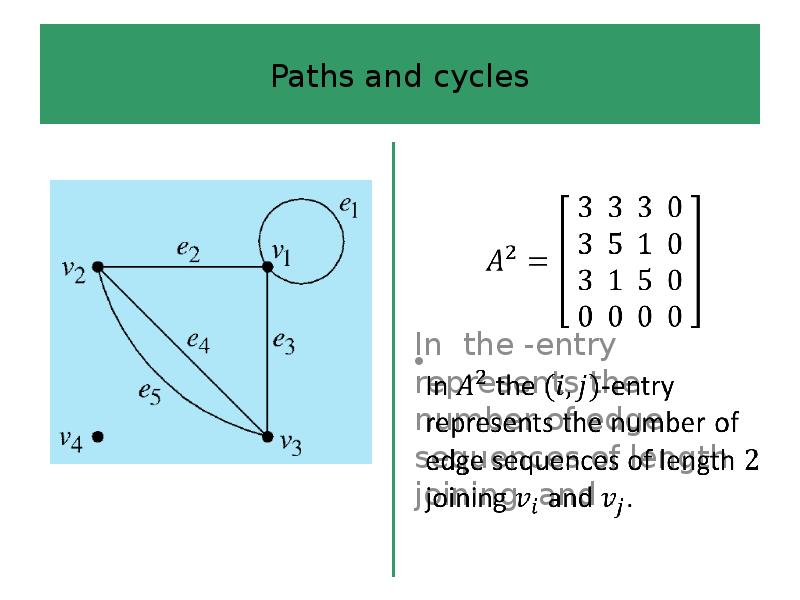
- 54. ? In the -entry represents the number of edge sequences of
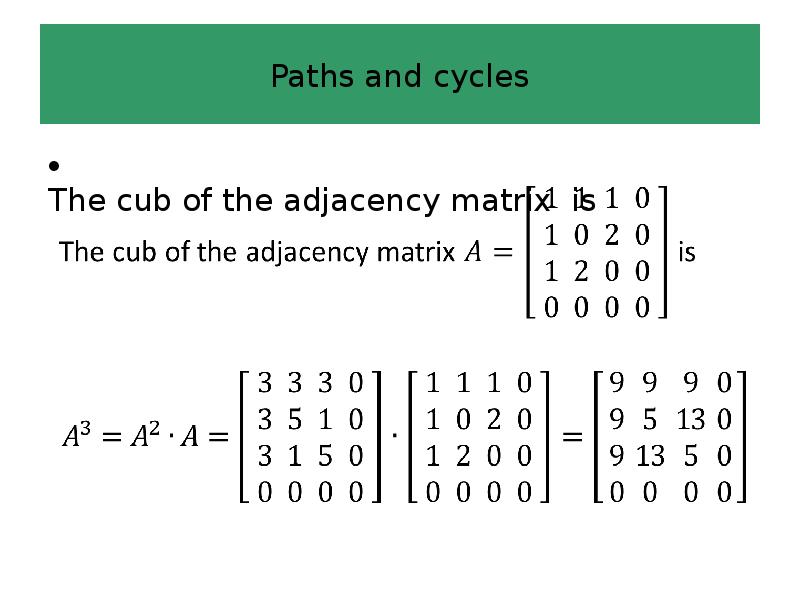
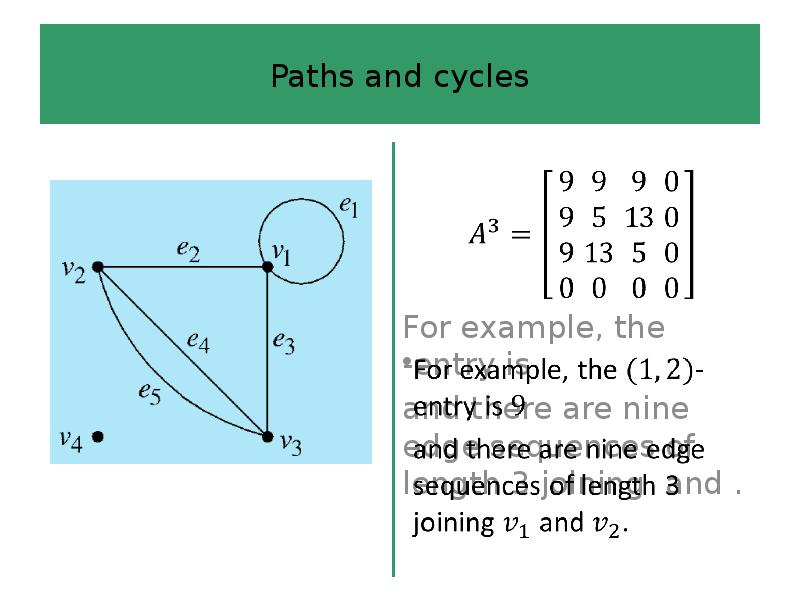
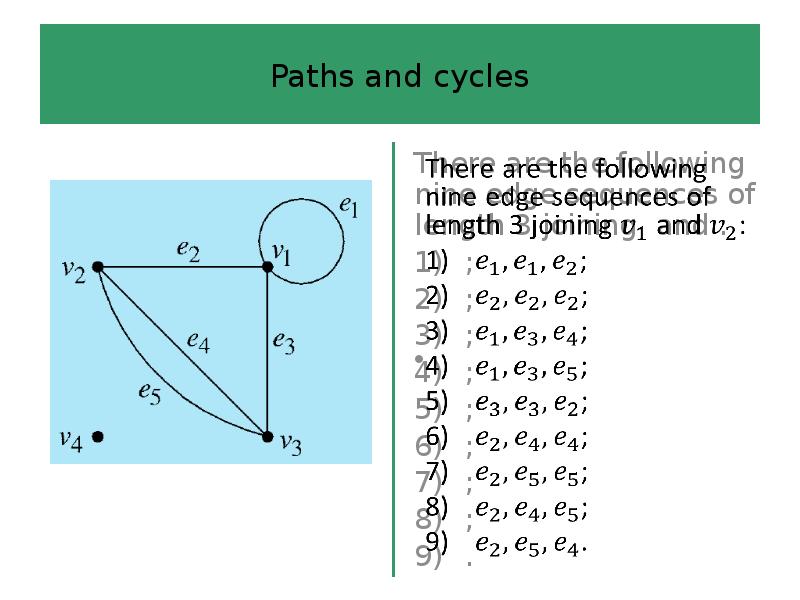
- 55. Paths and cycles The cub of the adjacency matrix is
- 56. Paths and cycles
- 57. Paths and cycles
- 58. Paths and cycles Theorem 1 Let be a graph with vertex
- 59. Paths and cycles In an intuitively obvious sense, some graphs are
- 60. Paths and cycles Definition 7 A graph is connected if, given
- 61. Paths and cycles An arbitrary graph naturally splits up into a
- 62. Paths and cycles This means that is a component of if
- 63. Paths and cycles The components of a graph are just its
- 64. Paths and cycles There is an alternative way of defining the
- 65. Paths and cycles if and only if and can be joined
- 66. Paths and cycles if and only if and can be joined
- 67. Paths and cycles
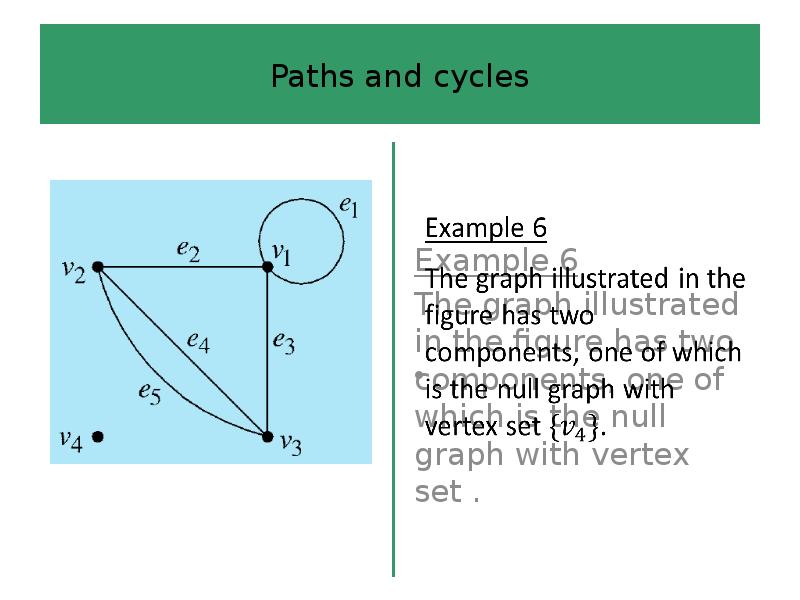
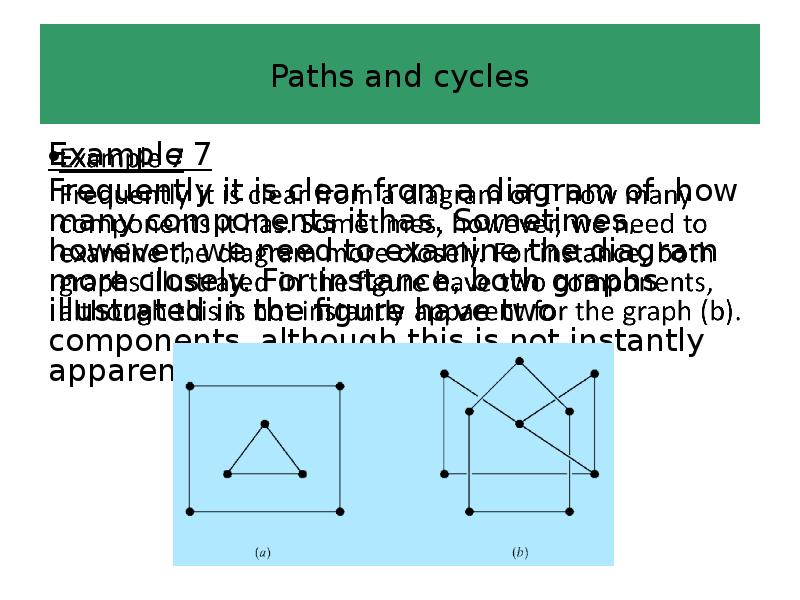
- 68. Paths and cycles Example 7 Frequently it is clear from a
- 69. Скачать презентацию


























Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Graph theory irina prosvirnina. Definitions and examples. Paths and cycles можно ниже:
Похожие презентации