Types of Hearing Aids презентация
Содержание
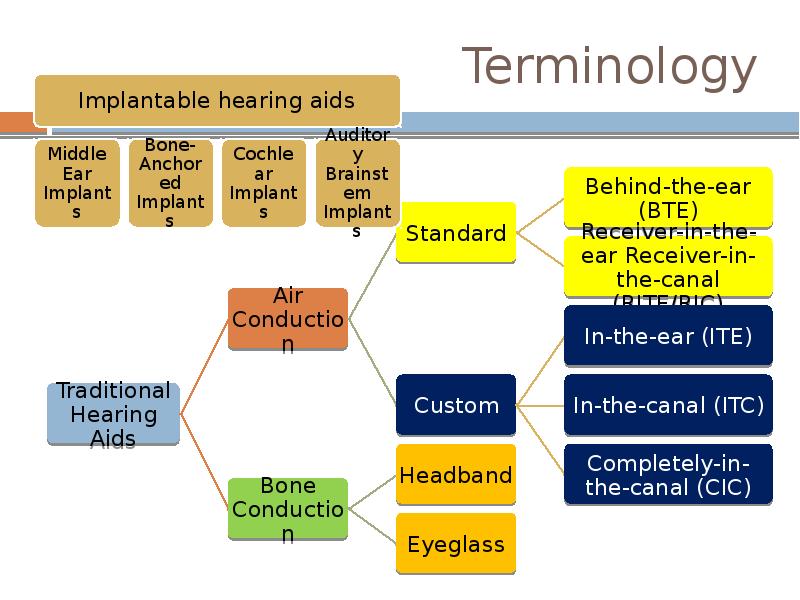
- 2. Terminology
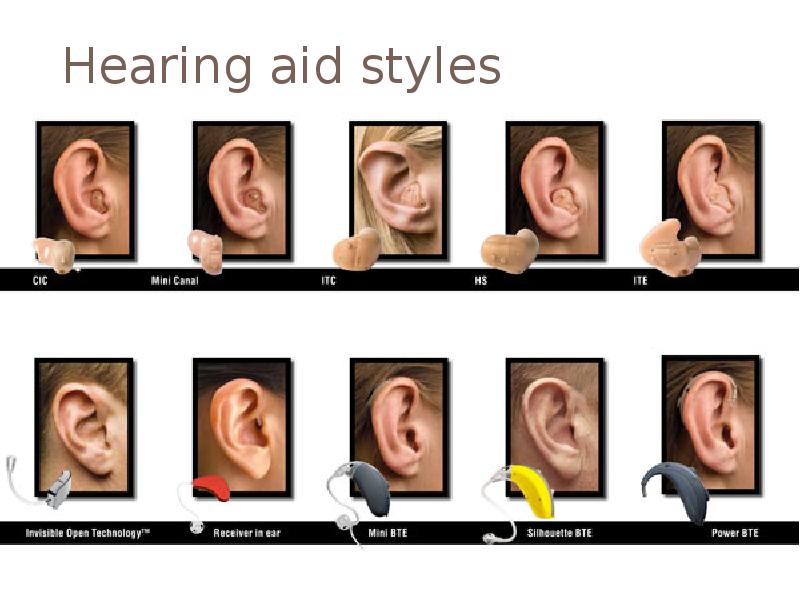
- 3. Hearing aid styles
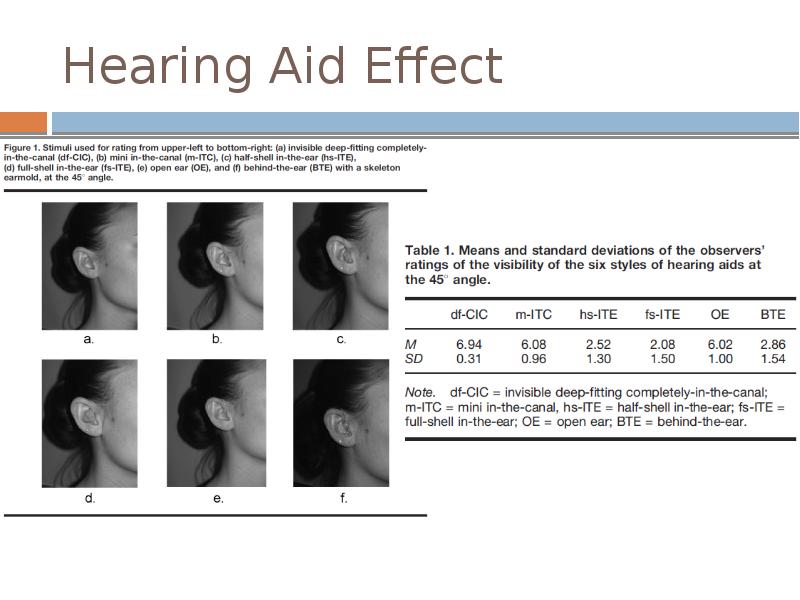
- 4. Hearing Aid Effect
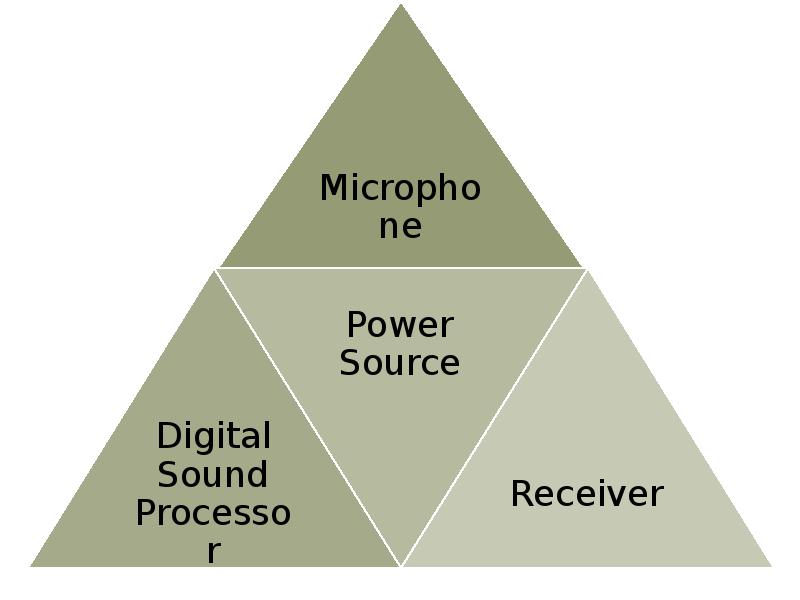
- 5. Hearing Aid Components
- 7. Batteries
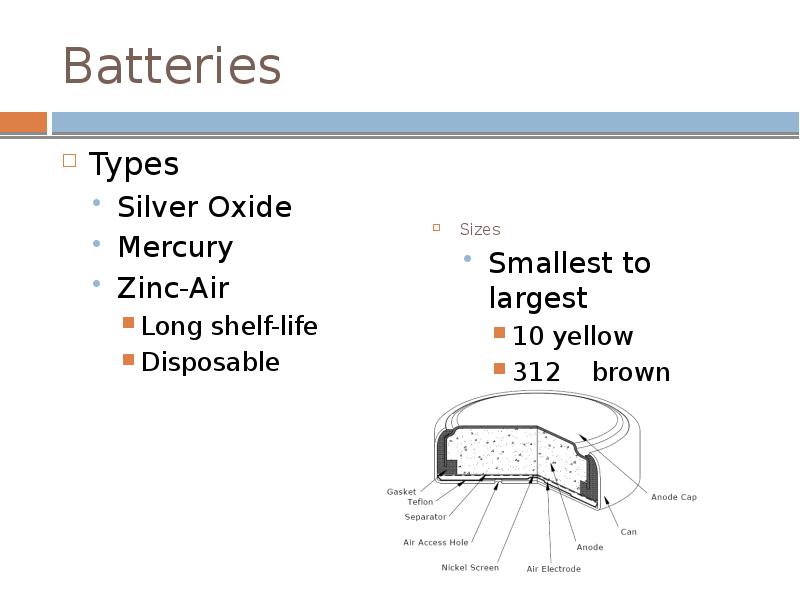
- 8. Batteries Types Silver Oxide Mercury Zinc-Air Long shelf-life Disposable
- 9. Zinc-Air batteries Require air to work Battery compartment of hearing aid
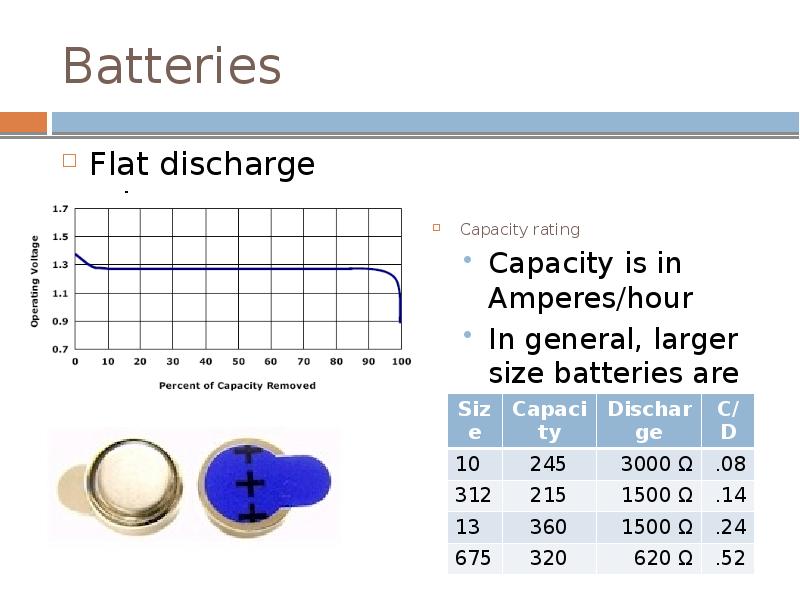
- 10. Batteries Flat discharge rate
- 11. Batteries 2320 cases of battery ingestion 1983 – 1990 952
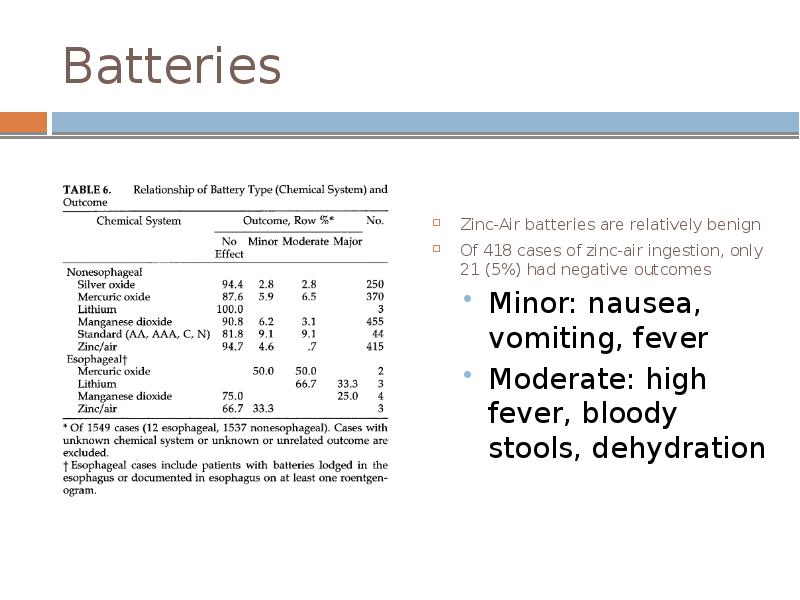
- 12. Batteries Zinc-Air batteries are relatively benign Of 418 cases of zinc-air
- 13. Batteries If anyone ingests a battery, this is what you should
- 14. Batteries Don't induce vomiting. Don't eat or drink until the x-ray
- 15. Microphones
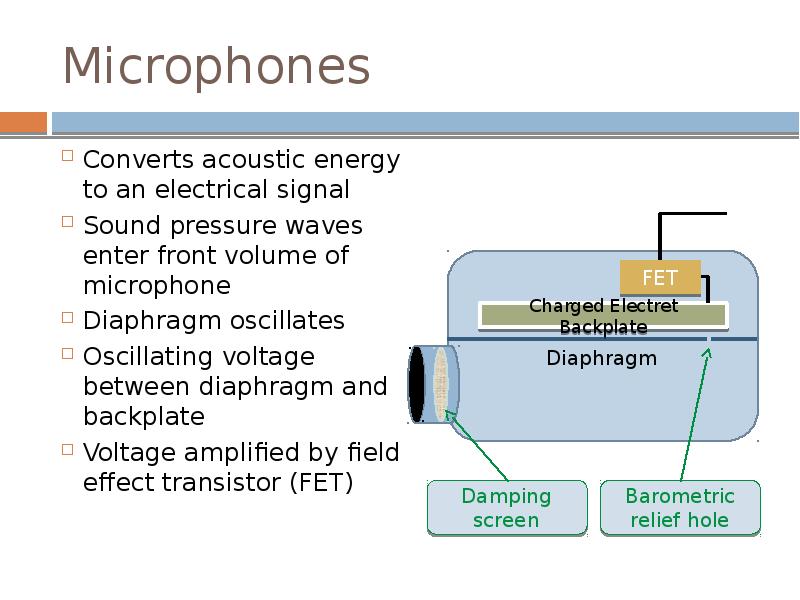
- 16. Microphones Converts acoustic energy to an electrical signal Sound pressure waves
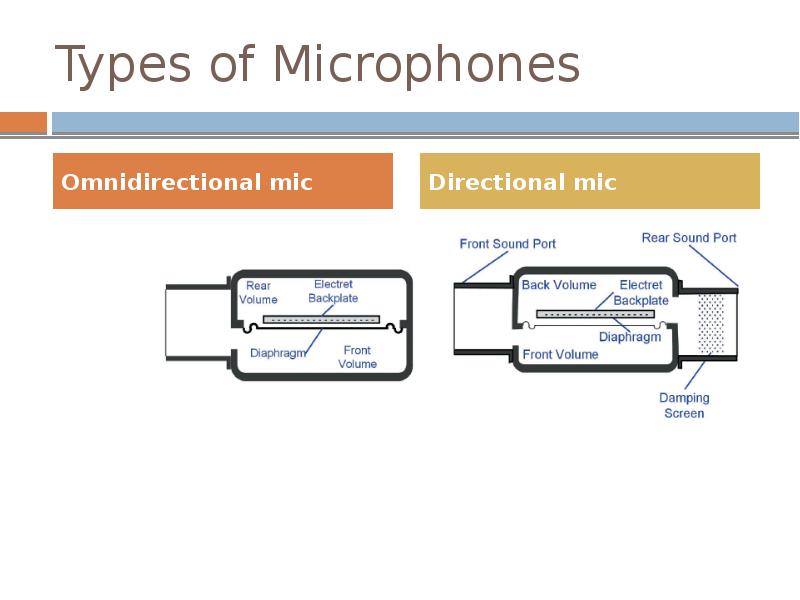
- 17. Types of Microphones Omnidirectional mic
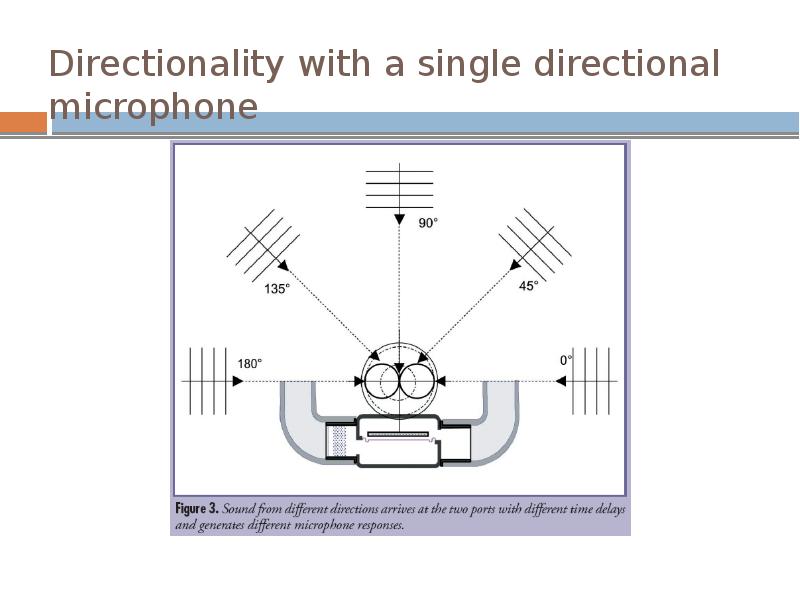
- 18. Directionality with a single directional microphone
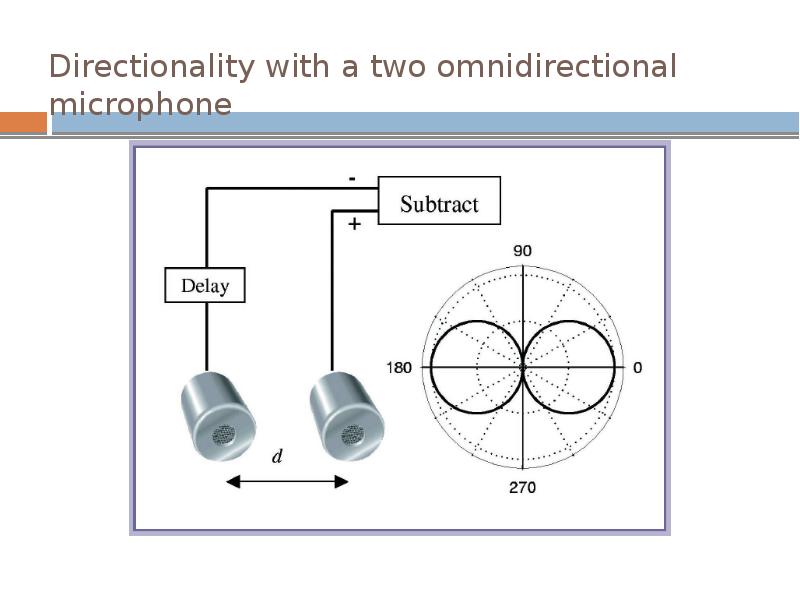
- 19. Directionality with a two omnidirectional microphone
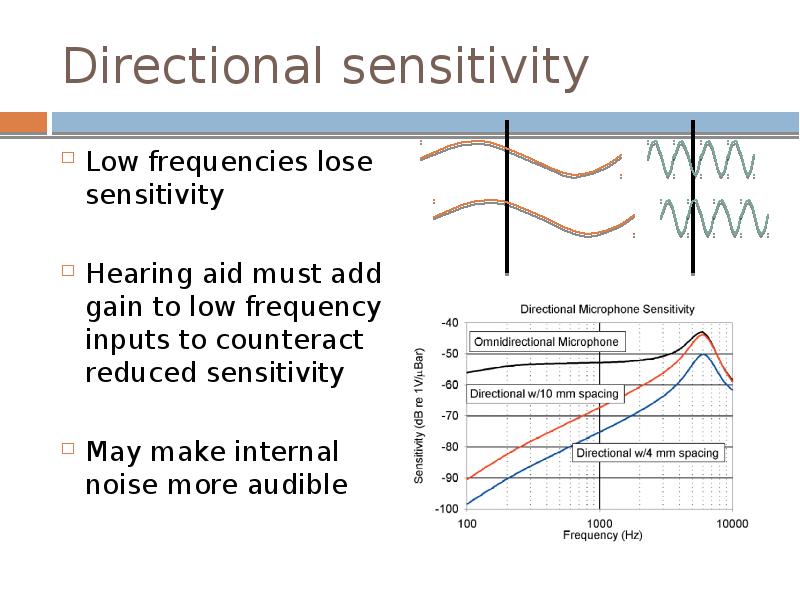
- 20. Directional sensitivity Low frequencies lose sensitivity Hearing aid must add gain
- 21. Broken microphone? Listening check No feedback, no sound? Check for debris
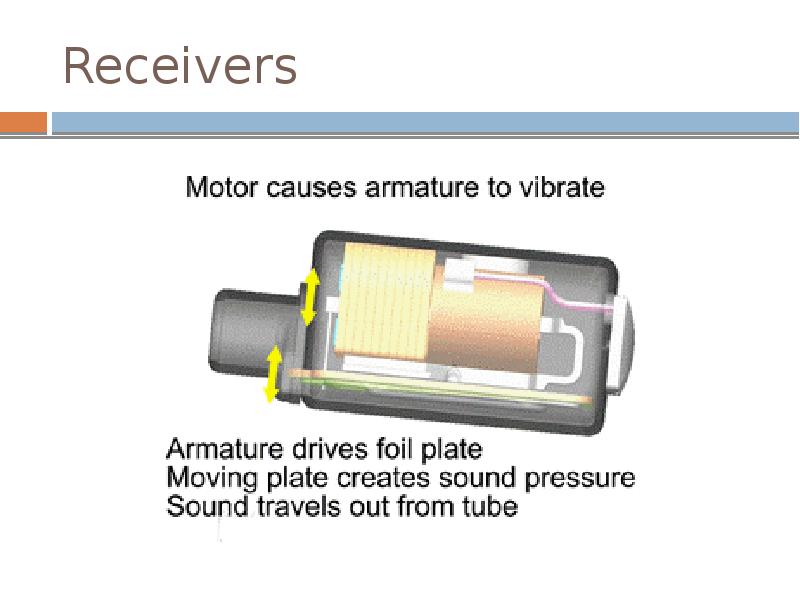
- 22. Receivers
- 23. Receivers
- 24. Signal Processors
- 25. Signal processor
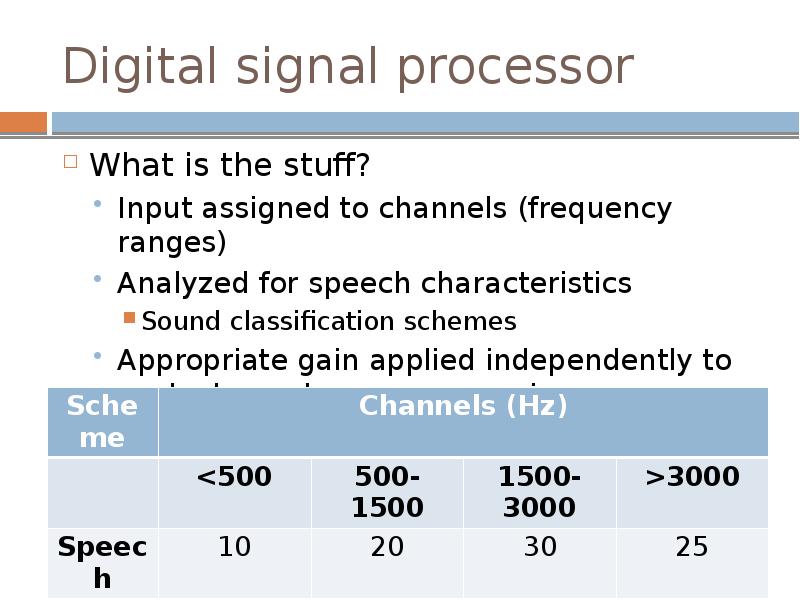
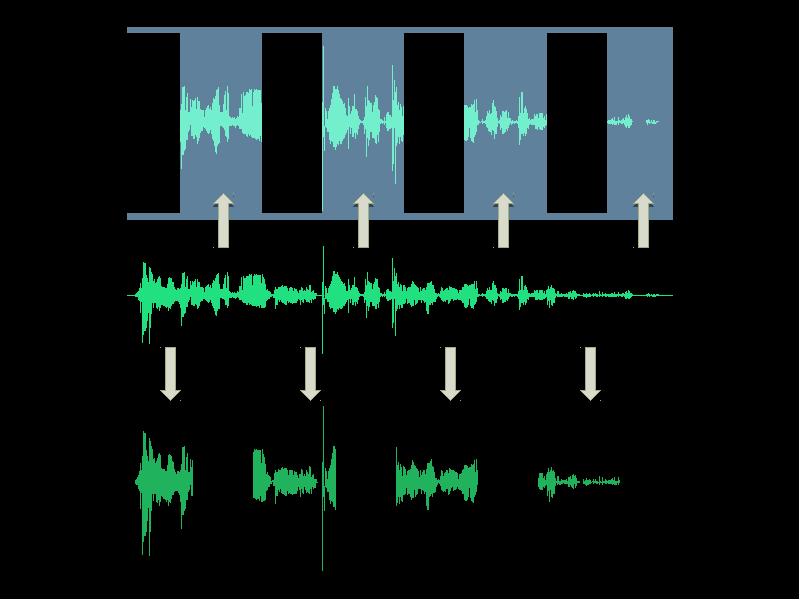
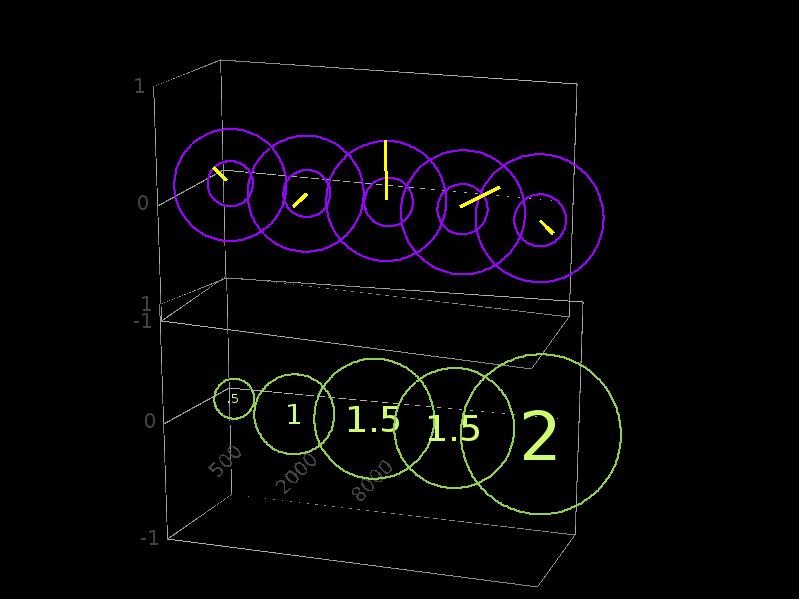
- 26. Digital signal processor What is the stuff? Input assigned to channels
- 30. Other aids
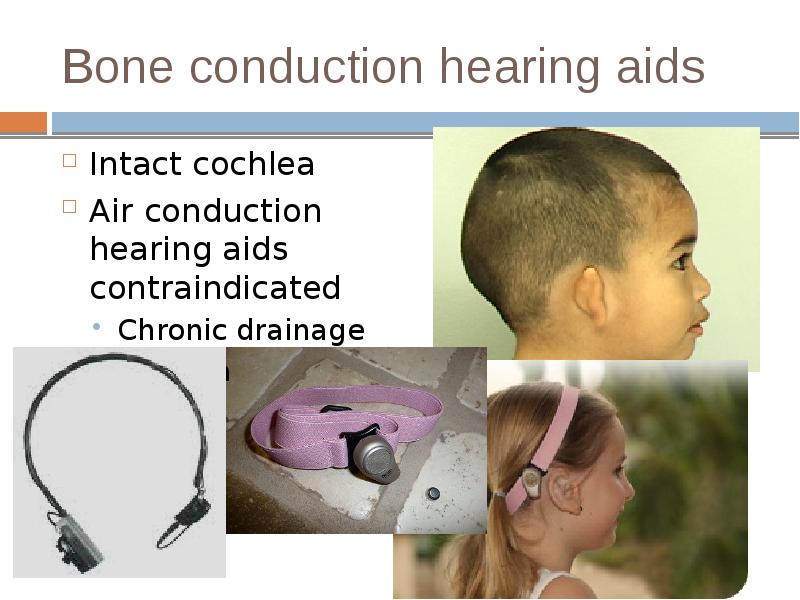
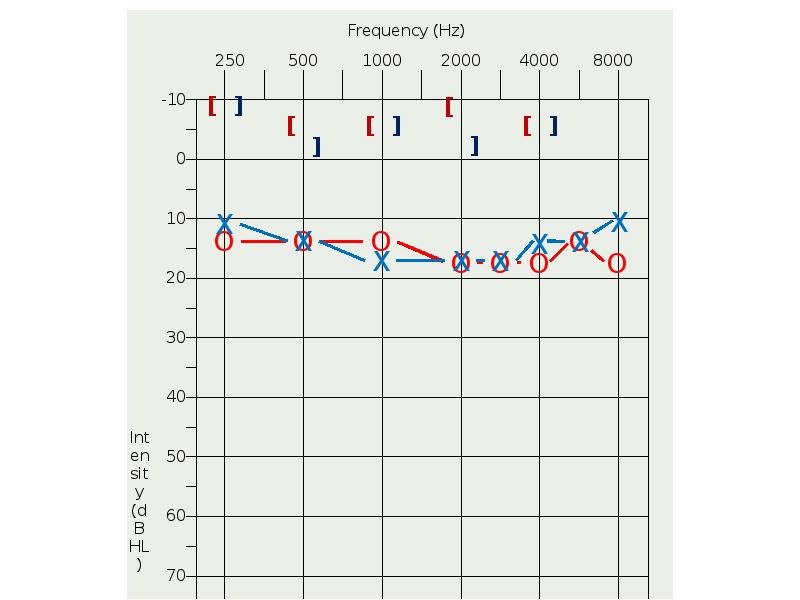
- 31. Bone conduction hearing aids Intact cochlea Air conduction hearing aids contraindicated
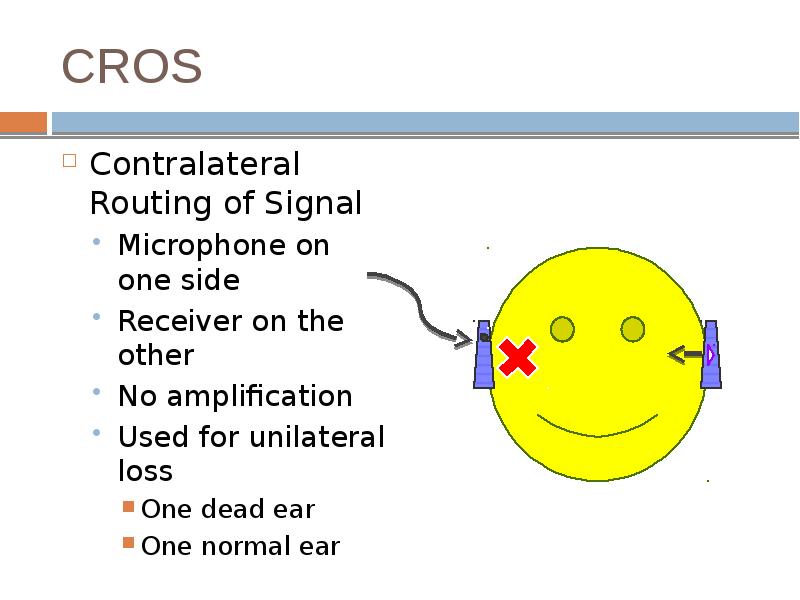
- 33. CROS Contralateral Routing of Signal Microphone on one side Receiver on
- 35. Скачать презентацию













Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации