Solutions. Acid–base equilibrium in biological systems презентация
Содержание
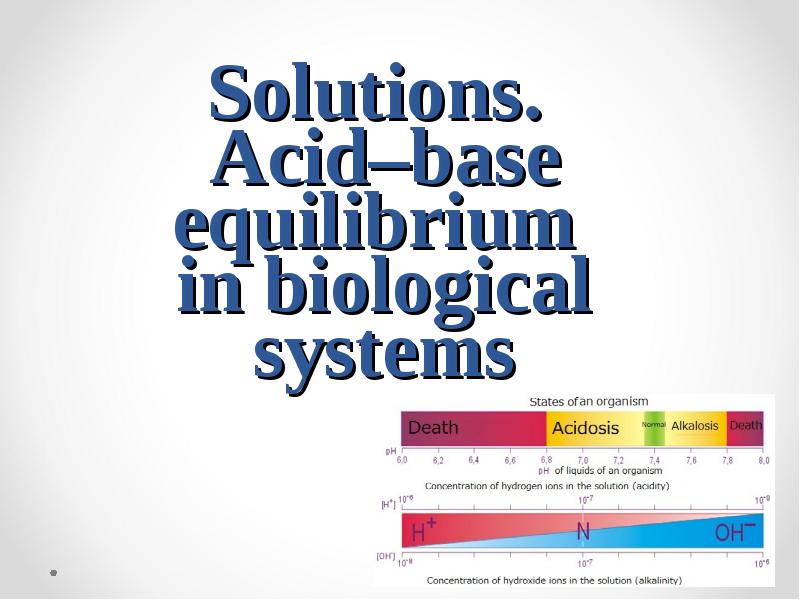
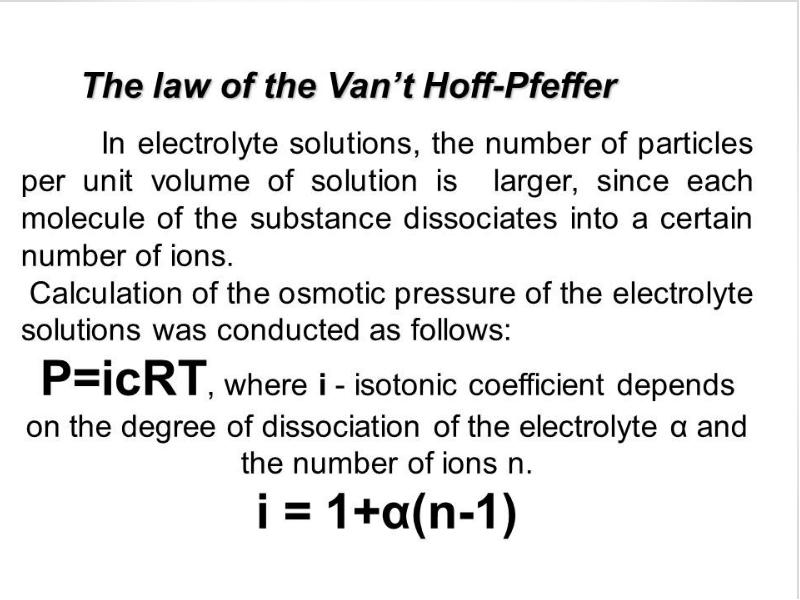
- 2. Plan 0. Solutions and their colligative properties 1. The theory
- 20. The theory of electrolytic dissociation
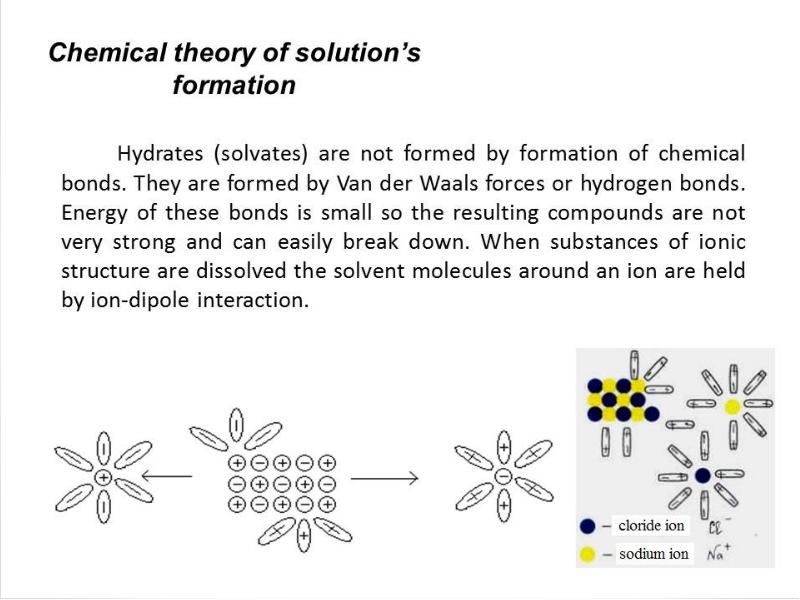
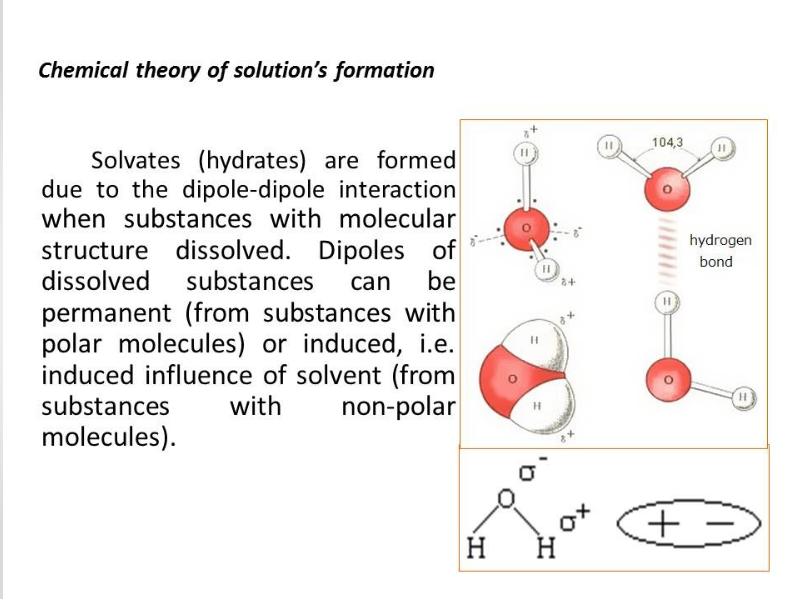
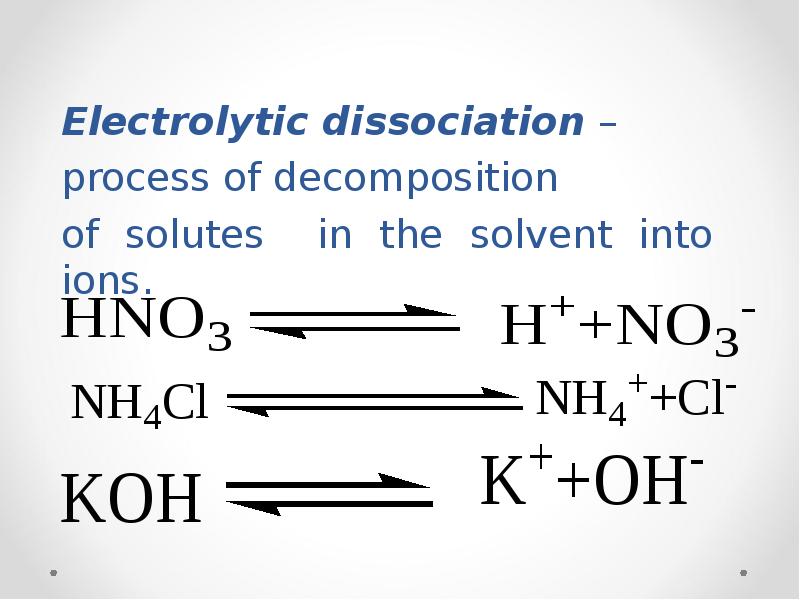
- 22. Electrolytic dissociation – process of decomposition of solutes in
- 23. 1) Substances dissociating in solutions or melts into positively charged Cat+(cations)
- 24. Dissociation of bases, acides and salts in water solutions
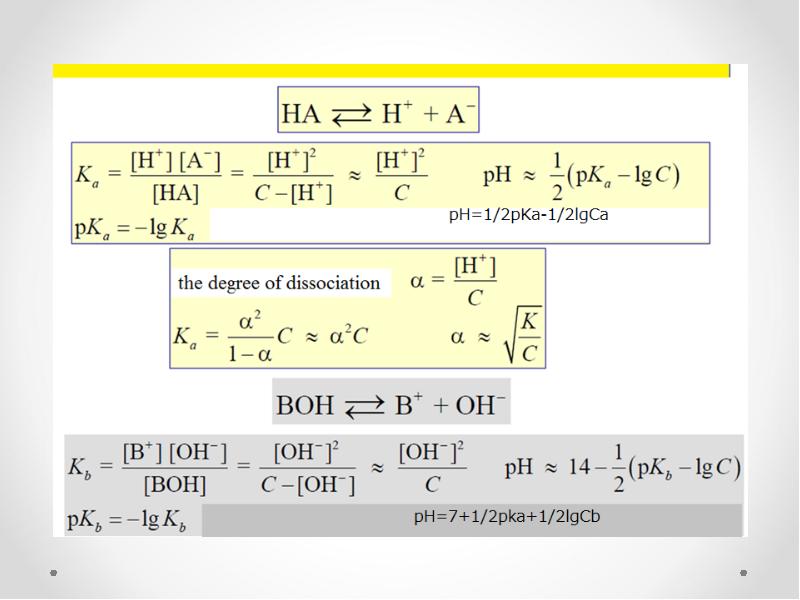
- 25. Acides are compounds dissociating in aqueous solutions with the formation of
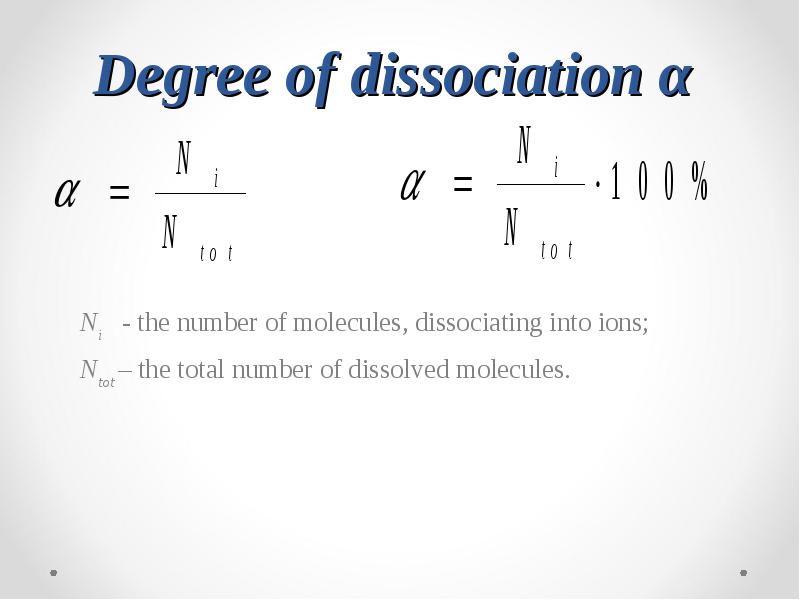
- 27. Degree of dissociation α Ni - the number of molecules,
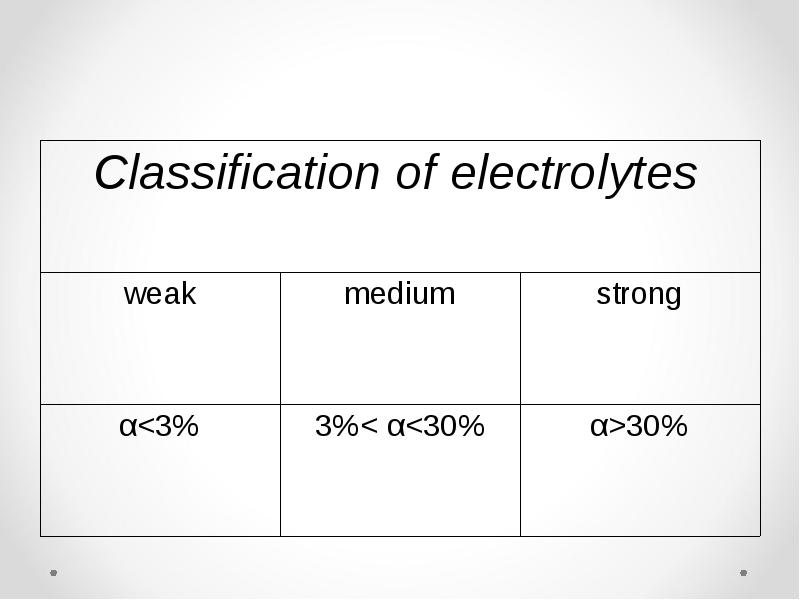
- 29. Strong electrolytes Majority of salts. Some acids (HCl, HBr, HI,
- 30. Weak electrolytes Majority of acids and bases (H2S, H2CO3, Al(OH)3,
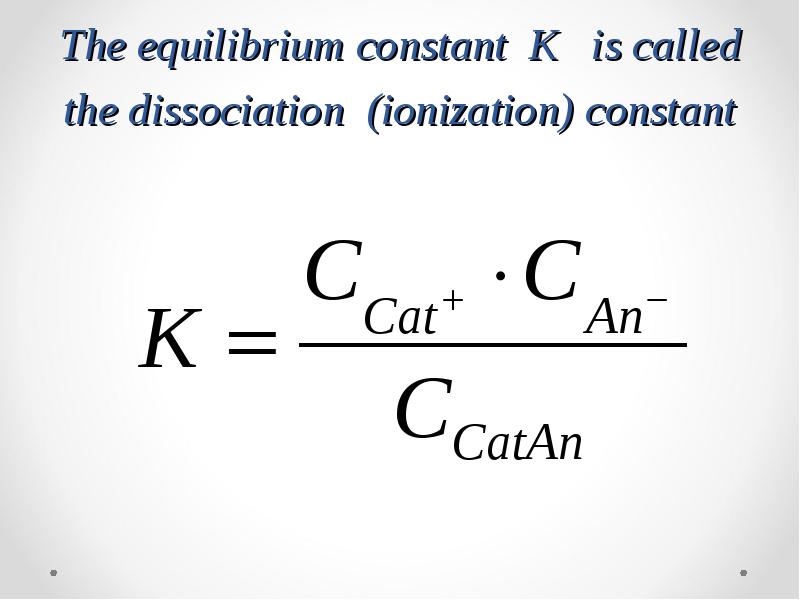
- 31. The dissociation of weak electrolytes is a reversible process CatAn
- 32. The equilibrium constant K is called the dissociation (ionization) constant
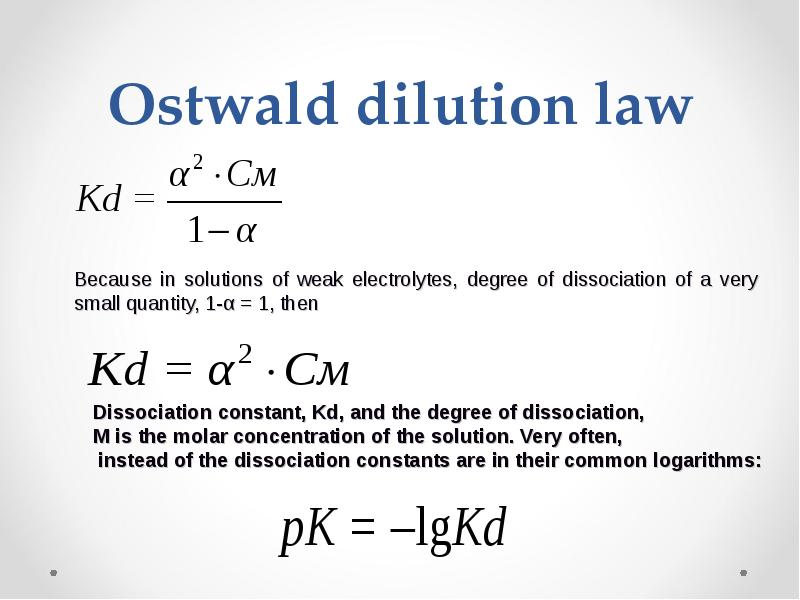
- 33. Ostwald dilution law
- 34. Acidity and basicity constants The dissociation constants of acids and bases,
- 36. Dissociation of water H2O H+ + OH-
- 37. Kw is constant, ion product of water.
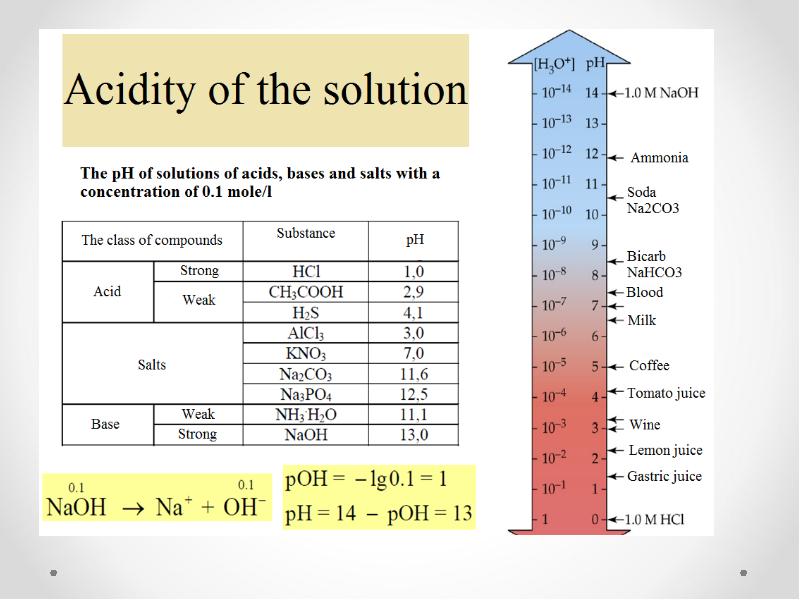
- 38. Hydrogen ion exponent pH= -lg [H+]
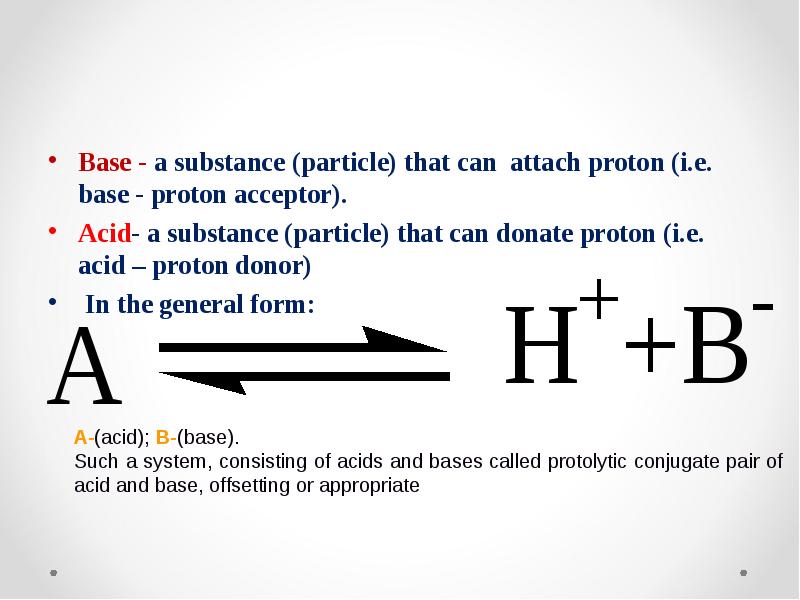
- 41. Protolytic theory Danish physicist and chemist Johannes Brønsted and the English
- 42. Base - a substance (particle) that can attach proton (i.e. base
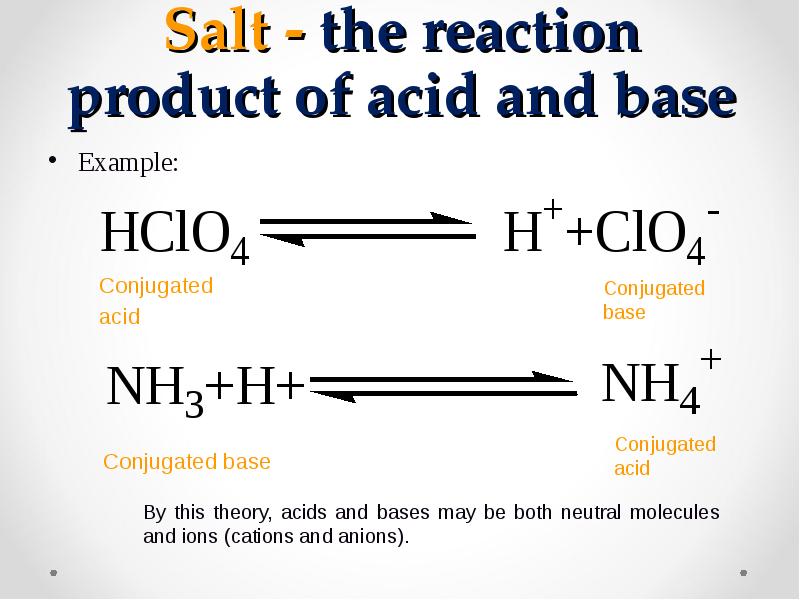
- 43. Salt - the reaction product of acid and base Example:
- 44. The homeostasis. The importancy of pH maintenance in human body The
- 45. The constancy of hydrogen ions concentration is one of important constant
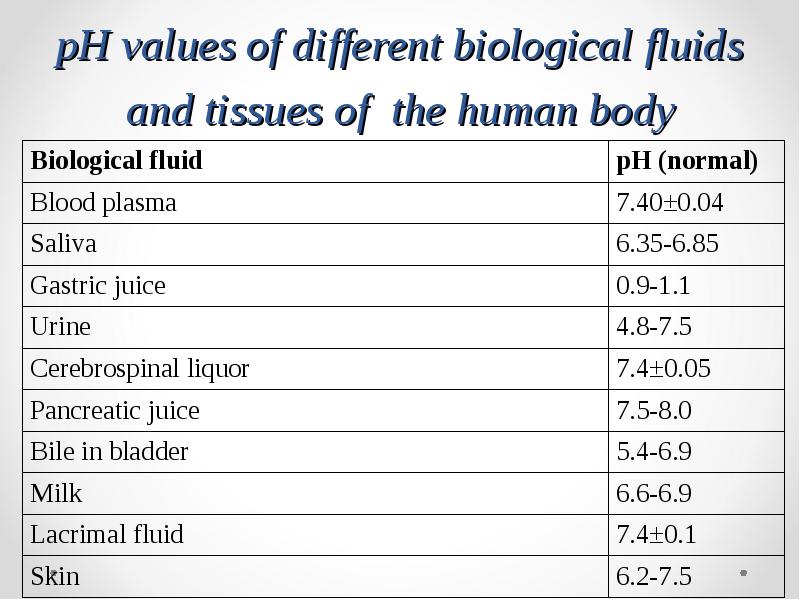
- 46. pH values of different biological fluids and tissues of the human
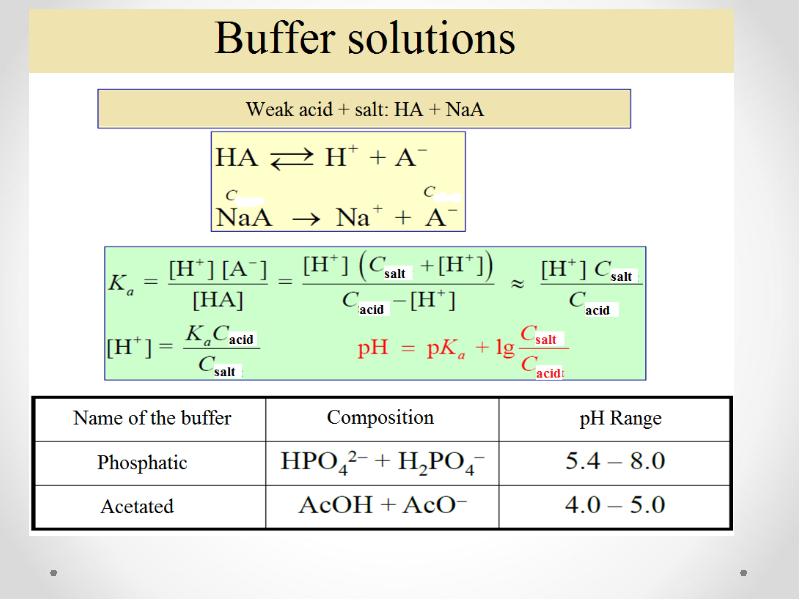
- 47. The concept of buffer solutions Buffer solutions are solutions that resist
- 49. The resistive action is the result of the equilibrium between the
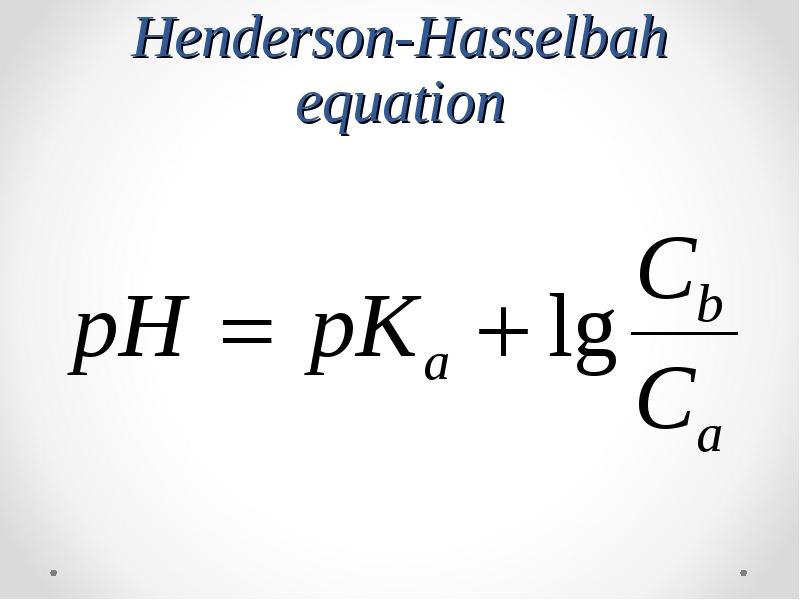
- 50. Henderson-Hasselbah equation
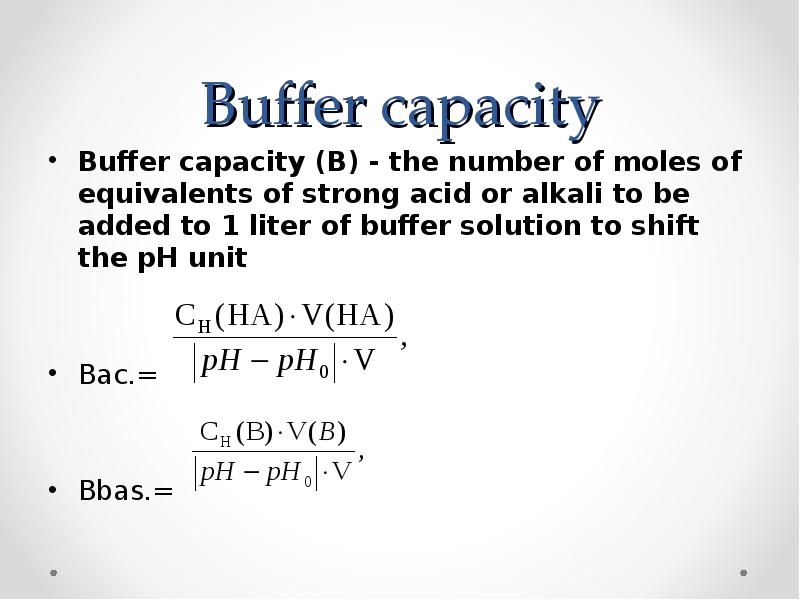
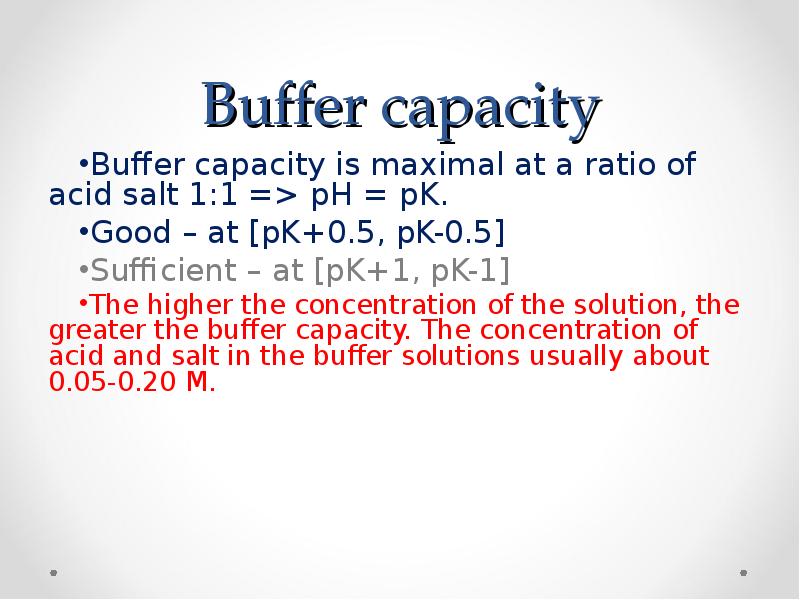
- 51. Buffer capacity Buffer capacity (B) - the number of moles of
- 52. Buffer capacity Buffer capacity is maximal at a ratio of acid
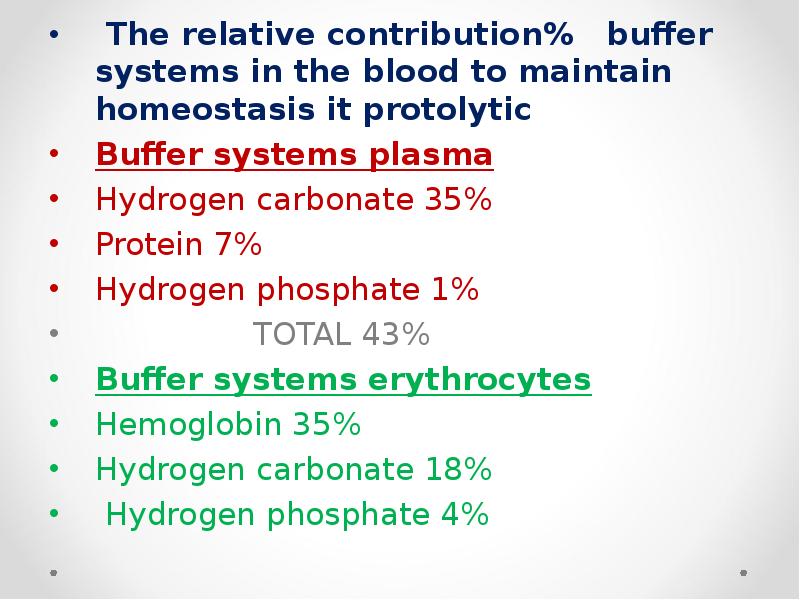
- 53. The relative contribution% buffer systems in the blood to maintain
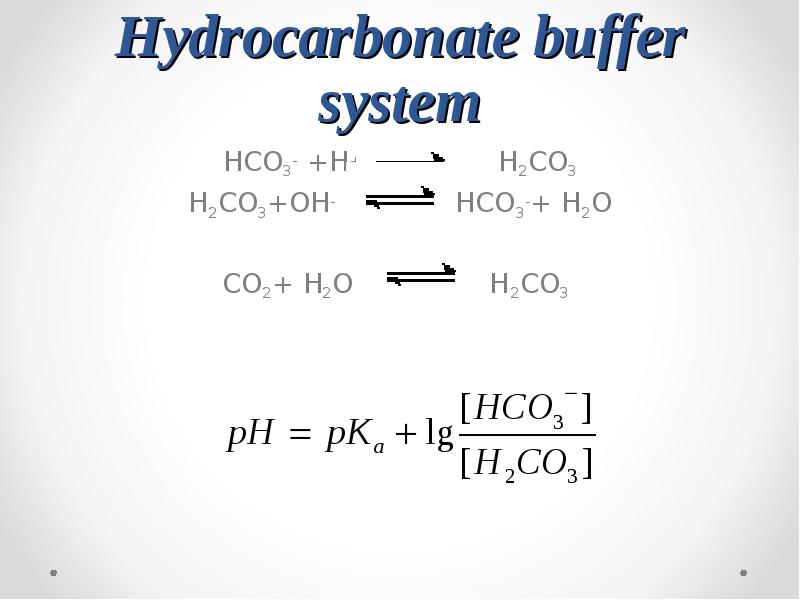
- 54. Hydrocarbonate buffer system HCO3- +H+ H2CO3 H2CO3+OH-
- 55. pKa1(H2CO3)=6.1 pKa1(H2CO3)=6.1 pH of a blood plasma = 7.4
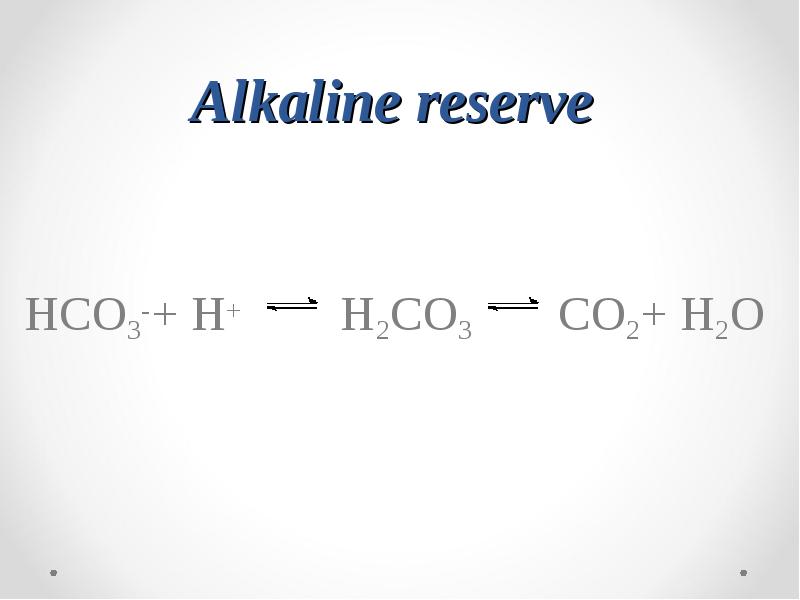
- 56. Alkaline reserve HCO3-+ H+ H2CO3 CO2+ H2O
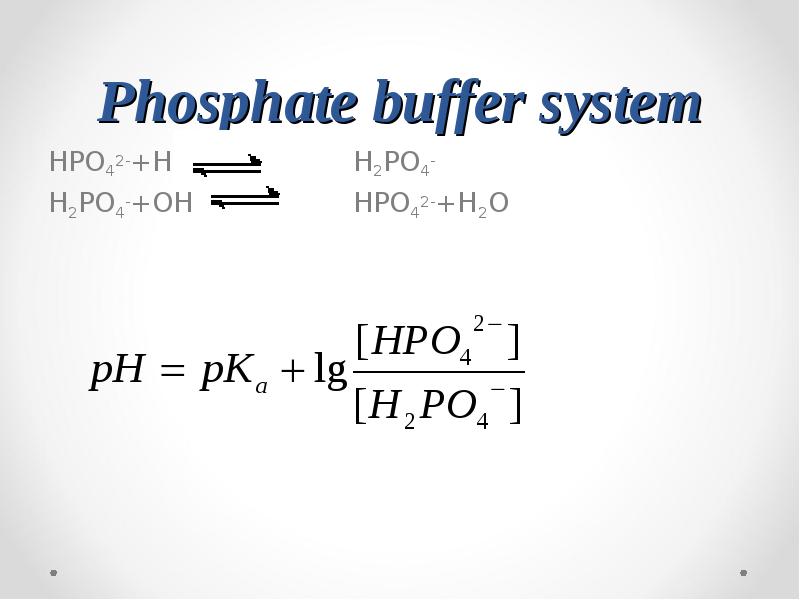
- 57. Phosphate buffer system HPO42-+H+ H2PO4- H2PO4-+OH-
- 58. The mechanism of action of phosphate buffer: 1. acid addition
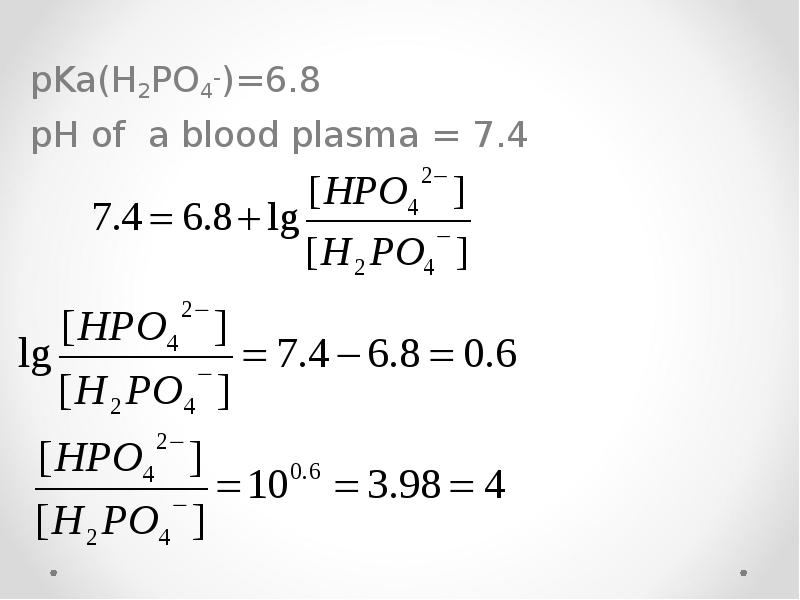
- 59. pKa(H2PO4-)=6.8 pH of a blood plasma = 7.4
- 60. Protein buffer systems The plasma proteins (albumins, globulins) are less important
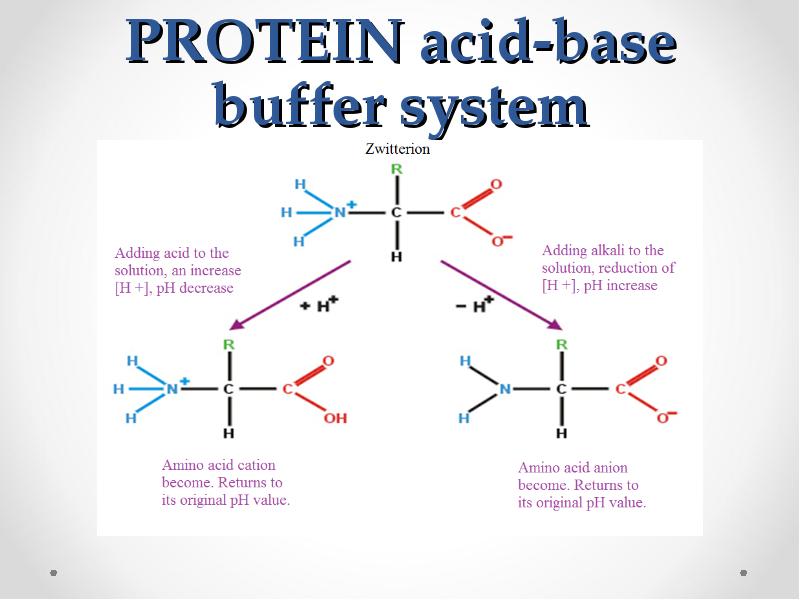
- 61. PROTEIN acid-base buffer system
- 62. Hemoglobin buffer system
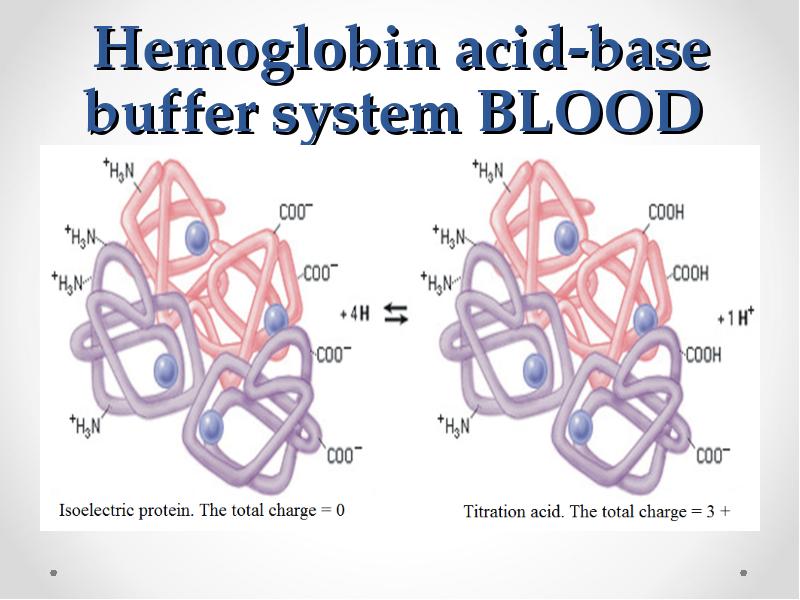
- 64. Hemoglobin acid-base buffer system BLOOD
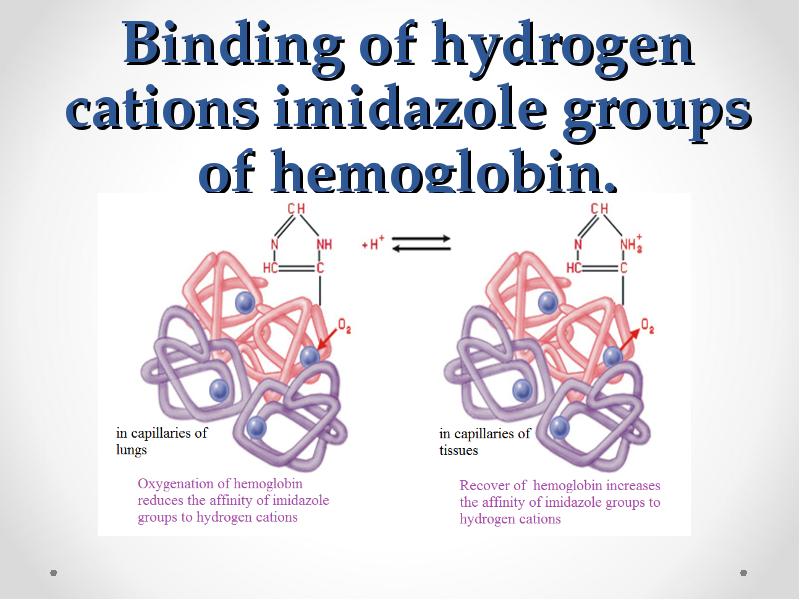
- 65. Binding of hydrogen cations imidazole groups of hemoglobin.
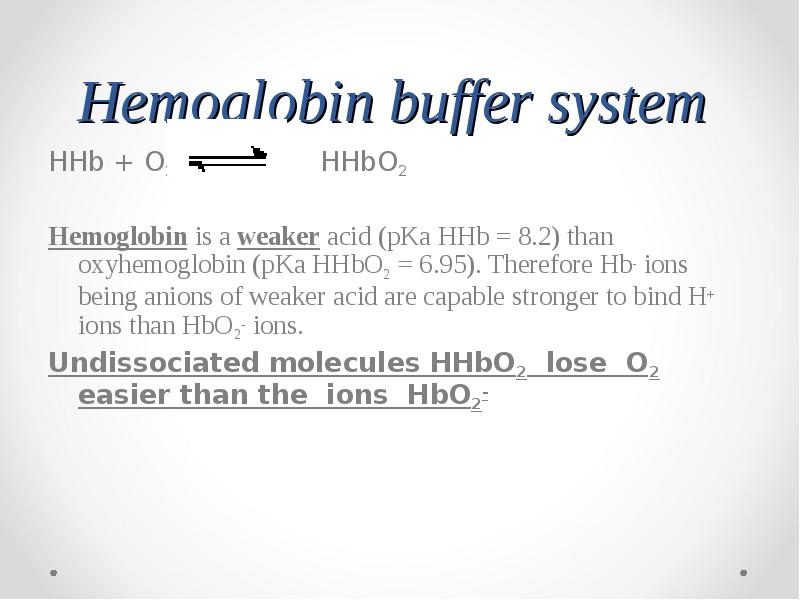
- 66. Hemoglobin buffer system HHb + O2
- 67. a) the hemoglobin buffer system: HHb H+ + Hb-;
- 68. In erythrocytes: HHbO2 HHb + O2 (1) HHbO2
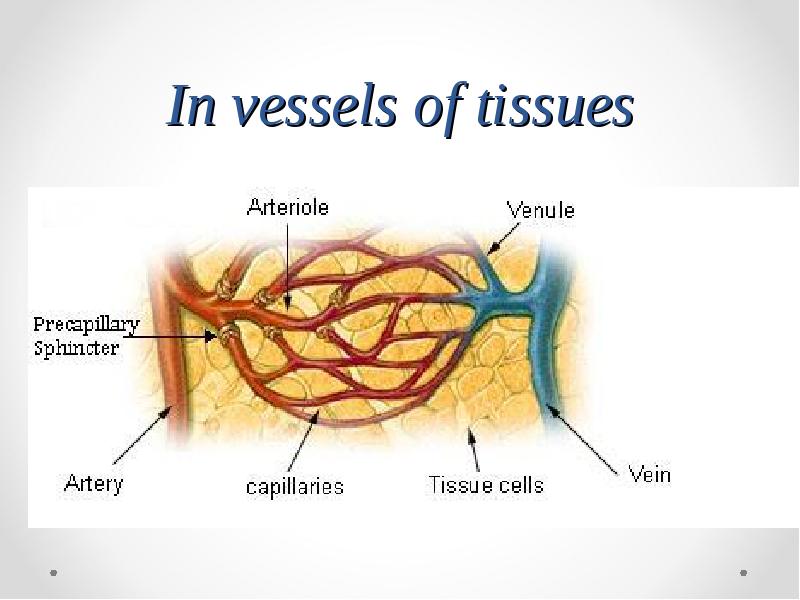
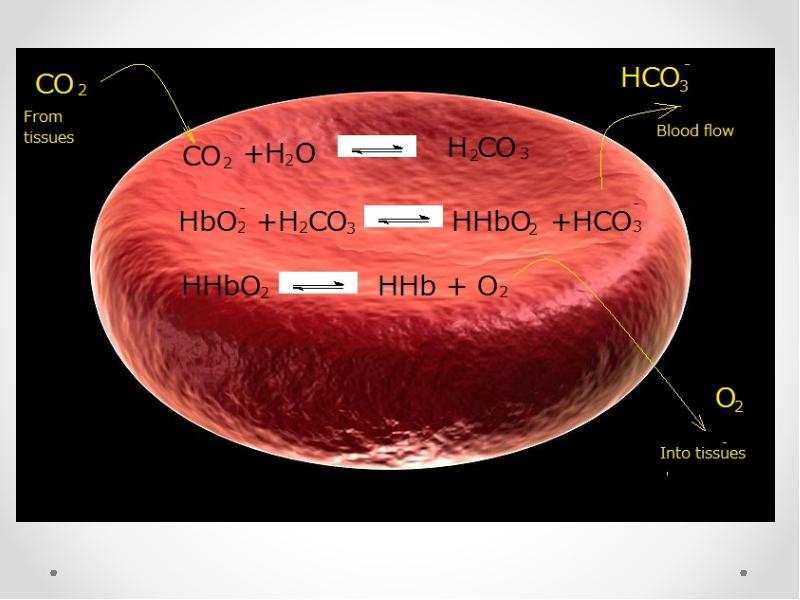
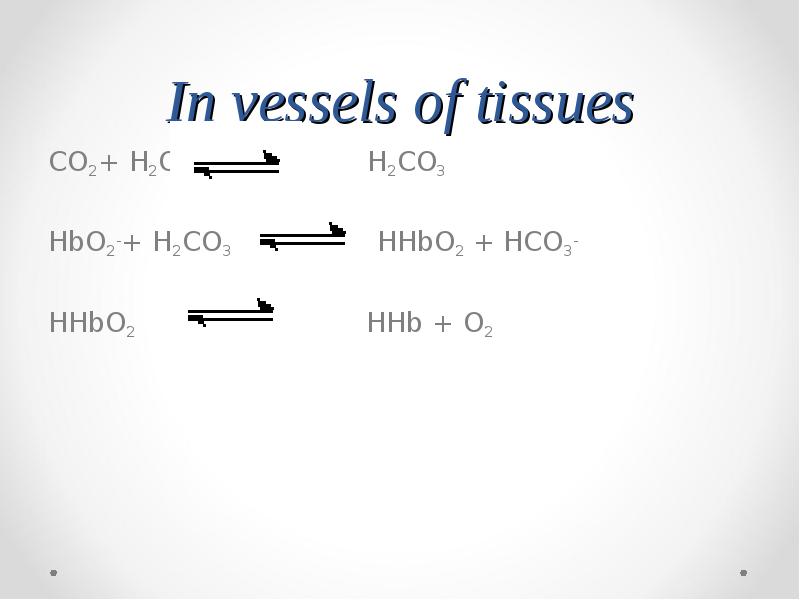
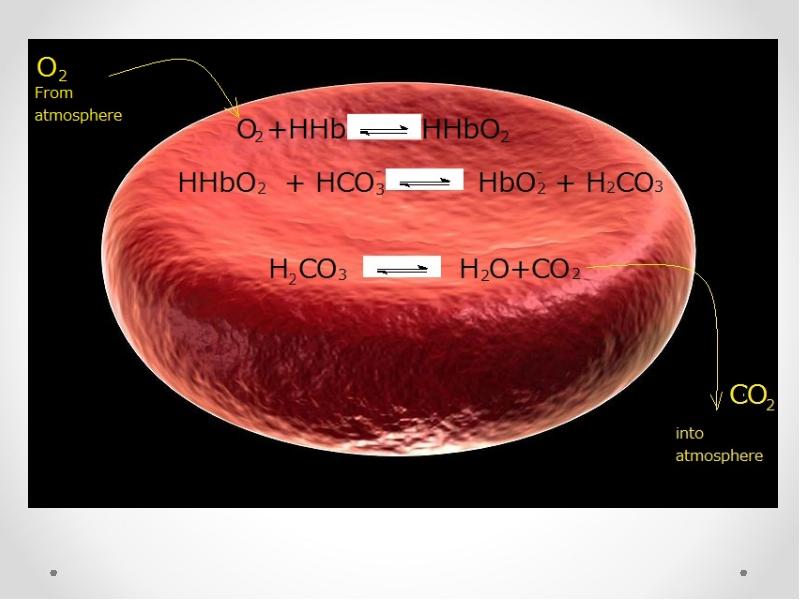
- 69. In vessels of tissues
- 71. In vessels of tissues CO2+ H2O
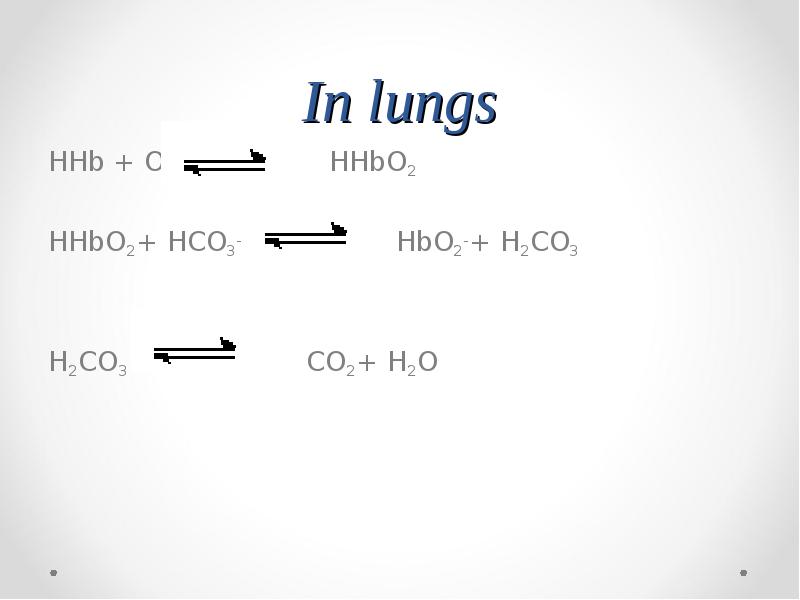
- 72. In lungs
- 74. In lungs HHb + O2 HHbO2 HHbO2+
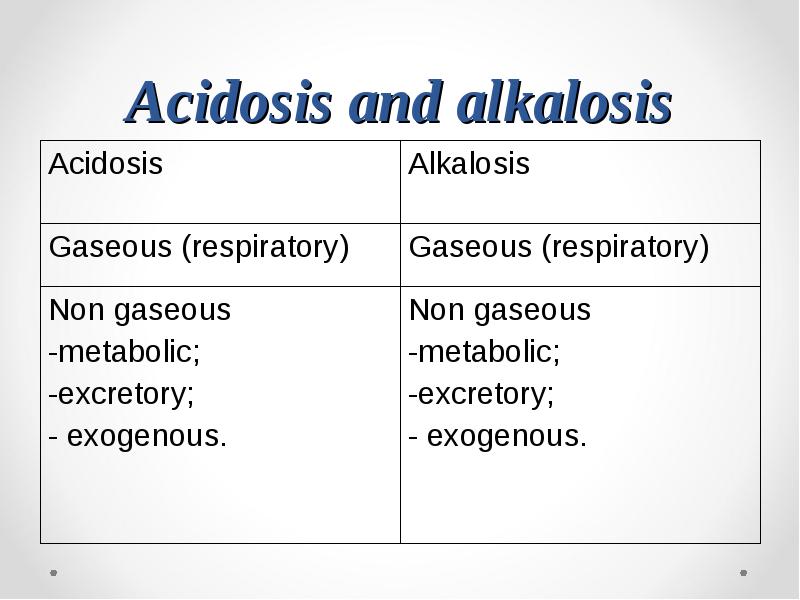
- 75. Acidosis and alkalosis
- 76. Literature 1. Medical Chemistry : textbook / V. A. Kalibabchuk [and al.]
- 77. Скачать презентацию




















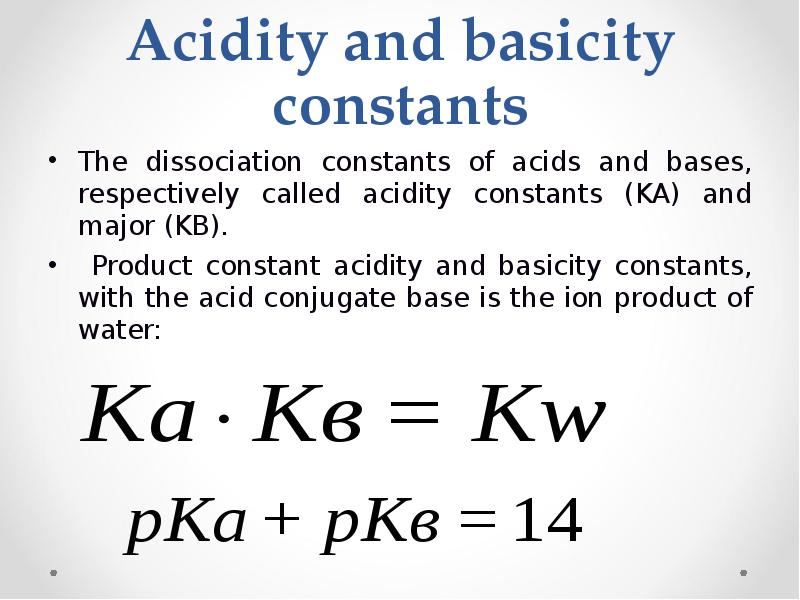

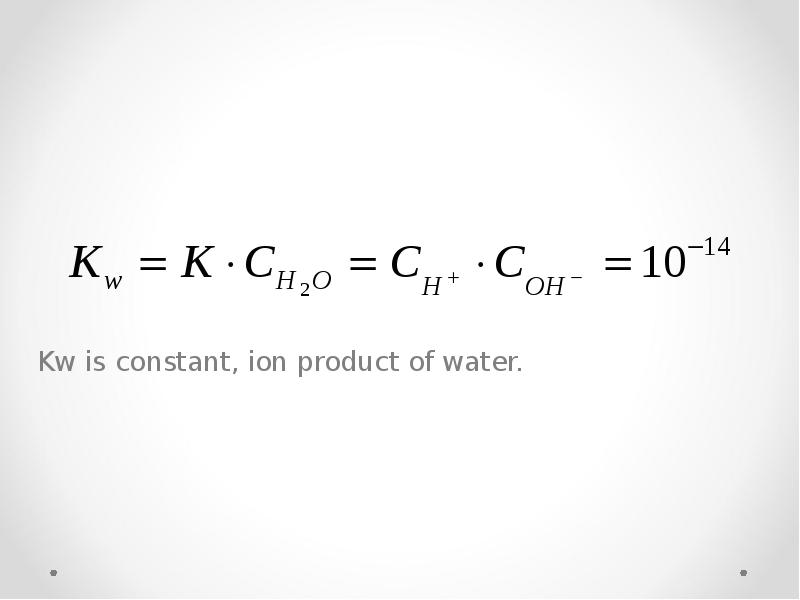
![Hydrogen ion exponent
pH= -lg [H+] Hydrogen ion exponent
pH= -lg [H+]](/documents_3/016b5b8ace93c2dcf36c2aca72edf584/img37.jpg)











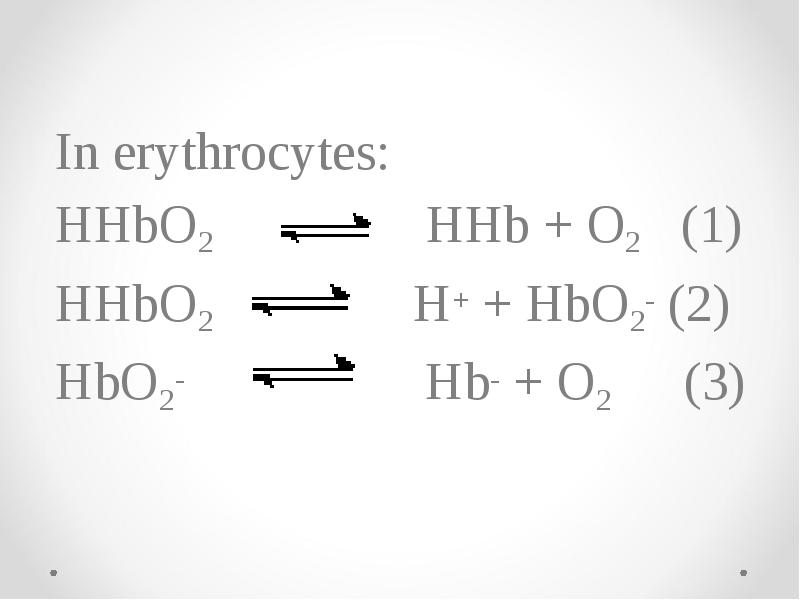
![Literature
1. Medical Chemistry : textbook / V. A. Kalibabchuk [and al.] Literature
1. Medical Chemistry : textbook / V. A. Kalibabchuk [and al.]](/documents_3/016b5b8ace93c2dcf36c2aca72edf584/img75.jpg)
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Скачать презентацию на тему Solutions. Acid–base equilibrium in biological systems можно ниже:
Похожие презентации