OPEC. Outline. Basic Facts презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Basic Facts on OPEC Influence of OPEC Production of OPEC
- 3. Basic Facts OPEC was formed in Baghdad in 1960 to coordinate
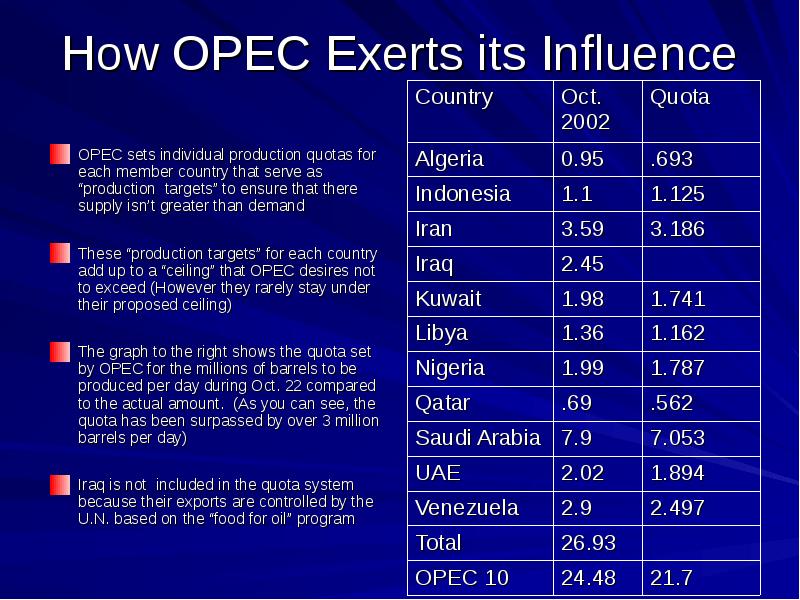
- 4. How OPEC Exerts its Influence OPEC sets individual production quotas for
- 6. Middle East Although OPEC is not an organization of Middle Eastern
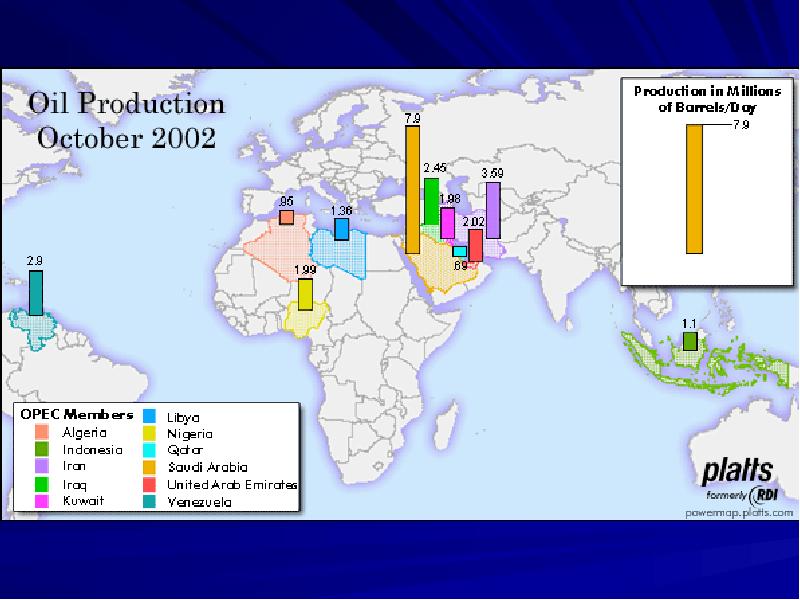
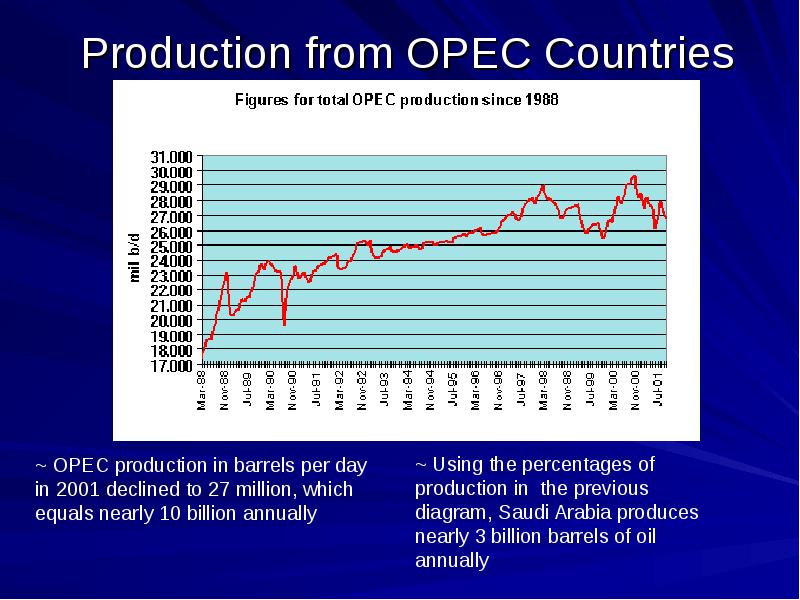
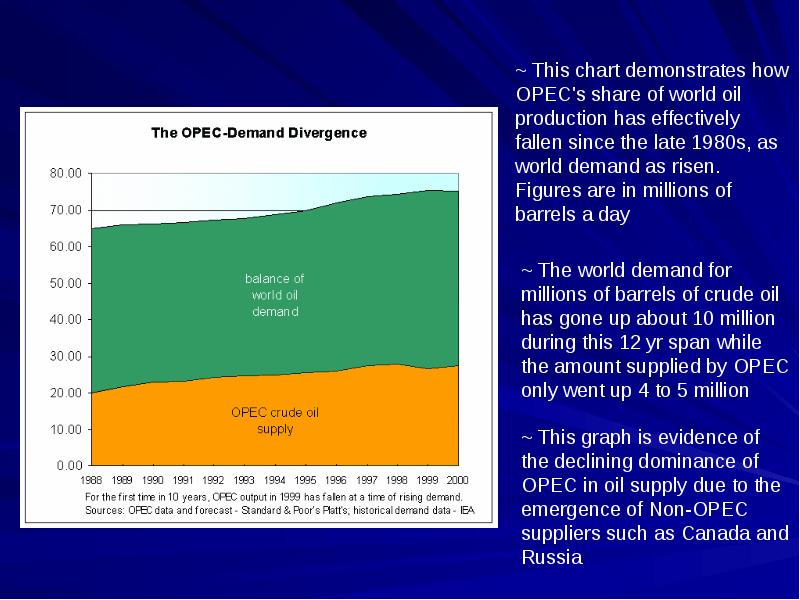
- 9. Production from OPEC Countries
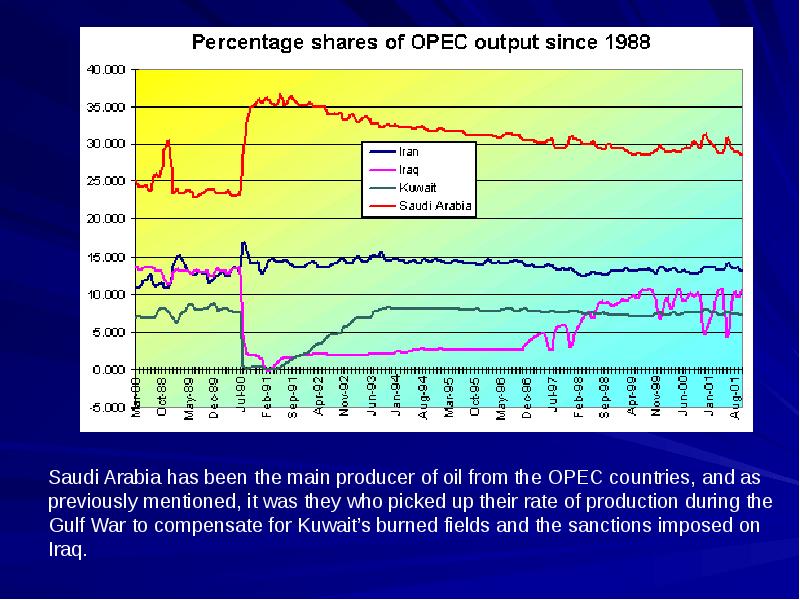
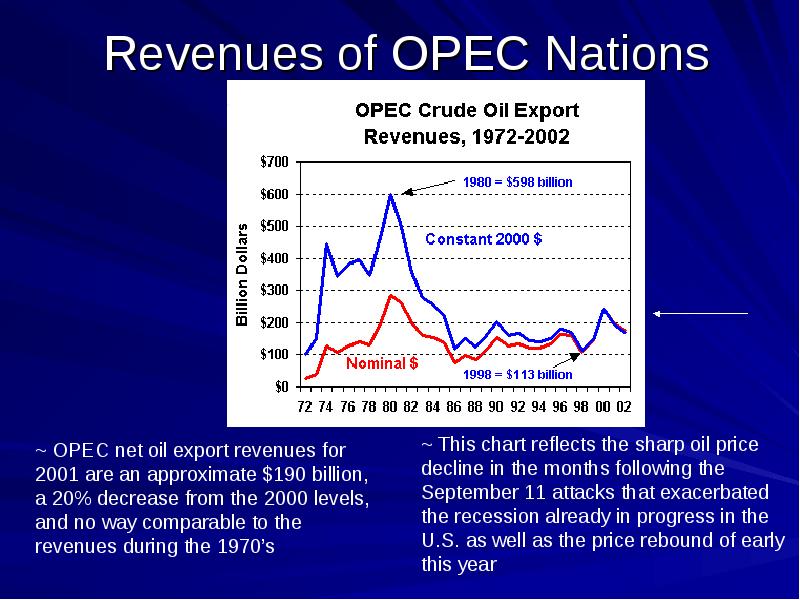
- 11. Revenues of OPEC Nations
- 13. Summary While OPEC still has considerable influence in determining the price
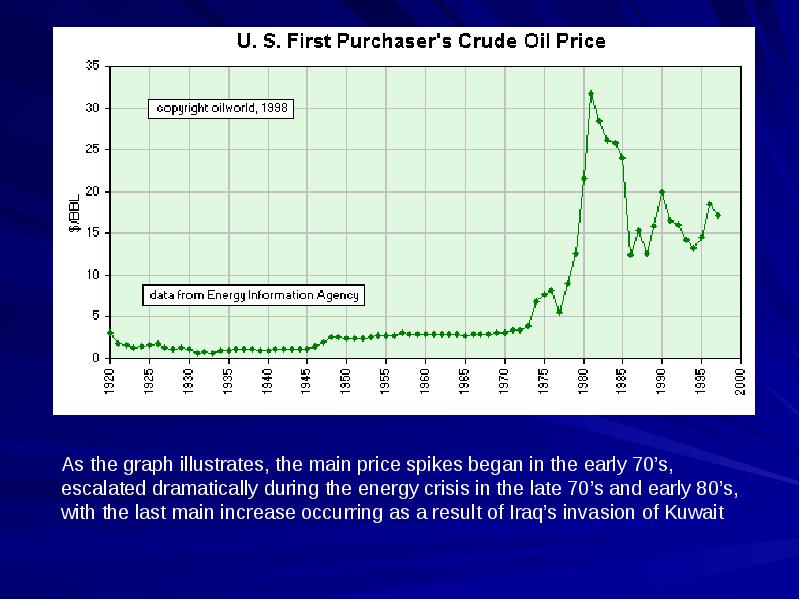
- 14. OPEC and the U.S. As I touched upon in my first
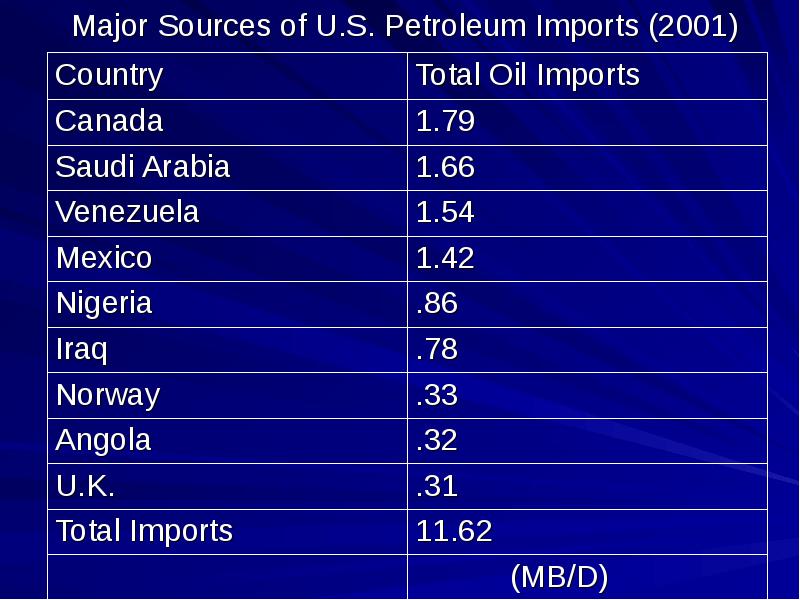
- 15. Major Sources of U.S. Petroleum Imports (2001)
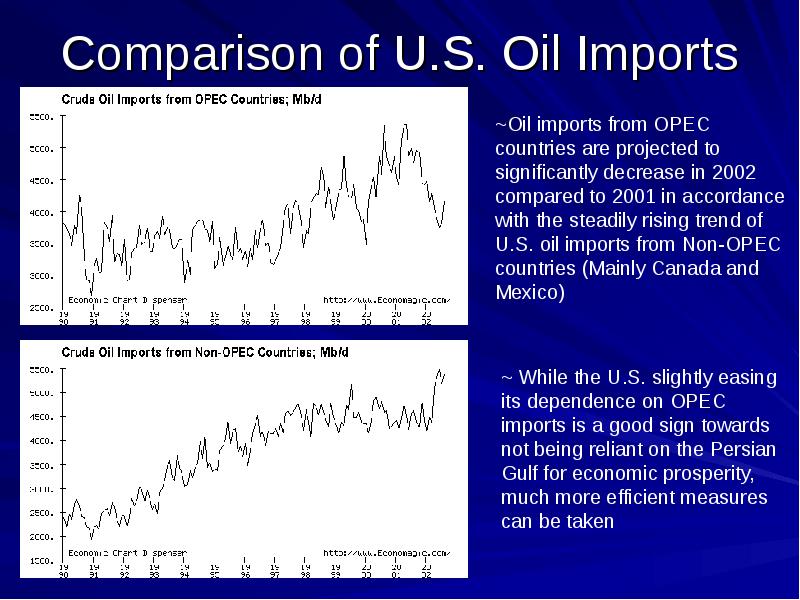
- 16. Comparison of U.S. Oil Imports
- 17. Assuring Independence from OPEC Imports ~ Drilling in the ANWR- Screw
- 20. Conclusion OPEC still has considerable influence in determining the price per
- 21. Скачать презентацию











Слайды и текст этой презентации
Похожие презентации





























